Abstract
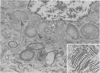
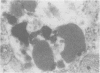
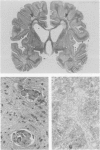
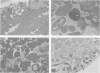
The spectrum of metabolic neuromuscular disorders is wide. Most inherited metabolic diseases are related to enzyme defects within lysosomes but recent advances emphasize abnormalities of mitochondria, peroxisomes and intermediate filaments. In this overview, organelle pathology is described in the context of both the clinical manifestations and the biochemical and/or molecular aspects of the disease. Among the many clinical presentations of mitochondrial disorders three emerge as distinctive entities: mitochondrial encephalopathy with lactic acidosis and stroke-like symptoms, mitochondrial encephalopathy with ragged-red fibers, and Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Peroxisomal disorders are associated with numerous biochemical defects, the most frequent of which are Zellweger's syndrome, neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy, and infantile Refsum's disease. Disorders of cytoskeletal proteins are associated with distinctive pathological accumulation of intermediate filaments but are without confirmed evidence of a biochemical defect. Understanding the role that organelle pathology plays in the pathogenesis of cellular disturbance or demise is essential to the elucidation of the pathogenesis of metabolic disorders.
Full text
PDF



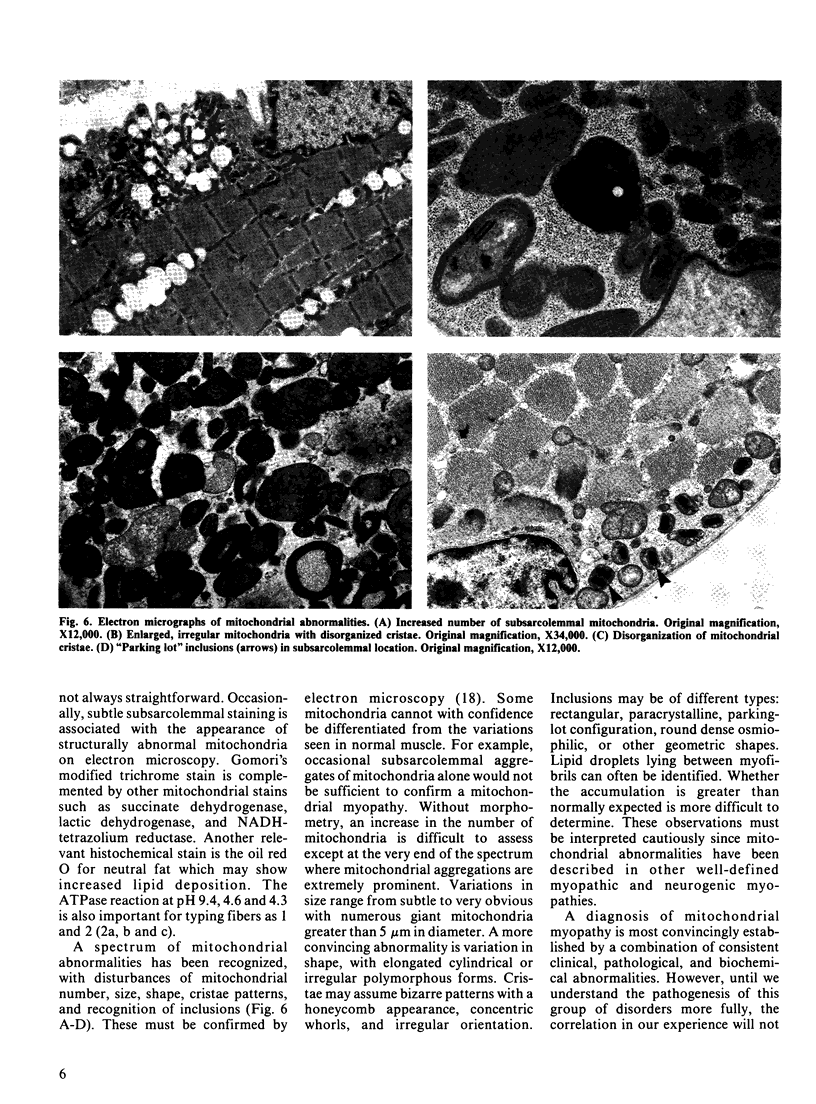





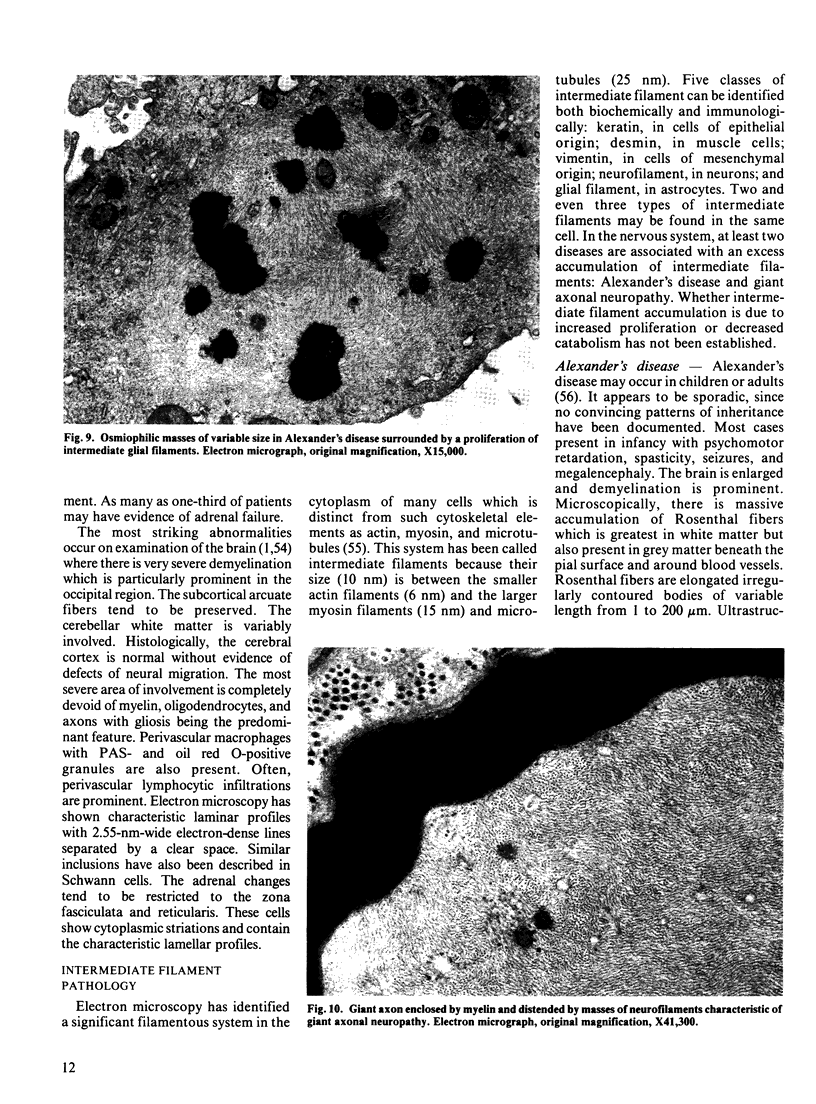


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEU F. P., TERRY R. D., ZELLWEGER H. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF TWO CEREBRAL BIOPSIES IN GARGOYLISM. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1965 Apr;24:304–317. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196504000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agamanolis D. P., Robinson H. B., Jr, Timmons G. D. Cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome. Report of a case with histochemical and ultrastructural observations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1976 May;35(3):226–246. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197605000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubourg P., Robain O., Rocchiccioli F., Dancea S., Scotto J. The cerebro-hepato-renal (Zellweger) syndrome: lamellar lipid profiles in adrenocortical, hepatic mesenchymal, astrocyte cells and increased levels of very long chain fatty acids and phytanic acid in the plasma. J Neurol Sci. 1985 May-Jun;69(1-2):9–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(85)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg B. O., Rosenberg S. H., Asbury A. K. Giant axonal neuropathy. Pediatrics. 1972 Jun;49(6):894–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F. R., 3rd, McAdams A. J., Cummins J. W., Konkol R., Singh I., Moser A. B., Moser H. W. Cerebro-hepato-renal (Zellweger) syndrome and neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy: similarities in phenotype and accumulation of very long chain fatty acids. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1982 Dec;151(6):344–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne E. Biochemical defects in mitochondrial cytopathies: a new classification. Aust Paediatr J. 1988;24 (Suppl 1):58–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne E., Marzuki S., Dennett X. Current perspectives in the study of human mitochondriopathies. Med J Aust. 1988 Jul 4;149(1):30–33. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1988.tb120480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Mitochondrial pathology: an overview. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;488:1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb46544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N. S., Wilson G. N., Hajra A. K. Deficiency of enzymes catalyzing the biosynthesis of glycerol-ether lipids in Zellweger syndrome. A new category of metabolic disease involving the absence of peroxisomes. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 25;311(17):1080–1083. