Abstract
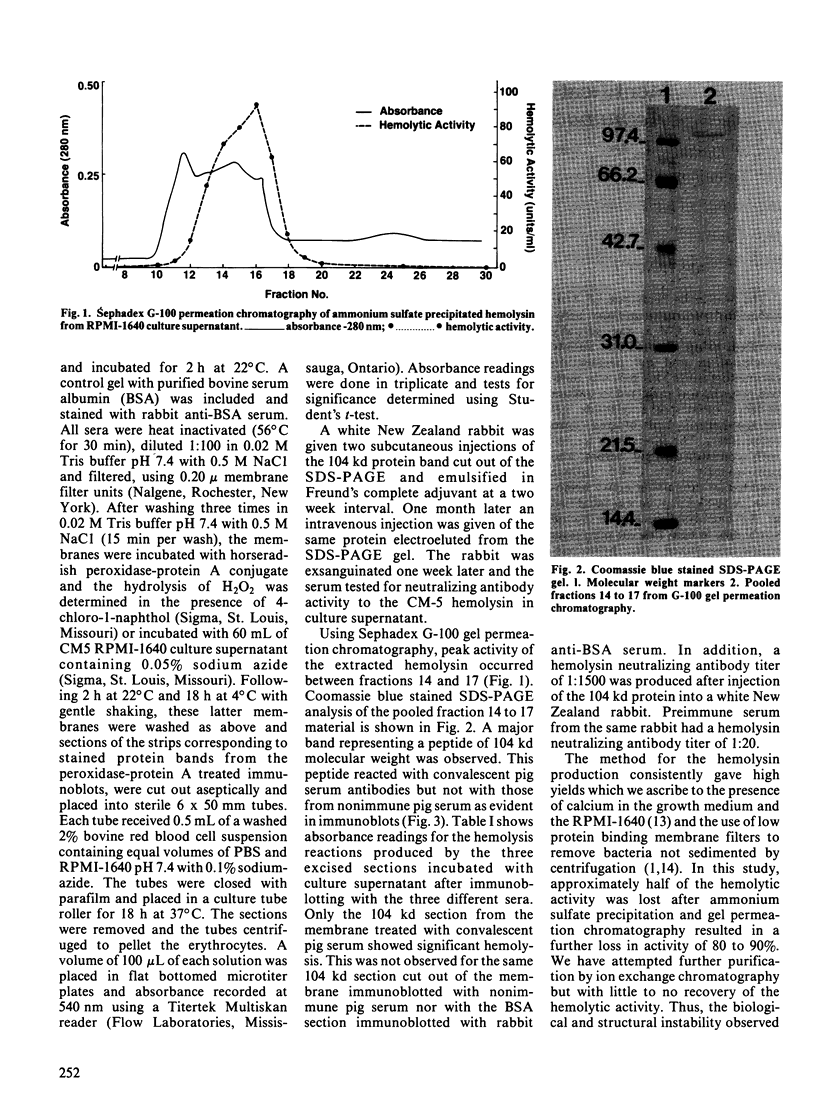
The heat-labile hemolysin of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 1 strain CM-5 was partially purified using ammonium sulfate precipitation and gel permeation chromatography. This partially purified material was subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and blotted onto nylon filters. The filters were treated with convalescent pig serum and subsequently with CM-5 culture supernatant containing active hemolysin. A 104 kd peptide was identified as the hemolysin because it bound antibodies in convalescent pig serum which cross-linked active hemolysin. The same 104 kd protein when injected into a rabbit produced neutralizing antibodies to the CM-5 hemolysin in culture supernatant.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fenwick B. W., Osburn B. I. Immune responses to the lipopolysaccharides and capsular polysaccharides of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae in convalescent and immunized pigs. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):575–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.575-582.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick B. W., Osburn B. I., Olander H. J. Isolation and biological characterization of two lipopolysaccharides and a capsular-enriched polysaccharide preparation from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jul;47(7):1433–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liggett A. D., Harrison L. R., Farrell R. L. Acute inflammatory effects of intratracheally instilled Escherichia coli endotoxin and sonicated suspension of Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae in swine. Can J Vet Res. 1986 Oct;50(4):526–531. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacInnes J. I., Rosendal S. Analysis of major antigens of Haemophilus (Actinobacillus) pleuropneumoniae and related organisms. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1626–1634. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1626-1634.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. G., Lachance P., Niven D. F. Production of RNA-dependent haemolysin by Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Can J Microbiol. 1985 May;31(5):456–462. doi: 10.1139/m85-085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley J. R., Kadis S. Growth and hemolysin production by Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae cultivated in a chemically defined medium. Can J Microbiol. 1986 Oct;32(10):801–805. doi: 10.1139/m86-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley J. R., Kadis S., Mayberry W. R. Isolation, purification, and partial characterization of a lipopolysaccharide from Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):501–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.501-506.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muilerman H. G., ter Hart H. G., Van Dijk W. Specific detection of inactive enzyme protein after polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis by a new enzyme-immunoassay method using unspecific antiserum and partially purified active enzyme: application to rat liver phosphodiesterase I. Anal Biochem. 1982 Feb;120(1):46–51. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90315-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S., Devenish J., MacInnes J. I., Lumsden J. H., Watson S., Xun H. Evaluation of heat-sensitive, neutrophil-toxic, and hemolytic activity of Haemophilus (Actinobacillus) pleuropneumoniae. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;49(7):1053–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebunya T. N., Saunders J. R. Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae infection in swine: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1983 Jun 15;182(12):1331–1337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udeze F. A., Latimer K. S., Kadis S. Role of haemophilus pleuropneumoniae lipopolysaccharide endotoxin in the pathogenesis of porcine Haemophilus pleuropneumonia. Am J Vet Res. 1987 May;48(5):768–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J., Dorssers L., Zabel P. Antibody-linked polymerase assay on protein blots: a novel method for identifying polymerases following SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):233–237. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]