Abstract
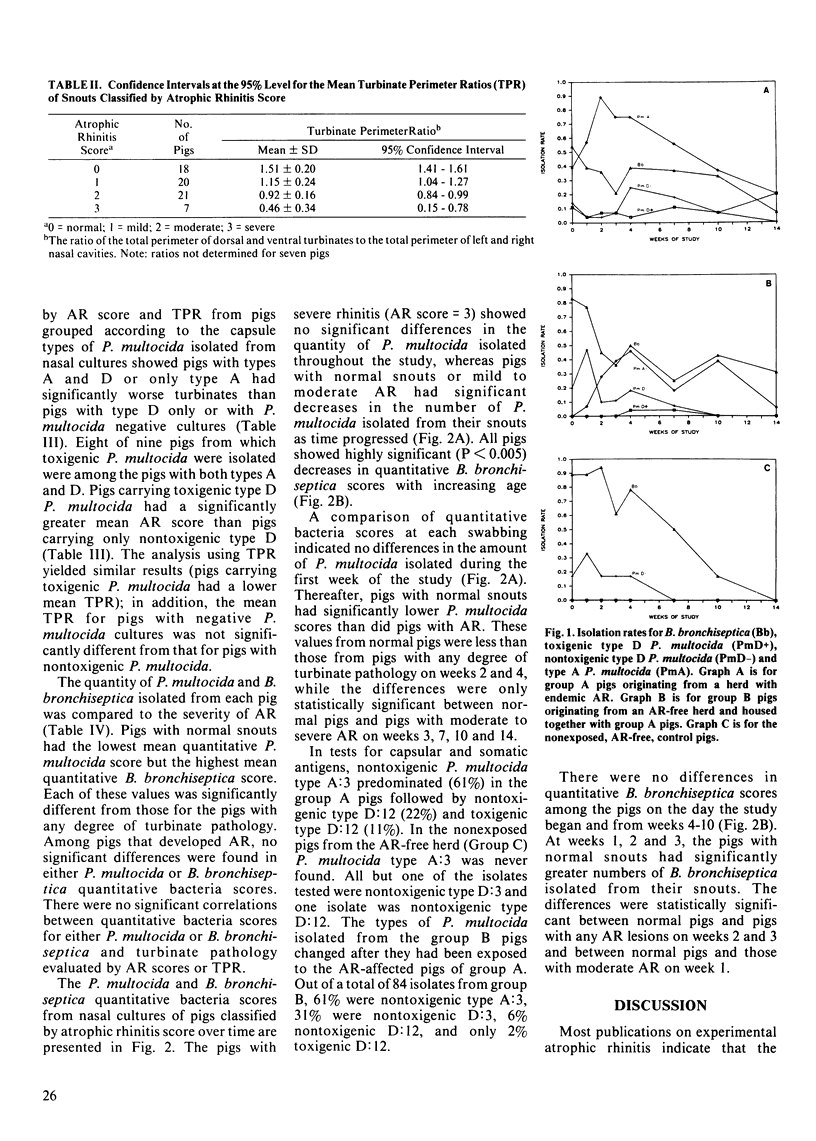
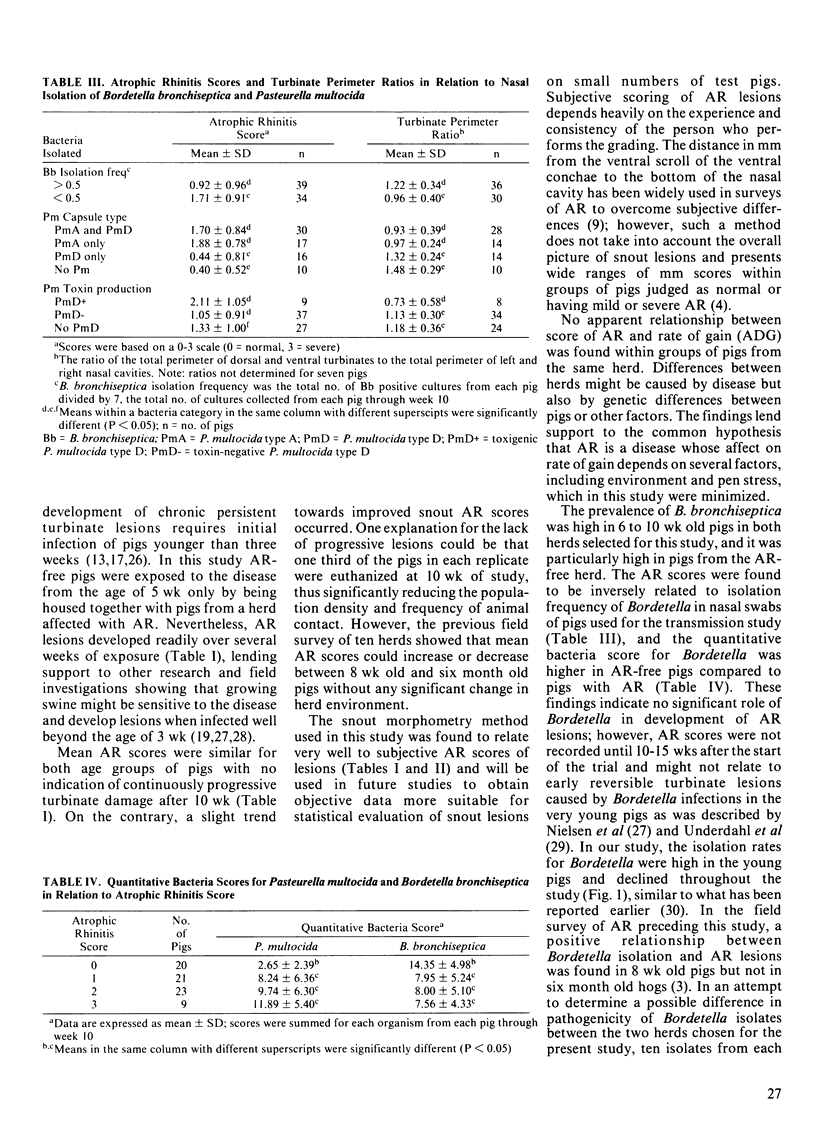
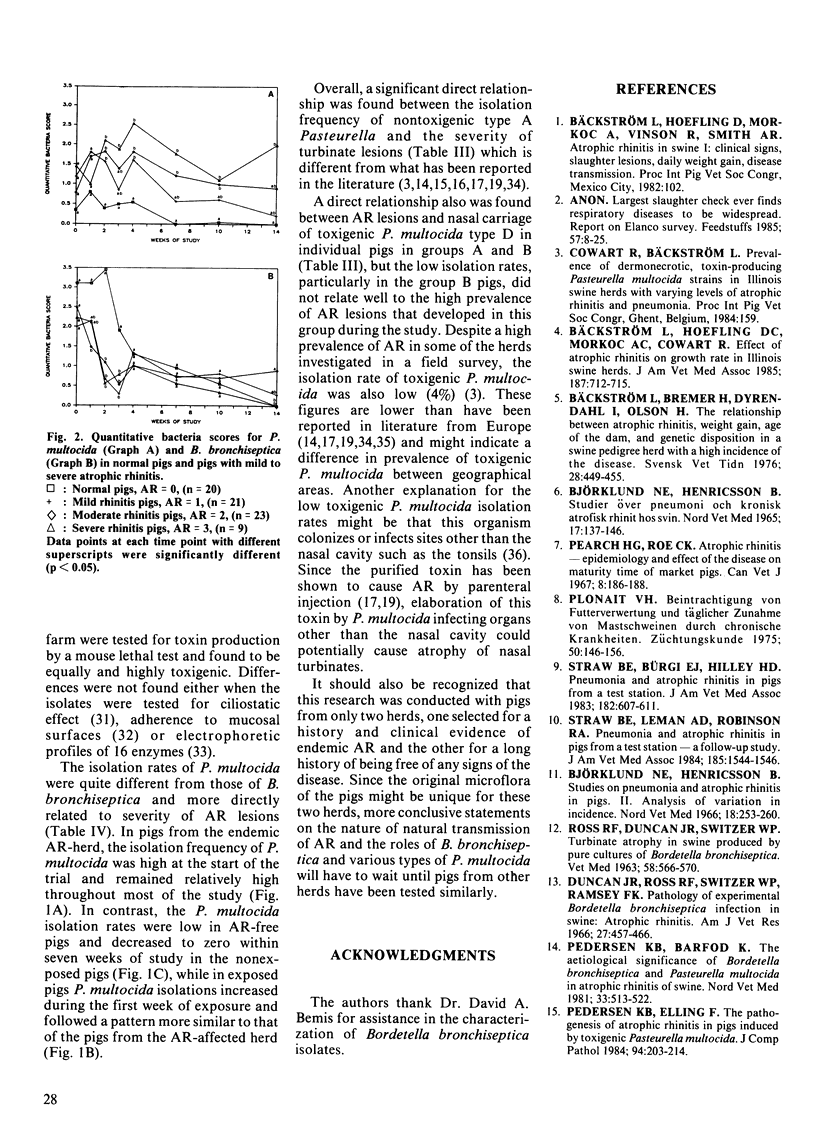
Natural transmission of atrophic rhinitis from pigs from a herd with an endemic atrophic rhinitis problem to pigs from a herd free of atrophic rhinitis was demonstrated. Six replicates each with five pigs from the endemic atrophic rhinitis herd (Group A) and five pigs from the atrophic rhinitis-free herd (Group B) were housed together from 5 wk of age, with each replicate kept in isolation rooms maintained at optimal and controlled environmental conditions. Three replicates each with six pigs/room from the atrophic rhinitis-free herd (Group C), served as nonexposed controls. Group C pigs remained healthy and had no turbinate atrophy at either 10 or 17 wk of study (atrophic rhinitis score = 0 on a 0 to 3 scale). Group A pigs had a mean atrophic rhinitis score of 1.85 +/- 0.84, and group B pigs developed atrophic rhinitis to a mean score of 1.57 +/- 0.70. The isolation rate and quantity of Pasteurella multocida found on nasal swabs was directly related to lesions while those for Bordetella bronchiseptica were inversely related to turbinate atrophy. Of the various types of P. multocida evaluated, nontoxigenic type A and toxigenic type D were both directly related to atrophic rhinitis while nontoxigenic type D strains were not. No toxigenic type A P. multocida strains were isolated.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bemis D. A., Wilson S. A. Influence of potential virulence determinants on Bordetella bronchiseptica-induced ciliostasis. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):35–42. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.35-42.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäckström L., Bergström G. Atrophic rhinitis in swine fattener herds. A field study of the spread of the disease with infected pigs bought at market. Nord Vet Med. 1977 Dec;29(12):539–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäckström L., Hoefling D. C., Morkoc A. C., Cowart R. P. Effect of atrophic rhinitis on growth rate in Illinois swine herds. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1985 Oct 1;187(7):712–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. R., Rundell S. W. Identification of type A strains of P multocida using staphylococcal hyaluronidase. Vet Rec. 1975 Apr 12;96(15):343–343. doi: 10.1136/vr.96.15.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. R., Subronto P. Identification of type D strains of Pasteurella multocida with acriflavine. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Feb;34(2):293–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominick M. A., Rimler R. B. Turbinate atrophy in gnotobiotic pigs intranasally inoculated with protein toxin isolated from type D Pasteurella multocida. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;47(7):1532–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. R., Ross R. F., Switzer W. P., Ramsey F. K. Pathology of experimental Bordetella bronchiseptica infection in swine: atrophic rhinitis. Am J Vet Res. 1966 Mar;27(117):457–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrington D. O., Switzer W. P. Evaluation of nasal culturing procedures for the control of atrophic rhinitis caused by Bordetella bronchiseptica in swine. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1977 Jan 1;170(1):34–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood J. R., Pickett M. J., Martin W. J., Mack E. G. Heamophilus vaginalis (Corynebacterium vaginal): method for isolation and rapid biochemical identification. Health Lab Sci. 1977 Apr;14(2):102–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heddleston K. L., Gallagher J. E., Rebers P. A. Fowl cholera: gel diffusion precipitin test for serotyping Pasteruella multocida from avian species. Avian Dis. 1972 Jul-Sep;16(4):925–936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musser J. M., Hewlett E. L., Peppler M. S., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and relationships in populations of Bordetella spp. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):230–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.230-237.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce H. G., Roe C. K. Atrophic rhinitis-epidemiology and effect of the disease on maturity time of market pigs. Can Vet J. 1967 Aug;8(8):186–188. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. B., Barfod K. The aetiological significance of Bordetella bronchiseptica and Pasteurella multocida in atrophic rhinitis of swine. Nord Vet Med. 1981 Dec;33(12):513–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. B., Elling F. The pathogenesis of atrophic rhinitis in pigs induced by toxigenic Pasteurella multocida. J Comp Pathol. 1984 Apr;94(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(84)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips C. E., Longfield H. F., Miltimore J. E. Porcine Infectious Rhinitis Experiments. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1948 Oct;12(10):268–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotkin B. J., Bemis D. A. Adherence of Bordetella bronchiseptica to hamster lung fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):697–702. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.697-702.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. M. Atrophic rhinitis in swine. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1985;29:239–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. M., Taylor R. J., Crighton W. G., Robertson I. B., Benson J. A. Epidemiological study of Pasteurella multocida and Bordetella bronchiseptica in atrophic rhinitis. Vet Rec. 1984 Dec 15;115(24):615–619. doi: 10.1136/vr.115.24.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. M. Virulence of Pasteurella multocida in atrophic rhinitis of gnotobiotic pigs infected with Bordetella bronchiseptica. Res Vet Sci. 1983 May;34(3):287–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straw B. E., Bürgi E. J., Hilley H. D., Leman A. D. Pneumonia and atrophic rhinitis in pigs from a test station. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1983 Mar 15;182(6):607–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straw B. E., Leman A. D., Robinson R. A. Pneumonia and atrophic rhinitis in pigs from a test station--a follow-up study. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Dec 15;185(12):1544–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


