Abstract
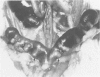
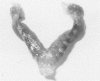
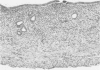
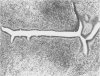
In the course of experiments on the effects of anabolic steroids on the myocardium of rat conceptuses, we found that subcutaneous implantation of 10 mg of estradiol, Dianabol or testosterone to rats in mid pregnancy, resulted in embryo resorption. Placental tissue was identified only in estradiol-treated rats which also demonstrated a large amount of serosanguineous fluid that dilated the horns considerably. The yellow nodules of placental attachment sites were represented histologically by cellular and vascular proliferations between the inner and outer layers of the myometrium. The nodular aggregates of cells had variable features according to the steroid administered. Neither decidual cells nor metrial glands that are reported to be the constituents of placental attachment sites were seen in our material. We conclude that anabolic steroids are potent agents for embryo resorption, and that the cells in the nodules of placental attachment sites are likely to be derived from the myometrium.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gupta M., Bandyopadhyay S., Paul B., Mazumdar S. K. Ovarian steroidogenesis and development of fetuses following ochratoxin A treatment in pregnant rats. Endokrinologie. 1981 Apr;77(2):152–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn D. W., Demers L. M., McGuire J. L. Studies on the mechanism of the antifertility activity of human chorionic gonadotropin in rodents. Contraception. 1980 May;21(5):551–560. doi: 10.1016/0010-7824(80)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurl R. N., Borthwick N. M. Action of testosterone on RNA synthesis in the rat uterus. Enzyme. 1983;29(3):213–216. doi: 10.1159/000469635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]