Abstract
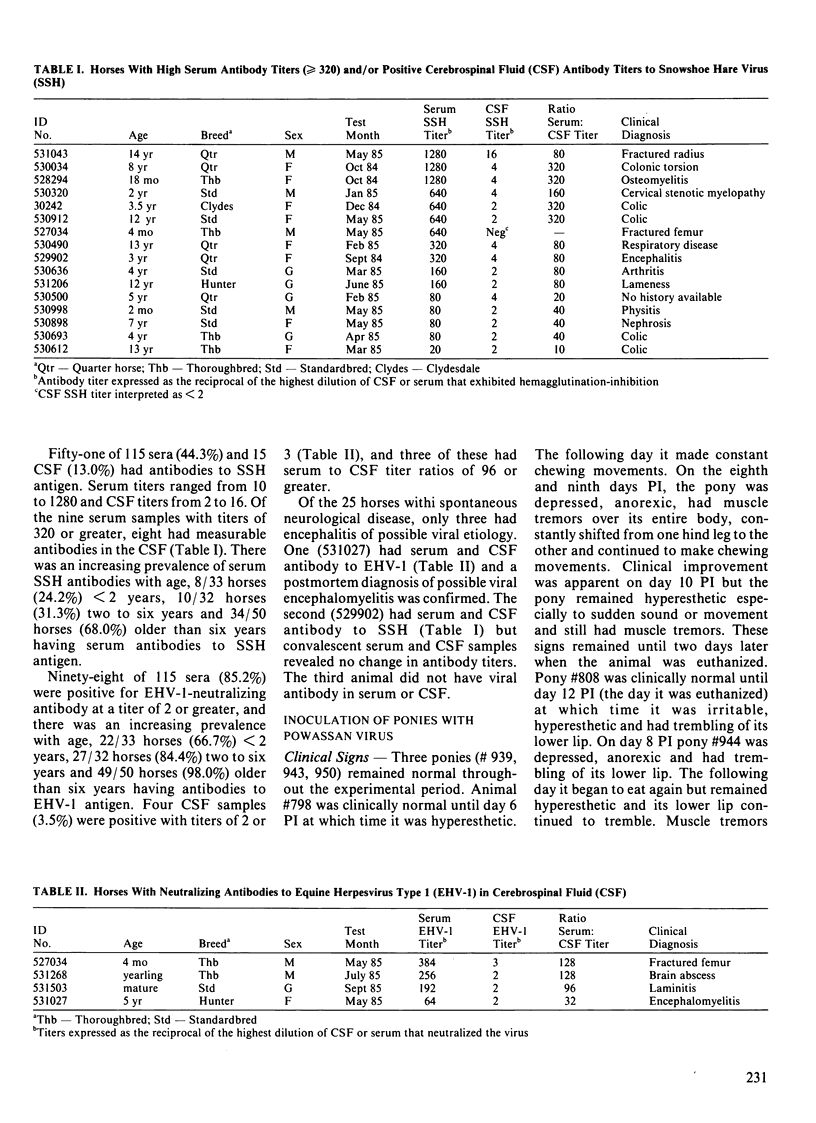
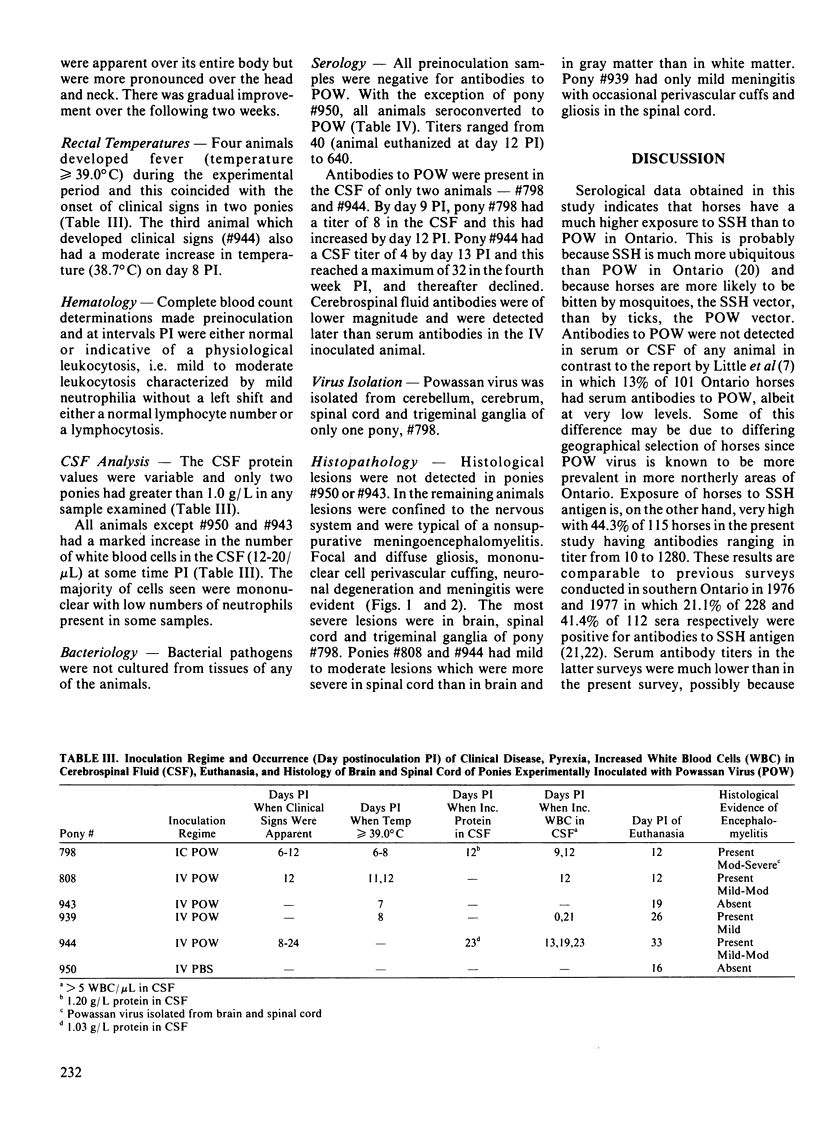
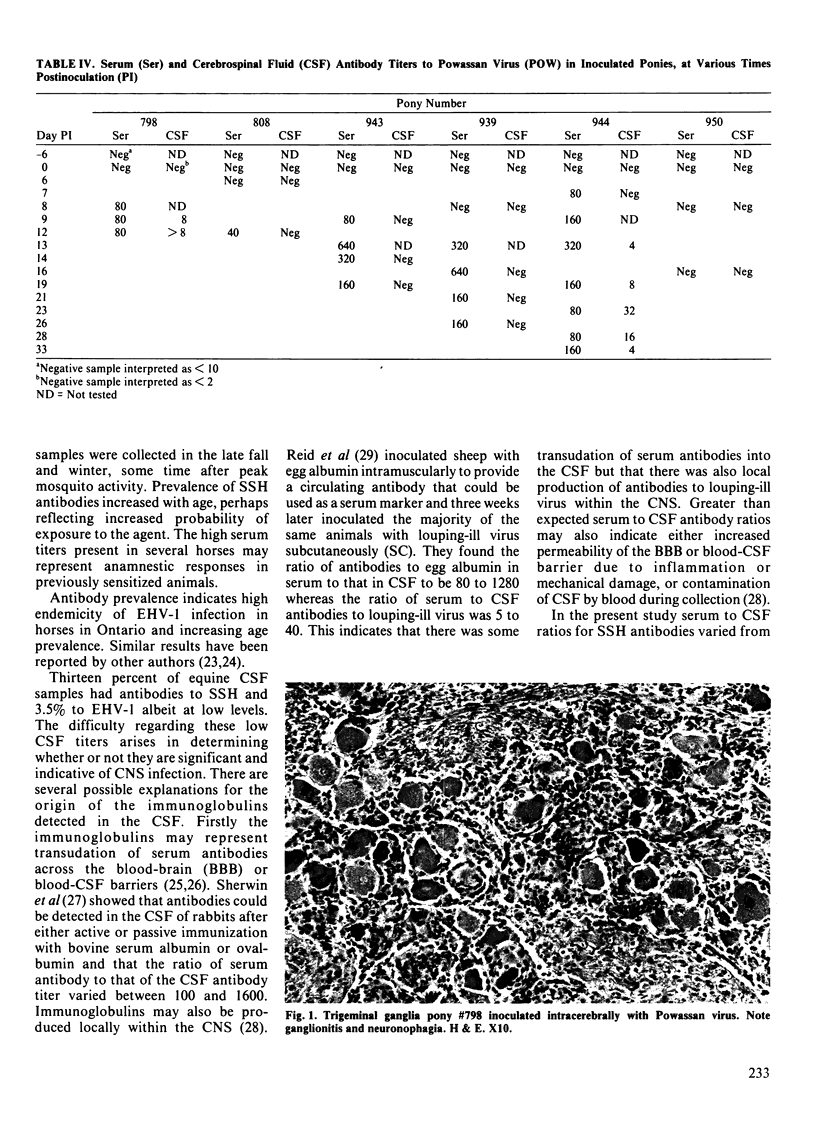
A survey was conducted by testing 115 paired equine serum and cerebrospinal fluid samples by hemagglutination-inhibition for antibodies to Powassan and snowshoe hare viruses, and by virus neutralization for antibodies to equine herpesvirus type 1. Twenty-five samples were from horses with spontaneous neurological disease and the remainder from horses euthanized because of various nonneurological disorders. All sera and cerebrospinal fluids were negative for antibodies to Powassan virus. Fifty-one sera (44.3%) and 15 cerebrospinal fluids (13.0%) had antibodies to snowshoe hare virus. Ninety-eight sera (85.2%) and four cerebrospinal fluids (3.5%) were positive for antibodies to equine herpesvirus type 1. Powassan virus was inoculated intracerebrally into one, and intravenously into four ponies. Neurological signs associated with a nonsuppurative encephalomyelitis occurred in three ponies. Antibodies to Powassan virus were detected in sera of all animals but in cerebrospinal fluids of only two. Powassan virus was isolated from brain and spinal cord of only the intracerebrally inoculated animal.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artsob H., Wright R., Shipp L., Spence L., Th'ng C. California encephalitis virus activity in mosquitoes and horses in southern Ontario, 1975. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Dec;24(12):1544–1547. doi: 10.1139/m78-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagust T. J., Pascoe R. R., Harden T. J. Studies on equine herpesviruses. 3. The incidence in Queensland of three different equine herpesvirus infections. Aust Vet J. 1972 Feb;48(2):47–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1972.tb05109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blythe L. L., Mattson D. E., Lassen E. D., Craig A. M. Antibodies against equine herpesvirus 1 in the cerebrospinal fluid in the horse. Can Vet J. 1985 Jul;26(7):218–220. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton K. M., Mitchell D., Girard A., Corner A. H. Meningoencephalomyelitis in horses associated with equine herpesvirus 1 infection. Vet Pathol. 1976;13(1):59–68. doi: 10.1177/030098587601300107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinter Z., Klingeborn B. Serological study of an outbreak of paresis due to equid herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1). Vet Rec. 1976 Jul 3;99(1):10–12. doi: 10.1136/vr.99.1.