Abstract
1. The amounts of total acetylcholine (ACh) and ATP, and of vesicle-bound ACh were measured at short time intervals in the electrogenic tissue of Torpedo marmorata. The aim of this study is to approach with biochemical analysis the speed of electrophysiological phenomena.
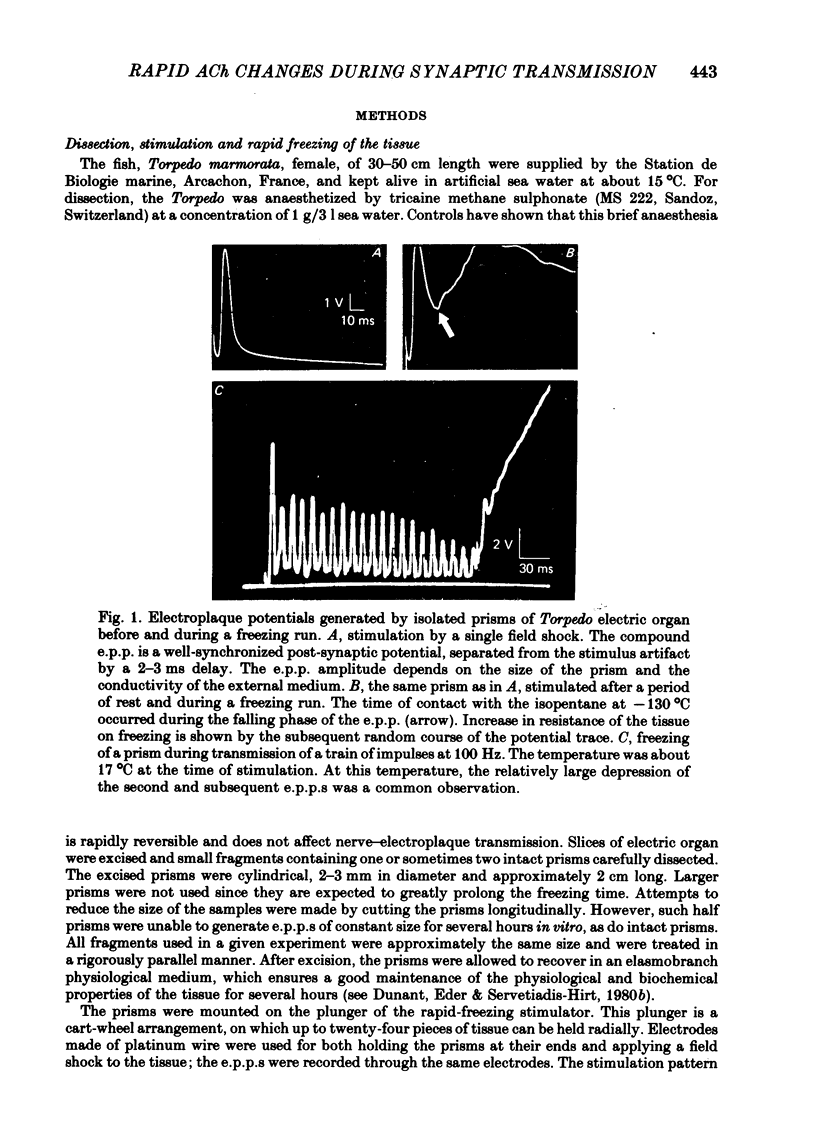
2. A stimulator coupled to a rapid freezer device was used to quench a number of tissue samples simultaneously, at different time intervals during transmission of a brief train of impulses at 100 Hz.
