Abstract
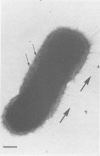
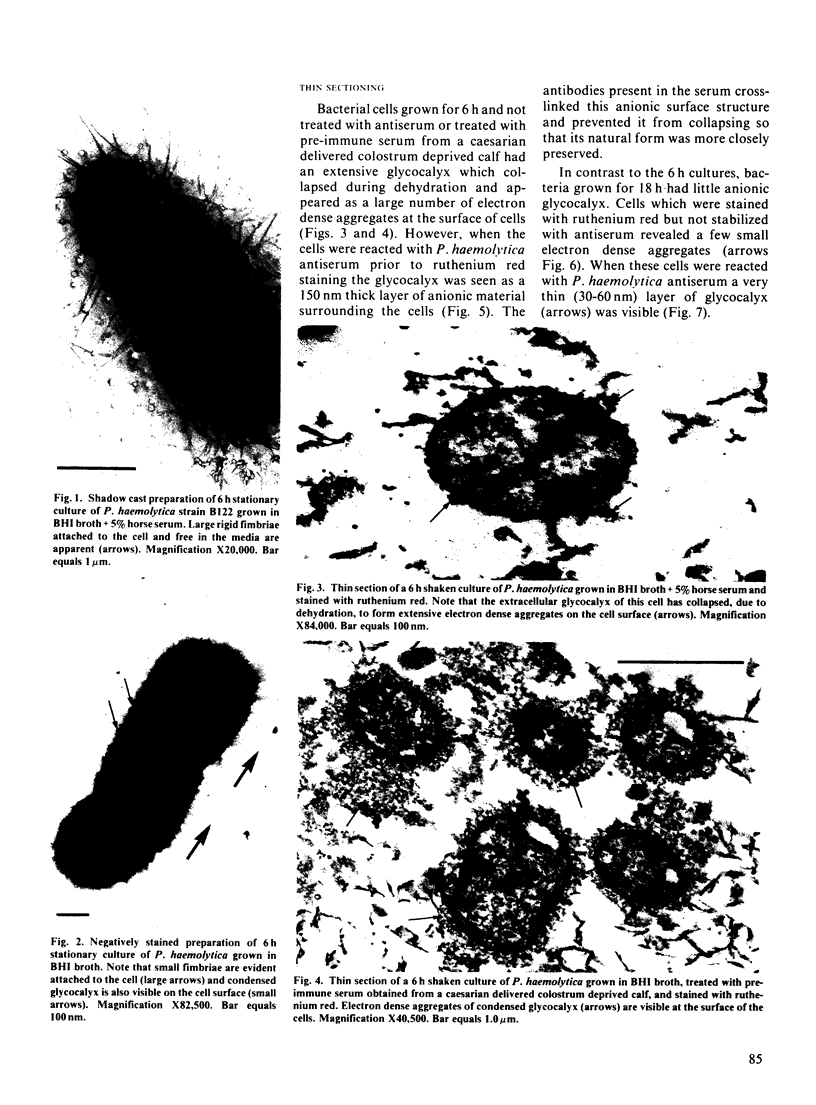
Several electron microscopic techniques were used to examine the surface of cells of Pasteurella haemolytica (biotype A, serotype 1) grown in vitro. All methods showed the presence of a very extensive glycocalyx on logarithmic phase (6 h) cells grown in liquid media. The anionic glycocalyx of these cells stained well with ruthenium red, but collapsed during dehydration for electron microscopy unless stabilized with specific antibodies. When the same techniques were used to examine cells in the stationary phase (18 h) the glycocalyx was much reduced. Large numbers of fimbriae were seen on both 6 h and 18 h cells grown in fluid media without shaking. In summary, logarithmic phase cells of P. haemolytica have both fimbriae and extensive anionic glycocalyx at their surface and we suggest that either or both of these structures may be important in the colonization of the bovine respiratory tract and the subsequent pathogenesis of Pasteurella pneumonia.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIBERSTEIN E. L., GILLS M., KNIGHT H. Serological types of Pasteurella hemolytica. Cornell Vet. 1960 Jul;50:283–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baluyut C. S., Simonson R. R., Bemrick W. J., Maheswaran S. K. Interaction of Pasteurella haemolytica with bovine neutrophils: identification and partial characterization of a cytotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Nov;42(11):1920–1926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley J. E., Orpin A., Adlam C. A comparison of immunoferritin, immuno-enzyme and gold-labelled protein A methods for the localization of capsular antigen on frozen thin sections of the bacterium, Pasteurella haemolytica. Histochem J. 1982 Sep;14(5):803–810. doi: 10.1007/BF01033629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielefeldt Ohmann H., Babiuk L. A. Viral-bacterial pneumonia in calves: effect of bovine herpesvirus-1 on immunologic functions. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):937–947. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Irvin R. T., Costerton J. W. Autochthonous and pathogenic colonization of animal tissues by bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):461–490. doi: 10.1139/m81-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corstvet R. E., Gentry M. J., Newman P. R., Rummage J. A., Confer A. W. Demonstration of age-dependent capsular material on Pasteurella haemolytica serotype 1. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Dec;16(6):1123–1126. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.6.1123-1126.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:299–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The role of bacterial surface structures in pathogenesis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1981;8(4):303–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418109085082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filion L. G., Cho H. J., Shewen P. E., Raybould T. J., Wilkie B. N. Comparison of serological techniques to measure antibody to Pasteurella haemolytica A1. Can J Comp Med. 1985 Jan;49(1):99–103. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank G. H. Serotypes of Pasteurella haemolytica in sheep in the midwestern United States. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Nov;43(11):2035–2037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour N. J., Menzies J. D., Donachie W., Fraser J. Electronmicroscopy of the surface of Pasteurella haemolytica. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Feb;19(1):25–34. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J. C., Jones G. W., Rush H. G., Pentler L. J., Darif C. A., Coward J. E. Adhesion of type A Pasteurella mulocida to rabbit pharyngeal cells and its possible role in rabbit respiratory tract infections. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1103–1109. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1103-1109.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmel M. E., Yates M. D., Lauerman L. H., Squire P. G. Purification and partial characterization of a macrophage cytotoxin from Pasteurella haemolytica. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):764–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Pierson R. E., Braddy P. M., Saari D. A., Lauerman L. H., England J. J., Keyvanfar H., Collier J. R., Horton D. P., McChesney A. E. Shipping fever pneumonia in yearling feedlot cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1976 Sep 1;169(5):500–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Jr, Woods D. E., Chaudhuri T. Association of respiratory tract colonization with adherence of gram-negative bacilli to epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jun;139(6):667–673. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.6.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaehler K. L., Markham R. J., Muscoplat C. C., Johnson D. W. Evidence of species specificity in the cytocidal effects of Pasteurella haemolytica. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):615–616. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.615-616.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. Fimbrial adhesions of Escherichia coli. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7(3):321–340. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.3.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magwood S. E., Barnum D. A., Thomson R. G. Nasal bacterial flora of calves in healthy and in pneumonia-prone herds. Can J Comp Med. 1969 Oct;33(4):237–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham R. J., Ramnaraine M. L., Muscoplat C. C. Cytotoxic effect of Pasteurella haemolytica on bovine polymorphonuclear leukocytes and impaired production of chemotactic factors by Pasteurella haemolytica-infected alveolar macrophages. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Feb;43(2):285–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Meek A. H., Davis D. G., Thomson R. G., Johnson J. A., Lopez A., Stephens L., Curtis R. A., Prescott J. F., Rosendal S. Factors associated with mortality in feedlot cattle: the Bruce County Beef Cattle Project. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Jan;44(1):1–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmos A., Biberstein E. L. Differentiation of Pasteurella haemolytica biotypes A and T with growth inhibitors. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):231–234. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.231-234.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pass D. A., Thompson R. G. Wide distribution of Pasteurella haemolytica type 1 over the nasal mucosa of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1971 Jul;35(3):181–186. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Cytotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica acting on bovine leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.91-94.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Cytotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica acting on bovine leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.91-94.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson R. G. A perspective on respiratory disease in feedlot cattle. Can Vet J. 1980 Jun;21(6):181–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Bass J. A. Role of fibronectin in the prevention of adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to buccal cells. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):784–790. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]