Abstract
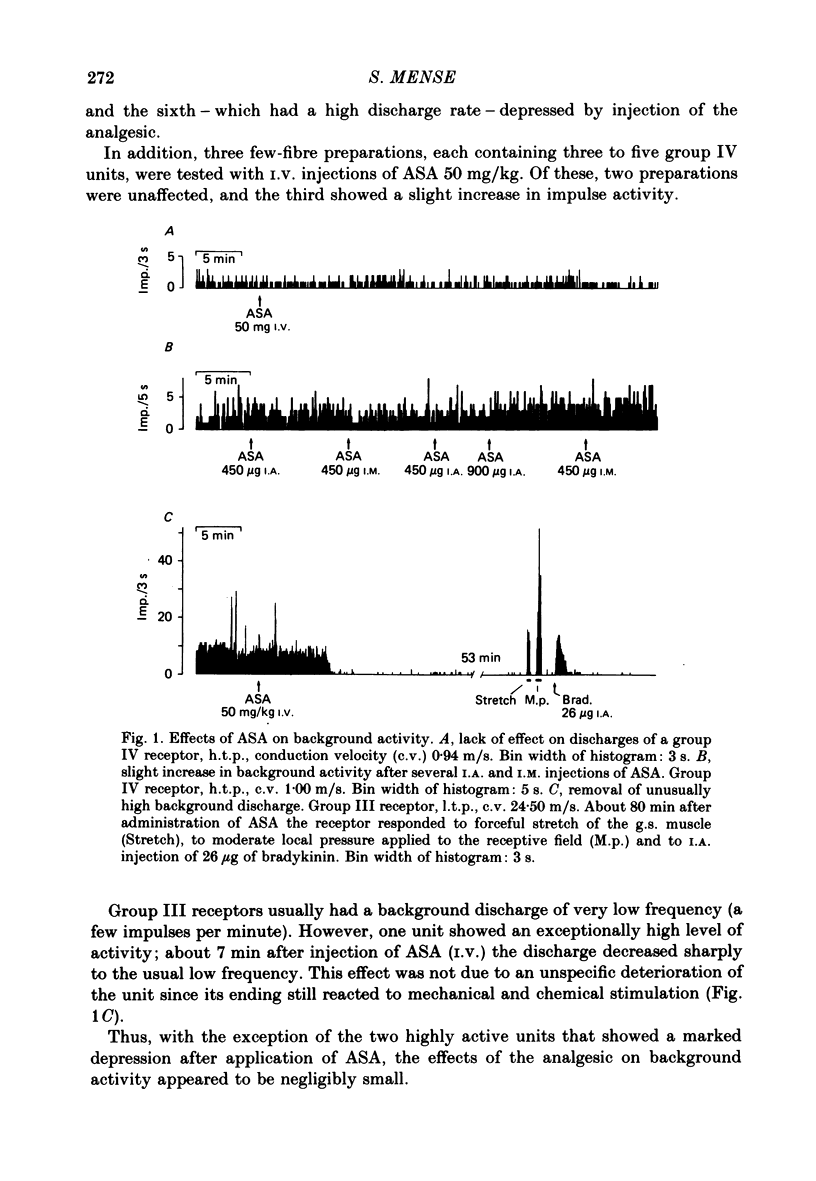
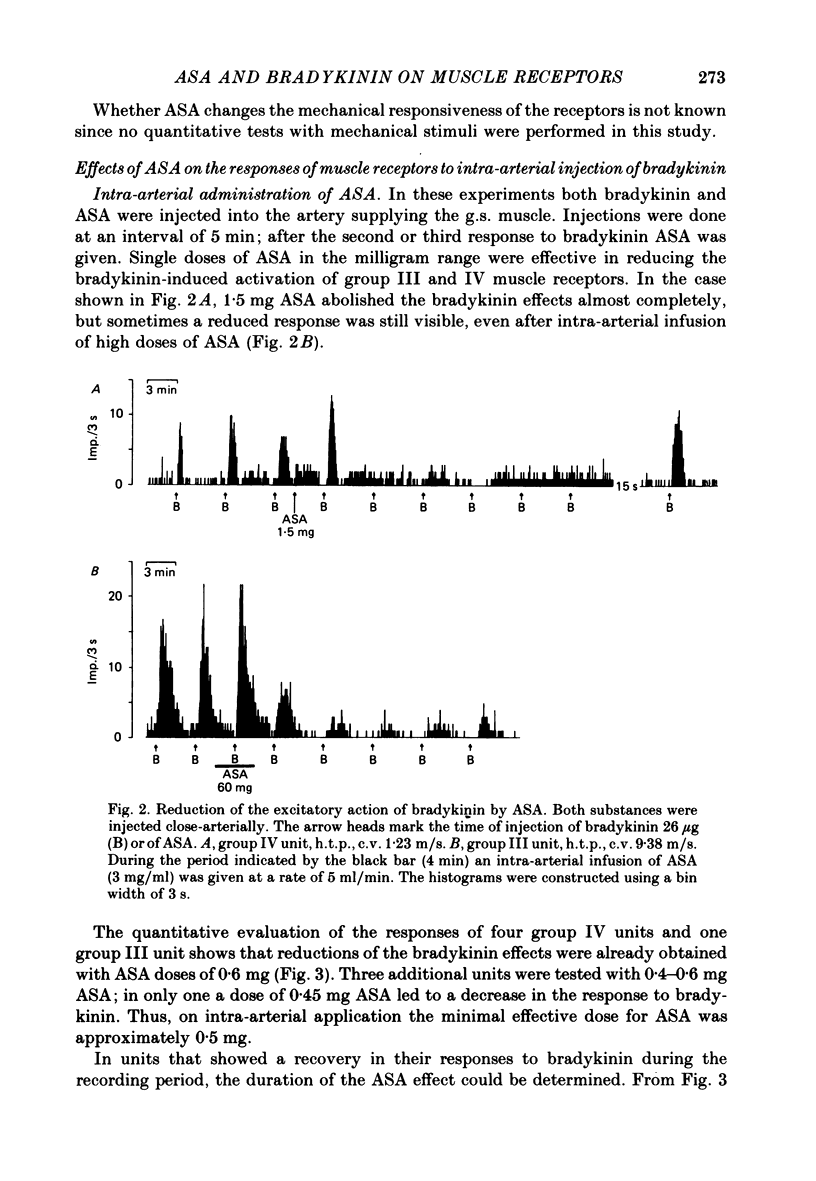
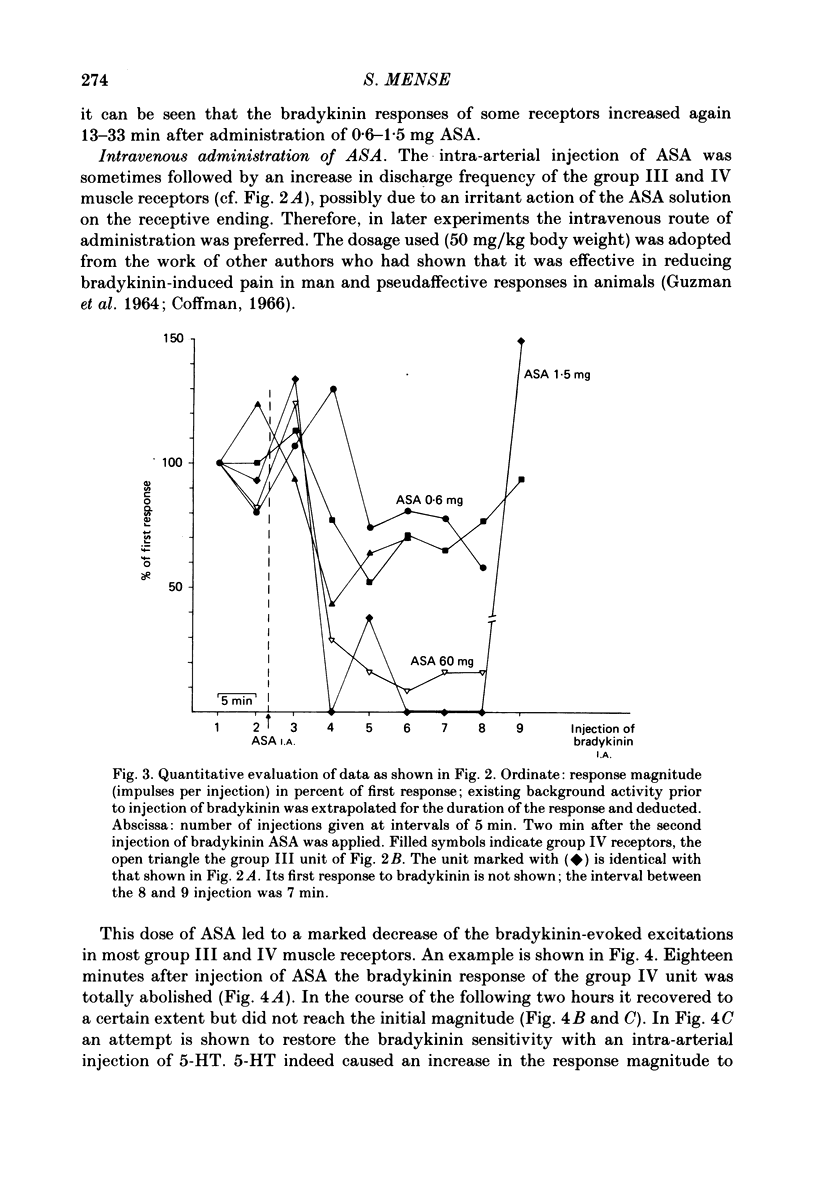
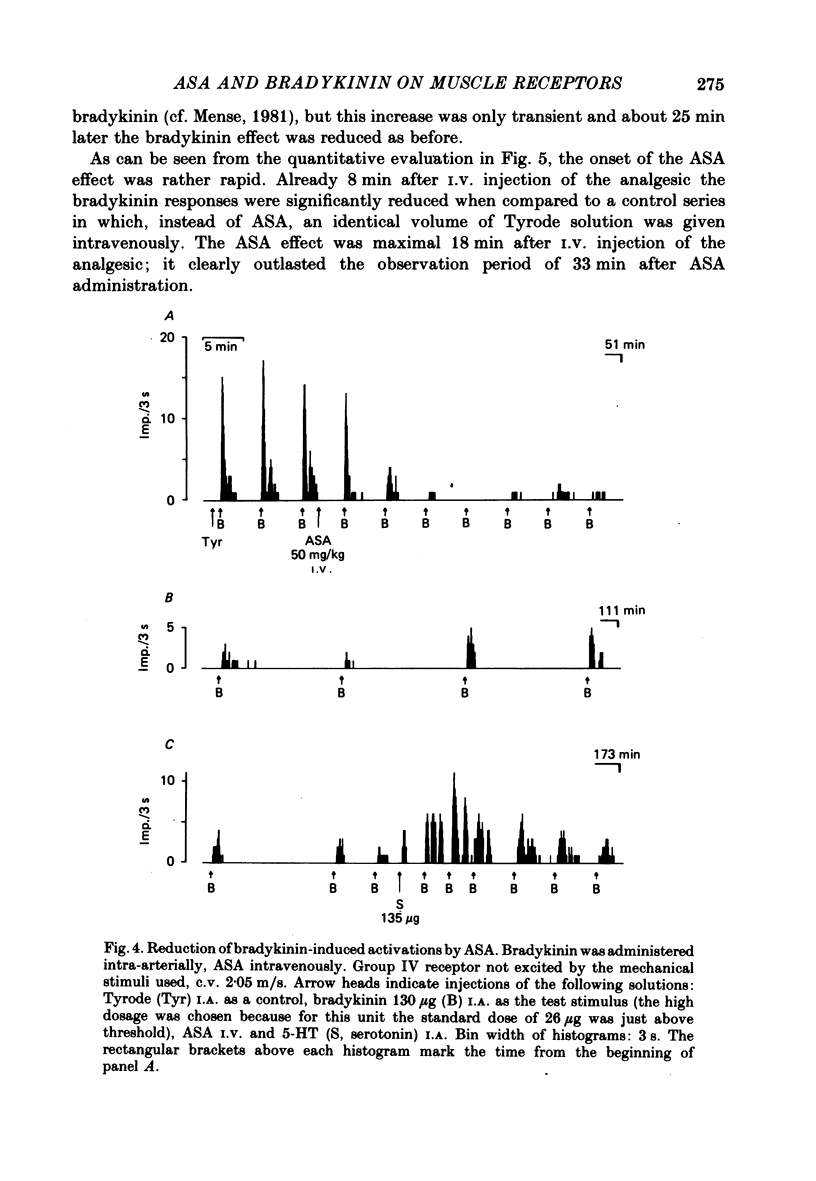
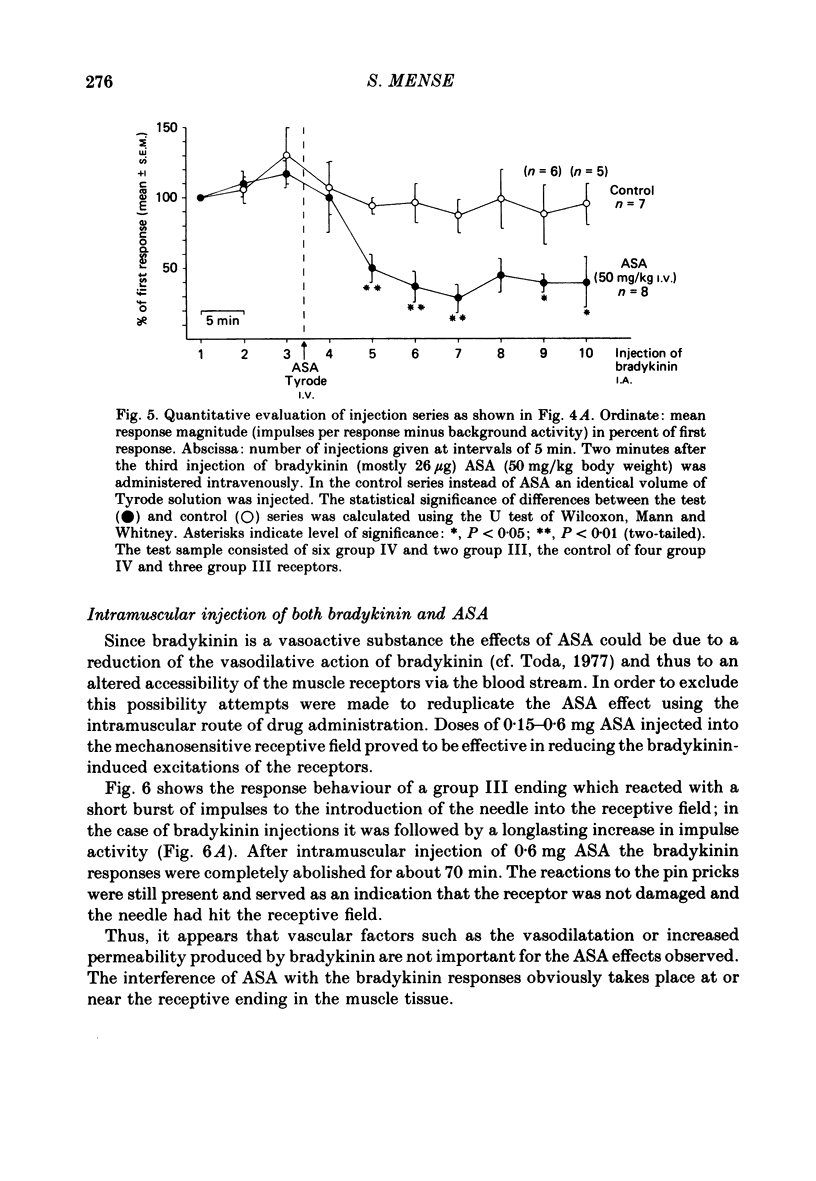
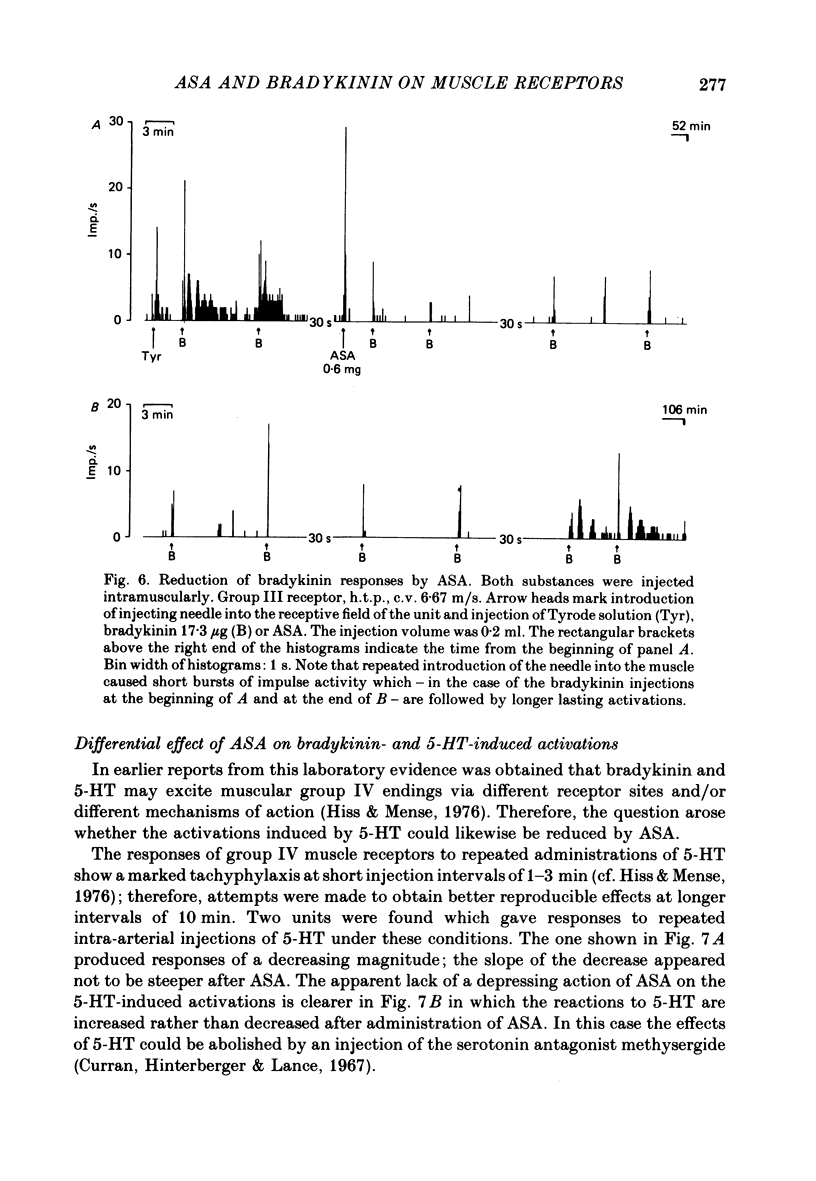
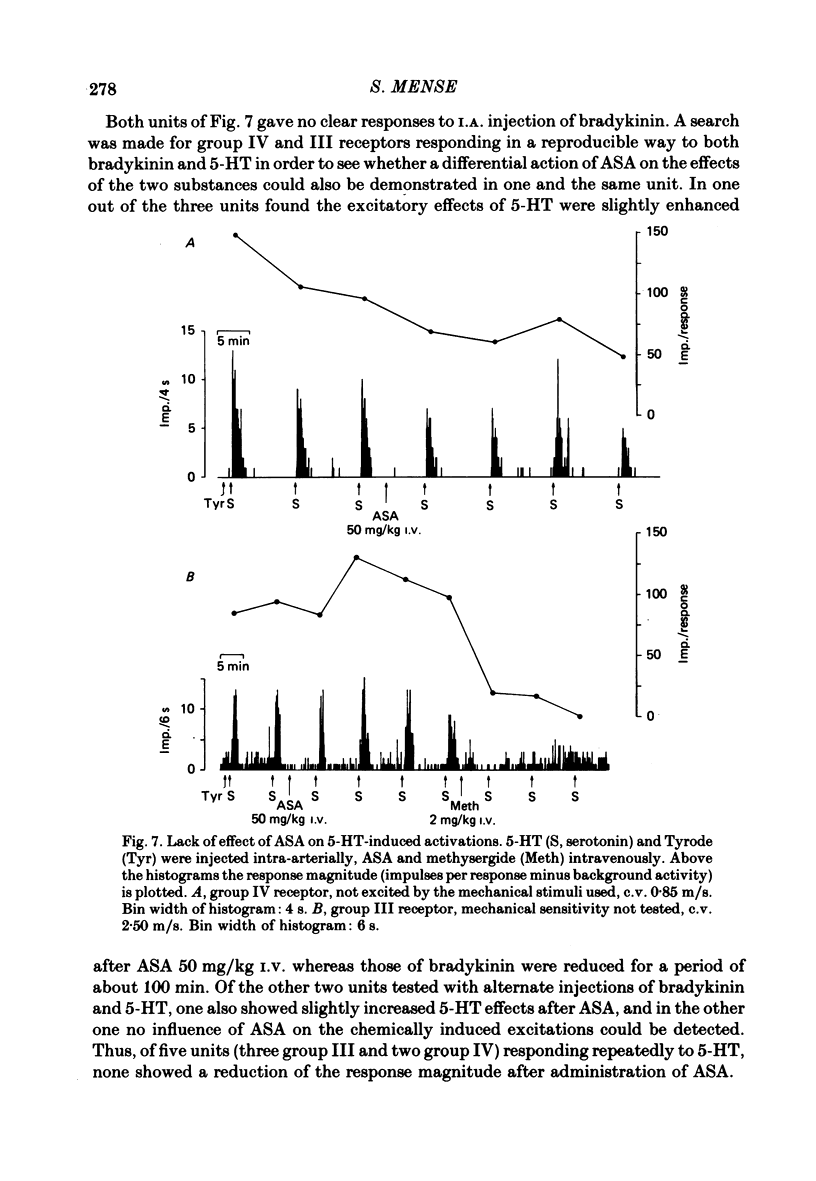
1. In chloralose-anaesthetized cats, the influence of systemically or locally applied acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) on the responses of thin-fibre muscle receptors to close-arterial injections of bradykinin was studied. 2. Many of the slowly conducting (group III and IV) muscle afferents had a background activity of low frequency. This discharge was either unaffected or slightly increased by the ASA doses used. In two units which had a very high discharge rate ASA led to a marked decrease in background activity. 3. On local (I.A. or I.M.) injection of ASA, doses below 1 mg were sufficient for reducing the bradykinin-induced activations of group III and IV muscle receptors. The reduction lasted for about 15-30 min. 4. On systemic (I.V.) administration of ASA (50 mg/kg body weight) the reduction in response magnitude to bradykinin became significant 8 min after injection of the analgesic. The effect was maximal about 10 min later and lasted for more than 60 min. 5. Five receptors were found which gave a repeated response to 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) injected at 10 min intervals. The 5-HT-induced activations could not be reduced by ASA (50 mg/kg I.V.). 