Abstract
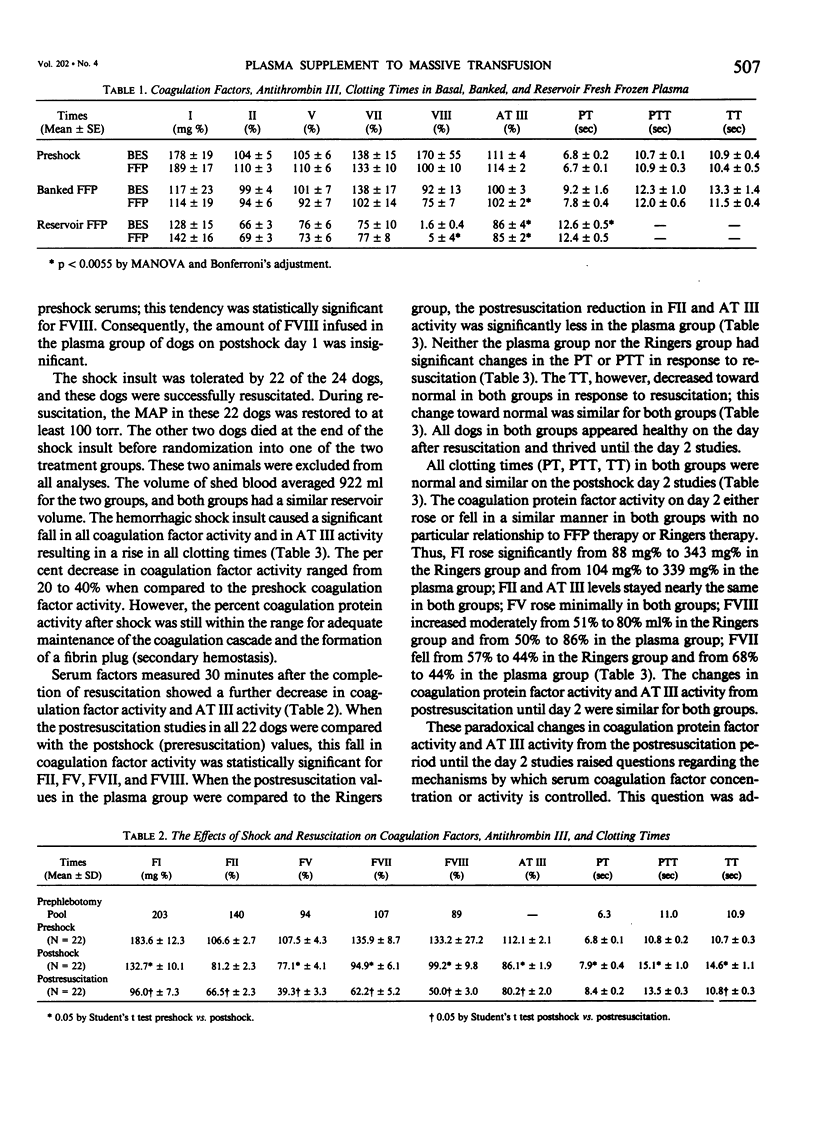
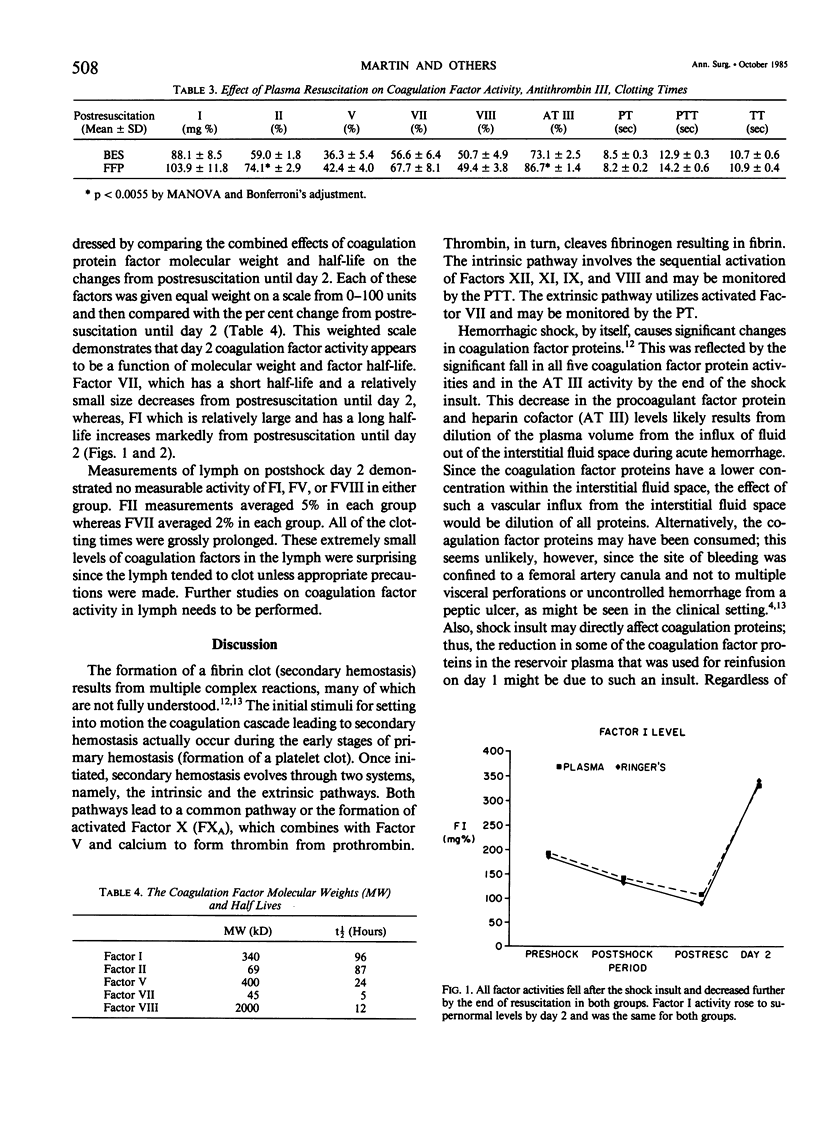
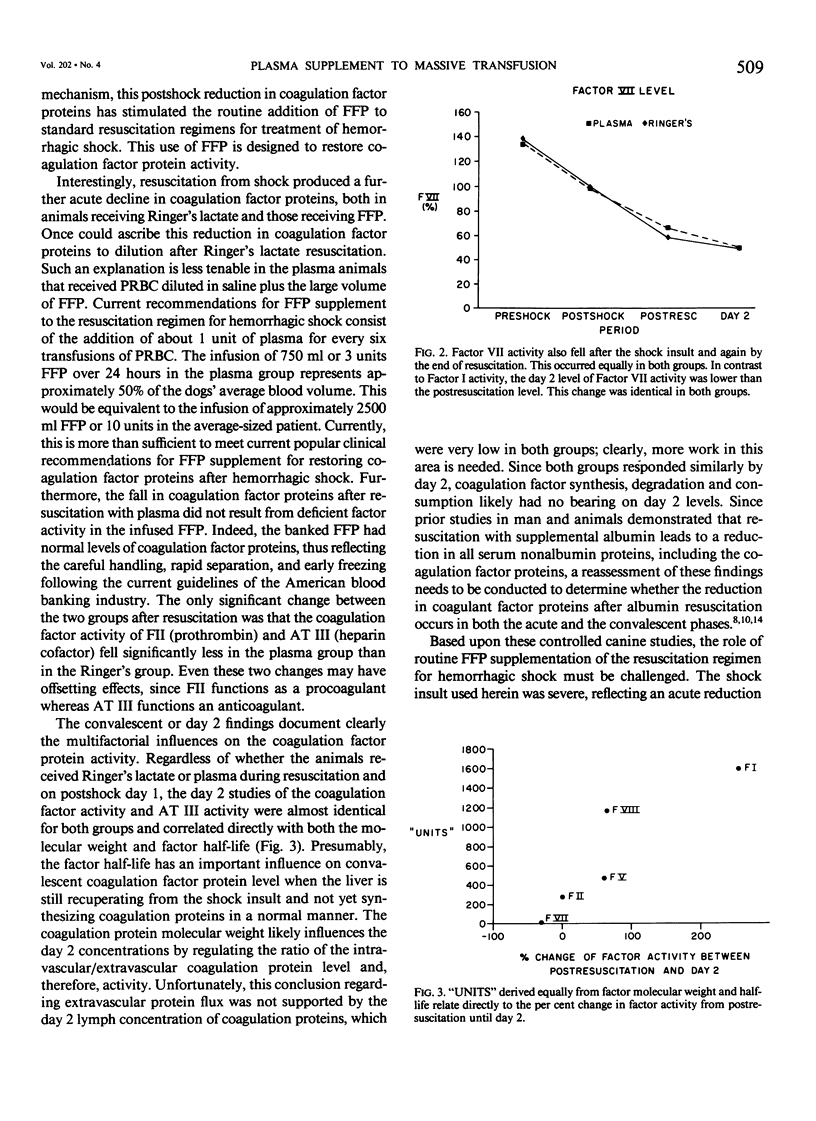
The efficacy of supplemental fresh frozen plasma (FFP) therapy after massive packed red cell (PRBC) replacement for hemorrhagic shock was studied in 22 conditioned dogs. Ten dogs were randomized to received FFP, balanced electrolyte solution (BES), and PRBC, while 12 dogs received BES and PRBC. Coagulation factor activity for Factors I, II, V, VII and VIII, as well as antithrombin III (AT III), prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and thrombin time, were measured at preshock, postshock, postresuscitation, and postshock day two. All coagulation factor activities fell with shock and decreased further with resuscitation in both groups. Factor II (a procoagulant) and AT III (an anticoagulant) fell significantly less after resuscitation in the plasma dogs; otherwise, no postresuscitation differences were seen. The changes in factor activity from postresuscitation until day two reflected factor half life and molecular weight, independent of FFP therapy. These data show that prophylactic FFP therapy does not efficiently restore coagulation activity. Consequently, routine FFP therapy for its procoagulant effects after hemorrhagic shock should be abandoned pending controlled studies in man.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins J. A. Problems associated with the massive transfusion of stored blood. Surgery. 