Abstract
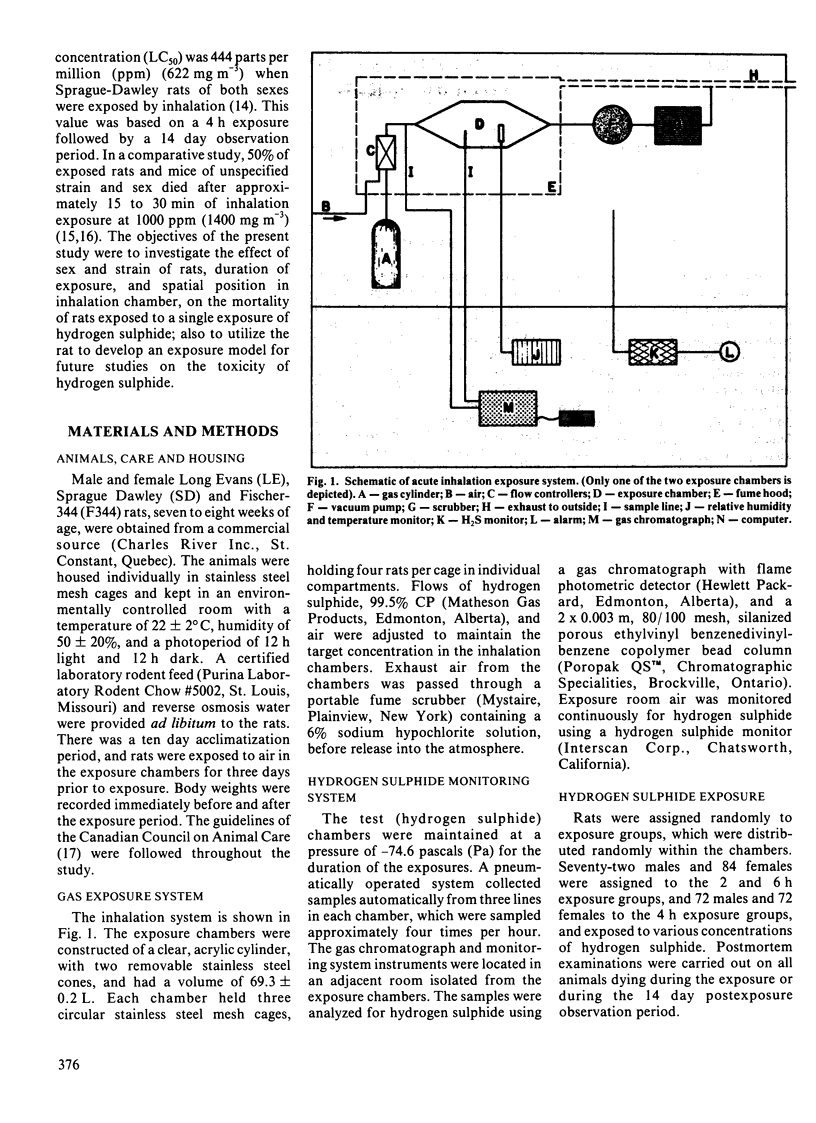
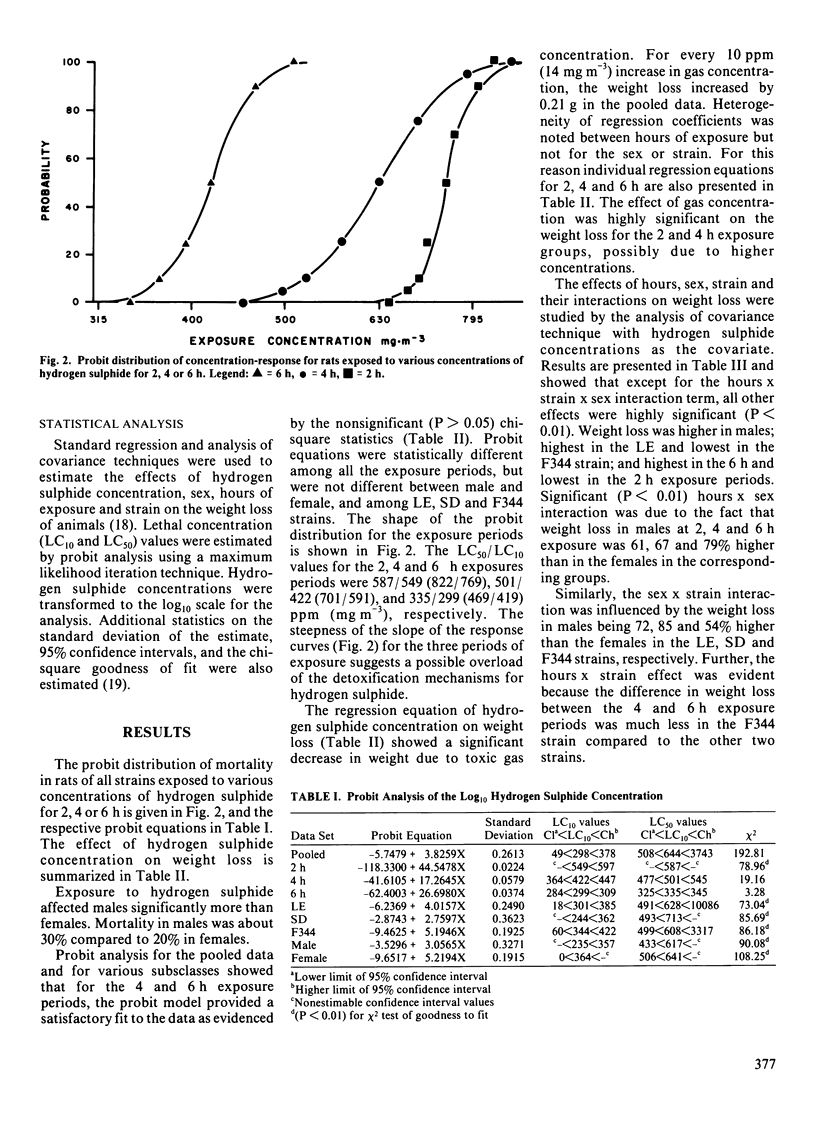
Concentration-time interactions were investigated in young male and female Sprague-Dawley, Long Evans and Fischer-344 rats exposed to hydrogen sulphide for two, four or six hours. Higher concentrations caused more deaths, with no significant difference for duration of exposure. A significant sex effect was noted with 30% mortality in males and 20% in females, with no significant difference among strains. Changes in weight were significant: increasing with concentration, higher in males than in females, different among strains (Fischer-344 less than Sprague Dawley less than Long Evans), and affected by duration of exposure. Lethal concentration values (LC50 and LC10) were estimated, for the pooled data set (n = 456); the probit equation was Y = -5.74749 + 3.8259X where X is log10 dose of hydrogen sulphide in parts per million. The LC50/LC10 values were 644/298 parts per million (902/417 mg m-3) respectively. Individual probit analyses were also performed for strain, hours of exposure and sex. The LC50 and LC10 values for male, female and strain were not different. Significant differences were observed among LC50/LC10 values for hours of exposure (2 h = 587/549 parts per million, 822/769 mg m-3; 4 h = 501/422 parts per million, 701/591 mg m-3; 6 h = 335/299 parts per million, 469/491 mg m-3). There was no effect of spatial position in the exposure chamber on the distribution of mortality. All rats of all strains dying had severe pulmonary edema.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beauchamp R. O., Jr, Bus J. S., Popp J. A., Boreiko C. J., Andjelkovich D. A. A critical review of the literature on hydrogen sulfide toxicity. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1984;13(1):25–97. doi: 10.3109/10408448409029321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett W. W., King E. G., Grace M., Hall W. F. Hydrogen sulfide poisoning: review of 5 years' experience. Can Med Assoc J. 1977 Dec 3;117(11):1277–1280. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis S. E., Anderson C. R., Simon J., Jensen A. H., Day D. L., Kelley K. W. Effects of aerial ammonia, hydrogen sulfide and swine-house dust on rate of gain and respiratory-tract structure in swine. J Anim Sci. 1975 Sep;41(3):735–739. doi: 10.2527/jas1975.413735x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond G. I., Powell C. A. Analogues of adenosine 3',-5'-cyclic phosphate as activators of phosphorylase b kinase and as substrates for cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;6(1):24–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klentz R. D., Fedde M. R. Hydrogen sulfide: effects on avian respiratory control and intrapulmonary CO2 receptors. Respir Physiol. 1978 Mar;32(3):355–367. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(78)90123-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A., Prior M., Yong S., Albassam M., Lillie L. E. Biochemical and cytologic alterations in the respiratory tract of rats exposed for 4 hours to hydrogen sulfide. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1987 Nov;9(4):753–762. doi: 10.1016/0272-0590(87)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tansy M. F., Kendall F. M., Fantasia J., Landin W. E., Oberly R., Sherman W. Acute and subchronic toxicity studies of rats exposed to vapors of methyl mercaptan and other reduced-sulfur compounds. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1981 Jul-Aug;8(1-2):71–88. doi: 10.1080/15287398109530051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


