Abstract
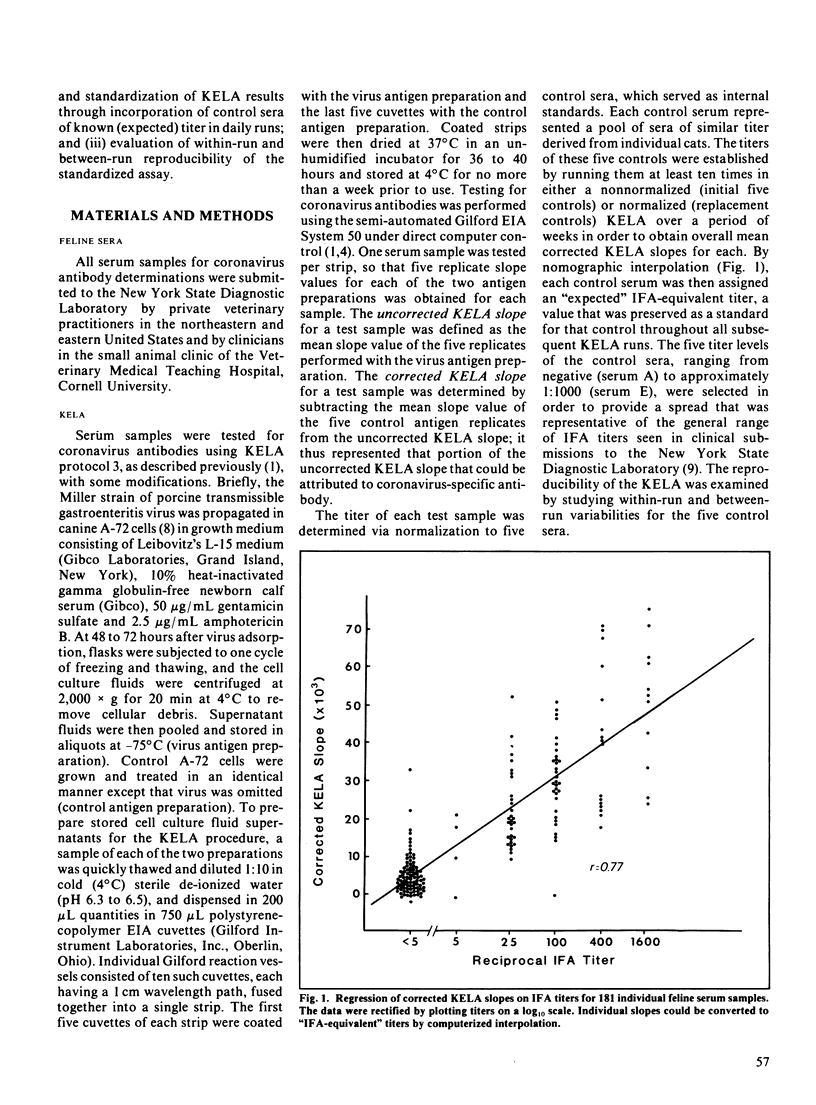
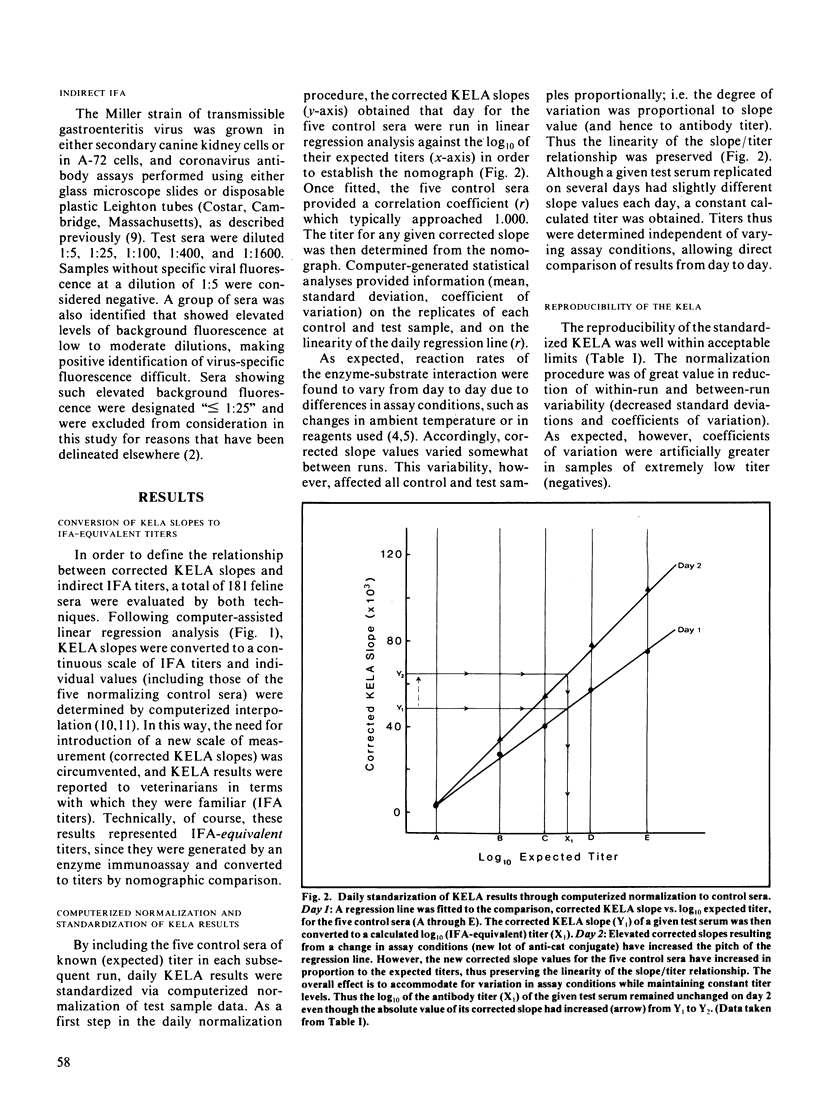
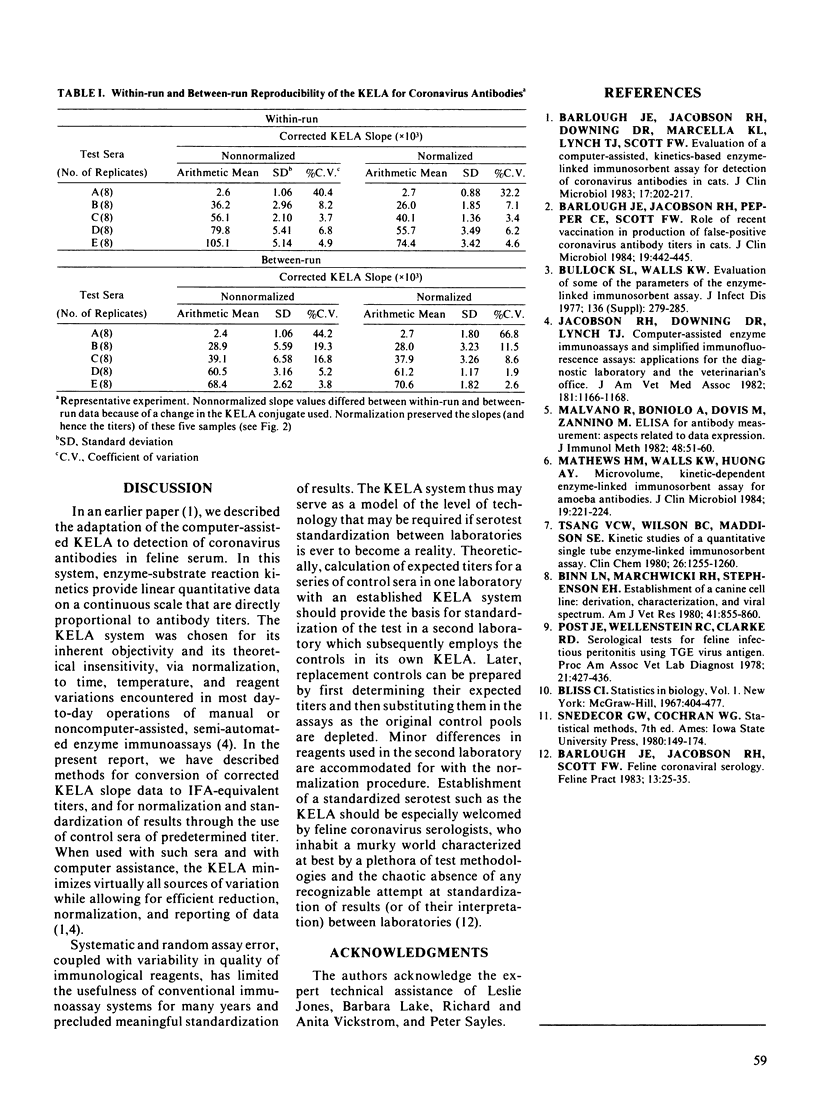
The computer-assisted, kinetics-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for coronavirus antibodies in cats was calibrated to the conventional indirect immunofluorescence assay by linear regression analysis and computerized interpolation (generation of "immunofluorescence assay-equivalent" titers). Procedures were developed for normalization and standardization of kinetics-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay results through incorporation of five different control sera of predetermined ("expected") titer in daily runs. When used with such sera and with computer assistance, the kinetics-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay minimized both within-run and between-run variability while allowing also for efficient data reduction and statistical analysis and reporting of results.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlough J. E., Jacobson R. H., Downing D. R., Marcella K. L., Lynch T. J., Scott F. W. Evaluation of a computer-assisted, kinetics-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of coronavirus antibodies in cats. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):202–217. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.202-217.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlough J. E., Jacobson R. H., Pepper C. E., Scott F. W. Role of recent vaccination in production of false-positive coronavirus antibody titers in cats. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):442–445. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.442-445.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binn L. N., Marchwicki R. H., Stephenson E. H. Establishment of a canine cell line: derivation, characterization, and viral spectrum. Am J Vet Res. 1980 Jun;41(6):855–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson R. H., Downing D. R., Lynch T. J. Computer-assisted enzyme immunoassays and simplified immunofluorescence assays: applications for the diagnostic laboratory and the veterinarian's office. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1982 Nov 15;181(10):1166–1168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malvano R., Boniolo A., Dovis M., Zannino M. ELISA for antibody measurement: aspects related to data expression. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews H. M., Walls K. W., Huong A. Y. Microvolume, kinetic-dependent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for amoeba antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):221–224. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.221-224.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Wilson B. C., Maddison S. E. Kinetic studies of a quantitative single-tube enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Clin Chem. 1980 Aug;26(9):1255–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


