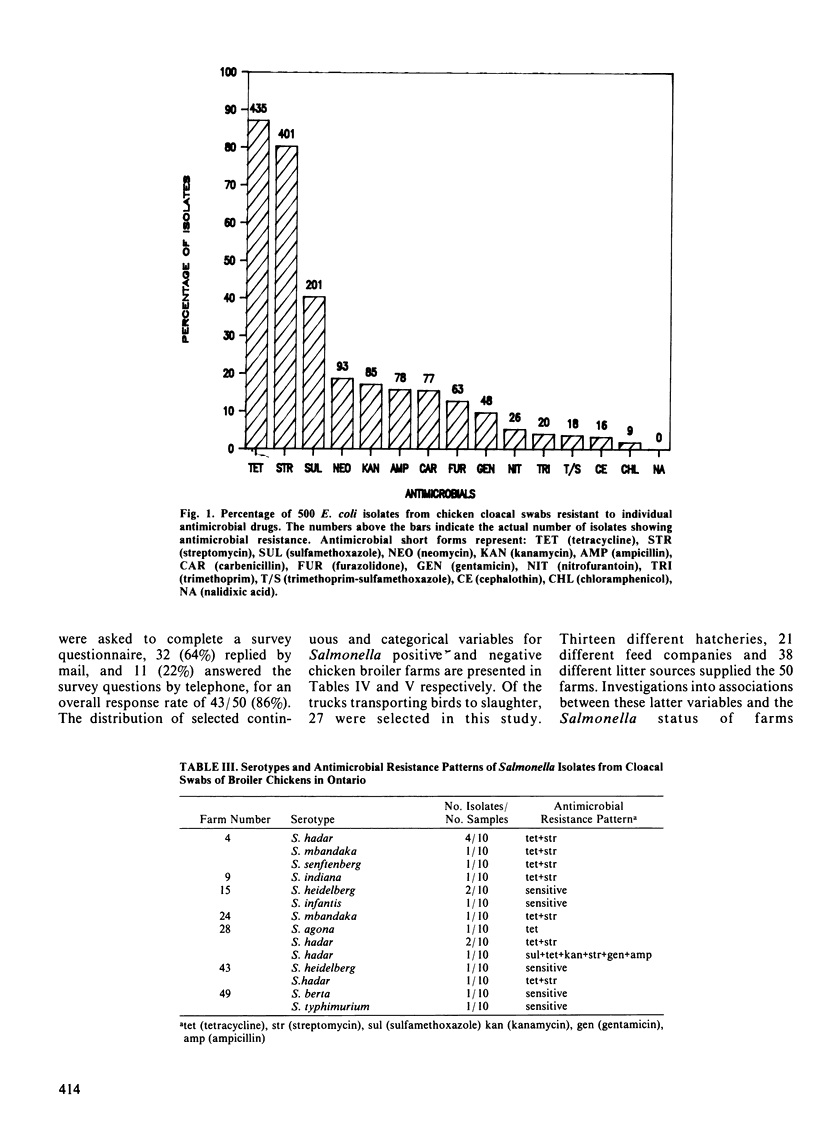
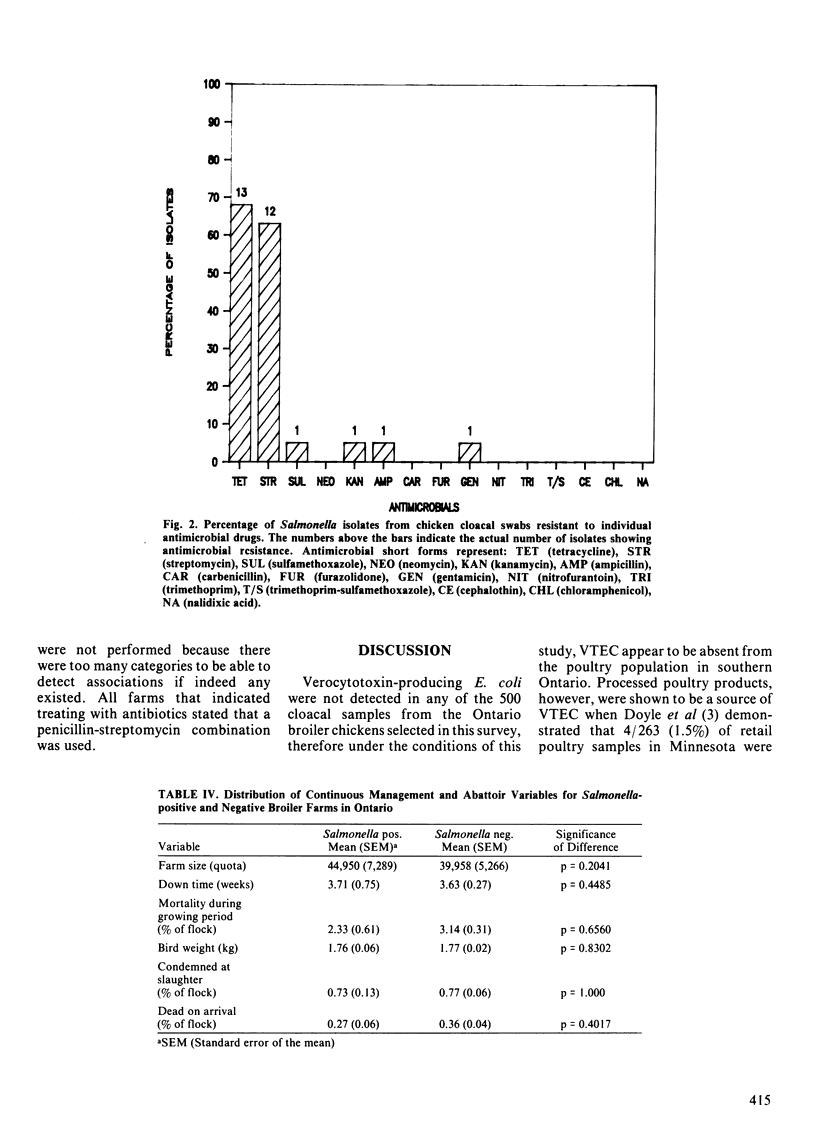
Abstract
The prevalence of verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli and Salmonella in Ontario broiler chickens was determined by culturing cloacal samples from 500 individual birds selected from 50 poultry farms. Resistance to antimicrobials was determined for each of the isolates. In addition, abattoir and farm-level management data were obtained to evaluate variables that may be considered risk factors for infection. The variables selected included: Percentage of birds condemned at slaughter, percentage of birds dead-on-arrival, bird weight, truck number, farm size, hatchery source, litter source and type, feed source, mortality levels, type of water drinker, water sanitization, down time, barn clean out and history of antibiotic treatment. None of the cloacal samples revealed the presence of verocytotoxin-producing E. coli, though 19/500 (3.8%) contained Salmonella organisms. Nine different Salmonella serotypes were isolated; the most common being S. hadar, S. heidelberg and S. mbandaka. Resistance to tetracycline and streptomycin was common among Salmonella (63%) and E. coli (25.2%) isolates. Resistance to two or more antimicrobials occurred in 420/500 (84%) of the E. coli isolates. No statistically significant associations between abattoir or farm-level management variables and the Salmonella-status of farms were demonstrated.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beery J. T., Doyle M. P., Schoeni J. L. Colonization of chicken cecae by Escherichia coli associated with hemorrhagic colitis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):310–315. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.310-315.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia T. R., McNabb G. D., Wyman H., Nayar G. P. Salmonella isolation from litter as an indicator of flock infection and carcass contamination. Avian Dis. 1979 Oct-Dec;23(4):838–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn B. O., Schlater L. K., Swanson M. R. Antibiotic resistance of members of the genus Salmonella isolated from chickens, turkeys, cattle, and swine in the United States during October 1981 through September 1982. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Jun;45(6):1245–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A. O., Borczyk A. A., Carlson J. A., Harvey B., Hockin J. C., Karmali M. A., Krishnan C., Korn D. A., Lior H. A severe outbreak of Escherichia coli O157:H7--associated hemorrhagic colitis in a nursing home. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 10;317(24):1496–1500. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712103172403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J. Salmonella contamination in a commercial poultry (broiler) processing operation. Poult Sci. 1974 Mar;53(2):814–821. doi: 10.3382/ps.0530814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Schoeni J. L. Isolation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from retail fresh meats and poultry. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Oct;53(10):2394–2396. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.10.2394-2396.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch M. J., Blake P. A. Foodborne outbreaks of campylobacteriosis: the United States experience, 1980-1982. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Aug;122(2):262–268. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon V. P., Gyles C. L., Friendship R. W. Characteristics of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli from pigs. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;52(3):331–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins R., Malo R., René-Roberge E., Gauthier R. Studies on the dissemination of Salmonella in nine broiler-chicken flocks. Avian Dis. 1982 Jan-Mar;26(1):26–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton M. Salmonella infection in chicks following the consumption of artificially contaminated feed. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Apr;100(2):247–256. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Osterholm M. T., Senger K. A., Cohen M. L. Drug-resistant Salmonella from animals fed antimicrobials. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 6;311(10):617–622. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409063111001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson G. A survey of antibiotic resistance of Escherichia Coli isolated from farm animals in Great Britain from 1971 to 1977. Vet Rec. 1981 Apr 11;108(15):325–328. doi: 10.1136/vr.108.15.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai H., Hashimoto H., Mitsuhashi S. Drug resistance and R plasmids in Escherichia coli strains isolated from broilers. Microbiol Immunol. 1983;27(6):471–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1983.tb00606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Cheung R., Arbus G. S. Sensitive method for detecting low numbers of verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in mixed cultures by use of colony sweeps and polymyxin extraction of verotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):614–619. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.614-619.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Petric M., Lim C., Fleming P. C., Arbus G. S., Lior H. The association between idiopathic hemolytic uremic syndrome and infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1985 May;151(5):775–782. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahellec C., Colin P., Bennejean G., Paquin J., Guillerm A., Debois J. C. Influence of resident Salmonella on contamination of broiler flocks. Poult Sci. 1986 Nov;65(11):2034–2039. doi: 10.3382/ps.0652034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H., Howe K., Bennett P. M., Richmond M. H., Whiteside E. J. The colonization of the human gut by antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli from chickens. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;43(3):465–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. L., Shipman L. D., Wells J. G., Potter M. E., Hedberg K., Wachsmuth I. K., Tauxe R. V., Davis J. P., Arnoldi J., Tilleli J. Isolation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from dairy cattle associated with two cases of haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet. 1986 Nov 1;2(8514):1043–1043. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92656-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarr C., Mitchell W. R., Carlson H. C., Fish N. A. An epidemiological study of Salmonellae in broiler chicken production. Can J Public Health. 1980 Jan-Feb;71(1):47–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Wells J. G. Salmonella contamination in a poultry-processing plant. Appl Microbiol. 1970 May;19(5):795–799. doi: 10.1128/am.19.5.795-799.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray C. J., Ratcliff R. M., Cameron P. A., Dixon S. F. The resistance of antimicrobial agents in salmonella from veterinary sources in Australia from 1975 to 1982. Aust Vet J. 1986 Sep;63(9):286–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1986.tb08068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F., Orskov I., Villar J. A. Cattle as reservoir of verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lancet. 1987 Aug 1;2(8553):276–276. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90860-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Gellner O. S. Intestinal carriage of Campylobacter jejuni and Salmonella by chicken flocks at slaughter. Can J Comp Med. 1984 Jul;48(3):329–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby C. E., Pettit J. R., Bentley A. H., Spencer J. L., Salomons M. O., Lior H. The relationships of salmonellae from infected broiler flocks, transport crates or processing plants to contamination of eviscerated carcases. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):272–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truscott R. B. Oral salmonella antigens for the control of salmonella in chickens. Avian Dis. 1981 Oct-Dec;25(4):810–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