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410253111704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Giustina E., Goffinet A. M., Landrieu P., Lyon G. A Golgi study of the brain malformation in Zellweger's cerebro-hepato-renal disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;55(1):23–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00691526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Mauro S., Trevisan C., Hays A. Disorders of lipid metabolism in muscle. Muscle Nerve. 1980 Sep-Oct;3(5):369–388. doi: 10.1002/mus.880030502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMauro S., Bonilla E., Lee C. P., Schotland D. L., Scarpa A., Conn H., Jr, Chance B. Luft's disease. Further biochemical and ultrastructural studies of skeletal muscle in the second case. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Feb;27(2):217–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMauro S., Bonilla E., Zeviani M., Nakagawa M., DeVivo D. C. Mitochondrial myopathies. Ann Neurol. 1985 Jun;17(6):521–538. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll P. F., Larsen P. D., Gruber A. B. MELAS syndrome involving a mother and two children. Arch Neurol. 1987 Sep;44(9):971–973. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520210065021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGEL W. K., CUNNINGHAM G. G. RAPID EXAMINATION OF MUSCLE TISSUE. AN IMPROVED TRICHROME METHOD FOR FRESH-FROZEN BIOPSY SECTIONS. Neurology. 1963 Nov;13:919–923. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.11.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson B. O., Lindstedt S., Nordin I. Hereditary defect in carnitine membrane transport is expressed in skin fibroblasts. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Aug;147(6):662–663. doi: 10.1007/BF00442488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfischer S., Collins J., Rapin I., Neumann P., Neglia W., Spiro A. J., Ishii T., Roels F., Vamecq J., Van Hoof F. Pseudo-Zellweger syndrome: deficiencies in several peroxisomal oxidative activities. J Pediatr. 1986 Jan;108(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80764-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E., Corbin E. Isolation of a major protein component of Rosenthal fibers. Am J Pathol. 1988 Mar;130(3):569–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govaerts L., Trijbels F., Monnens L., van Raay-Selten A. Pipecolic acid levels in serum and urine from neonates and normal infants: comparison with values reported in Zellweger syndrome. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1985;8(2):87–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01801673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishitsu T., Miike T., Kitano A., Haraguchi Y., Ohtani Y., Matsuda I., Shimoji A., Kimura H. Heterogeneous phenotypes of mitochondrial encephalomyopathy in a single kindred. Neurology. 1987 Dec;37(12):1867–1869. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.12.1867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch T., Schultz P., Williams R., Lampert P. Giant axonal neuropathy: a childhood disorder of microfilaments. Ann Neurol. 1977 May;1(5):438–451. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen A. H., Ronca N. A., Greenfield E. A., Hans M. B. Defective biosynthesis of proteolipid protein in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Ann Neurol. 1987 Feb;21(2):159–170. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT R., IKKOS D., PALMIERI G., ERNSTER L., AFZELIUS B. A case of severe hypermetabolism of nonthyroid origin with a defect in the maintenance of mitochondrial respiratory control: a correlated clinical, biochemical, and morphological study. J Clin Invest. 1962 Sep;41:1776–1804. doi: 10.1172/JCI104637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. E., Peters S. P., Glew R. H. Gaucher's disease: clinical, morphologic, and pathogenetic considerations. Pathol Annu. 1977;12(Pt 2):309–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb H., Tondeur M., Jonniaux G., Mockel-Pohl S., Vamos-Hurwitz E. Biochemical and ultrastructural studies in a case of mucopolysaccharidosis "F" (fucosidosis). Helv Paediatr Acta. 1969 Oct;24(5):519–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson J. I., Pollard A. C., Poulos A., Carter R. F. Infantile Refsum's disease: a peroxisomal storage disorder? Clin Exp Neurol. 