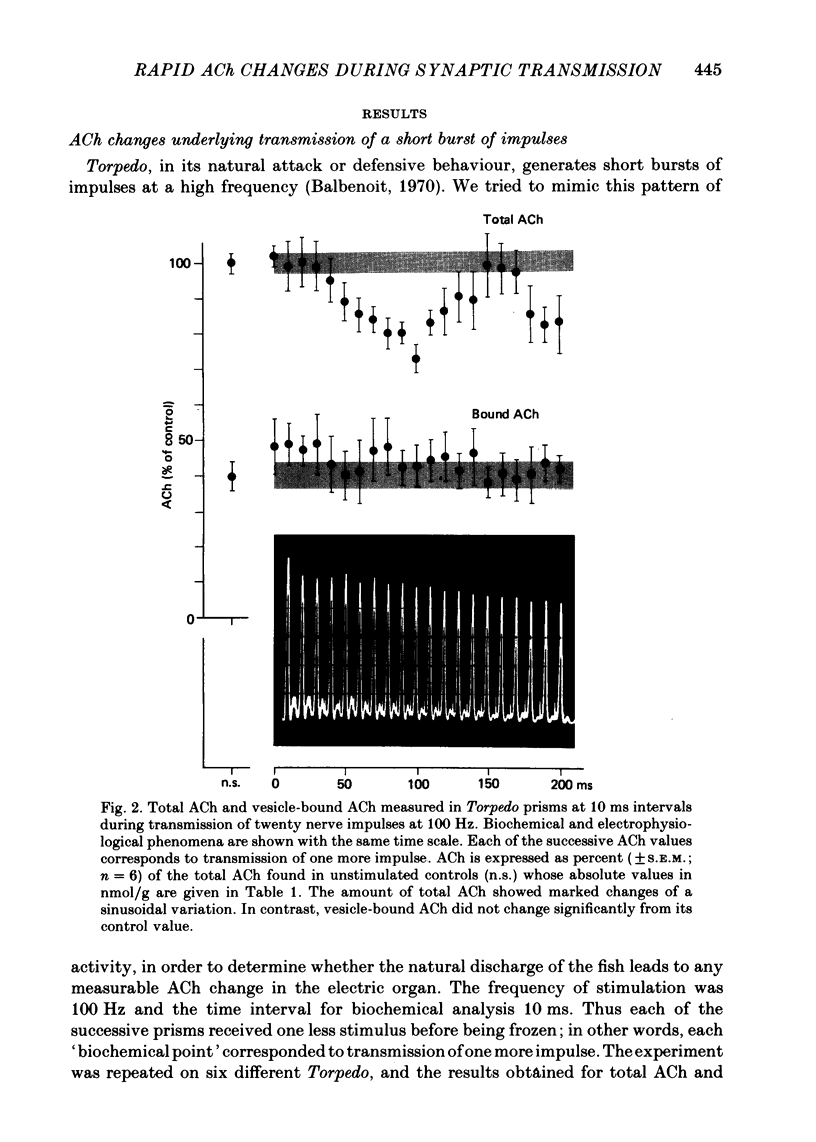
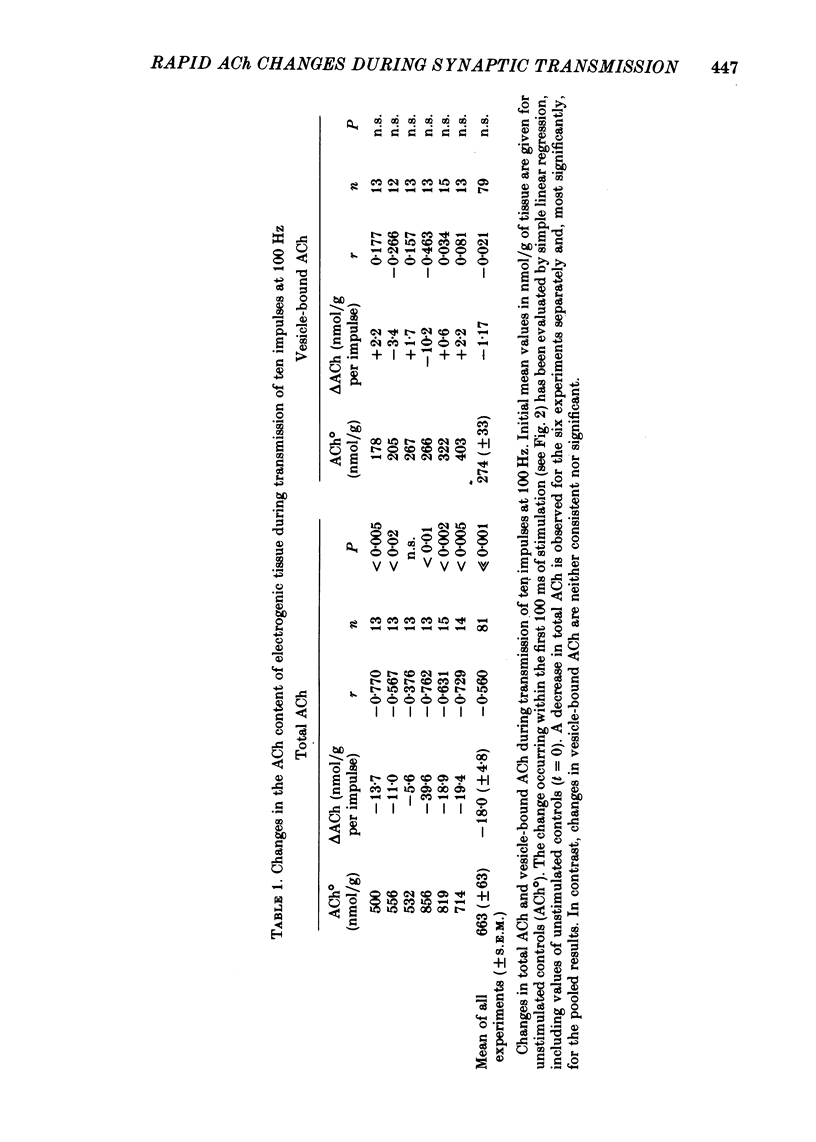
3. The level of total ACh decreased significantly with the first ten impulses. Then a rapid but transient increase in total ACh occurred, reaching a maximum value by the fifteenth to sixteenth impulse.
