Abstract
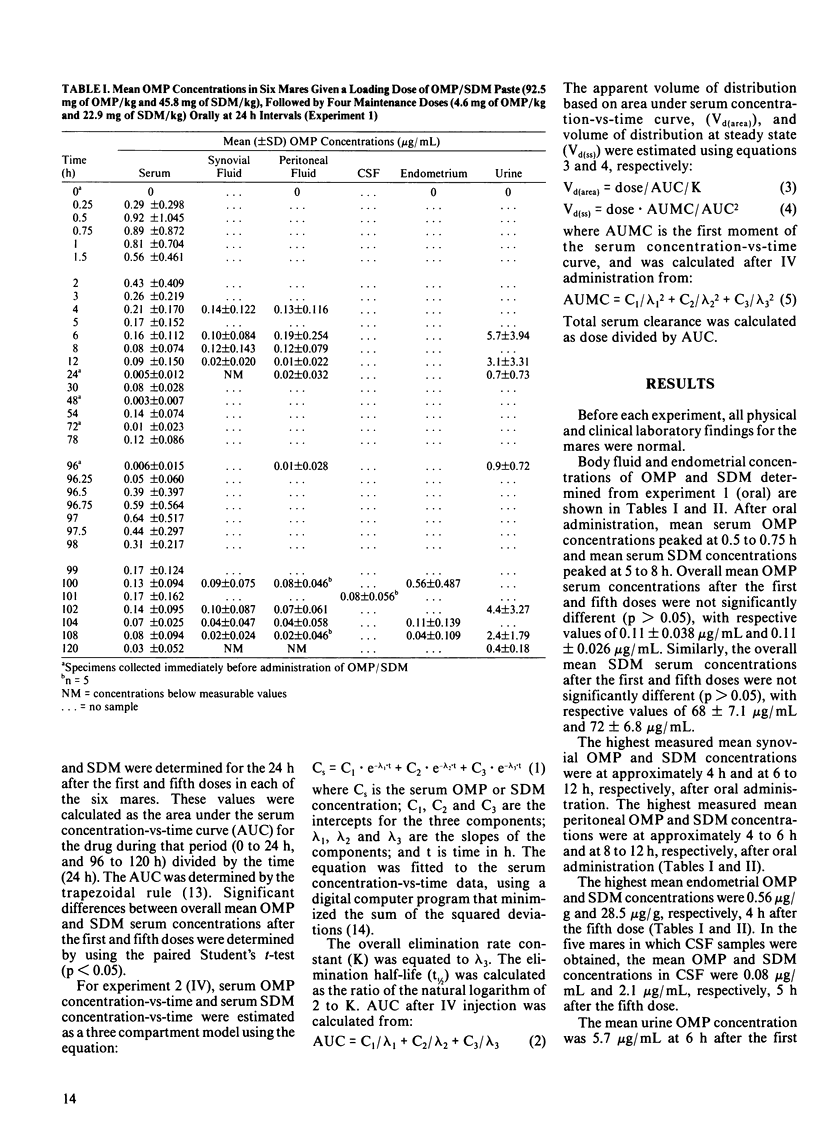
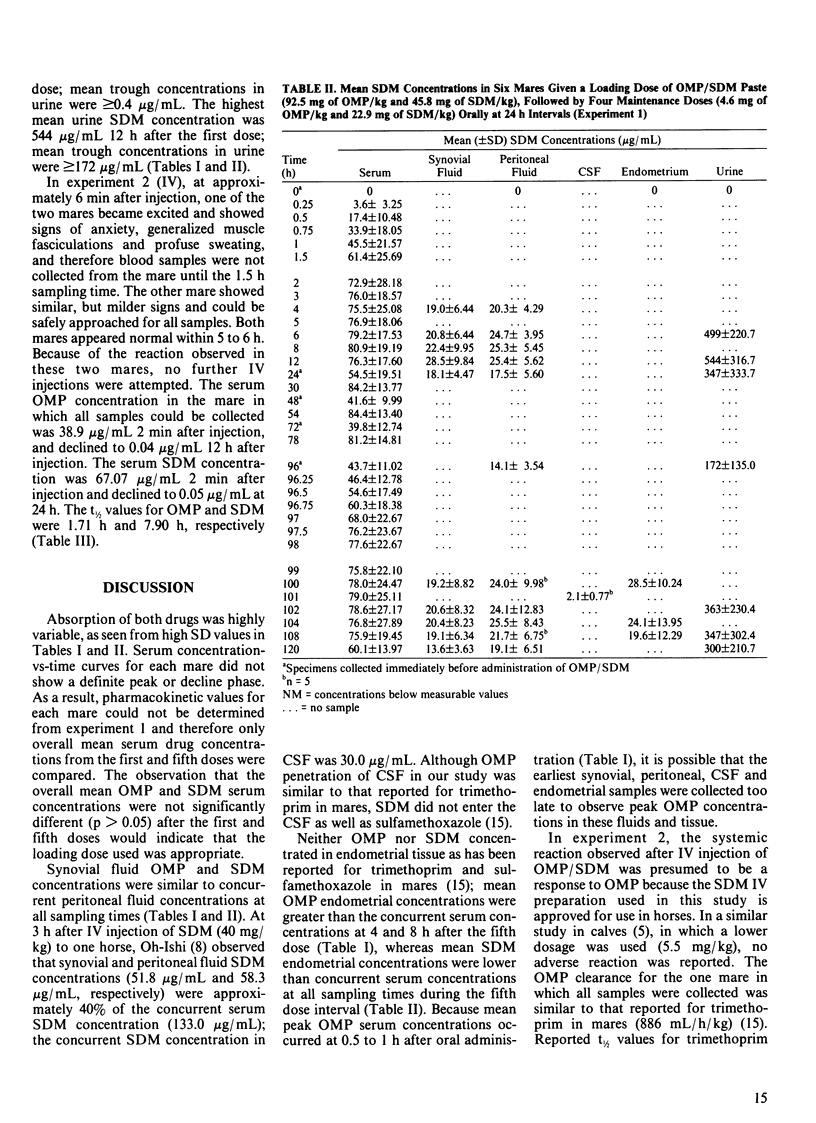
Six healthy adult mares were each given an oral loading dose of ormetoprim(OMP)-sulfadimethoxine (SDM) at a dosage of 9.2 mg of OMP/kg and 45.8 mg of SDM/kg, followed by four maintenance doses of 4.6 mg of OMP/kg and 22.9 mg of SDM/kg, at 24 h intervals. Ormetoprim and SDM concentrations were measured in serum, synovial fluid, peritoneal fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, urine and endometrium. The highest mean serum OMP concentration was 0.92 micrograms/mL 0.5 h after the first dose; the highest mean SDM concentration was 80.9 micrograms/mL 8 h after the first dose. The highest mean synovial fluid concentrations were 0.14 microgram of OMP/mL and 28.5 micrograms of SDM/mL 12 h after the first dose. The highest mean peritoneal fluid concentrations were 0.19 micrograms of OMP/mL 6 h after the first dose and 25.5 micrograms of SDM/mL 8 h after the fifth dose. The highest mean endometrial concentrations were 0.56 micrograms of OMP/g and 28.5 micrograms of SDM/g 4 h after the fifth dose. The mean cerebrospinal fluid concentrations were 0.08 micrograms of OMP/mL and 2.1 micrograms of SDM/mL 5 h after the fifth dose. Mean trough urine drug concentrations were greater than or equal to 0.4 micrograms of OMP/mL and greater than or equal to 172 micrograms of SDM/mL. Two of the mares were each given a single intravenous (IV) injection of OMP and SDM at a dosage of 9.2 mg of OMP/kg and 45.8 mg of SDM/kg. Excitation and muscle fasciculations were observed in both mares after IV administration and all scheduled blood samples could be collected from only one of the two mares.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson P. J., Wilson W. D., Hirsh D. C., Baggot J. D., Martin L. D. Susceptibility of equine bacterial isolates to antimicrobial agents. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Feb;46(2):447–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames T. R., Casagranda C. L., Werdin R. E., Hanson L. J. Effect of sulfadimethoxine-ormetoprim in the treatment of calves with induced Pasteurella pneumonia. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Jan;48(1):17–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggot J. D., Short C. R. Drug disposition in the neonatal animal, with particular reference to the foal. Equine Vet J. 1984 Jul;16(4):364–367. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1984.tb01945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett M., Bushby S. R. Trimethoprim and the sulphonamides. Vet Rec. 1970 Jul 11;87(2):43–51. doi: 10.1136/vr.87.2.