Abstract
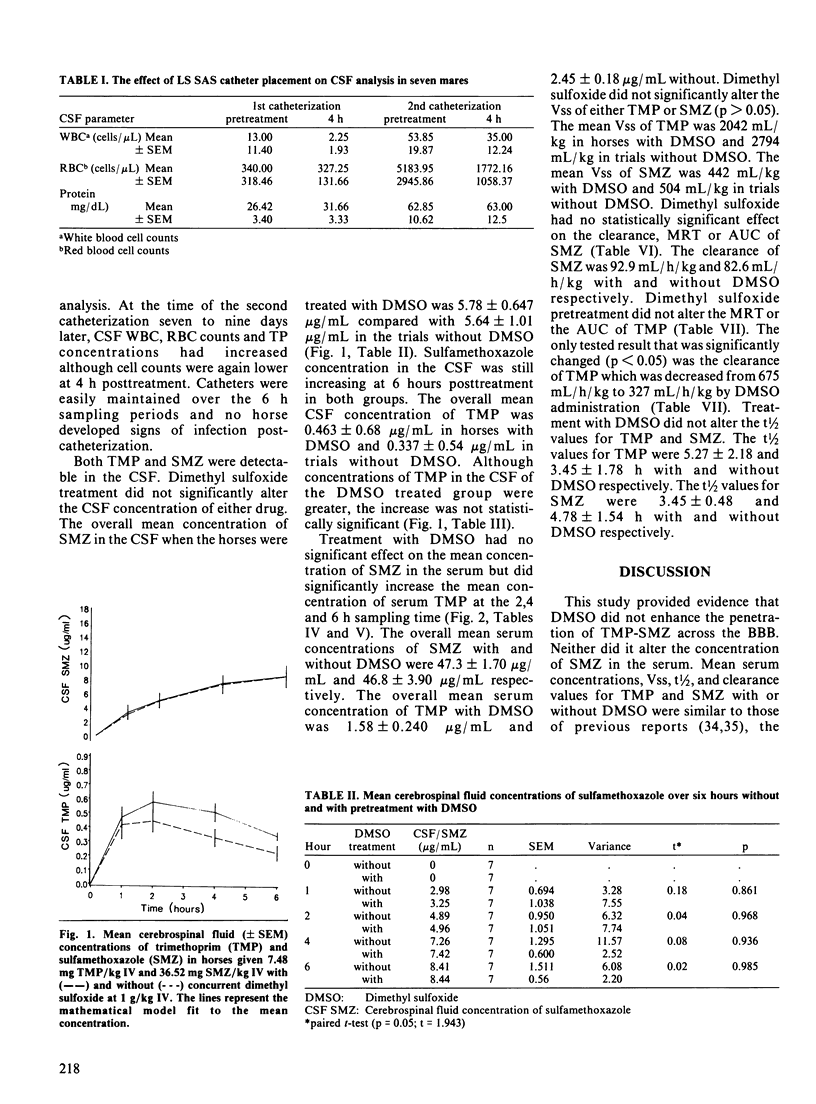
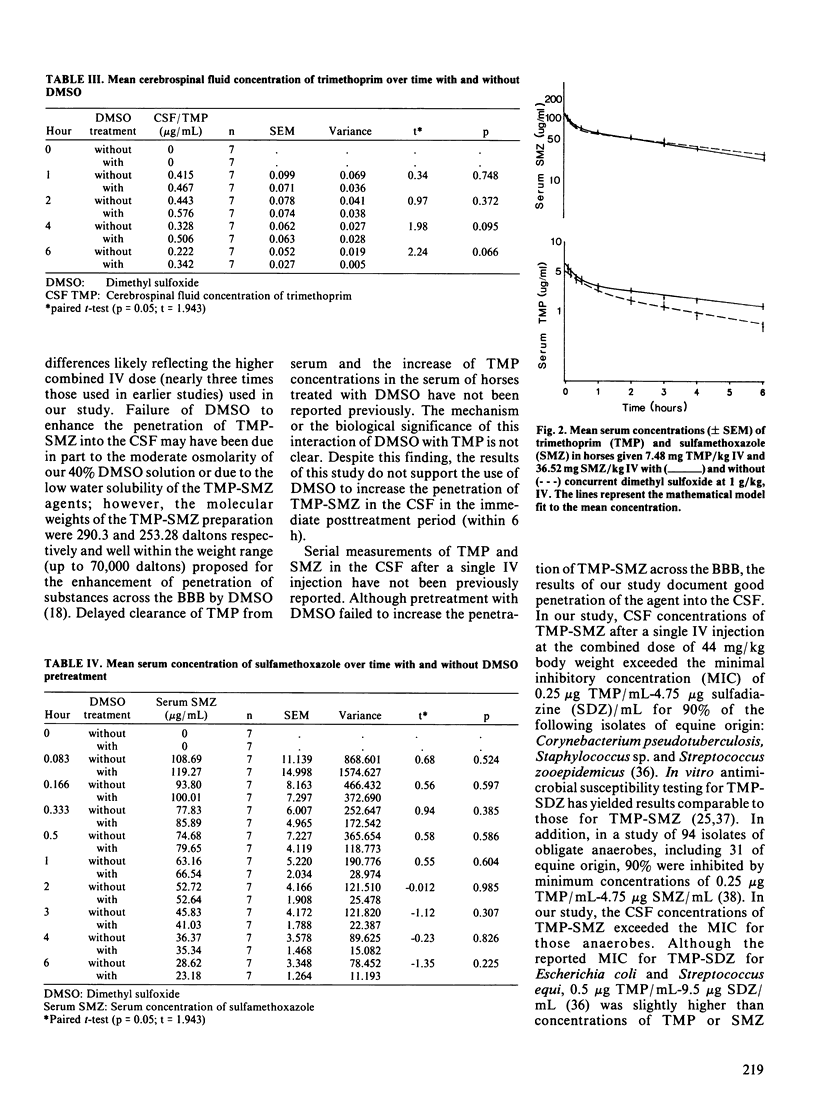
Each of seven mares was given an intravenous (IV) injection of 40% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) at a dosage of 1 g/kg, over 35 min, immediately followed by a single IV injection of a trimethoprim (TMP) and sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) combination (SMZ 83%, TMP 17%) at a combined dosage of 44 mg/kg (7.48 mg/kg TMP; 36.52 mg/kg SMZ). Each horse served as its own control and was alternately treated with an identical dose of TMP-SMZ treatment alone at least seven days following or preceding the DMSO and TMP-SMZ treatment. Serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentrations of TMP and SMZ were measured over a six hour period. Dimethyl sulfoxide treatment caused no significant difference in the mean serum concentration of SMZ or in the mean CSF concentrations of TMP or SMZ. The mean serum concentration of TMP was significantly (p less than 0.05) increased at the two, four and six hour sampling time in the mares receiving pretreatment with DMSO. The clearance of TMP was also significantly (p less than 0.05) decreased from 675 mL/h/kg to 327 mL/h/kg by DMSO administration. Concentrations of TMP and SMZ in the CSF in both treatment groups exceeded the minimum inhibitory concentrations for many common bacterial pathogens of equine origin. In addition, CSF concentration of TMP exceeded the serum concentrations required for 50% inhibition of dihydrofolate reductases of protozoan origin. Serum TMP and SMZ concentration were similar to those reported to be effective against Toxoplasma gondii in in vitro studies on the killing or inhibition of the organism.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson P. J., Wilson W. D., Hirsh D. C., Baggot J. D., Martin L. D. Susceptibility of equine bacterial isolates to antimicrobial agents. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Feb;46(2):447–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alsup E. M., DeBowes R. M. Dimethyl sulfoxide. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Nov 1;185(9):1011–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggot J. D., Prescott J. F. Antimicrobial selection and dosage in the treatment of equine bacterial infections. Equine Vet J. 1987 Mar;19(2):92–96. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-3306.1987.tb02596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barling R. W., Selkon J. B. The penetration of antibiotics into cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1978 May;4(3):203–227. doi: 10.1093/jac/4.3.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett M., Bushby S. R. Trimethoprim and the sulphonamides. Vet Rec. 1970 Jul 11;87(2):43–51. doi: 10.1136/vr.87.2.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayton C. F. Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO): a review. Cornell Vet. 1986 Jan;76(1):61–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. D. Therapeutic strategies involving antimicrobial treatment of the central nervous system in large animals. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Nov 15;185(10):1217–1221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadwell R. D., Salcman M., Kaplan R. S. Morphologic effect of dimethyl sulfoxide on the blood-brain barrier. Science. 1982 Jul 9;217(4555):164–166. doi: 10.1126/science.7089551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. P., Gronwall R., Castro L. Pharmacokinetics and body fluid and endometrial concentrations of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in mares. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Jun;49(6):918–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley M. N., Levitz R. E., Quintiliani R., Hickingbotham J. M., Nightingale C. H. Pharmacokinetics of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of adult patients with normal meninges. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):811–814. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egorin M. J., Kaplan R. S., Salcman M., Aisner J., Colvin M., Wiernik P. H., Bachur N. R. Cyclophosphamide plasma and cerebrospinal fluid kinetics with and without dimethyl sulfoxide. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Jul;32(1):122–128. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferone R., Burchall J. J., Hitchings G. H. Plasmodium berghei dihydrofolate reductase. Isolation, properties, and inhibition by antifolates. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;5(1):49–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. M., Cooper R. C. Continuous caudal epidural anesthesia in the horse. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1984 Apr 15;184(8):971–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig N. H., Sweeney D. J., Rapoport S. I. Inability of dimethyl sulfoxide to increase brain uptake of water-soluble compounds: implications to chemotherapy for brain tumors. Cancer Treat Rep. 1985 Mar;69(3):305–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman P. L., Remington J. S. The effect of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole on Toxoplasma gondii in vitro and in vivo. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979 May;28(3):445–455. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1979.28.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Indiveri M. C., Hirsh D. C. Susceptibility of obligate anaerobes to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1986 Jan 1;188(1):46–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB S. W., BISCHEL M., HERSCHLER R. J. DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE: EFFECTS ON THE PERMEABILITY OF BIOLOGIC MEMBRANES (PRELIMINARY REPORT). Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1964 Mar;6:193–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane D. M., Gray I., Panuska J. A. Ineffectiveness of dimethyl sulfoxide in altering the permeability of the blood-brain barrier. Cryobiology. 