4. Vesicle-bound ACh did not exhibit any changes parallel to those of total ACh, and did not decrease beyond the control level during transmission of twenty impulses at 100 Hz.
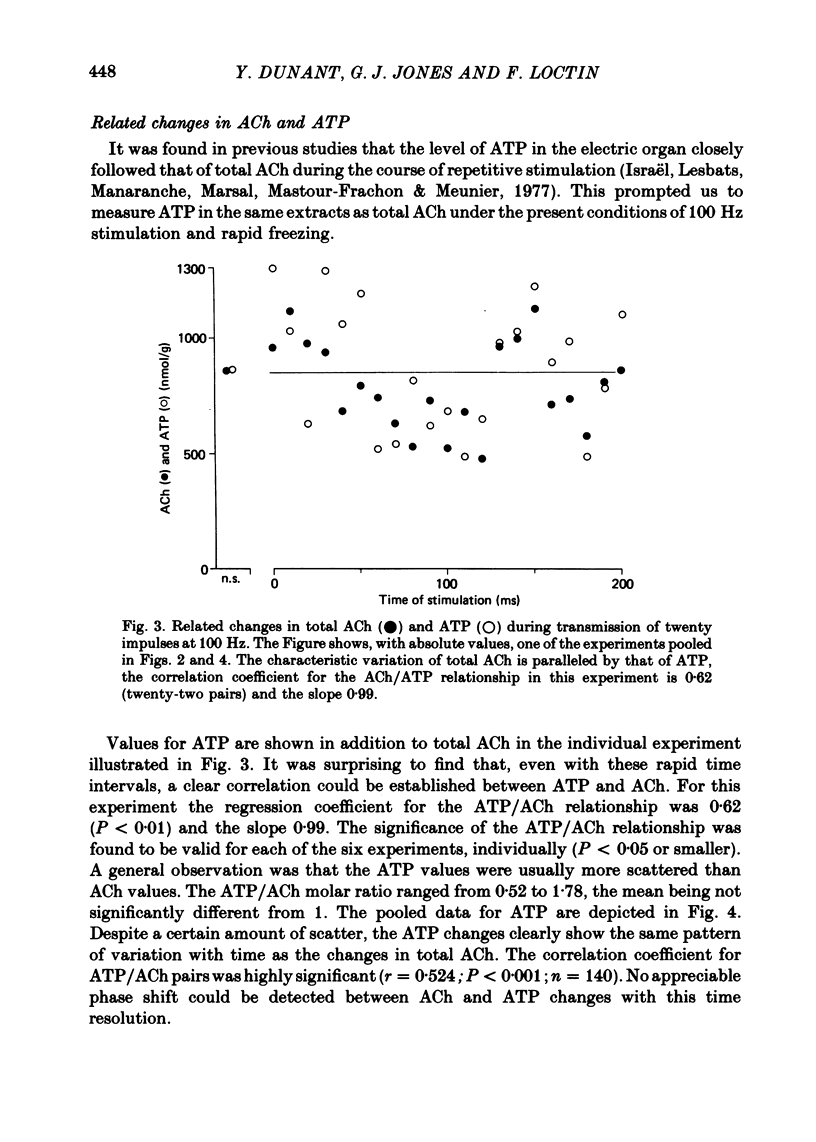
