Abstract
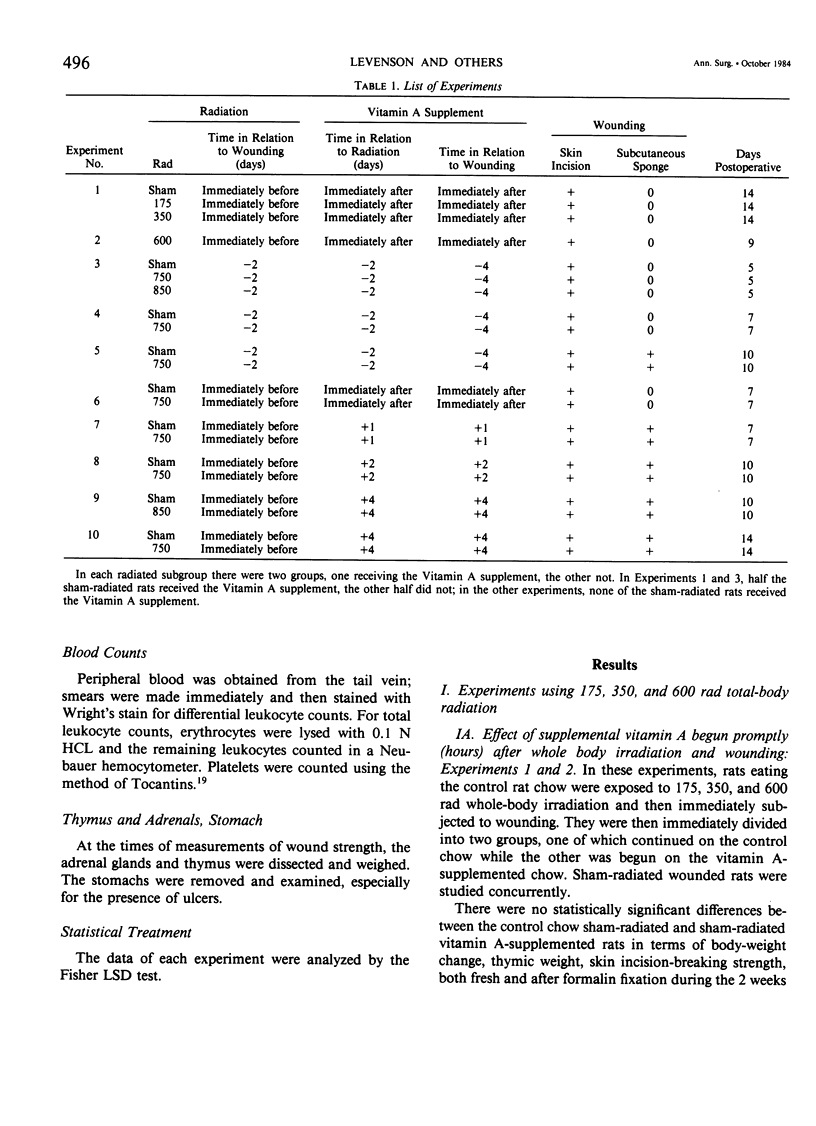
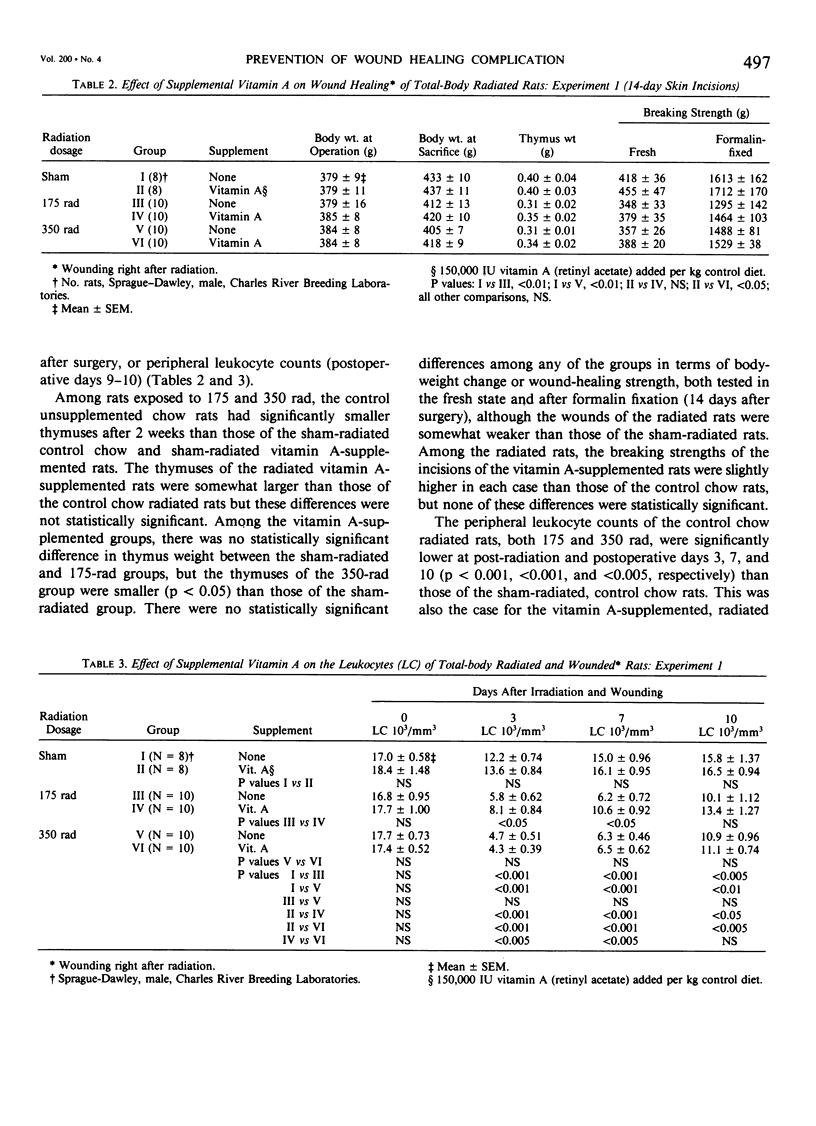
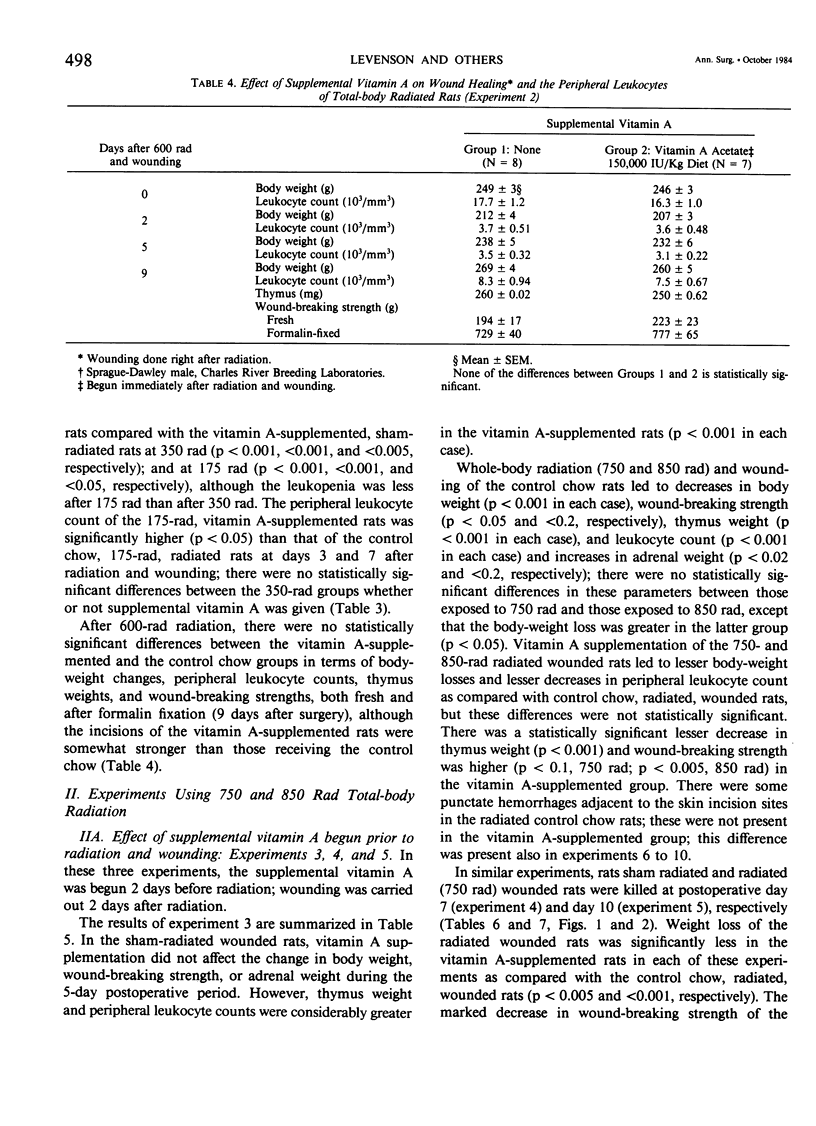
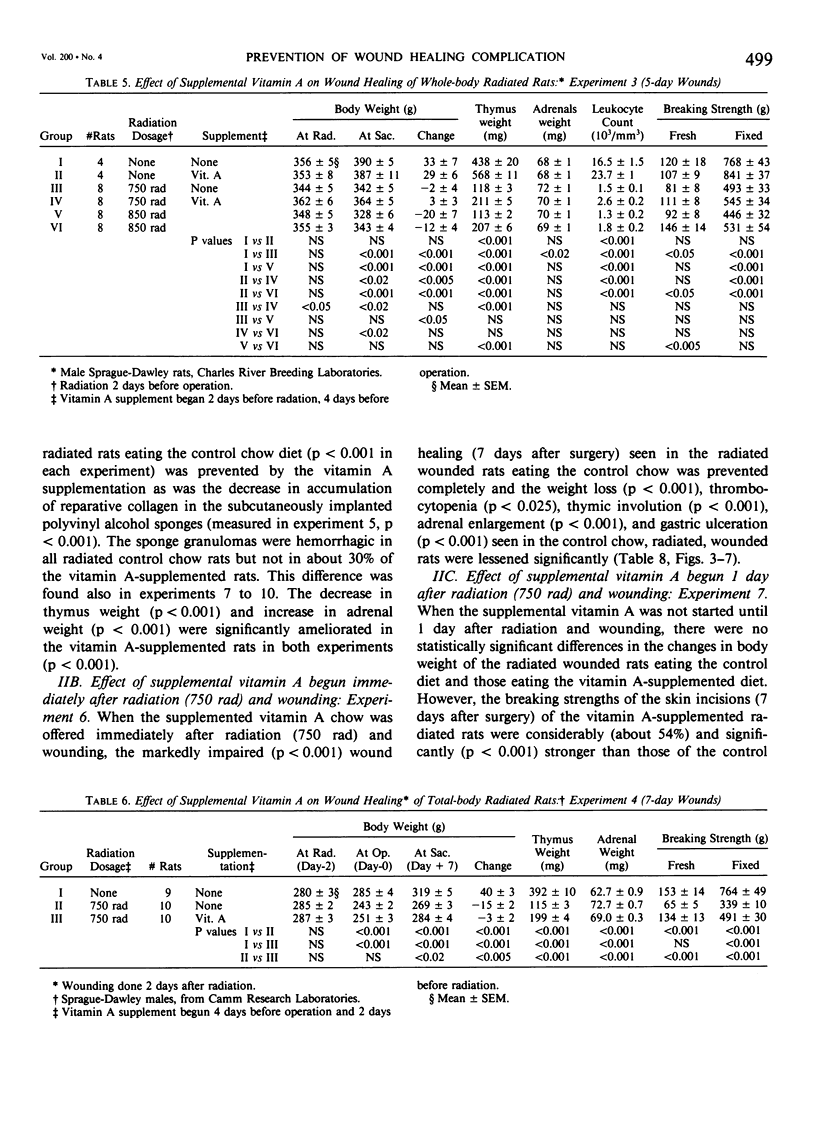
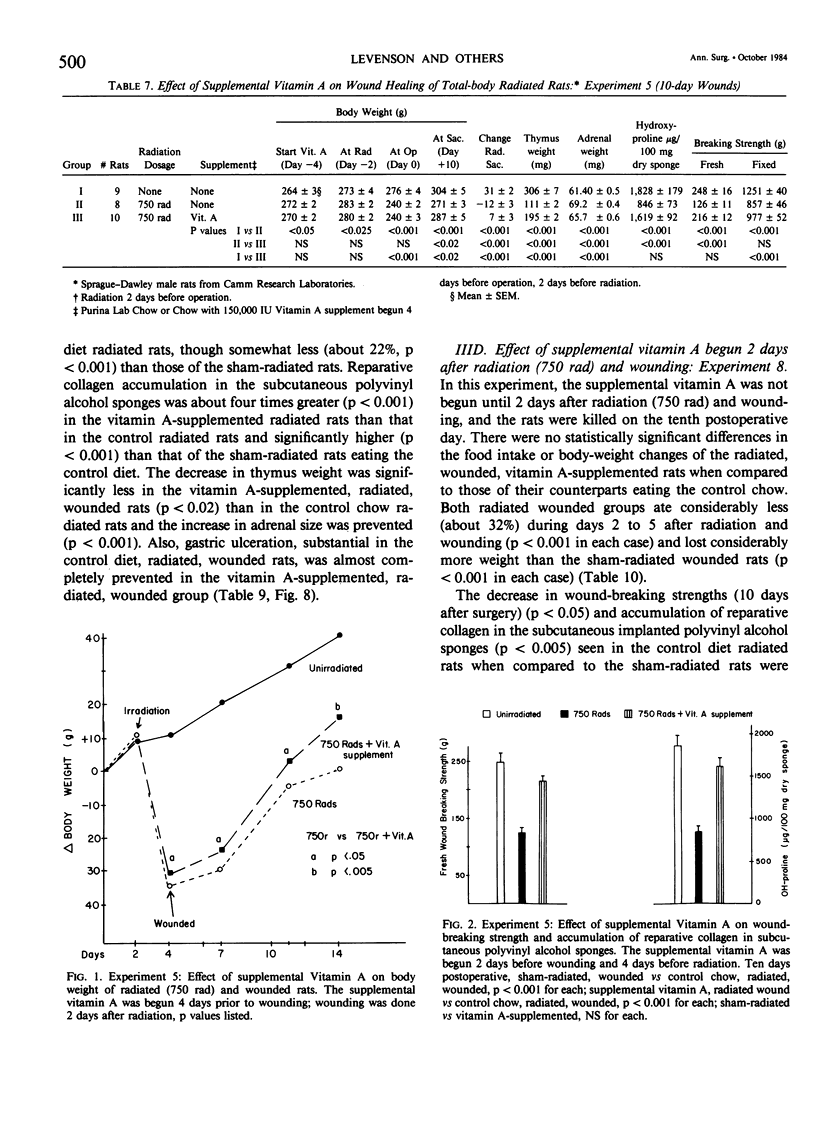
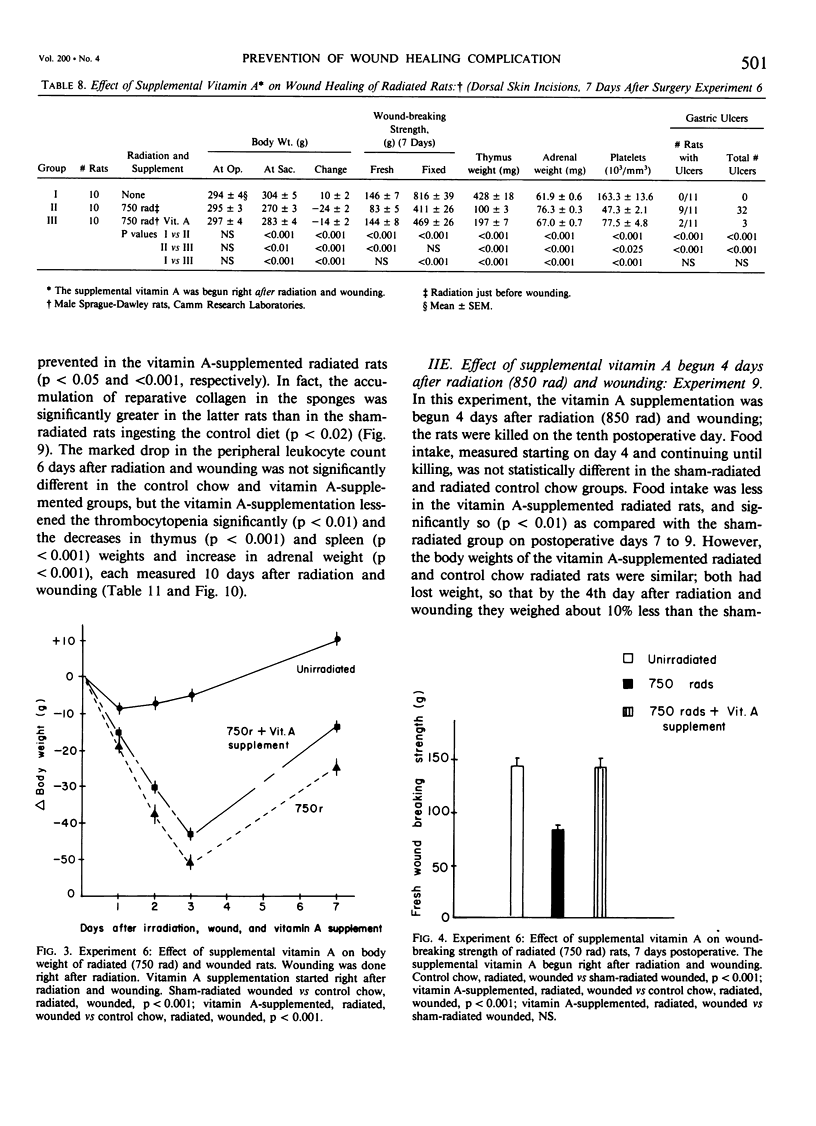
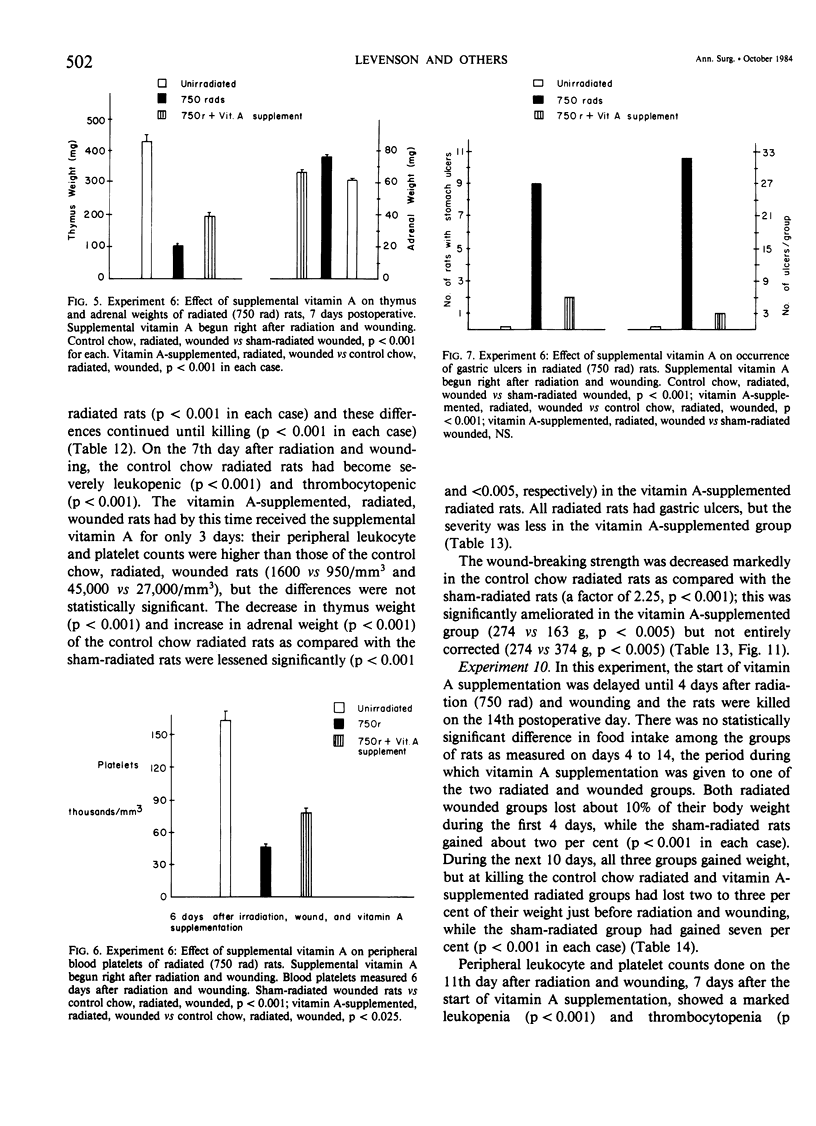
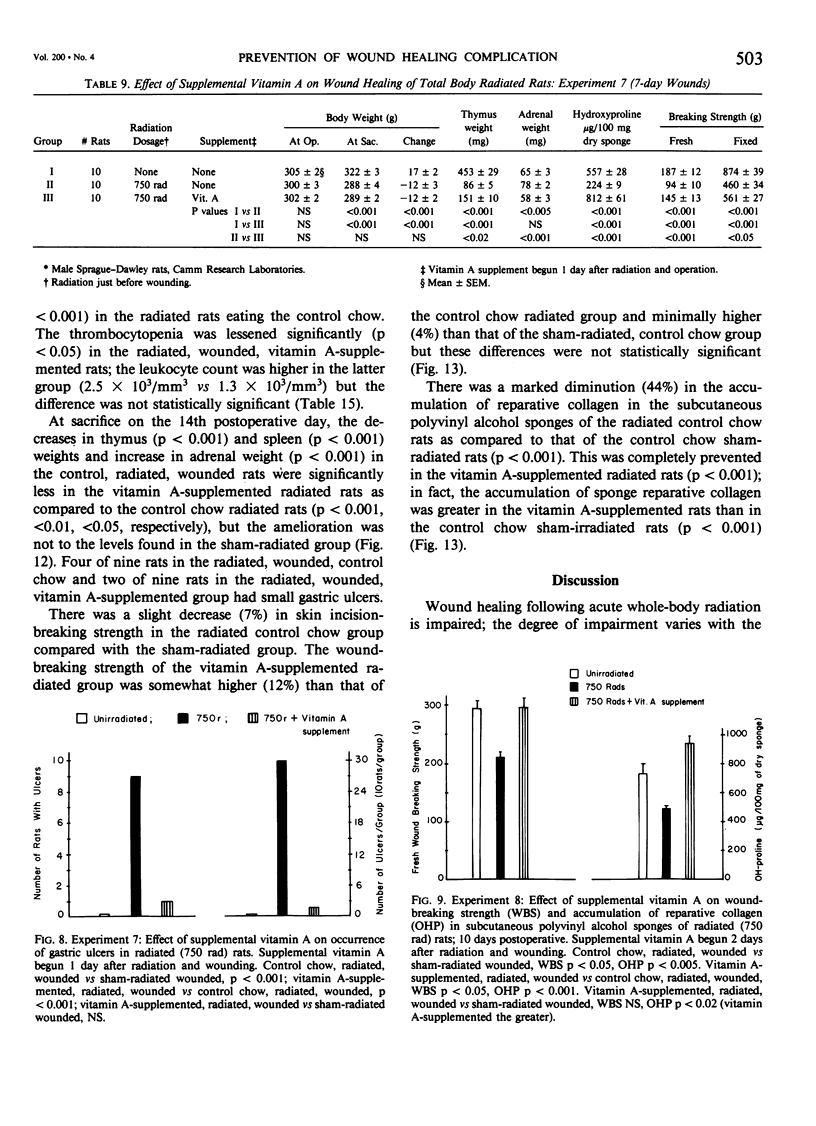
Acute radiation injury leads to thymic involution, adrenal enlargement, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, gastrointestinal ulceration, and impaired wound healing. The authors hypothesized that supplemental vitamin A would mitigate these adverse effects in rats exposed to acute whole-body radiation. This hypothesis was based on previous experiments in their laboratory that showed that supplemental vitamin A is thymotropic for normal rodents and lessens the thymic involution, lymphopenia, and adrenal enlargement that follows stress, trauma, and neoplasia, largely obviates the impaired wound healing induced by the radiomimetic drugs streptozotocin and cyclophosphamide, lessens the systemic response (thymic involution, adrenal enlargement, leukopenia, lymphocytopenia) to local radiation, and shifts the median lethal dose (LD50/30) following whole-body radiation to the right. To test their hypothesis, dorsal skin incisions and subcutaneous implantation of polyvinyl alcohol sponges were performed in anesthetized Sprague-Dawley rats at varying times following sham radiation or varying doses of whole-body radiation (175-850 rad). In each experiment, the control diet [which contains about 18,000 IU vit. A/kg chow (3 X the NRC RDA for normal rats)] was supplemented with 150,000 IU vit. A/kg diet beginning at, before, or after sham radiation and