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard W., Iwasaki Y., Koprowski H. The central nervous system-associated immune response to parainfluenza type I virus in mice. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1256–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimstad P. R., Artsob H., Karabatsos N., Calisher C. H. Production and use of a hemagglutinin for detecting antibody to Jamestown Canyon virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1557–1559. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1557-1559.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heremans J. F. Immunoglobulin formation and function in different tissues. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1968;45:131–203. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50109-8_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann H., Frisch-Niggemeyer W., Heinz F., Kunz C. Immunoglobulins to tick-borne encephalitis in the cerebrospinal fluid of man. J Med Virol. 1979;4(3):241–245. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISSLING R. E., CHAMBERLAIN R. W., EIDSON M. E., SIKES R. K., BUCCA M. A. Studies on the North American arthropod-borne encephalitides. II. Eastern equine encephalitis in horses. Am J Hyg. 1954 Nov;60(3):237–250. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A., Moore D. H., Landow H. AN ELECTROPHORETIC STUDY OF THE PROTEIN COMPONENTS IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID AND THEIR RELATIONSHIP TO THE SERUM PROTEINS. J Clin Invest. 1942 Sep;21(5):571–577. doi: 10.1172/JCI101335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOGRIPPO G. A. Investigations of the use of beta-propiolactone in virus inactivation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 13;83:578–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb40931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little P. B., Thorsen J., Moore W., Weninger N. Powassan viral encephalitis: a review and experimental studies in the horse and rabbit. Vet Pathol. 1985 Sep;22(5):500–507. doi: 10.1177/030098588502200510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. A., Binnington B. D., Artsob H. California serogroup virus infection in a horse with encephalitis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1985 Feb 15;186(4):389–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matumoto M., Ishizaki R., Shimizu T. Serologic survey of equine rhinopneumonitis virus infection among horses in various countries. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;15(5):609–624. doi: 10.1007/BF01245208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew I. G., Whitlock R. H., Tasker J. B. Equine cerebrospinal fluid: reference values of normal horses. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Aug;38(8):1271–1274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monath T. P., McLean R. G., Cropp C. B., Parham G. L., Lazuick J. S., Calisher C. H. Diagnosis of eastern equine encephalomyelitis by immunofluorescent staining of brain tissue. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Aug;42(8):1418–1421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgante O., Vance H. N., Shemanchuk J. A., Windsor R. Epizootic of western encephalomyelitis virus infection in equines in Alberta in 1965. Can J Comp Med. 1968 Apr;32(2):403–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesce M. A., Strande C. S. A new micromethod for determination of protein in cerebrospinal fluid and urine. Clin Chem. 1973 Nov;19(11):1265–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt H., Singh H., Whitwell K. E. Pathological observations on an outbreak of paralysis in broodmares. Equine Vet J. 1980 Jul;12(3):118–126. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1980.tb03398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid H. W., Doherty P. C., Dawson A. M. Louping-ill encephalomyelitis in the sheep. 3. Immunoglobulins in cerebrospinal fluid. J Comp Pathol. 1971 Oct;81(4):537–543. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(71)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERWIN A. L., RICHTER M., COSGROVE J. B., ROSE B. Studies of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier to antibodies and other proteins. Neurology. 1963 Feb;13:113–119. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.2.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsen J., Little P. B. Isolation of equine herpesvirus type 1 from a horse with an acute paralytic disease. Can J Comp Med. 1975 Jul;39(3):358–359. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb H. E., Smith C. E. Relation of immune response to development of central nervous system lesions in virus infections of man. Br Med J. 1966 Nov 12;2(5523):1179–1181. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5523.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




