Abstract
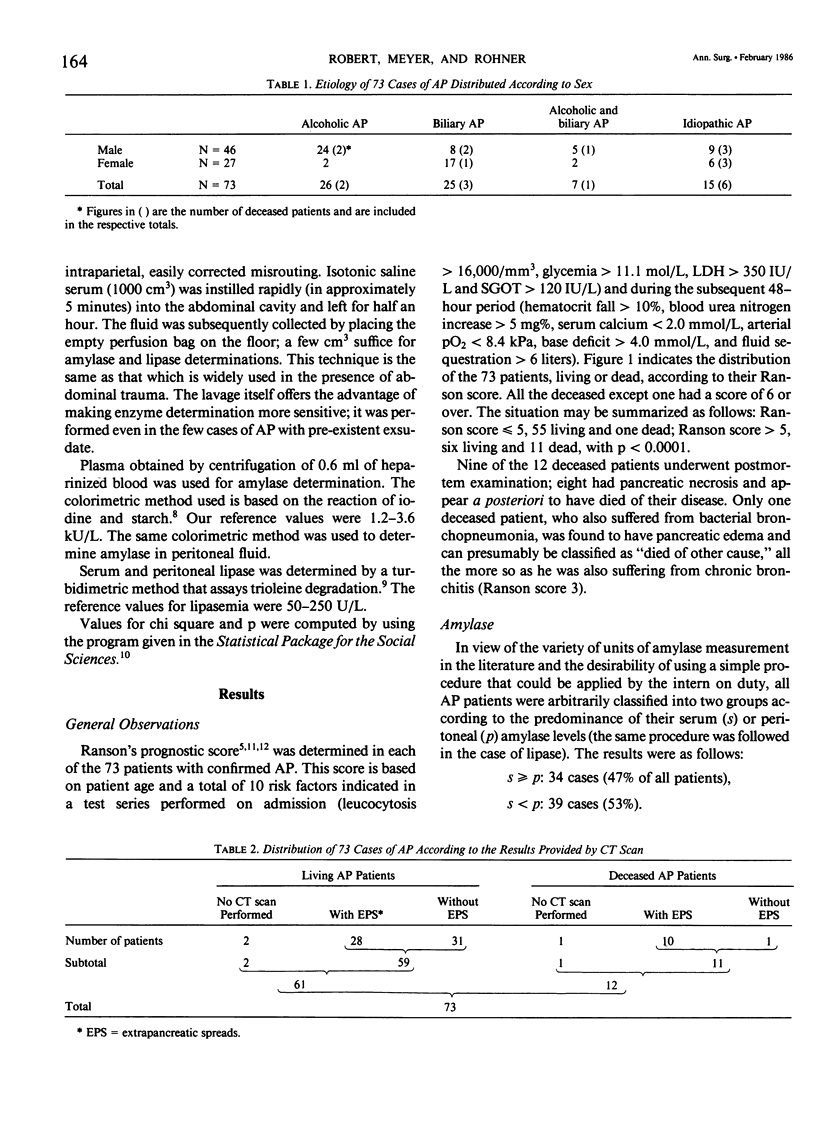
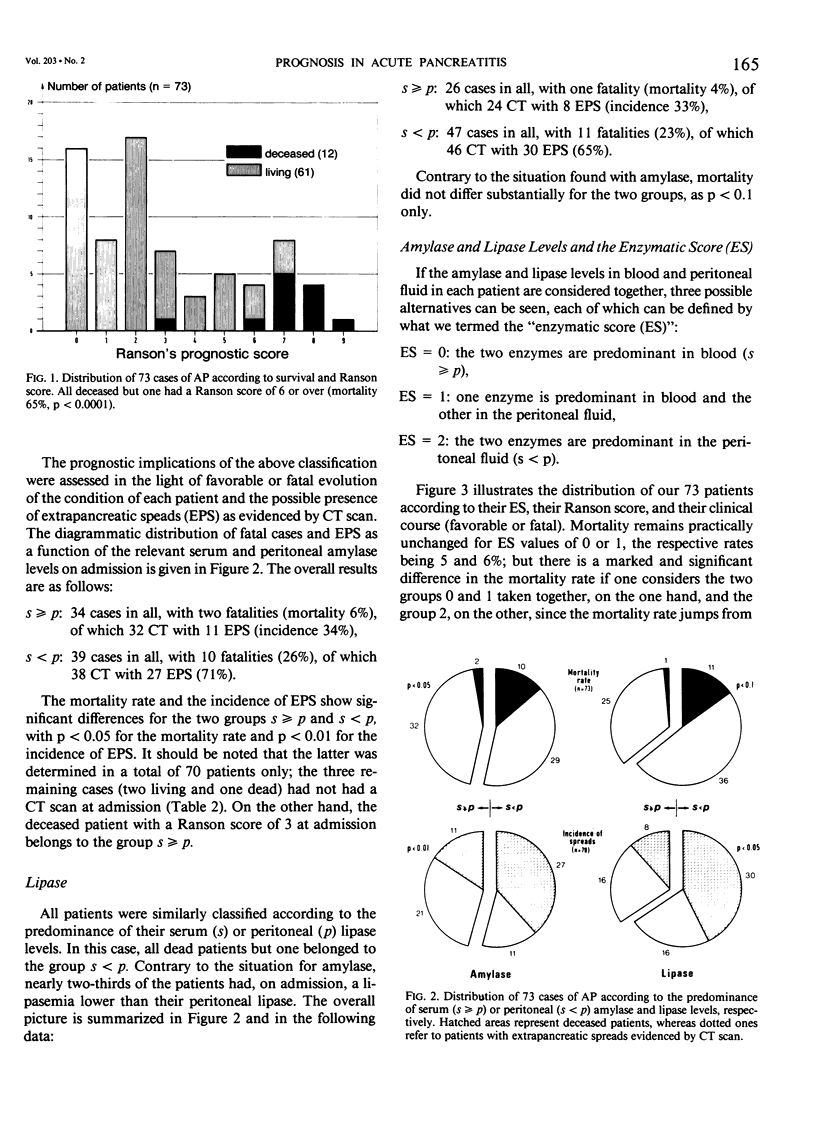
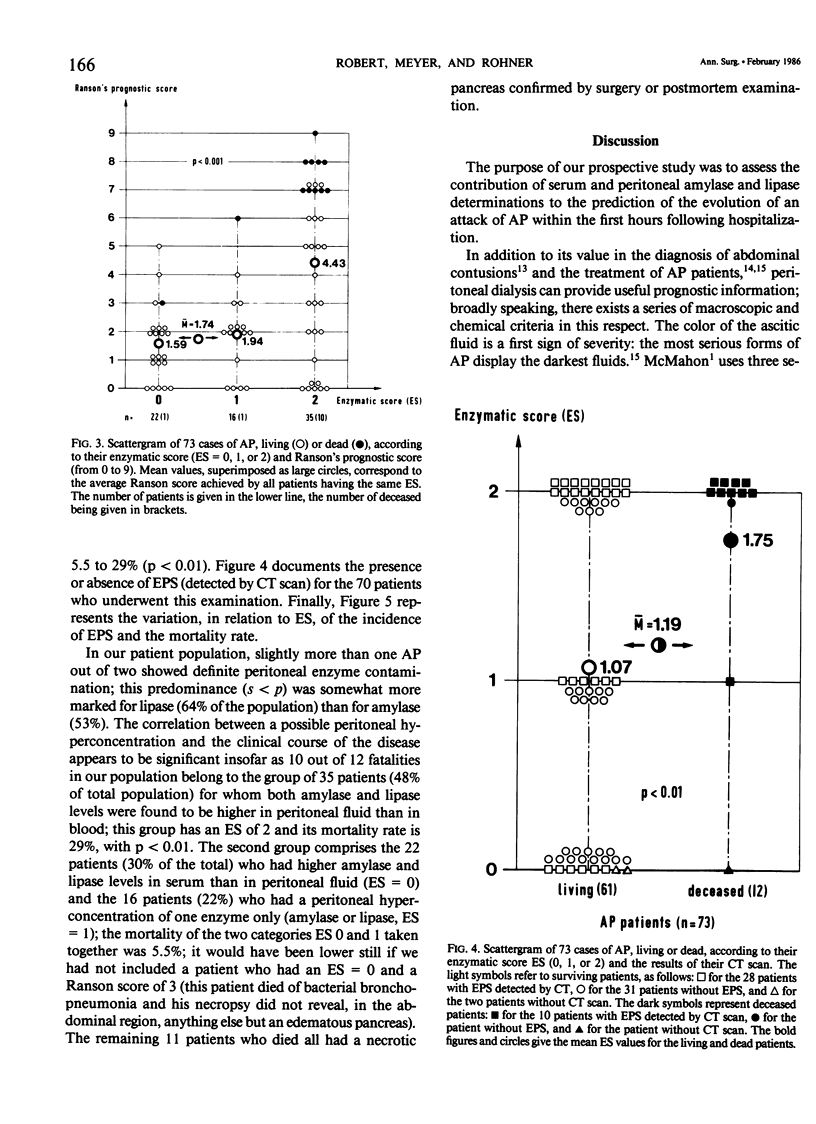
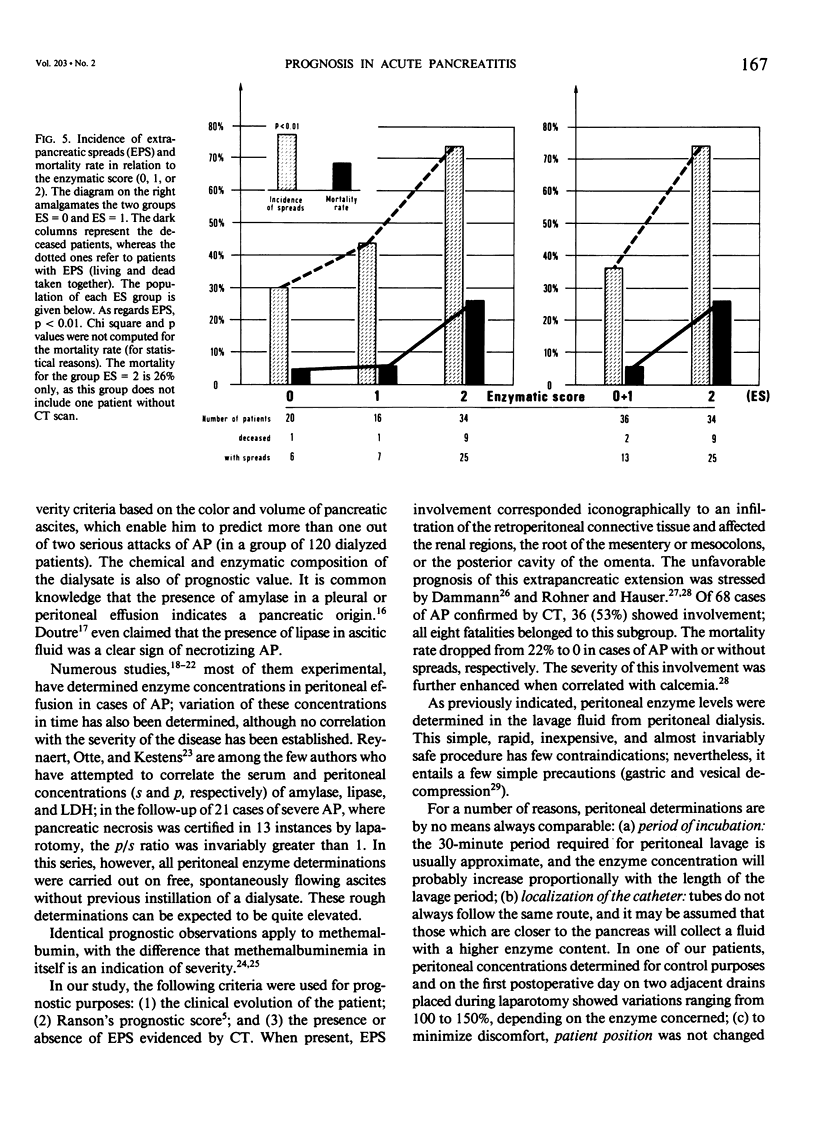
Serum and peritoneal amylase and lipase levels were determined at an early stage in 73 patients with acute pancreatitis confirmed by computed tomography (CT scan), surgery, and/or postmortem. Each patient was given an enzymatic score (ES), which reflects the predominance of the serum or peritoneal concentration of the two enzymes, as the case may be. This score can thus be either 0, 1, or 2; ES = 0 if neither enzyme is predominant in the peritoneal fluid, ES = 1 if amylase or lipase alone are predominant therein, and ES = 2 if both enzymes are predominant. This enzymatic score appears to be a good indicator of severity of disease, being as it is directly and significantly related to mortality rate, prognostic score as proposed by Ranson, and incidence of extrapancreatic spreads as demonstrated by CT scan. In 38 patients (including two fatalities) with an enzymatic score of 0 or 1, mortality was 5%, whereas in 35 patients (10 fatalities) with ES = 2, mortality was 29% (p less than 0.01).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolooki H., Gliedman M. L. Peritoneal dialysis in treatment of acute pancreatitis. Surgery. 