1974 Feb;75(2):274–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Counts R. B., Haisch C., Simon T. L., Maxwell N. G., Heimbach D. M., Carrico C. J. Hemostasis in massively transfused trauma patients. Ann Surg. 1979 Jul;190(1):91–99. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197907000-00020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrigan C., Lucas C. E., Ledgerwood A. M., Walz D. A., Mammen E. F. Serial changes in primary hemostasis after massive transfusion. Surgery. 1985 Oct;98(4):836–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. D., Lucas C. E., Gerrick S. J., Ledgerwood A. M., Higgins R. F. Altered coagulation after albumin supplements for treatment of oligemic shock. Arch Surg. 1979 Apr;114(4):379–383. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1979.01370280033005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibold W. C., Lucas C. E., Ledgerwood A. M., Mammen E. F., Denis R., Grabow D., Staricco R. J. Effect of albumin resuscitation on canine coagulation activity and content. Ann Surg. 1983 Nov;198(5):630–633. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198311000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim R. C., Jr, Olcott C., 4th, Robinson A. J., Blaisdell F. W. Platelet response and coagulation changes following massive blood replacement. J Trauma. 1973 Jul;13(7):577–582. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197307000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C. E., Ledgerwood A. M. Clinical significance of altered coagulation tests after massive transfusion for trauma. Am Surg. 1981 Mar;47(3):125–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C. E., Ledgerwood A. M., Mammen E. F. Altered coagulation protein content after albumin resuscitation. Ann Surg. 1982 Aug;196(2):198–202. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198208000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara J. J., Burran E. L., Stremple J. F., Molot M. D. Coagulopathy after major combat injury: occurrence, management, and pathophysiology. Ann Surg. 1972 Aug;176(2):243–246. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197208000-00021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. D., Robbins T. O., Tong M. J., Barton S. L. Coagulation defects associated with massive blood transfusions. Ann Surg. 1971 Nov;174(5):794–801. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197111000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. W., Ledgerwood A. M., Lucas C. E., Higgins R., Bouwman D. L., Johnson S. D. Pulmonary effects of albumin resuscitation for severe hypovolemic shock. Arch Surg. 1978 Apr;113(4):387–392. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1978.01370160045006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


