Abstract
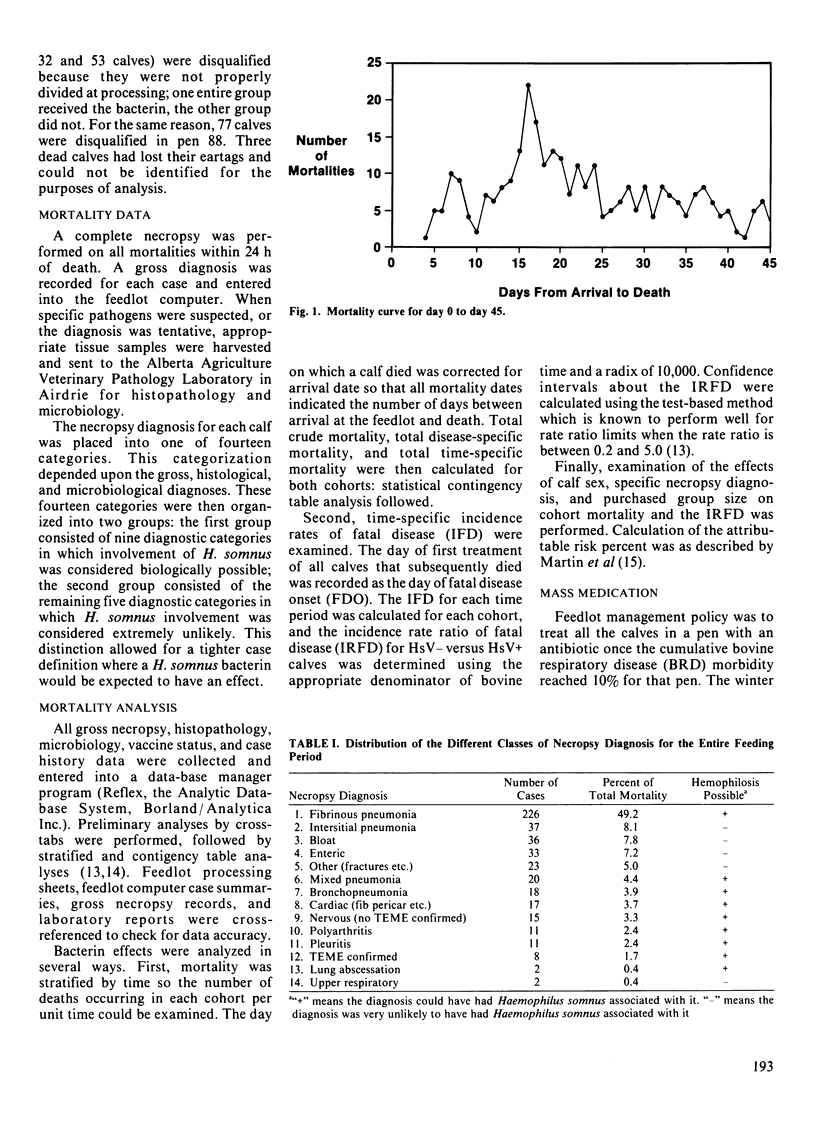
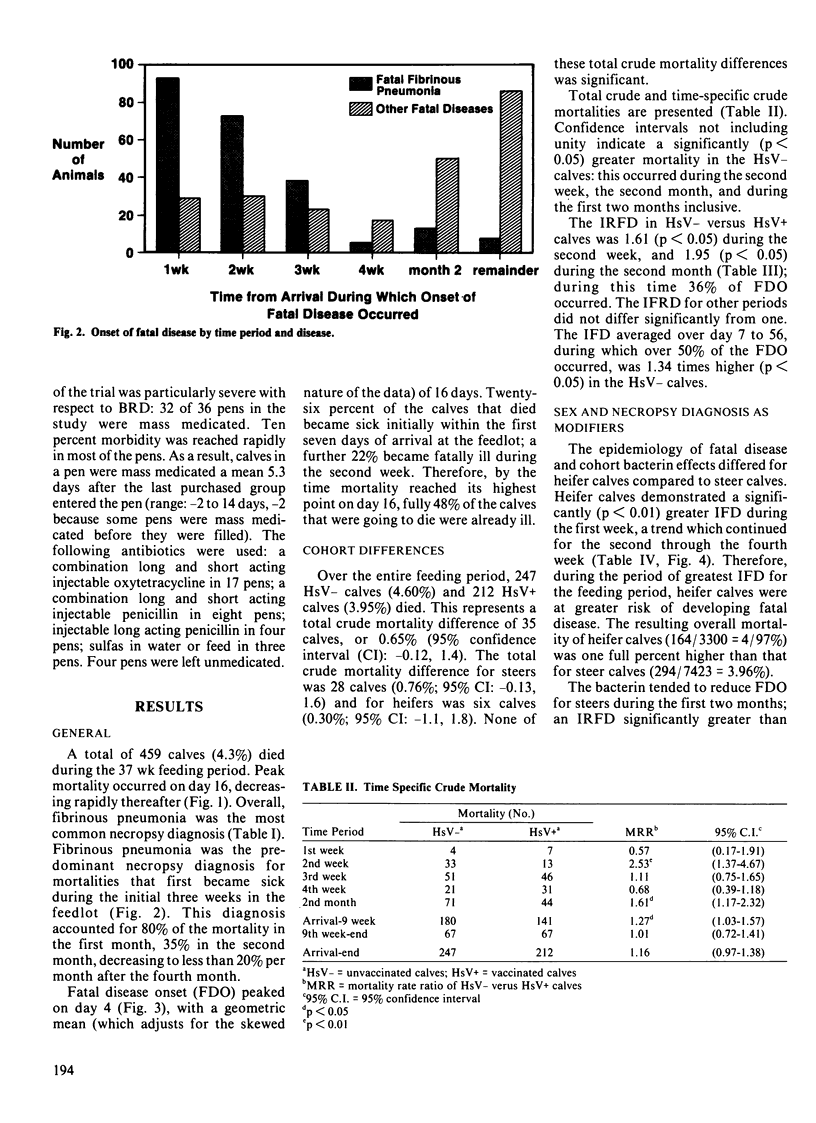
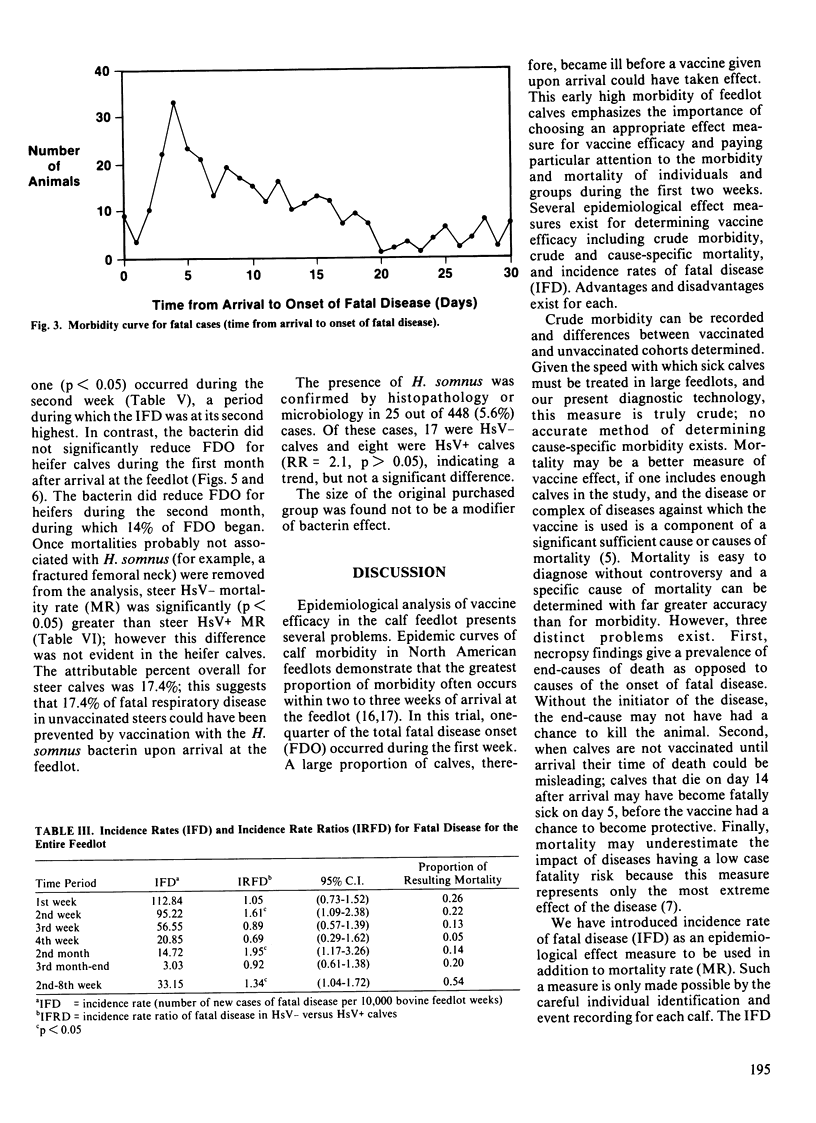
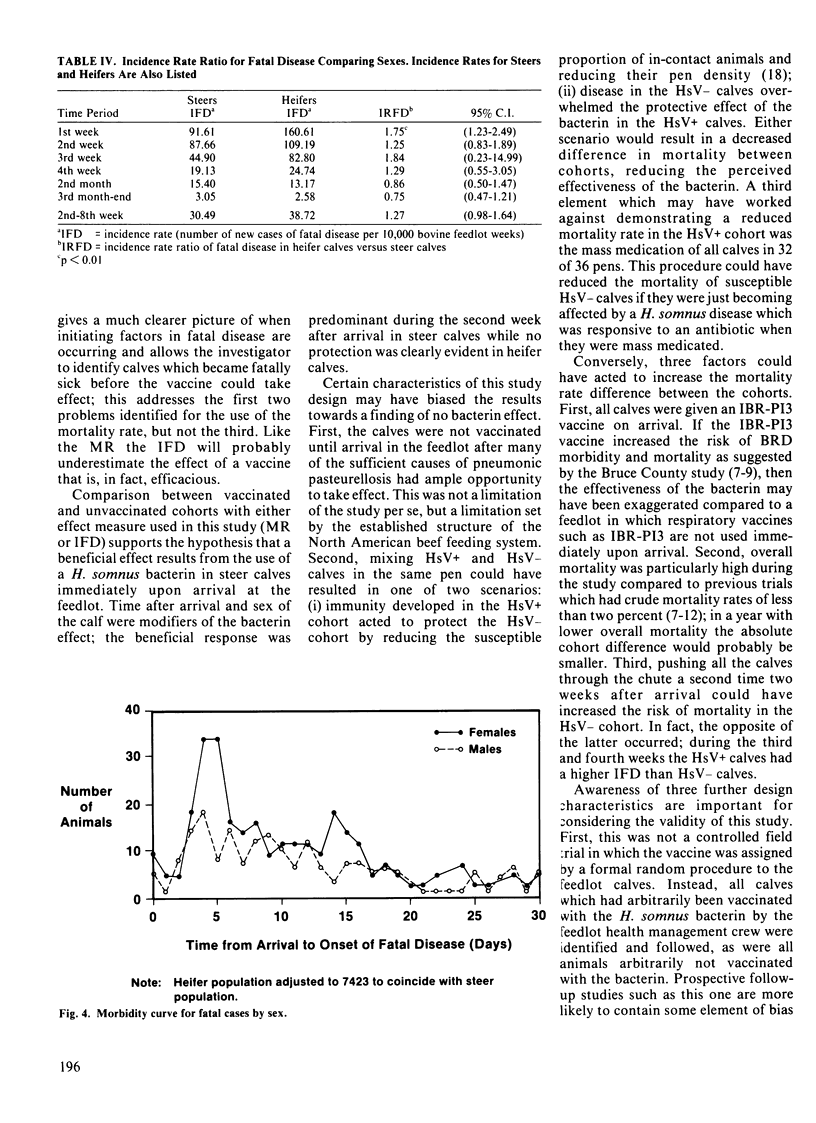
Two cohorts, consisting of 10,723 calves total, were identified in this prospective follow-up study to investigate whether immunization of auction market beef calves immediately upon arrival at the feedlot with a commercial Haemophilus somnus whole cell killed bacterin would reduce subsequent mortality. In addition to mortality rate, the use of incidence rate of fatal disease is introduced as an effect measure to examine vaccine efficacy in the feedlot. The Haemophilus somnus bacterin had no significant effect on the overall crude mortality rate; however, the bacterin appeared to significantly (p less than 0.05) reduce the incidence rate of fatal disease and the mortality rate during the first two months in the feedlot, when risk of fatal disease onset was highest. Once mortalities likely not associated with hemophilosis (for example, a fractured femoral neck) were removed from the analysis, steer mortality rate, but not heifer mortality rate, was reduced significantly (p less than 0.05) in the vaccinated group. The