1968 Aug;64(2):466–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doutre L. P., Perissat J., Beraud C., Hirigoyen P., Tamarelle C. Diagnostic des nécroses pancréatiques. Intérêt de la ponction-lavage du péritoine. Nouv Presse Med. 1972 Feb 19;1(8):515–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN L., DOUBILET H. A rapid serum amylase test. J Am Med Assoc. 1955 Mar 12;157(11):908–909. doi: 10.1001/jama.1955.02950280032010b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollender L. F., Meyer C. Traitement chirurgical des pancréatites aiguës. Chirurgie. 1977;103(9):864–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ W., SILVERSTEIN M., KOBOLD E. E., THAL A. P. TRYPSIN RELEASE, KININ PRODUCTION, AND SHOCK; RELATIONSHIP IN EXPERIMENTAL AND HUMAN PANCREATITIS. Arch Surg. 1964 Aug;89:322–331. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1964.01320020086014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler D. F., Eckfeldt J. H., Levitt M. D. Diagnostic value of routine isoamylase assay of hyperamylasemic serum. Gastroenterology. 1982 May;82(5 Pt 1):887–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon M. J., Playforth M. J., Pickford I. R. A compaative study of methods for the prediction of severity of attacks of acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1980 Jan;67(1):22–25. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800670107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Tegner H. Experimental pancreatitis in the dog. Demonstration of trypsin in ascitic fluid, lymph and plasma. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1973;8(2):129–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. C., Bivins B. A., Bell R. M. Diagnostic peritoneal lavage. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1982 Aug;155(2):257–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranson J. H. Acute pancreatitis--where are we? Surg Clin North Am. 1981 Feb;61(1):55–70. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)42332-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranson J. H., Pasternack B. S. Statistical methods for quantifying the severity of clinical acute pancreatitis. J Surg Res. 1977 Feb;22(2):79–91. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(77)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranson J. H., Spencer F. C. The role of peritoneal lavage in severe acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1978 May;187(5):565–575. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197805000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosato E. F., Mullis W. F., Rosato F. E. Peritoneal lavage therapy in hemorrhagic pancreatitis. Surgery. 1973 Jul;74(1):106–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satiani B., Stone H. H. Predictability of present outcome and future recurrence in acute pancreatitis. Arch Surg. 1979 Jun;114(6):711–716. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1979.01370300065010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller W. R., Suriyapa C., Anderson M. C. A review of experimental pancreatitis. J Surg Res. 1974 Jan;16(1):69–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(74)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER M. D., CORRELL W. W., FAIN W. R., CONN J. H., COCKRELL J. V. ENZYME LEVELS IN PANCREATIC TISSUE AND BODY FLUIDS DURING EXPERIMENTAL PANCREATITIS. J Surg Res. 1963 Dec;3:485–490. doi: 10.1016/s0022-4804(63)80027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell J. E., Rigby C. C., Talbot C. H., Duncan E. H. A controlled trial of Trasylol in the treatment of acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1974 Mar;61(3):177–182. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800610303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARTER J., METAIS P., WEILL J. P., STORCK D. [Value of the enzymatic study of various effusions in the course of diseases of the pancreas]. Rev Int Hepatol. 1962;12:1033–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall A. J. Peritoneal dialysis in the treatment of severe acute pancreatitis. Med J Aust. 1965 Aug 14;2(7):281–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. W., Bouwman D. L., Walt A. J., Clink D., Resto A., Stephany J. A correlation between clinical pancreatitis and isoenzyme patterns of amylase. Surgery. 1982 Oct;92(4):576–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