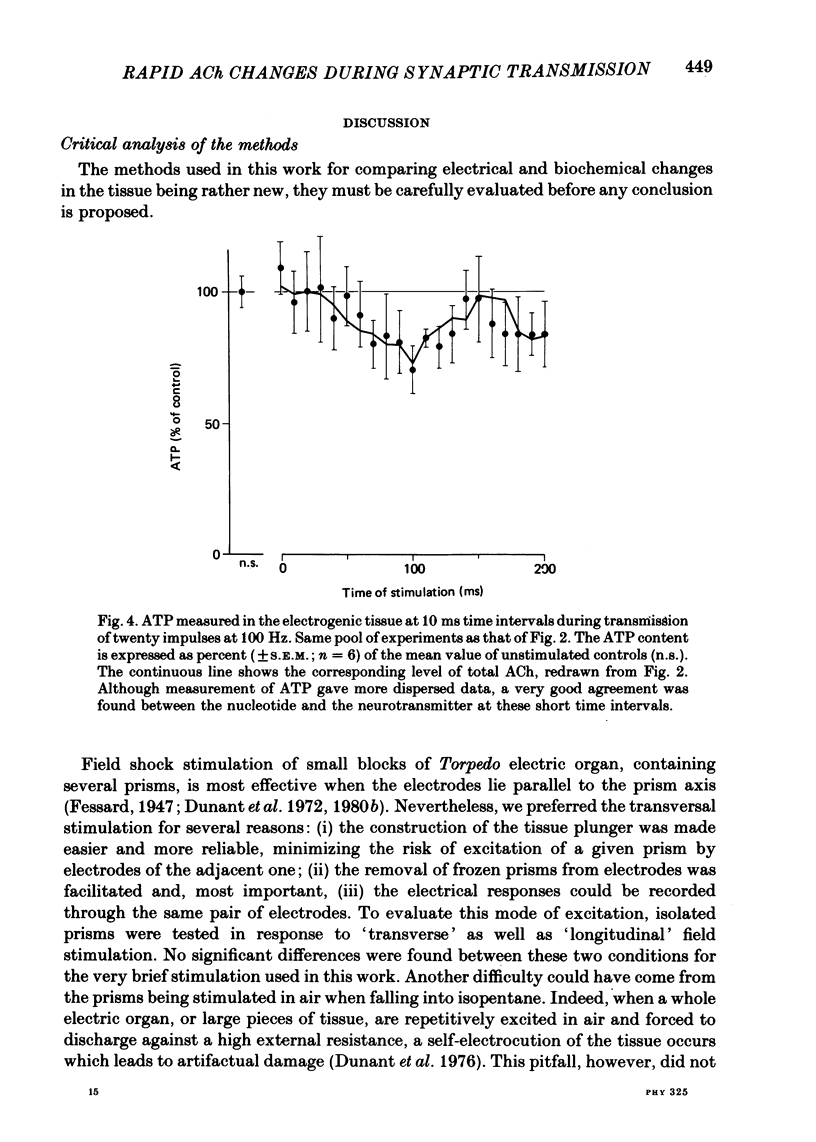
5. The amount of ATP in the tissue varied in close relation to that of total ACh. No significant phase shift was observed between the transmitter and the nucleotide and the ACh/ATP molar ratio was not significantly different from 1.