attributable percent overall for steers was 17.4%; this suggests that 17.4% of fatal respiratory disease in the unvaccinated steers could have been prevented by vaccination with the H. somnus bacterin. Heifer calves demonstrated a significantly (p less than 0.01) higher incidence rate of fatal disease during the first week than did steer calves, indicating that a different pattern of fatal disease existed for the two sexes. Use of a second vaccination two weeks after arrival did little to decrease mortality risk.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Corbeil L. B., Widders P. R., Gogolewski R., Arthur J., Inzana T. J., Ward A. C. Haemophilus somnus: Bovine Reproductive and Respiratory Disease. Can Vet J. 1986 Feb;27(2):90–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Pierson R. E., Braddy P. M., Saari D. A., Lauerman L. H., England J. J., Horton D. P., McChesney A. E. Diseases of yearling feedlot cattle in Colorado. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1976 Sep 1;169(5):497–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Pierson R. E., Braddy P. M., Saari D. A., Lauerman L. H., England J. J., Keyvanfar H., Collier J. R., Horton D. P., McChesney A. E. Shipping fever pneumonia in yearling feedlot cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1976 Sep 1;169(5):500–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly A. P., Janzen E. D. A review of morbidity and mortality rates and disease occurrence in north american feedlot cattle. Can Vet J. 1986 Dec;27(12):496–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Meek A. H., Davis D. G., Johnson J. A., Curtis R. A. Factors associated with morbidity and mortality in feedlot calves: the Bruce County beef project, year two. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Apr;45(2):103–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Meek A. H., Davis D. G., Johnson J. A., Curtis R. A. Factors associated with mortality and treatment costs in feedlot calves: the Bruce County Beef Project, years 1978, 1979, 1980. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Oct;46(4):341–349. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Meek A. H., Davis D. G., Thomson R. G., Johnson J. A., Lopez A., Stephens L., Curtis R. A., Prescott J. F., Rosendal S. Factors associated with mortality in feedlot cattle: the Bruce County Beef Cattle Project. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Jan;44(1):1–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Willson P., Curtis R., Allen B., Acres S. A field trial, of preshipment vaccination, with intranasal infectious bovine rhinotracheitis-parainfluenza-3 vaccines. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Jul;47(3):245–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman K. J. Causes. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Dec;104(6):587–592. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. R., Janzen E. D. Haemophilus somnus infections. II. A Canadian field trial of a commercial bacterin: clinical and serological results. Can Vet J. 1980 Aug;21(8):219–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. R., Thiessen W. A., Janzen E. D. Haemophilus somnus infections I. A ten year (1969-1978) retrospective study of losses in cattle herds in Western Canada. Can Vet J. 1980 Apr;21(4):119–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Little P. B., Wilkie B. N., Barnum D. A. Infectious thromboembolic meningoencephalitis in cattle: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1981 Feb 15;178(4):378–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