6. Most of the receptors responding to bradykinin had a high threshold on mechanical stimulation and thus were probably nociceptors. It is concluded that the reduction of their bradykinin-induced activations reflects the suppression of nociceptive information by an analgesic. Since the recordings were obtained from primary afferent units the data constitute direct evidence for a peripheral action of ASA.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURCH G. E., DEPASQUALE N. P. Bradykinin, digital blood flow, and the arteriovenous anastomoses. Circ Res. 1962 Jan;10:105–115. doi: 10.1161/01.res.10.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barabe J., Park W. K., Regoli D. Application of drug receptor theories to the analysis of the myotropic effects of bradykinin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;53(3):345–353. doi: 10.1139/y75-050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst W. E. Role of kinins and prostaglandins in inflammation. Proc R Soc Med. 1971 Jan;64(1):4–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER H. O., HAMMOND A. R., HORWOOD-BARRETT S., SCHNEIDER C. RAPID INDUCTION BY ACETYLCHOLINE, BRADYKININ AND POTASSIUM OF A NOCICEPTIVE RESPONSE IN MICE AND ITS SELECTIVE ANTAGONISM BY ASPIRIN. Nature. 1964 Dec 26;204:1316–1318. doi: 10.1038/2041316b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLIER H. O., SHORLEY P. G. Analgesic antipyretic drugs as antagonists of bradykinin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1960 Dec;15:601–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1960.tb00288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman J. D. The effect of aspirin on pain and hand blood flow responses to intra-arterial injection of bradykinin in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1966 Jan-Feb;7(1):26–37. doi: 10.1002/cpt19667126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., Schneider C. Nociceptive response to prostaglandins and analgesic actions of aspirin and morphine. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):141–143. doi: 10.1038/newbio236141a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damas J., Deby C. Libération de prostaglandines par la bradykinine chez le rat. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1974;168(2-3):375–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damas J., Deby C. Sur la libération des prostaglandines et de leurs précurseurs, par la bradykinine. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1976 Apr;84(2):293–304. doi: 10.3109/13813457609073980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMELE J. F., SHANAMAN J. BRADYKININ WRITHING: A METHOD FOR MEASURING ANALGESIA. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Dec;114:680–682. doi: 10.3181/00379727-114-28768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins and the mechanism of analgesia produced by aspirin-like drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;49(1):86–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H. Prostaglandins, aspirin-like drugs and analgesia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 13;240(102):200–203. doi: 10.1038/newbio240200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz M., Mense S. Muscle receptors with group IV afferent fibres responding to application of bradykinin. Brain Res. 1975 Jul 18;92(3):369–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90323-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUZMAN F., BRAUN C., LIM R. K., POTTER G. D., RODGERS D. W. NARCOTIC AND NON-NARCOTIC ANALGESICS WHICH BLOCK VISCERAL PAIN EVOKED BY INTRA-ARTERIAL INJECTION OF BRADYKININ AND OTHER ALGESIC AGENTS. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1964 Jun 1;149:571–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellekant G., Gopal V. Depression of taste responses by local or intravascular administration of salicylates in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1975 Nov;95(3):286–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1975.tb10052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiss E., Mense S. Evidence for the existence of different receptor sites for algesic agents at the endings of muscular group IV afferent units. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Mar 30;362(2):141–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00583640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juan H. Mechanism of action of bradykinin-induced release of prostaglandin E. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;300(1):77–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00505082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krane S. M. Action of salicylates. N Engl J Med. 1972 Feb 10;286(6):317–318. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197202102860611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa T., Mizumura K. Chemical responses of polymodal receptors of the scrotal contents in dogs. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:219–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIM R. K., GUZMAN F., RODGERS D. W., GOTO K., BRAUN C., DICKERSON G. D., ENGLE R. J. SITE OF ACTION OF NARCOTIC AND NON-NARCOTIC ANALGESICS DETERMINED BY BLOCKING BRADYKININ-EVOKED VISCERAL PAIN. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1964 Nov 1;152:25–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Juan H. Interaction of prostaglandins and indomethacin with algesic substances. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;285(4):301–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00501460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lembeck F., Popper H., Juan H. Release of prostaglandins by bradykinin as an intrinsic mechanism of its algesic effect. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;294(1):69–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00692786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim R. K., Miller D. G., Guzman F., Rodgers D. W., Rogers R. W., Wang S. K., Chao P. Y., Shih T. Y. Pain and analgesia evaluated by the intraperitoneal bradykinin-evoked pain method in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1967 Jul-Aug;8(4):521–542. doi: 10.1002/cpt196784521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Terragno N. A., Malik K. U., Lonigro A. J. Release of a prostaglandin E-like substance from canine kidney by bradykinin. Circ Res. 1972 Jul;31(1):36–43. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mense S. Nervous outflow from skeletal muscle following chemical noxious stimulation. J Physiol. 1977 May;267(1):75–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mense S. Sensitization of group IV muscle receptors to bradykinin by 5-hydroxytryptamine and prostaglandin E2. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 23;225(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90320-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messina E. J., Weiner R., Kaley G. Inhibition of bradykinin vasodilation and potentiation of norepinephrine and angiotensin vasoconstriction by inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis in skeletal muscle of the rat. Circ Res. 1975 Oct;37(4):430–437. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.4.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis as the mechanism of analgesia of aspirin-like drugs in the dog knee joint. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Apr;31(2):250–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Key S. L., Denny S. E., Isakson P. C., Marshall G. R. Mechanism and modification of bradykinin-induced coronary vasodilation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2060–2063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perl E. R., Kumazawa T., Lynn B., Kenins P. Sensitization of high threshold receptors with unmyelinated (C) afferent fibers. Prog Brain Res. 1976;43:263–277. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCHA E SILVA M., ROSENTHAL S. R. Release of pharmacologically active substances from the rat skin in vivo following thermal injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Apr;132:110–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccioppo Neto F. Further studies on the actions of salicylates on nerve membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Nov 21;68(2):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossoni G., Omini C., Vigano T., Mandelli V., Folco G. C., Berti F. Bronchoconstriction by histamine and bradykinin in guinea pigs: relationship to thromboxane A2 generation and the effect of aspirin. Prostaglandins. 1980 Sep;20(3):547–557. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(80)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SICUTERI F., FRANCIULLACCI M., FRANCHI G., DELBIANCO P. L. SEROTONIN--BRADYKININ POTENTIATION ON THE PAIN RECEPTORS IN MAN. Life Sci. 1965 Feb;4:309–316. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorderet M., Straub R. W. Effects of non-narcotic analgesics and nonsteroid anti-inflammatory agents upon inorganic phosphates, intracellular potassium and impulse conduction in mammalian nerve fibers. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Jul;20(7):1355–1361. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90262-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. S., West G. B. The effect of bradykinin and anti-inflammatory agents on isolated arteries. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1966 Dec;18(12):838–840. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1966.tb07827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira N., Nakayama K., Hashimoto K. Vocalization response of puppies to intra-arterial administration of bradykinin and other algesic agents, and mode of actions of blocking agents. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1968 Dec;96(4):365–377. doi: 10.1620/tjem.96.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terragno D. A., Crowshaw K., Terragno N. A., McGiff J. C. Prostaglandin synthesis by bovine mesenteric arteries and veins. Circ Res. 1975 Jun;36(6 Suppl 1):76–80. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.6.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N. Actions of bradykinin on isolated cerebral and peripheral arteries. Am J Physiol. 1977 Mar;232(3):H267–H274. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1977.232.3.H267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolman E. L., Partridge R. Multiple sites of interaction between prostaglandins and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Prostaglandins. 1975 Mar;9(3):349–359. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(75)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Murao S. Bradykinin-induced excitation of afferent cardiac sympathetic nerve fibers. Jpn Heart J. 1974 Jan;15(1):84–91. doi: 10.1536/ihj.15.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Murao S. Potassium-induced excitation of afferent cardiac sympathetic nerve fibers. Am J Physiol. 1974 Mar;226(3):603–607. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.3.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting J., Salata K., Bailey J. M. Aspirin: an unexpected side effect on prostacyclin synthesis in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.6776627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. Y., Terragno D. A., Terragno N. A., McGiff J. C. Dual effects of bradykinin on prostaglandin metabolism: relationship to the dissimilar vascular actions of kinins. Prostaglandins. 1977 Jun;13(6):1113–1125. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