1985;21:283–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manz H. J., Schuelein M., McCullough D. C., Kishimoto Y., Eiben R. M. New phenotypic variant of adrenoleukodystrophy. Pathologic, ultrastructural, and biochemical study in two brothers. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Mar;45(2-3):245–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. B. Molecular genetic studies in the neuropsychiatric disorders. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Apr;12(4):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montagna P., Gallassi R., Medori R., Govoni E., Zeviani M., Di Mauro S., Lugaresi E., Andermann F. MELAS syndrome: characteristic migrainous and epileptic features and maternal transmission. Neurology. 1988 May;38(5):751–754. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.5.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser A. E., Singh I., Brown F. R., 3rd, Solish G. I., Kelley R. I., Benke P. J., Moser H. W. The cerebrohepatorenal (Zellweger) syndrome. Increased levels and impaired degradation of very-long-chain fatty acids and their use in prenatal diagnosis. N Engl J Med. 1984 May 3;310(18):1141–1146. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405033101802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. W. New approaches in peroxisomal disorders. Dev Neurosci. 1987;9(1):1–18. doi: 10.1159/000111604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Höcker J., Walther J. U., Bise K., Pongratz D., Hübner G. Mitochondrial myopathy with loosely coupled oxidative phosphorylation in a case of Zellweger syndrome. A cytochemical-ultrastructural study. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1984;45(2):125–138. doi: 10.1007/BF02889859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa T., Tanaka M., Suzuki H., Nishikimi M. Structure and function of mitochondria: their organization and disorders. Brain Dev. 1987;9(2):76–81. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(87)80021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passarge E., McAdams A. J. Cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome. A newly recognized hereditary disorder of multiple congenital defects, including sudanophilic leukodystrophy, cirrhosis of the liver, and polycystic kidneys. J Pediatr. 1967 Nov;71(5):691–702. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. K., Harding A. E., Morgan-Hughes J. A. The clinical features of mitochondrial myopathy. Brain. 1986 Oct;109(Pt 5):915–938. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.5.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos A., Singh H., Paton B., Sharp P., Derwas N. Accumulation and defective beta-oxidation of very long chain fatty acids in Zellweger's syndrome, adrenoleukodystrophy and Refsum's disease variants. Clin Genet. 1986 May;29(5):397–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb00511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers J. M., Tummons R. C., Moser A. B., Moser H. W., Huff D. S., Kelley R. I. Neuronal lipidosis and neuroaxonal dystrophy in cerebro-hepato-renal (Zellweger) syndrome. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;73(4):333–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00688256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing H. S., Hopkins L. C., Wallace D. C., Epstein C. M., Weidenheim K. Maternally inherited mitochondrial myopathy and myoclonic epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1985 Mar;17(3):228–237. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaumburg H. H., Powers J. M., Raine C. S., Suzuki K., Richardson E. P., Jr Adrenoleukodystrophy. A clinical and pathological study of 17 cases. Arch Neurol. 1975 Sep;32(9):577–591. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490510033001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutgens R. B., Heymans H. S., Wanders R. J., van den Bosch H., Tager J. M. Peroxisomal disorders: a newly recognised group of genetic diseases. Eur J Pediatr. 