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. P., Gronwall R., Castro L. Pharmacokinetics and body fluid and endometrial concentrations of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in mares. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jun;49(6):918–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. P., Kelly R. H., Stover S. M., Gronwall R. Trimethoprim-sulfadiazine in the horse: serum, synovial, peritoneal, and urine concentrations after single-dose intravenous administration. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Apr;44(4):540–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. P., Stover S. M., Kelly R. H., Farver T. B., Knight H. D. Oxytetracycline hydrochloride in the horse: serum, synovial, peritoneal and urine concentrations after single dose intravenous administration. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Mar;4(1):7–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.1981.tb00703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürr A., Frutiger C., Lior D., Pilloud M., Schlatter T., Tschudi P., Schatzmann H. J. Die Bedeutung der Pharmakokinetik für die Dosierung in der Chemotherapie. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1980 Jun;122(6):307–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronwall R., Brown M. P., Merritt A. M., Stone H. W. Body fluid concentrations and pharmacokinetics of chloramphenicol given to mares intravenously or by repeated gavage. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Dec;47(12):2591–2595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maestrone G., Thompson E., Yeisley H., Mitrovic M. Prophylactic and therapeutic activity of Rofenaid-40A in an experimental Escherichia coli airsac infection in chickens. Avian Dis. 1979 Jul-Sep;23(3):682–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi S., Nakajima T. [Blood levels of long-acting sufonamides in horses after oral or intravenous administration]. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1964 Dec;26(6):343–347. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.26.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. D., George L. W., Baggot J. D., Adamson P. J., Hietala S. K., Mihalyi J. E. Ormetoprim-sulfadimethoxine in cattle: pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, distribution to the tears, and in vitro activity against Moraxella bovis. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Mar;48(3):407–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


