Abstract
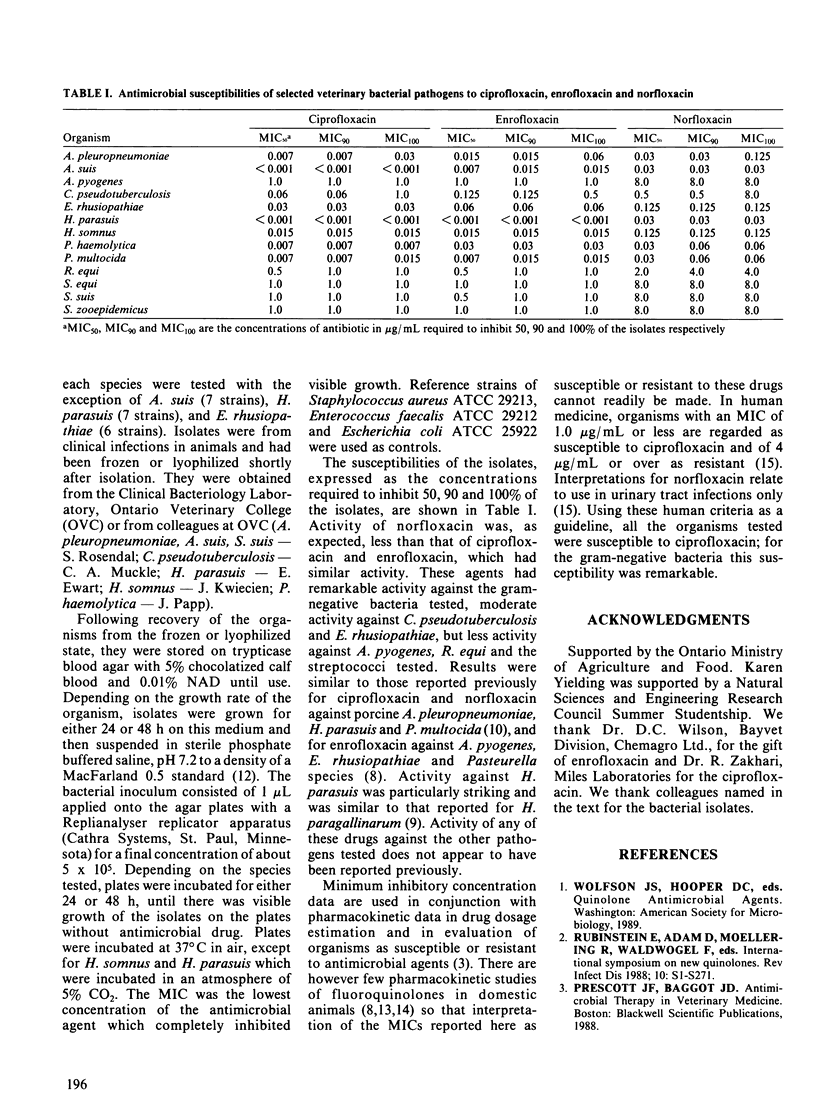
The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin, and norfloxacin were tested for approximately ten clinical isolates of each of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Actinobacillus suis, Actinomyces pyogenes, Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis, Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, Haemophilus parasuis, Haemophilus somnus, Pasteurella haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, Rhodococcus equi, Streptococcus equi, Streptococcus suis and Streptococcus zooepidemicus. Ciprofloxacin and enrofloxacin had similar activity and were more active than norfloxacin. All isolates had an MIC of 1.0 microgram/mL or less for ciprofloxacin and enrofloxacin, and these drugs had particularly marked activity against the gram-negative bacteria tested.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gedek W. Antibakterielle Wirkung von neueren Chinolonen und Nalidixinsäure gegenüber Mastitiserregern vom Rind. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1987 Nov-Dec;94(10):545–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannan P. C., O'Hanlon P. J., Rogers N. H. In vitro evaluation of various quinolone antibacterial agents against veterinary mycoplasmas and porcine respiratory bacterial pathogens. Res Vet Sci. 1989 Mar;46(2):202–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lekeux P., Art T. Effect of enrofloxacin therapy on shipping fever pneumonia in feedlot cattle. Vet Rec. 1988 Aug 20;123(8):205–207. doi: 10.1136/vr.123.8.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer T. M. Clinical pharmacologic features of fluoroquinolone antimicrobial drugs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1988 Sep 1;193(5):577–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouws J. F., Mevius D. J., Vree T. B., Baars A. M., Laurensen J. Pharmacokinetics, renal clearance and metabolism of ciprofloxacin following intravenous and oral administration to calves and pigs. Vet Q. 1988 Jul;10(3):156–163. doi: 10.1080/01652176.1988.9694165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poumarat F., Martel J. L. Antibiosensibilité in vitro des souches françaises de Mycoplasma bovis. Ann Rech Vet. 1989;20(2):145–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. D., Stein G. E., Budsberg S. C., Rosser E. J., Jr, MacDonald K. H. Serum and tissue fluid norfloxacin concentrations after oral administration of the drug to healthy dogs. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jan;50(1):154–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


