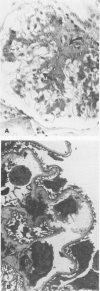
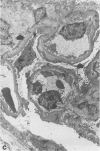
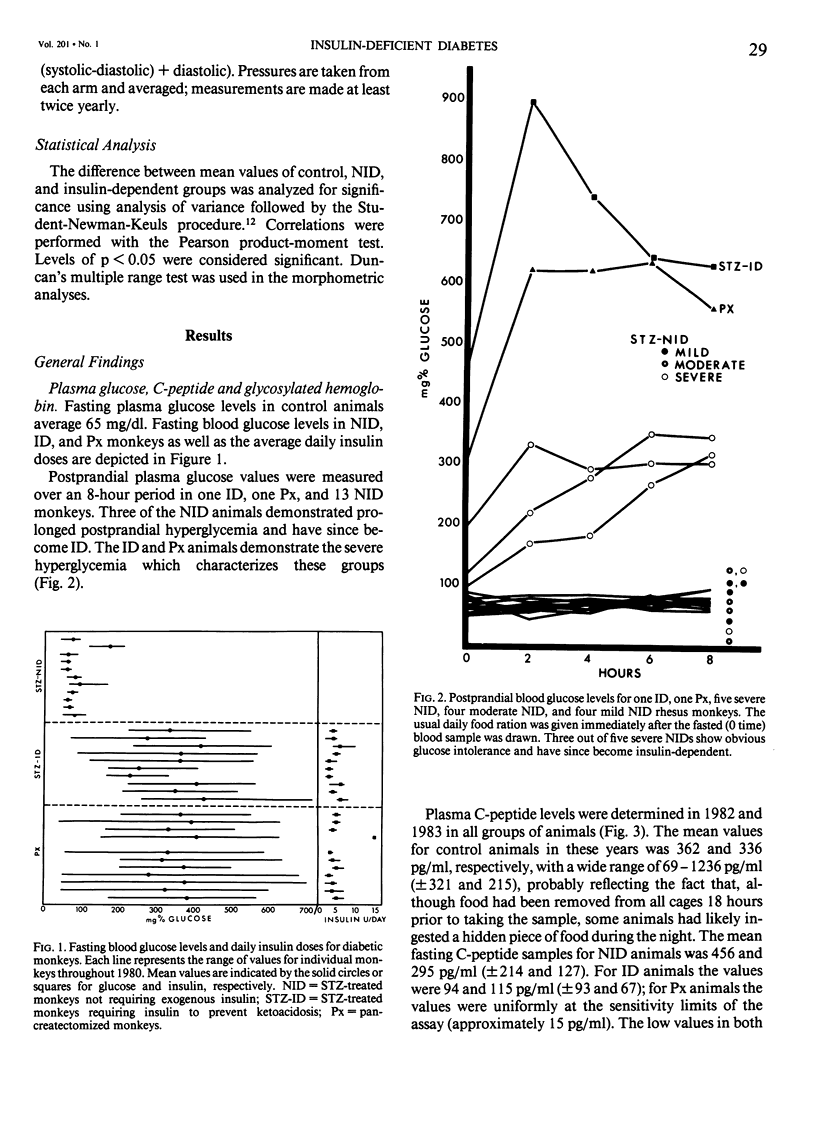
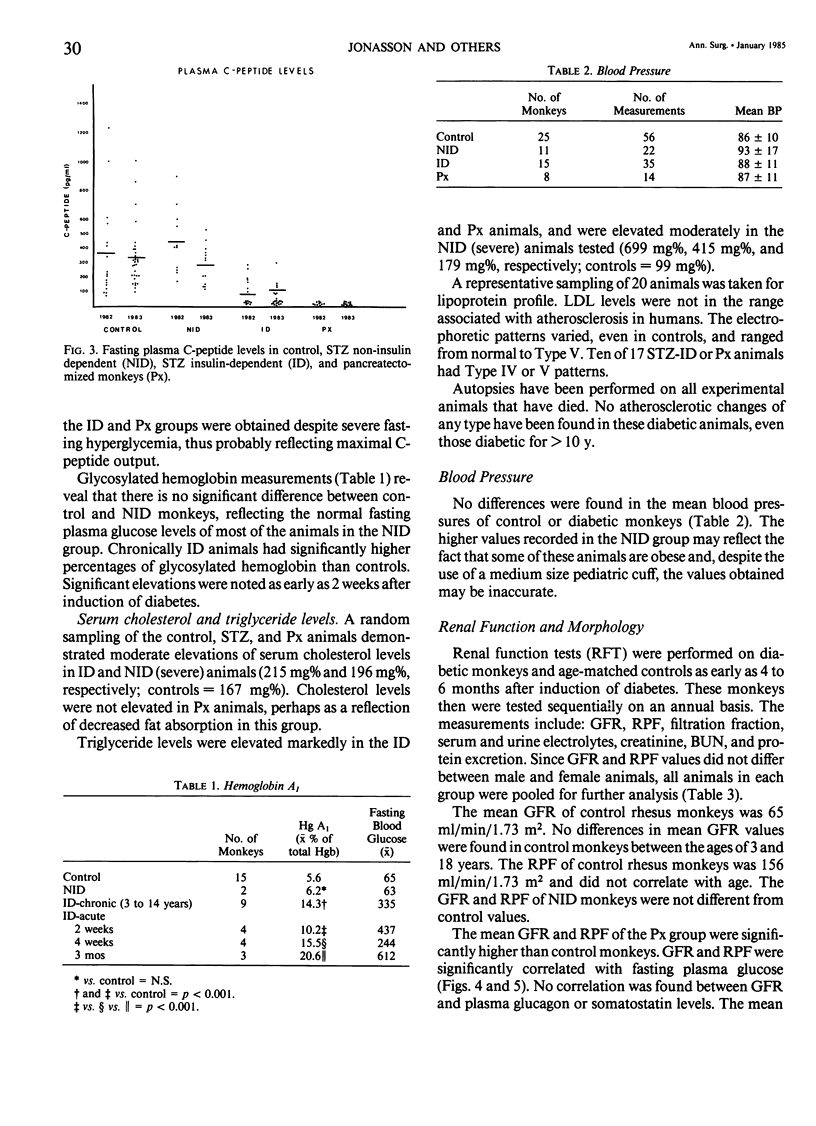
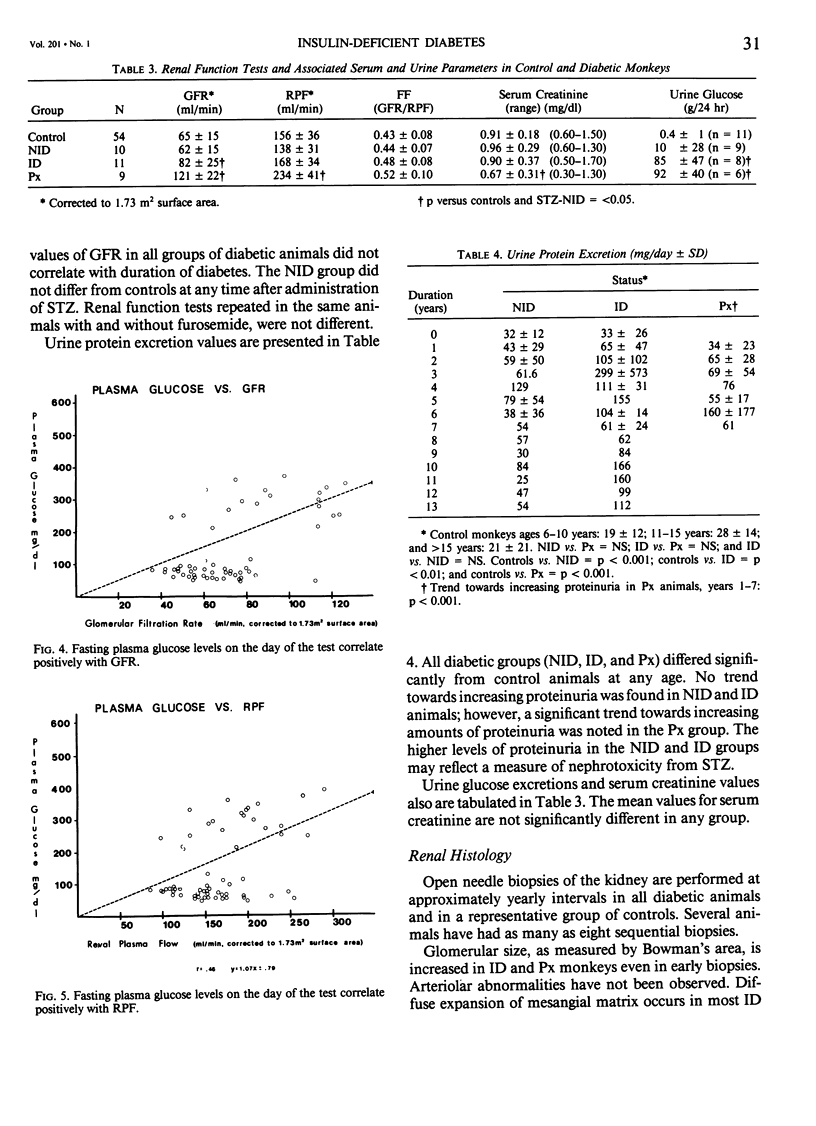
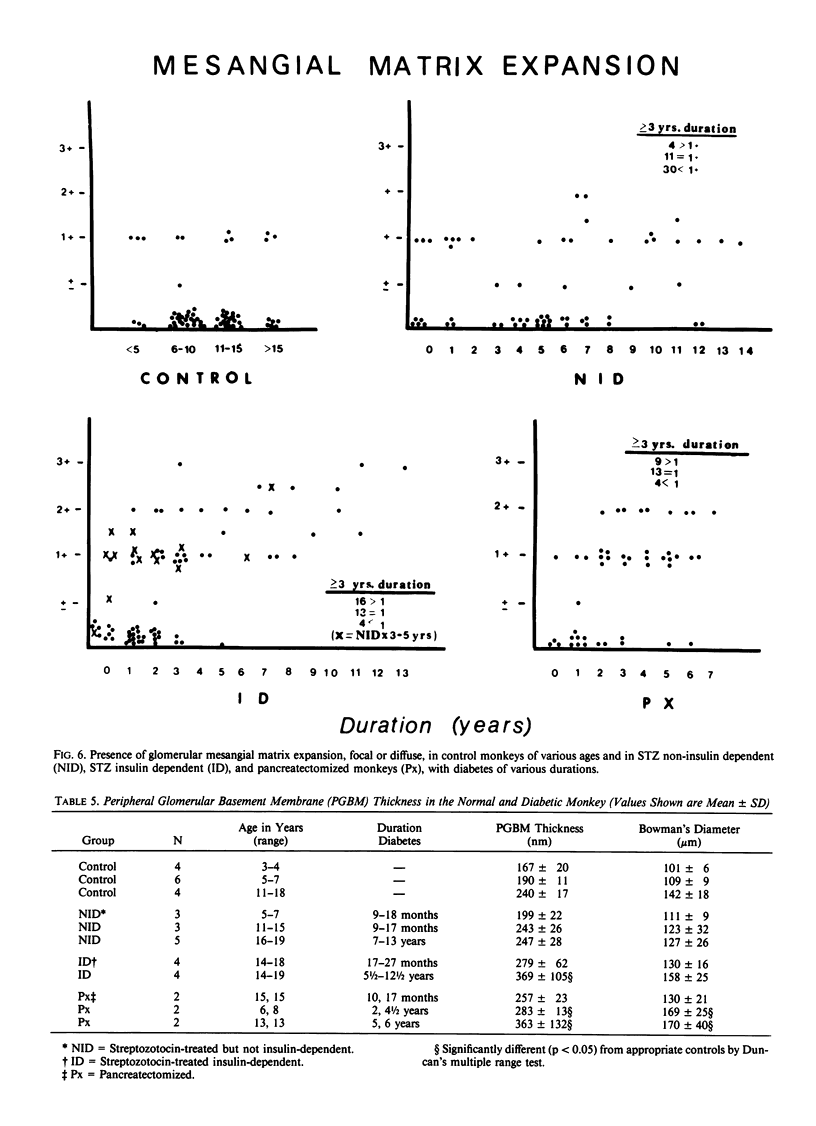
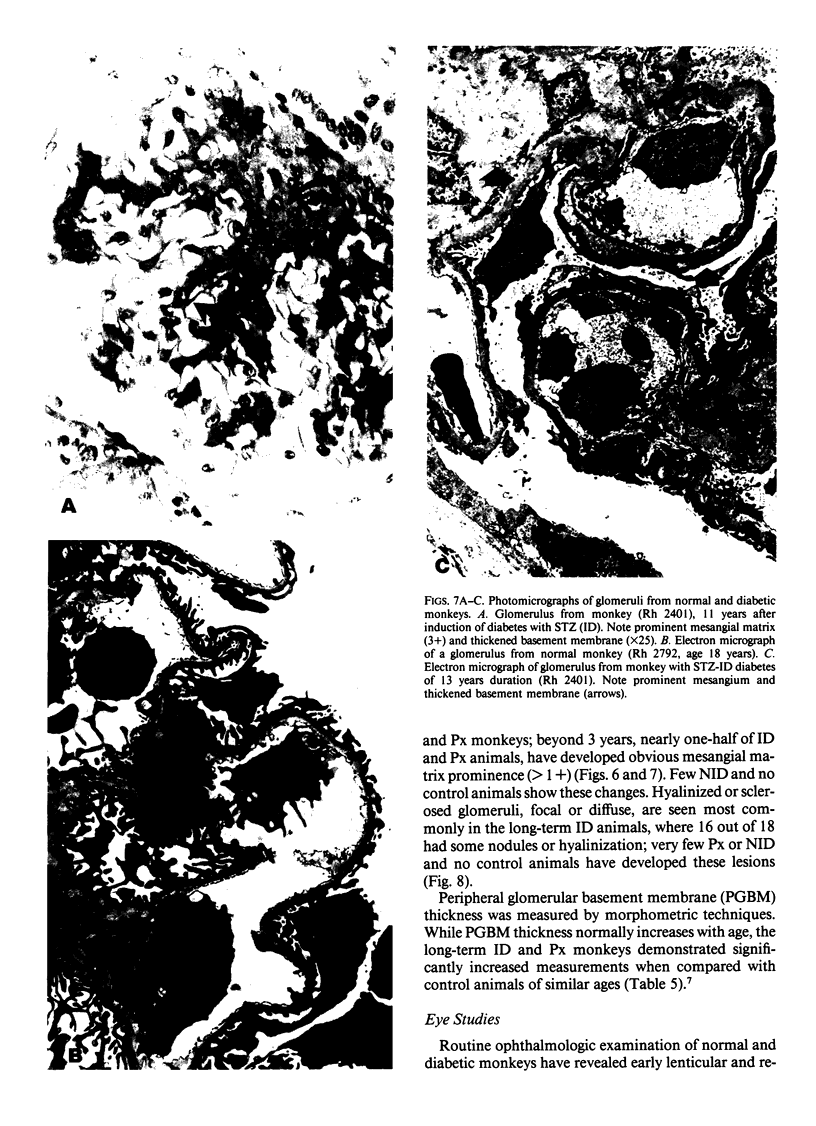
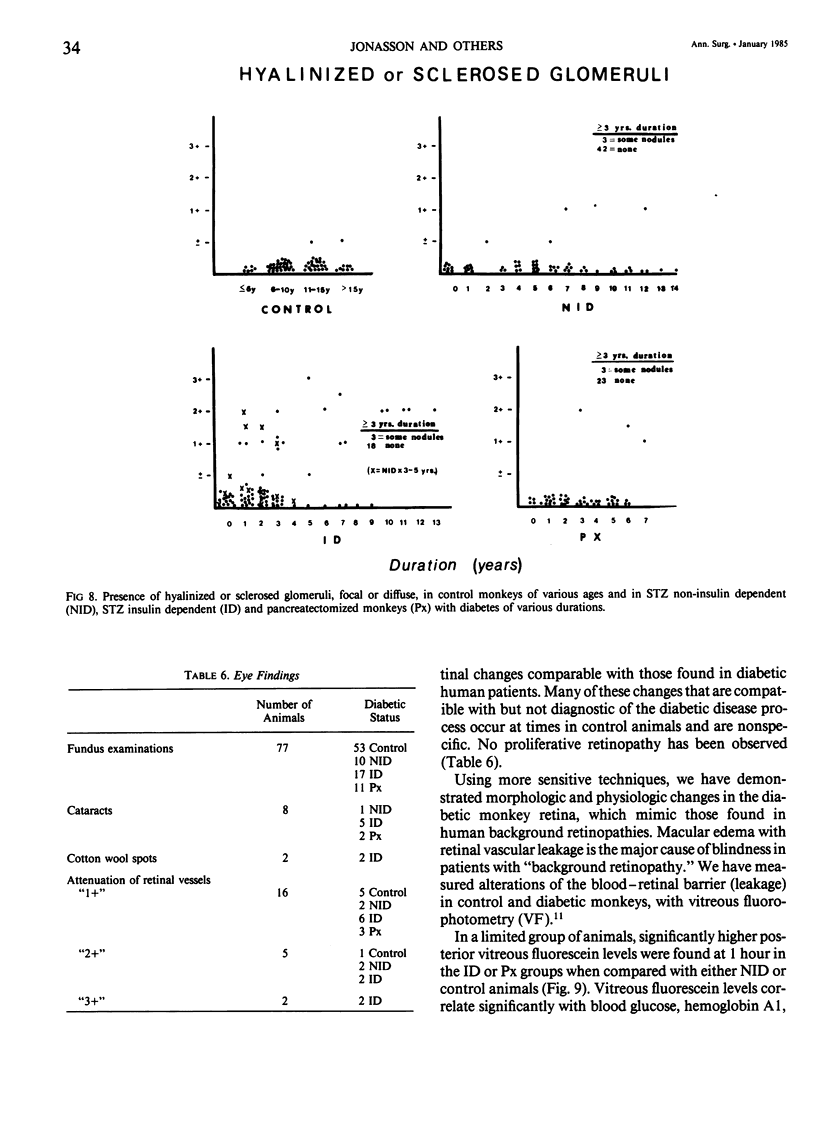
Abstract
In an 11-year study of experimental insulin-deficient diabetes (IDDM) induced in rhesus monkeys by streptozotocin or total pancreatectomy, the authors have found that pathophysiologic changes occur in eye and kidney, which closely resemble the early stages of human insulin deficient diabetes mellitus (IDDM). In addition, morphologic changes of thickening of glomerular capillary basement membrane and expansion of mesangial matrix (by light microscopy) appear within 3 years of onset of hyperglycemia. However, progression to irreversible complications of advanced diabetic nephropathy or proliferative retinopathy, have not occurred. This animal model resembles human disease in that the animals tend to become ketotic unless maintained with exogenous insulin; C-peptide production is low to absent, and large amounts of glycosylated hemoglobin develop within a month of onset. The monkeys differ from humans in the absence of hypertension and hyperlipidemia. The authors suggest that the abnormalities in basement membrane form and function caused by hyperglycemia form the necessary background upon which other factors, such as hypertension and hyperlipidemia, then act to cause irreversible complications. The role of pancreatic transplantation is in prevention of these background changes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett P. H., Rushforth N. B., Miller M., LeCompte P. M. Epidemiologic studies of diabetes in the Pima Indians. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1976;32:333–376. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571132-6.50021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkman J., Rifkin H. Unilateral nodular diabetic glomerulosclerosis (Kimmelstiel-Wilson): report of a case. Metabolism. 1973 May;22(5):715–722. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Hostetter T. H., Olson J. L., Rennke H. G., Venkatachalam M. A. The role of glomerular hyperfiltration in the initiation and progression of diabetic nephropathy. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1981;242:7–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAIRD F. I. Survival of diabetics with proteinuria. Diabetes. 1961 May-Jun;10:178–181. doi: 10.2337/diab.10.3.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha-Vaz J., Faria de Abreu J. R., Campos A. J. Early breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier in diabetes. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975 Nov;59(11):649–656. doi: 10.1136/bjo.59.11.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. M., Wise P. H., Craig R. J., Thomas D. W., Murchland J. B. Visual acuity and retinal changes in South Australian Aborigines. Aust N Z J Med. 1976 Jun;6(3):205–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1976.tb03655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engerman R., Finkelstein D., Aguirre G., Diddie K. R., Fox R. R., Frank R. N., Varma S. D. Ocular complications. Diabetes. 1982;31(Suppl 1 Pt 2):82–88. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.1.s82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELLMAN D. D., PIRANI C. L., SOOTHILL J. F., MUEHRCKE R. C., KARK R. M. Diabetic nephropathy: a clinical and pathologic study based on renal biopsies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1959 Dec;38:321–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRY R. J., SEGALOVE M., SOBEL C. Turbidimetric determination of proteins with sulfosalicylic and trichloracetic acids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Aug-Sep;92(4):748–751. doi: 10.3181/00379727-92-22601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy M. A., Lau H. T., Weber C., Reemtsma K. Pancreatic islet transplantation: immuno-alteration with ultraviolet irradiation. World J Surg. 1984 Apr;8(2):207–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01655137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. W., Reynolds W. A., Hoganson G. E. Streptozotocin diabetes in the monkey: plasma levels of glucose, insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin, with corresponding morphometric analysis of islet endocrine cells. Diabetes. 1980 Jul;29(7):536–546. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.7.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. W., West M. S., Hong D. T., Jonasson O. Peripheral glomerular basement membrane thickness in the normal and diabetic monkey. Lab Invest. 1984 Aug;51(2):193–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOWLES H. C., Jr, GUEST G. M., LAMPE J., KESSLER M., SKILLMAN T. G. THE COURSE OF JUVENILE DIABETES TREATED WITH UNMEASURED DIET. Diabetes. 1965 May;14:239–273. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.5.