Abstract
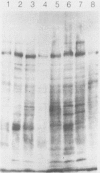
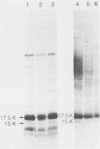
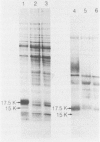
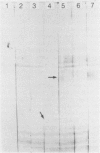
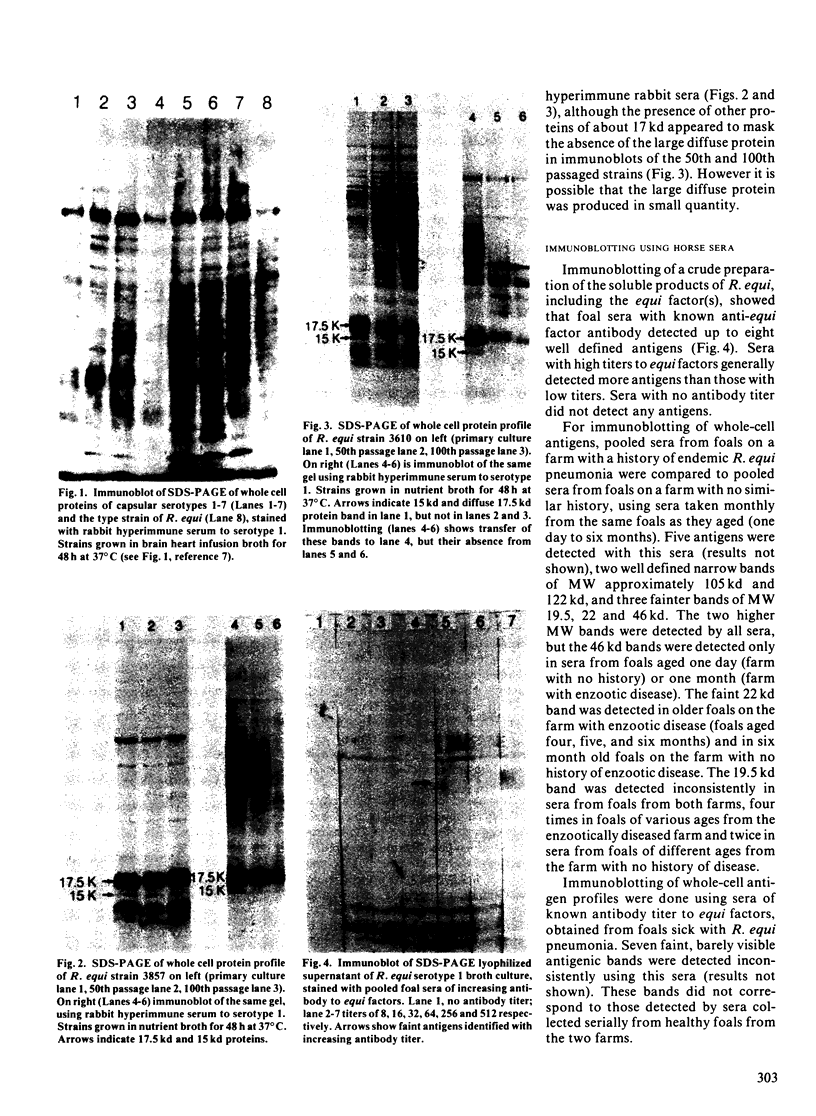
The antigens extracted from strains belonging to seven capsular serotypes of Rhodococcus equi, as well as from two wild strains isolated from pneumonic foals, were examined. Whole-cell antigens and soluble products present in broth culture supernatants were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, electroblotted onto nitrocellulose, and stained with serum from hyperimmunized rabbits or foals. Foal sera used included sera from pneumonic animals with known titer to equi factors; from animals bled monthly on a farm with enzootic pneumonia, and from animals bled monthly on a farm with no history of R. equi pneumonia. The humoral response of foals to somatic antigen preparations was negligible, with few differences noted between sera from healthy, subclinically affected, and sick foals. The humoral response to R. equi broth culture supernatant products appeared more marked and was related to equi factor antibody titer. These findings suggest that the humoral response to R. equi whole-cell antigens is unimportant in protection against disease, which is consistent with the behavior of the organism as a facultative intracellular pathogen.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chirino-Trejo J. M., Prescott J. F. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of whole-cell preparations of Rhodococcus equi. Can J Vet Res. 1987 Jul;51(3):297–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. D., Goodfellow M., Minnikin D. E. Fatty acid composition of some mycolic acid-containing coryneform bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Nov;128(11):2503–2509. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-11-2503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elissalde G. S., Renshaw H. W., Walberg J. A. Corynebacterium equi: an interhost review with emphasis on the foal. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1980;3(4):433–445. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(80)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hietala S. K., Ardans A. A., Sansome A. Detection of Corynebacterium equi-specific antibody in horses by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Jan;46(1):13–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A. W., Faulkner P. Monoclonal antibodies to baculovirus structural proteins: determination of specificities by Western blot analysis. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):432–444. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. A., Prescott J. F., Markham R. J. The pathology of experimental Corynebacterium equi infection in foals following intrabronchial challenge. Vet Pathol. 1983 Jul;20(4):440–449. doi: 10.1177/030098588302000407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight H. D. Corynebacterial infections in the horse: problems of prevention. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1969 Jul 15;155(2):446–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder R., Bernheimer A. W. Enzymatic oxidation of membrane cholesterol in relation to lysis of sheep erythrocytes by corynebacterial enzymes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Feb;213(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90565-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. S. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from fixed and stained gels. Anal Biochem. 1984 Sep;141(2):409–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F. Capsular serotypes of Corynebacterium equi. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Apr;45(2):130–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Coshan-Gauthier R., Barksdale L. Antibody to equi factor(s) in the diagnosis of Corynebacterium equi pneumonia of foals. Can J Comp Med. 1984 Oct;48(4):370–373. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Markham R. J., Johnson J. A. Cellular and humoral immune response of foals to vaccination with Corynebacterium equi. Can J Comp Med. 1979 Oct;43(4):356–364. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka B., Svastová A. Two techniques for detection of antibodies against Corynebacterium (Rhodococcus) equi in horse sera. Vet Microbiol. 1985 Apr;10(3):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(85)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]