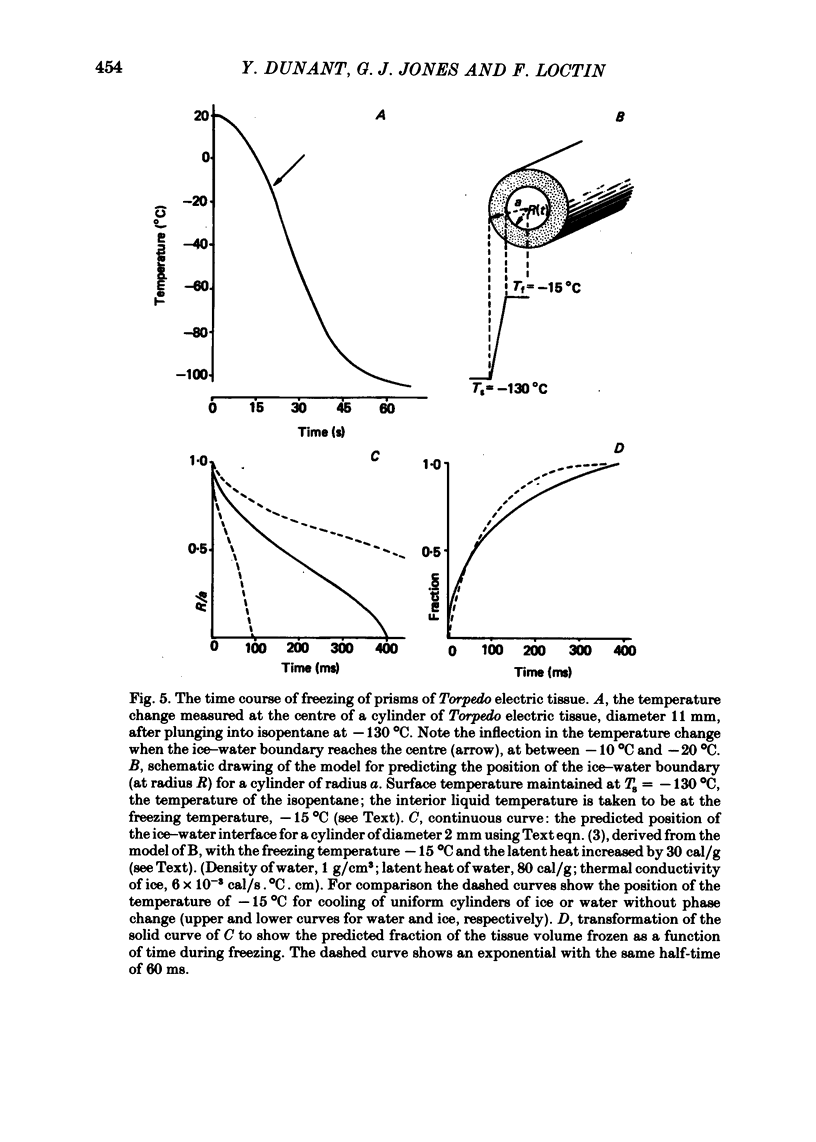
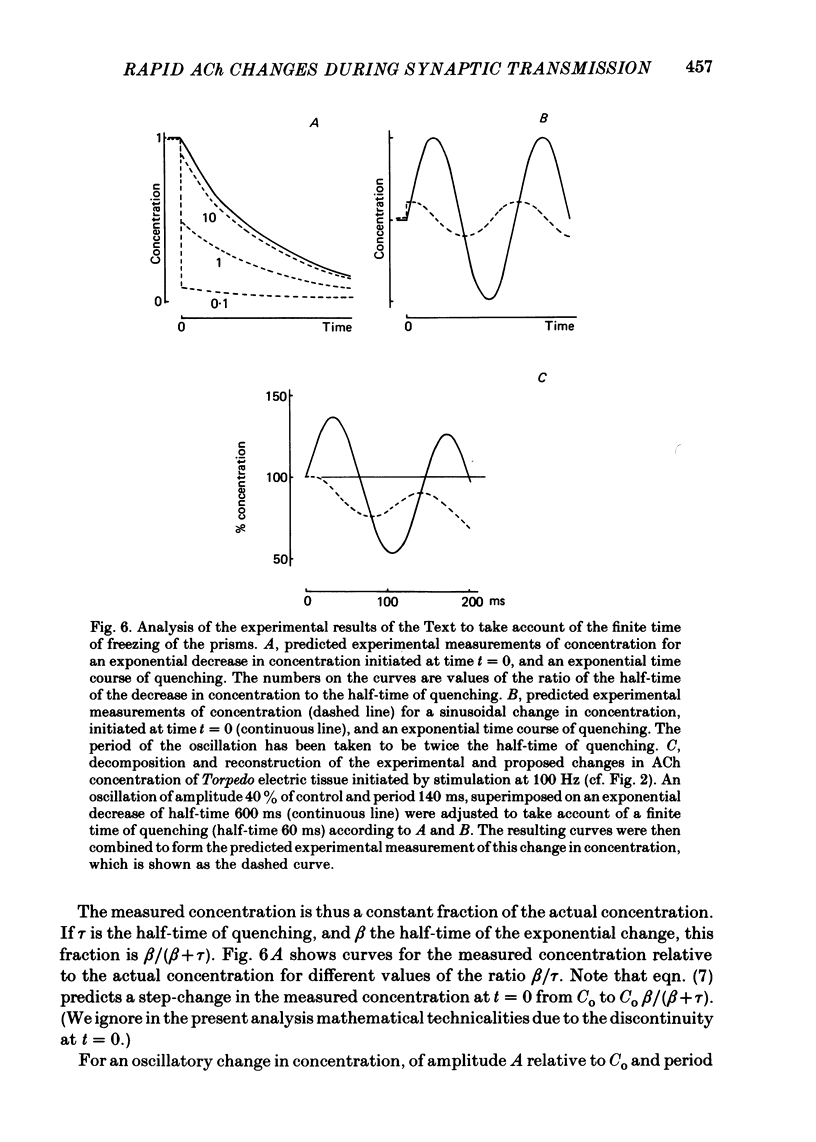
6. The shortest time interval investigated in this work was 10 ms. The rate at which the pieces of tissue are quenched for biochemical measurements when plunged into a liquid at low temperature has been estimated. It has also been evaluated to what extent the freezing rate may distort measurements of the biochemical changes occurring in the tissue.