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowler W. C., Bennett P. H., Ballintine E. J. Increased incidence of retinopathy in diabetics with elevated blood pressure. A six-year follow-up study in Pima Indians. N Engl J Med. 1980 Mar 20;302(12):645–650. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198003203021201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles H. C., Jr Magnitude of the renal failure problem in diabetic patients. Kidney Int Suppl. 1974 Oct;(1):2–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty K. J., Prowse S. J., Simeonovic C. J., Warren H. S. Immunobiology of tissue transplantation: a return to the passenger leukocyte concept. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:143–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel T. E., Collier S., Hoffman L., Pyke K., Carter W. M., Koulmanda M. Isotransplantation of fetal mouse pancreas in experimental diabetes. Effect of gestational age and organ culture. Lab Invest. 1982 Nov;47(5):477–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Steffes M. W., Azar S., Sandberg S. K., Brown D. M. The effects of Goldblatt hypertension on development of the glomerular lesions of diabetes mellitus in the rat. Diabetes. 1978 Jul;27(7):738–744. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.7.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Steffes M. W., Connett J., Najarian J. S., Sutherland D. E., Barbosa J. The development of lesions in the glomerular basement membrane and mesangium after transplantation of normal kidneys to diabetic patients. Diabetes. 1983 Oct;32(10):948–952. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.10.948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menard L., Dempsey M. E., Blankstein L. A., Aleyassine H., Wacks M., Soeldner J. S. Quantitiative determination of glycosylated hemoglobin A1 by agar gel electrophoresis. Clin Chem. 1980 Oct;26(11):1598–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Antihypertensive treatment inhibiting the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1980;238:103–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. E., Sutherland D. E., Steffes M. W., Najarian J. S., Bach F. H. H-2 antigen class: effect on mouse islet allograft rejection. Science. 1983 Mar 18;219(4590):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.6402817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterby R. A quantitative electron microscopic study of mesangial regions in glomeruli from patients with short term juvenile diabetes mellitus. Lab Invest. 1973 Jul;29(1):99–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterby R., Gundersen H. J. Glomerular size and structure in diabetes mellitus. I. Early abnormalities. Diabetologia. 1975 Jun;11(3):225–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00422326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osuntokun B. O. Diabetic retinopathy in Nigerians. A study of 758 patients. Br J Ophthalmol. 1969 Oct;53(10):652–663. doi: 10.1136/bjo.53.10.652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otim M. A. Preliminary observations on diabetic retinopathy in Ugandan Africans attending Mulago Diabetic Clinic. East Afr Med J. 1975 Feb;52(2):63–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALOMON M. DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY: CLINICOPATHOLOGIC CORRELATION. A STUDY BASED ON RENAL BIOPSIES. Metabolism. 