Abstract
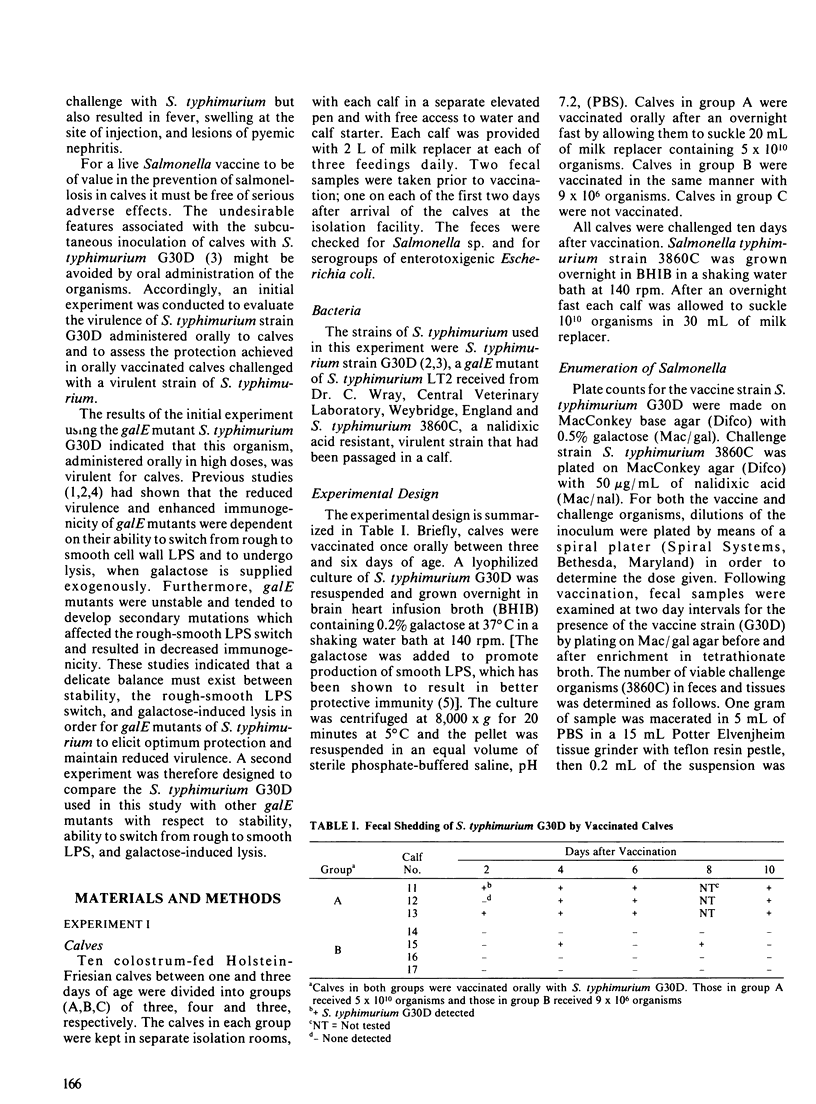
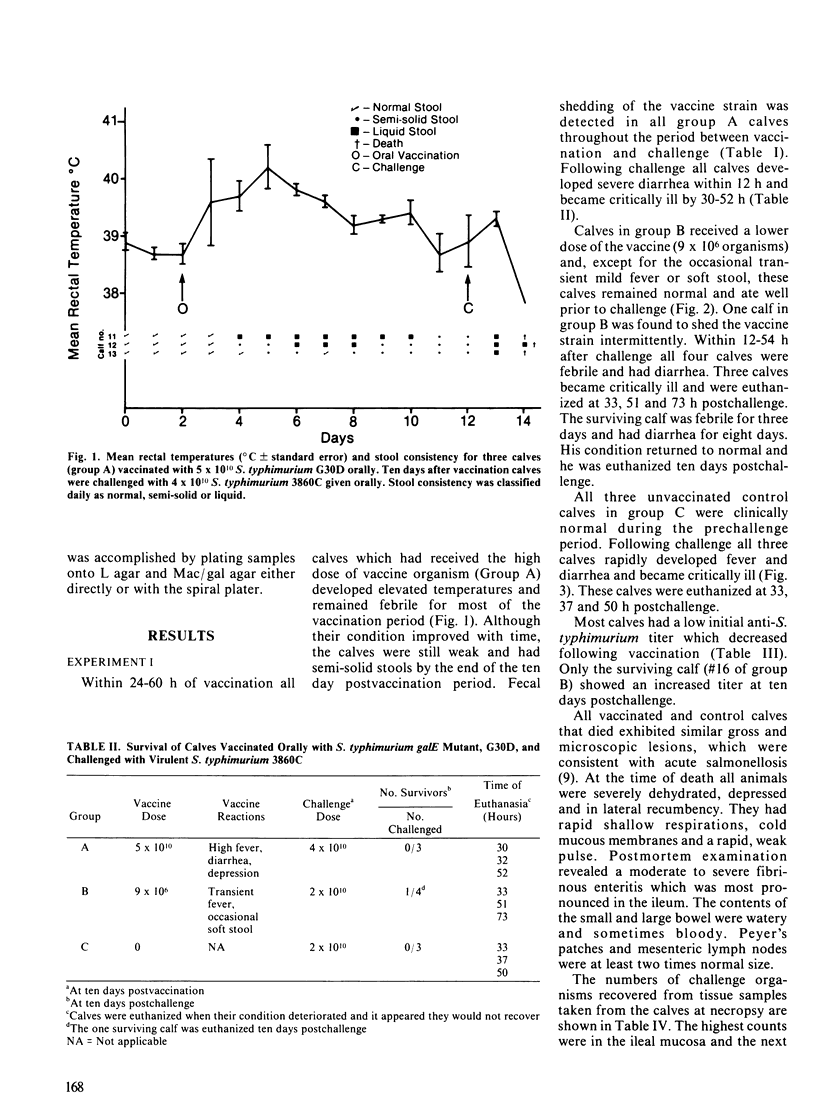
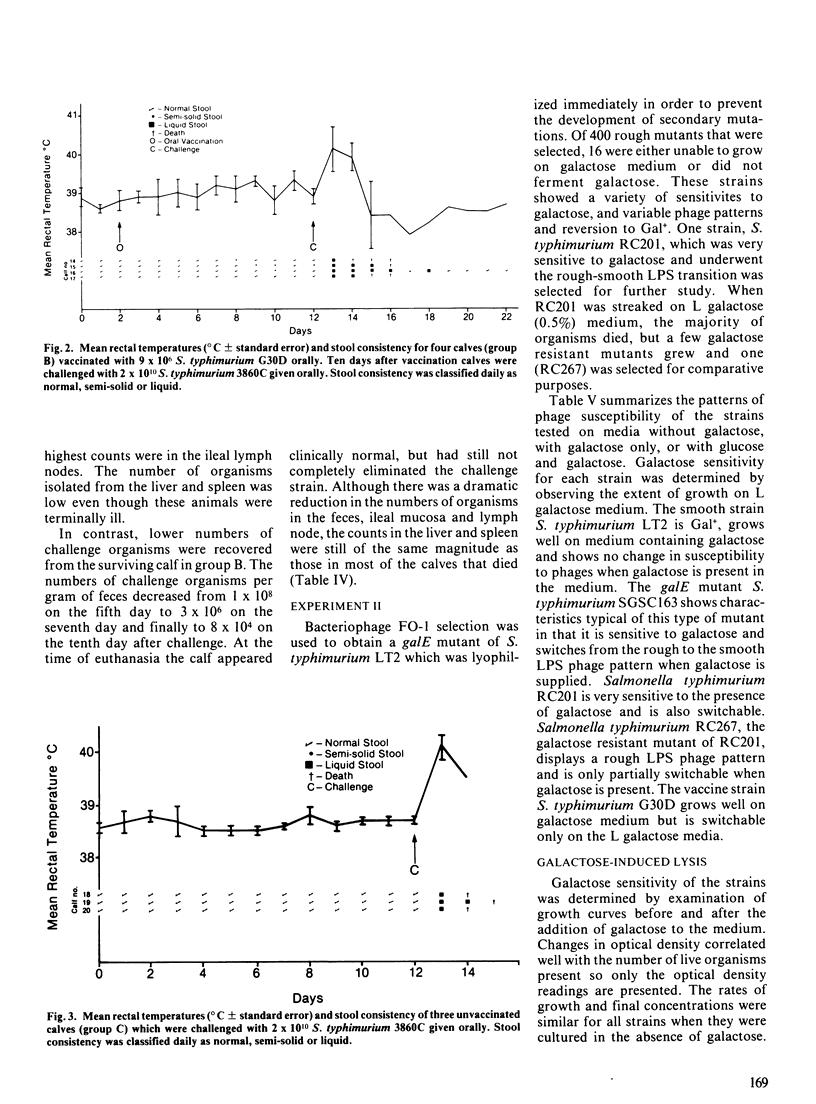
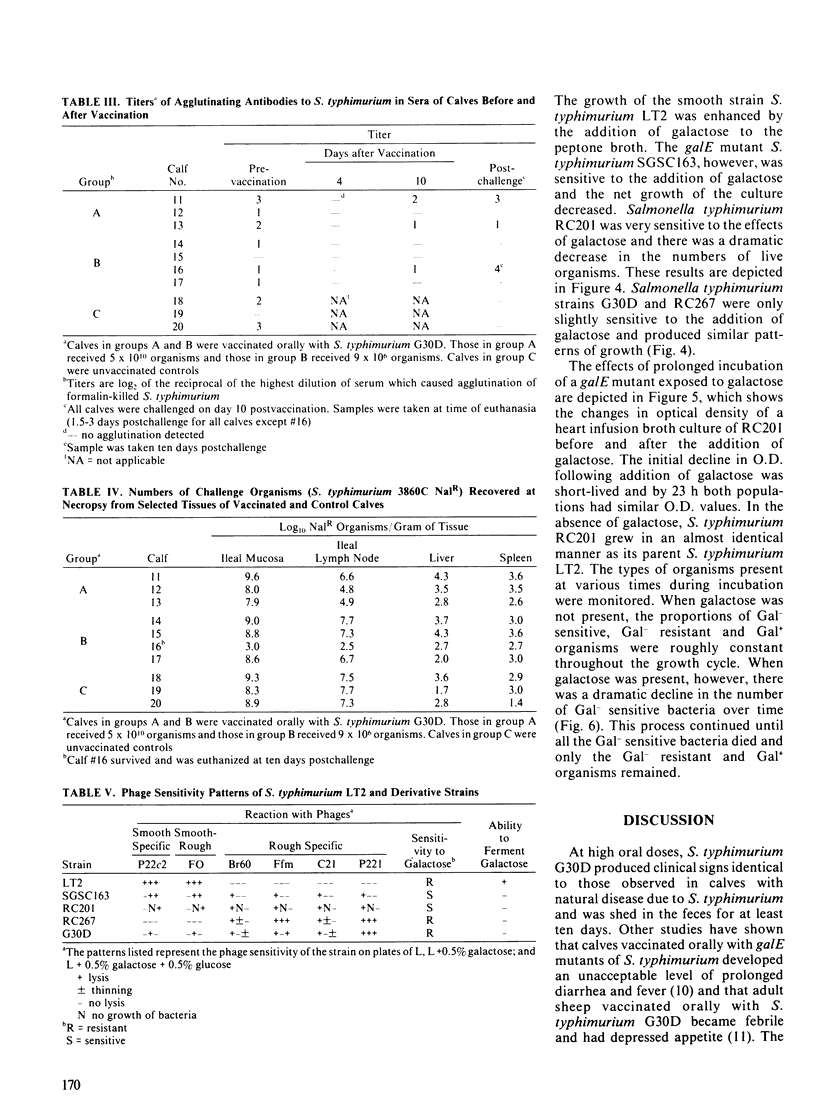
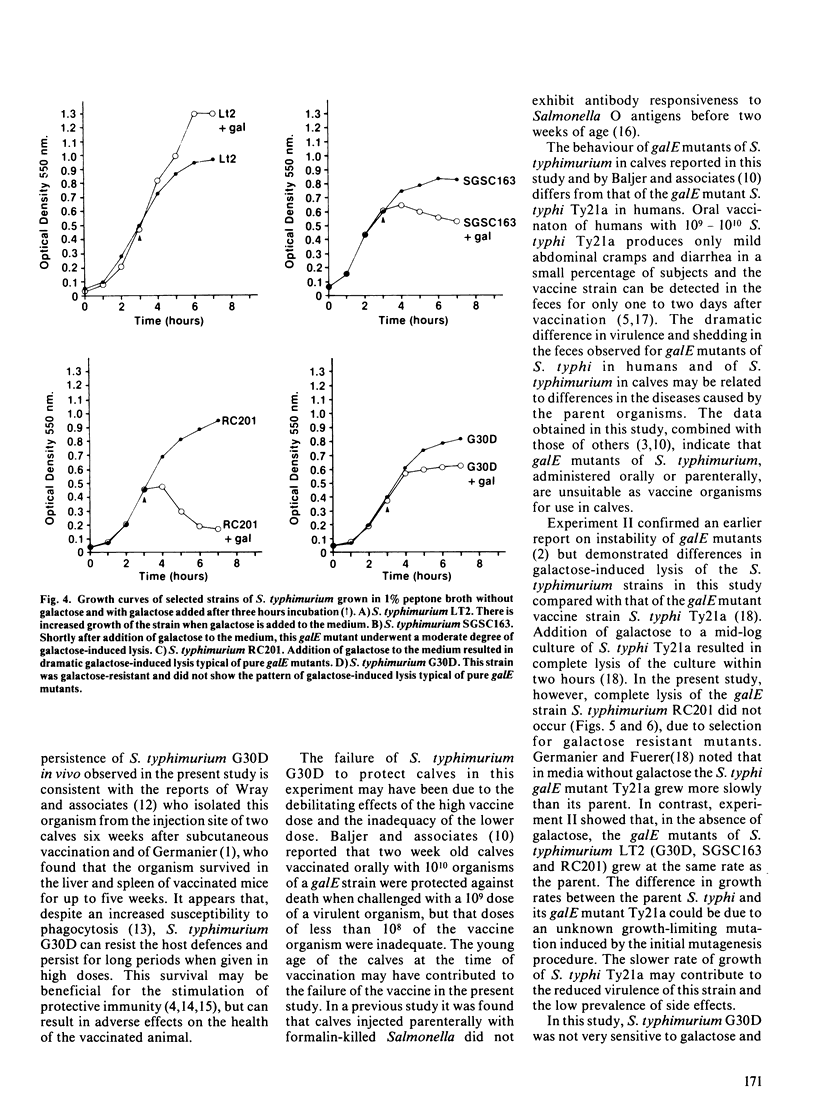
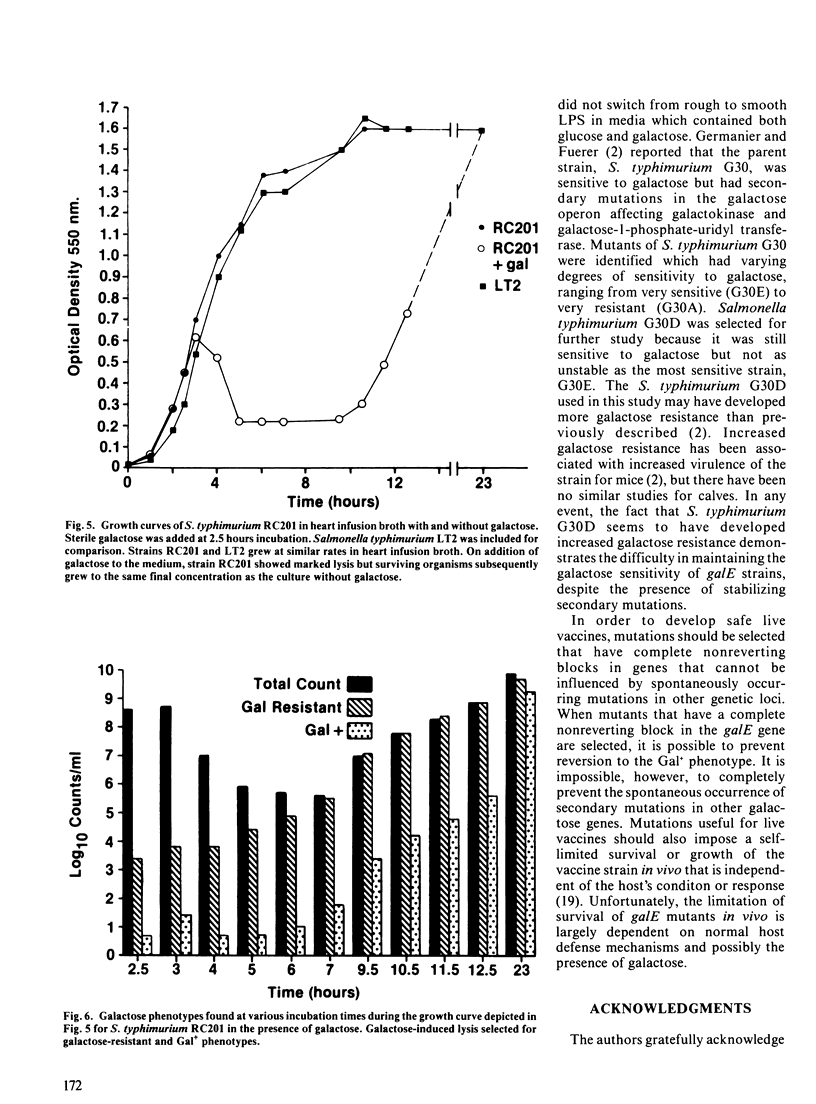
The purpose of the study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a galactose epimeraseless mutant of Salmonella typhimurium administered as an oral vaccine to one week old calves and to investigate properties of galactose epimeraseless mutants which affect their virulence and immunogenicity. The galactose epimeraseless mutant S. typhimurium strain G30D caused diarrhea and fever in three calves to which it was administered orally at a dose of 10(10) organisms; all three calves died following challenge with virulent S. typhimurium ten days postvaccination. Mild illness developed in four calves vaccinated with a dose of 9 X 10(6) organisms and one of these calves survived challenge. Three unvaccinated calves died following challenge. The vaccine organism persisted in tissues and was shed for a prolonged period by calves which received 10(10) organisms. Studies of characteristics of galactose epimeraseless mutants of S. typhimurium showed that, in the presence