7. It is concluded that fast freezing appears to be a valuable approach for investigating the rapid biochemical changes underlying cholinergic transmission; a better time resolution might be reached at the price, however, of greatly reducing the size of the samples. The second conclusion is that transmission of a brief train of impulses is accompanied by significant changes in the amount of extravesicular ACh.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bull G., Hebb C., Morris D. Synthesis of acetylcholine in the electric organ of Torpedo. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1969 Jan;28(1):11–28. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(69)91318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chmouliovsky-Moghissi M., Dunant Y. Breakdown of creatine phosphate and ATP in nerve terminals and electroplaques of the Torpedo electric organ: comparison with the electrical energy dissipated. J Neurochem. 1979 Apr;32(4):1287–1294. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdall M. J., Zimmermann H. Evidence for heterogeneous pools of acetylcholine in isolated cholinergic synaptic vesicles. Brain Res. 1974 May 10;71(1):160–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90201-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunant Y., Eder L., Servetiadis-Hirt L. Acetylcholine release evoked by single or a few nerve impulses in the electric organ of Torpedo. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:185–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunant Y., Gautron J., Israël M., Lesbats B., Manaranche R. Evolution de la décharge de l'organe électrique de la Torpille et variations simultanées de l'acétylcholine au cours de la stimulation. J Neurochem. 1974 Oct;23(4):635–643. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunant Y., Gautron J., Israël M., Lesbats B., Manaranche R. Les compartiments d'acetylcholine de l'organe electrique de la torpille et leurs modifications par la stimulation. J Neurochem. 1972 Aug;19(8):1987–2002. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunant Y., Israël M., Lesbats B., Manaranche R. Loss of vesicular acetycholine in the Torpedo electric organ on discharge against high external resistance. J Neurochem. 1976 Oct;27(4):975–977. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb05166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunant Y., Israël M., Lesbats B., Manaranche R. Oscillation of acetylcholine during nerve activity in the Torpedo electric organ. Brain Res. 1977 Apr 8;125(1):123–140. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90364-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Fessard A. The cholinergic nature of the nerves to the electric organ of the Torpedo (Torpedo marmorata). J Physiol. 1942 Aug 18;101(2):200–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1942.sp003975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautron J. Localisation des cholinestérases au niveau de la jonction nerfélectroplaque de l'organe électrique de la torpille marbrée. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Aug 24;271(8):714–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harreveld A. V., Trubatch J. Synaptic changes in frog brain after stimulation with potassium chloride. J Neurocytol. 1975 Feb;4(1):33–46. doi: 10.1007/BF01099093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S., Dennis M. J., Jan Y., Jan L., Evans L. Synaptic vesicle exocytosis captured by quick freezing and correlated with quantal transmitter release. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):275–300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel M., Lesbats B., Manaranche R., Marsal J., Mastour-Frachon P., Meunier F. M. Related changes in amounts of ACh and ATP in resting and active Torpedo nerve electroplaque synapses. J Neurochem. 1977 Jun;28(6):1259–1267. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb12319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur P. The role of intracellular freezing in the death of cells cooled at supraoptimal rates. Cryobiology. 1977 Jun;14(3):251–272. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(77)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar P. C., Polak R. L. Acetylcholine synthesizing enzymes in frog skeletal muscle. J Neurochem. 1980 Nov;35(5):1021–1025. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb07855.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suszkiw J. B., Zimmermann H., Whittaker V. P. Vesicular storage and release of acetylcholine in Torpedo electroplaque synapses. J Neurochem. 1978 Jun;30(6):1269–1280. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb10455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucek S., Zelená J., Ge I., Vyskocil F. Choline acetyltransferase in transected nerves, denervated muscles and Schwann cells of the frog: correlation of biochemical electron microscopical and electrophysiological observations. Neuroscience. 1978;3(8):709–724. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Venrooij G. E., Aertsen A. M., Hax W. M., Ververgaert P. H., Verhoeven J. J., Van der Vorst H. A. Freeze-etching: freezing velocity and crystal size at different locations in samples. Cryobiology. 1975 Feb;12(1):46–61. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(75)90040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