1986 Feb;144(5):430–440. doi: 10.1007/BF00441734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shy G. M., Gonatas N. K., Perez M. Two childhood myopathies with abnormal mitochondria. I. Megaconial myopathy. II. Pleoconial myopathy. Brain. 1966 Mar;89(1):133–158. doi: 10.1093/brain/89.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung J. H., Hayano M., Desnick R. J. Mannosidosis: pathology of the nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1977 Sep-Oct;36(5):807–820. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197709000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY R. D., WEISS M. Studies in Tay-Sachs disease. II. Ultrastructure of the cerebrum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1963 Jan;22:18–55. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196301000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takamiya S., Yanamura W., Capaldi R. A., Kennaway N. G., Bart R., Sengers R. C., Trijbels J. M., Ruitenbeek W. Mitochondrial myopathies involving the respiratory chain: a biochemical analysis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;488:33–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb46546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Miyabayashi S., Nishikimi M., Suzuki H., Shimomura Y., Ito K., Narisawa K., Tada K., Ozawa T. Extensive defects of mitochondrial electron-transfer chain in muscular cytochrome c oxidase deficiency. Pediatr Res. 1988 Oct;24(4):447–454. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198810000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treem W. R., Stanley C. A., Finegold D. N., Hale D. E., Coates P. M. Primary carnitine deficiency due to a failure of carnitine transport in kidney, muscle, and fibroblasts. N Engl J Med. 1988 Nov 17;319(20):1331–1336. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198811173192006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trijbels J. M., Berden J. A., Monnens L. A., Willems J. L., Janssen A. J., Schutgens R. B., van den Broek-Van Essen M. Biochemical studies in the liver and muscle of patients with Zellweger syndrome. Pediatr Res. 1983 Jun;17(6):514–517. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198306000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripp M. E., Katcher M. L., Peters H. A., Gilbert E. F., Arya S., Hodach R. J., Shug A. L. Systemic carnitine deficiency presenting as familial endocardial fibroelastosis: a treatable cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 13;305(7):385–390. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108133050707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vianey-Liaud C., Divry P., Gregersen N., Mathieu M. The inborn errors of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1987;10 (Suppl 1):159–200. doi: 10.1007/BF01812855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J., Adams R. D. Cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome of Zellweger: an inherited disorder of neuronal migration. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;20(3):175–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00686900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C., Singh G., Lott M. T., Hodge J. A., Schurr T. G., Lezza A. M., Elsas L. J., 2nd, Nikoskelainen E. K. Mitochondrial DNA mutation associated with Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1427–1430. doi: 10.1126/science.3201231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C., Zheng X. X., Lott M. T., Shoffner J. M., Hodge J. A., Kelley R. I., Epstein C. M., Hopkins L. C. Familial mitochondrial encephalomyopathy (MERRF): genetic, pathophysiological, and biochemical characterization of a mitochondrial DNA disease. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):601–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90218-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. N., Holmes R. G., Custer J., Lipkowitz J. L., Stover J., Datta N., Hajra A. Zellweger syndrome: diagnostic assays, syndrome delineation, and potential therapy. Am J Med Genet. 1986 May;24(1):69–82. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320240109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]