of galactose, there is selection for secondary mutants which are galactose resistant. The studies indicate that galactose epimeraseless mutants of S. typhimurium are not good candidate live vaccine organisms for use in calves.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baljer G., Hoerstke M., Dirksen G., Seitz A., Sailer J., Mayr A. Vergleichende Untersuchungen über die Wirksamkeit einer oralen Immuniseirung mit hitzeinaktivierten und vermehrungsfähigen, avirulenten (Gal E-) S. typhimurium-Keimen gegen die Salmonellose des Kalbes. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1981;28(9-10):759–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. L., Klein G. C., McKinney F. T., Jones W. L. Safranin O-stained antigen microagglutination test for detection of brucella antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):398–400. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.398-400.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Recall of immunity in mice vaccinated with Salmonella enteritidis or Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2014–2021. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2014-2021.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R., Füer E. Isolation and characterization of Gal E mutant Ty 21a of Salmonella typhi: a candidate strain for a live, oral typhoid vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):553–558. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R., Fürer E. Immunity in experimental salmonellosis. II. Basis for the avirulence and protective capacity of gal E mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1971 Dec;4(6):663–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.6.663-673.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R. Immunity in Experimental Salmonellosis I. Protection Induced by Rough Mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Sep;2(3):309–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.3.309-315.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R. Immunity in experimental salmonellosis. 3. Comparative immunization with viable and heat-inactivated cells of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):792–797. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.792-797.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman R. H., Hornick R. B., Woodard W. E., DuPont H. L., Snyder M. J., Levine M. M., Libonati J. P. Evaluation of a UDP-glucose-4-epimeraseless mutant of Salmonella typhi as a liver oral vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1977 Dec;136(6):717–723. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.6.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek P. D., Robertson G. M., Millar C. Vaccination of sheep with a live gal e mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Aust Vet J. 1982 Jul;59(1):31–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1982.tb02710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnapillai V. Uridinediphosphogalactose-4-epimerase deficiency in Salmonella typhimurium and its correction by plasmoid-borne galactose genes of Escherichia coli K-12: effects on mouse virulence, phagocytosis, and serum sensitivity. Infect Immun. 1971 Sep;4(3):177–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.3.177-188.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smih A. N., Ingram D. G. Immunological responses of young animals. II. Antibody production in calves. Can Vet J. 1965 Sep;6(9):226–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker B. A., Hoiseth S. K., Smith B. P. Aromatic-dependent "Salmonella sp." as live vaccine in mice and calves. Dev Biol Stand. 1983;53:47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiba D. Two types of immunity in experimental typhoid; "cellular immunity" and "humoral immunity". Keio J Med. 1965 Jun;14(2):45–61. doi: 10.2302/kjm.14.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahdan M. H., Sippel J. E., Mikhail I. A., Rahka A. E., Anderson E. S., Sparks H. A., Cvjetanović B. Controlled field trial of a typhoid vaccine prepared with a nonmotile mutant of Salmonella typhi Ty2. Bull World Health Organ. 1975;52(1):69–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Non-smooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: differentiation by phage sensitivity and genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):527–554. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray C., Sojka W. J., Morris J. A., Brinley Morgan W. J. The immunization of mice and calves with gal E mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Hyg (Lond) 1977 Aug;79(1):17–24. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400052803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray C., Sojka W. J., Pritchard D. G., Morris J. A. Immunization of animals with gal E mutants of "Salmonella typhimurium". Dev Biol Stand. 1983;53:41–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