1963 Aug;12:687–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIGMAN E. M., ELWOOD C., REAGAN M. E., MORRIS A. M., CATANZARO A. THE RENAL CLEARANCE OF I-131 LABELLED SODIUM IOTHALAMATE IN MAN. Invest Urol. 1965 Mar;2:432–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffes M. W., Brown D. M., Mauer S. M. Diabetic glomerulopathy following unilateral nephrectomy in the rat. Diabetes. 1978 Jan;27(1):35–41. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso M. O., Shih C. Y., McLean I. W. Is there a blood-brain barrier at the optic nerve head? Arch Ophthalmol. 1975 Sep;93(9):815–825. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1975.01010020703008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viberti G. C., Pickup J. C., Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Effect of control of blood glucose on urinary excretion of albumin and beta2 microglobulin in insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 22;300(12):638–641. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197903223001202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE P. Natural course and prognosis of juvenile diabetes. Diabetes. 1956 Nov-Dec;5(6):445–450. doi: 10.2337/diab.5.6.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. J., Blainey J. D., Brewer D. B., Fitzgerald M. G., Malins J. M., O'Sullivan D. J., Pinto J. A. The natural history of diabetic renal disease. A follow-up study of a series of renal biopsies. Q J Med. 1972 Oct;41(164):437–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West K. M., Erdreich L. J., Stober J. A. A detailed study of risk factors for retinopathy and nephropathy in diabetes. Diabetes. 1980 Jul;29(7):501–508. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.7.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]