Abstract
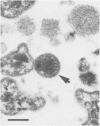
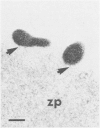
Ureaplasma diversum has been associated with infertility in the cow experimentally and in naturally occurring cases. However, the pathogenic mechanism is undetermined. The purpose of this study was to determine whether ureaplasmas are pathogenic for bovine morulae in vitro. Twenty-one morulae were recovered from three superovulated, mature, Holstein cows six or seven days postestrus. The embryos were divided into three groups (A,B,C) and incubated for 16 hours at 37 degrees C in humidified air with 10% CO2. Group A was incubated in embryo culture medium alone, Group B was incubated in culture medium with sterile ureaplasma broth added and Group C was incubated in culture medium containing 1.7 X 10(6) colony forming units Ureaplasma diversum strain 2312. After incubation, the morulae were examined using an electron microscope. Structures morphologically identical to U. diversum were present on the outer surface of the zonae pellucidae of all the morulae exposed to the organism and none were present on the unexposed control embryos. No other morphological differences were observed in either the ureaplasma-exposed embryos or the two groups of control embryos. Ureaplasma diversum was isolated from three of the five embryos incubated in culture medium with sterile ureaplasma broth added. These three embryos were recovered from one donor cow which cultured positive for U. diversum from the vulva and flush fluid. This finding suggests that the contaminating organisms entered the embryo culture wells either in the embryo collection medium or attached to the embryos.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball H. J., Neill S. D., Ellis W. A., O'Brien J. J., Ferguson H. W. The isolation of mycoplasma from bovine foetuses and their dams. Br Vet J. 1978 Nov-Dec;134(6):584–589. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)33342-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black F. T., Birch-Andersen A., Freundt E. A. Morphology and ultrastructure of human T-mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):254–259. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.254-259.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blom E. Studies on seminal vesiculitis in the bull. I. Semen examination methods and post mortem findings. Nord Vet Med. 1979 May;31(5):193–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolin S. R., Runnels L. J., Sawyer C. A., Gustafson D. P. Experimental transmission of pseudorabies virus in swine by embryo transfer. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Feb;43(2):278–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen R. A., Elsden R. P., Seidel G. E., Jr Infection of early bovine embryos with bovine herpesvirus-1. Am J Vet Res. 1985 May;46(5):1095–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P. A., Ruhnke H. L., MacKay A. L., Palmer N. C. Bovine granular vulvitis associated with ureaplasma infection. Can Vet J. 1979 Apr;20(4):89–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P. A., Ruhnke H. L., Palmer N. C. Experimental bovine genital ureaplasmosis. I. Granular vulvitis following vulvar inoculation. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Jul;44(3):252–258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P. A., Ruhnke H. L., Palmer N. C. Experimental bovine genital ureaplasmosis. II. Granular vulvitis, endometritis and salpingitis following uterine inoculation. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Jul;44(3):259–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser L. R., Taylor-Robinson D. T. The effect of Mycoplasma pulmonis on fertilization and preimplantation development in vitro of mouse eggs. Fertil Steril. 1977 Apr;28(4):488–498. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)42503-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourlay R. N. The isolation of T-strains of mycoplasma from pneumonic calf lungs. Res Vet Sci. 1968 Jul;9(4):376–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heap R. B., Flint A. P., Gadsby J. E. Role of embryonic signals in the establishment of pregnancy. Br Med Bull. 1979 May;35(2):129–135. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Gourlay R. N. Identification of ureaplasmas from cattle using antisera prepared in gnotobiotic calves. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Oct;126(2):365–369. doi: 10.1099/00221287-126-2-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Gourley R. N. An electron-microscopic examination of certain bovine mycoplasmas stained with ruthenium red and the demonstration of a capsule on Mycoplasma dispar. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Aug;83(2):393–398. doi: 10.1099/00221287-83-2-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston C. W., Jr Isolation of T-strain of mycoplasma from Texas feedlot cattle. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Oct;33(10):1925–1929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Black F. T. Direct and indirect immunofluorescence of unfixed and fixed Mycoplasma colonies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):615–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhnke H. L., Doig P. A., MacKay A. L., Gagnon A., Kierstead M. Isolation of Ureaplasma from bovine granular vulvitis. Can J Comp Med. 1978 Apr;42(2):151–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhnke H. L., Palmer N. C., Doig P. A., Miller R. B. Bovine abortion and neonatal death associated with Ureaplasma diversum. Theriogenology. 1984 Feb;21(2):295–301. doi: 10.1016/0093-691x(84)90415-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhnke H. L., Von Dreumel A. A. The isolation of T-mycoplasma from pneumonic lungs of a calf. Can J Comp Med. 1972 Jul;36(3):317–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shea B. F. Evaluating the bovine embryo. Theriogenology. 1981 Jan;15(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/s0093-691x(81)80016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh E. L., Eaglesome M. D., Thomas F. C., Papp-Vid G., Hare W. C. Embryo transfer as a means of controlling the transmission of viral infections. I. The in vitro exposure of preimplantation bovine embryos to akabane, bluetongue and bovine viral diarrhea viruses. Theriogenology. 1982 Apr;17(4):437–444. doi: 10.1016/0093-691x(82)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh E. L., Thomas F. C., Papp-Vid G., Eaglesome M. D., Hare W. C. Embryo transfer as a means of controlling the transmission of viral infections. II. The in vitro exposure of preimplantation bovine embryos to infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Theriogenology. 1982 Aug;18(2):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0093-691x(82)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalheim O. H., Proctor S. J., Gallagher J. E. Growth and effects of ureaplasmas (T mycoplasmas) in bovine oviductal organ cultures. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):915–925. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.915-925.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Haig D. A., Williams M. H. Bovine T-strain mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):517–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Williams M. H., Haig D. A. The isolation and comparative biological and physical characteristics of T-mycoplasmas of cattle. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Nov;54(1):33–46. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornber P. M. Ureaplasma association with bovine infertility in south-west Scotland. Vet Rec. 1982 Dec 18;111(25-26):591–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitescarver J., Furness G. T-mycoplasmas: a study of the morphology, ultrastructure and mode of division of some human strains. J Med Microbiol. 1975 May;8(2):349–355. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. H. Electron microscopy of T-strains. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):397–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]