wounding or radiation and wounding. The supplemental vitamin A prevented the impaired wound healing and lessened the weight loss, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, thymic involution, adrenal enlargement, decrease in splenic weight, and gastric ulceration of the radiated (750-850 rad) wounded rats. This was true whether the supplemental vitamin A was begun before (2 or 4 days) or after (1-2 hours to 4 days) radiation and wounding; the supplemental vitamin A was more effective when started before or up to 2 days after radiation and wounding. The authors believe that prevention of the impaired wound healing following radiation by supplemental vitamin A is due to its enhancing the early inflammatory reaction to wounding, including increasing the number of monocytes and macrophages at the wound site; possible effect on modulating collagenase activity; effect on epithelial cell (and possible mesenchymal cell) differentiation; stimulation of immune responsiveness; and lessening of the adverse effects of radiation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbul A., Thysen B., Rettura G., Levenson S. M., Seifter E. White cell involvement in the inflammatory, wound healing, and immune actions of vitamin A. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1978 May;2(2):129–138. doi: 10.1177/014860717800200208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bark S., Rettura G., Goldman D., Seifter E., Levenson S. M., Demetriou A. A. Effect of supplemental vitamin A on the healing of colon anastomosis. J Surg Res. 1984 May;36(5):470–474. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(84)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernov M. S., Hale H. W., Jr, Wood M. Prevention of stress ulcers. Am J Surg. 1971 Nov;122(5):674–677. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(71)90298-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. E., Gill G., Cullen P. R., Morris P. J. Reversal of postoperative immunosuppression in man by vitamin A. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1979 Nov;149(5):658–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin J. J., Walker R. I., Hirsch E. F. Current concepts in the management of radiation injuries and associated trauma. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1983 Jun;156(6):809–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F. Retinoic acid metabolism. Fed Proc. 1979 Oct;38(11):2519–2523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demetriou A. A., Franco I., Bark S., Rettura G., Seifter E., Levenson S. M. Effects of vitamin A and beta carotene on intra-abdominal sepsis. Arch Surg. 1984 Feb;119(2):161–165. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1984.01390140027005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demetriou A. A., Seifter E., Levenson S. M. Effect of vitamin A and Citral on peritoneal adhesion formation. J Surg Res. 1974 Nov;17(5):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(74)90138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donati R. M. Combined surgical and radiation injury. IV. Effect of antimicrobials on the wound healing pattern of the x-irradiated rat. Arch Surg. 1971 Feb;102(2):132–135. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1971.01350020042011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donati R. M., McLaughlin M. M., Stromberg L. R. Combined surgical and radiation injury. 8. The effect of the gnotobiotic state on wound closure. Experientia. 1973 Nov 15;29(11):1388–1390. doi: 10.1007/BF01922835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. P., Hunt T. K. Effects of cortisone and vitamin A on wound healing. Ann Surg. 1968 Mar;167(3):324–328. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196803000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. B., Woodward S. C. An experimental study of wound healing accelerators. Am Surg. 1972 Jan;38(1):26–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. K., Ehrlich H. P., Garcia J. A., Dunphy J. E. Effect of vitamin A on reversing the inhibitory effect of cortisone on healing of open wounds in animals and man. Ann Surg. 1969 Oct;170(4):633–641. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196910000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurin M., Tannock I. F. Influence of vitamin A on immunological response. Immunology. 1972 Sep;23(3):283–287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGAN B. M., KAISER E. Vitamin A metabolism in infection; effect on sterile abscesses in the rat on serum and tissue vitamin A. J Nutr. 1955 Oct 10;57(2):277–286. doi: 10.1093/jn/57.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVENSON S. M., CROWLEY L. V., GEEVER E. F., ROSEN H., BERARD C. W. SOME STUDIES OF WOUND HEALING: EXPERIMENTAL METHODS, EFFECT OF ASCORBIC ACID AND EFFECT OF DEUTERIUM OXIDE. J Trauma. 1964 Sep;4:543–566. doi: 10.1097/00005373-196409000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVENSON S. M., GEEVER E. F., CROWLEY L. V., OATES J. F., 3rd, BERARD C. W., ROSEN H. THE HEALING OF RAT SKIN WOUNDS. Ann Surg. 1965 Feb;161:293–308. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196502000-00019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVENSON S. M., OATES J. F., GEEVER E. F. Effects of whole body x-irradiation on wound healing. Surg Forum. 1960;10:840–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledney G. D., Exum E. D., Sheehy P. A. Survival enhanced by skin-wound trauma in mice exposed to 60Co radiation. Experientia. 1981 Feb 15;37(2):193–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01963228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledney G. D., Stewart D. A., Exum E. D., Sheehy P. A. Skin wound-enhanced survival and myelocytopoiesis in mice after whole-body irradiation. Acta Radiol Oncol. 1981;20(1):29–38. doi: 10.3109/02841868109130187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Dennert G. Stimulatory effects of vitamin A analogs on induction of cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vivo. Cancer Res. 1979 Jan;39(1):55–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R. Effects of vitamin A and its analogs (retinoids) on normal and neoplastic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 12;605(1):33–91. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucy J. A., Lichti F. U. Reactions of vitamin A with acceptors of electrons. Interactions with iodine and the formation of iodide. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(2):231–241. doi: 10.1042/bj1120231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLAUGHLIN M. M., DACQUISTO M. P., JACOBUS D. P., HOROWITZ R. E. EFFECTS OF THE GERMFREE STATE ON RESPONSES OF MICE TO WHOLE-BODY IRRADIATION. Radiat Res. 1964 Nov;23:333–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkovský M., Edwards A. J., Hunt R., Palmer L., Medawar P. B. T-cell-mediated enhancement of host-versus-graft reactivity in mice fed a diet enriched in vitamin A acetate. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):338–340. doi: 10.1038/302338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. S., Lambert R., Martin F., André C. Effet protecteur de la vitamine A sur l'ulcère de contrainte du rat. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1967;161(12):2527–2530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medawar P. B., Hunt R. Anti-cancer action of retinoids. Immunology. 1981 Feb;42(2):349–353. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messerschmidt O. Strahlenbelastung und offene Hautwunde. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1966;227(1):329–335. doi: 10.1007/BF00502851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADAKOVICH M., DUTTON A. M., SCHILLING J. A. The effect of total body irradiation on wound closure. Ann Surg. 1954 Feb;139(2):186–194. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195402000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai K., Courtemanche A. D. Vitamin A assay in burned patients. J Trauma. 1975 May;15(5):419–424. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197505000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettura G., Barbul A., Levenson S. M., Seifter E. Increased survival in mice with C3H breast adenocarcinoma after tumor excision and vitamin A supplementation. Surg Forum. 1978;29:170–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettura G., Levenson S. M., Schittek A., Seifter E. Vitamin A: actions in oncogenesis and skin graft rejection. Surg Forum. 1975;26:301–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettura G., Schittek A., Hardy M., Levenson S. M., Demetriou A., Seifter E. Antitumor action of vitamin A in mice inoculated with adenocarcinoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jun;54(6):1489–1491. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.6.1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettura G., Stratford F., Levenson S. M., Seifter E. Prophylactic and therapeutic actions of supplemental beta-carotene in mice inoculated with C3HBA adenocarcinoma cells: lack of therapeutic action of supplemental ascorbic acid. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Jul;69(1):73–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifter E., Crowley L. V., Rettura G., Nakao K., Gruber C., Kan D., Levenson S. M. Influence of vitamin A on wound healing in rats with femoral fracture. Ann Surg. 1975 Jun;181(6):836–841. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197506000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifter E., Padawer J., Rettura G., Goodwin P., Levenson S. M. Cancer control: X-ray induced C3HBA tumor regression and prevention of its regrowth by beta-carotene or vitamin A. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;130:237–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifter E., Rettura G., Padawer J., Stratford F., Goodwin P., Levenson S. M. Regression of C3HBA mouse tumor due to X-ray therapy combined with supplemental beta-carotene or vitamin A. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Aug;71(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifter E., Rettura G., Padawer J., Stratford F., Kambosos D., Levenson S. M. Impaired wound healing in streptozotocin diabetes. Prevention by supplemental vitamin A. Ann Surg. 1981 Jul;194(1):42–50. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198107000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifter E., Rettura G., Stratford F., Yee C., Weinzweig J., Jacobson N. L., Levenson S. M. Vitamin A inhibits some aspects of systemic disease due to local x-radiation. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1981 Jul-Aug;5(4):288–294. doi: 10.1177/0148607181005004288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromberg L. R., McLaughlin M. M., Donati R. M. Combined surgical and radiation injury. 3. The effect of pre-irradiation radioprotective drug treatment. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Oct;129(1):140–143. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromberg L. R., Woodward K. T., Mahin D. T., Donati R. M. Altered wound healing in x-irradiated rats: the effect of bone marrow shielding. Experientia. 1967 Dec 15;23(12):1064–1065. doi: 10.1007/BF02136454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromberg L. W., Woodward K. T., Mahin D. T., Donati R. M. Combined surgical and radiation injury. The effect of timing of wounding and whole body gamma irradiation on 30 day mortality and rate of wound contracture in the rodent. Ann Surg. 1968 Jan;167(1):18–22. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196801000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOESSNER J. F., Jr The determination of hydroxyproline in tissue and protein samples containing small proportions of this imino acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:440–447. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90291-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