1977 Oct;14(5):592–597. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(77)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. W., Griffith R. S., Campbell R. L. Antibiotic penetration of the brain. A comparative study. J Neurosurg. 1969 Sep;31(3):295–302. doi: 10.3171/jns.1969.31.3.0295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz R. E., Quintiliani R. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for bacterial meningitis. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Jun;100(6):881–890. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-6-881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew I. G. Collection of cerebrospinal fluid from the horse. Cornell Vet. 1975 Oct;65(4):500–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew I. G., Greiner E. C. Protozoal diseases. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract. 1986 Aug;2(2):439–459. doi: 10.1016/s0749-0739(17)30726-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew I. G., Whitlock R. H., Tasker J. B. Equine cerebrospinal fluid: reference values of normal horses. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Aug;38(8):1271–1274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuwelt E. A., Barnett P., Barranger J., McCormick C., Pagel M., Frenkel E. Inability of dimethyl sulfoxide and 5-fluorouracil to open the blood-brain barrier. Neurosurgery. 1983 Jan;12(1):29–34. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198301000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuwelt E. A., Frenkel E. P., Diehl J., Vu L. H., Rapoport S., Hill S. Reversible osmotic blood-brain barrier disruption in humans: implications for the chemotherapy of malignant brain tumors. Neurosurgery. 1980 Jul;7(1):44–52. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198007000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuwelt E. A., Frenkel E. P. Is there a therapeutic role for blood-brain barrier disruption? Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):137–139. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuwelt E. A., Pagel M., Barnett P., Glassberg M., Frenkel E. P. Pharmacology and toxicity of intracarotid adriamycin administration following osmotic blood-brain barrier modification. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4466–4470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby R. A review of the penetration of antibiotics into CSF and its clinical significance. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):296–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Oldendorf W. H., Cancilla P., Frank H. J. Blood-brain barrier: interface between internal medicine and the brain. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Jul;105(1):82–95. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-1-82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein E., Lev-El A. The effect of dimethyl sulfoxide on tissue distribution of gentamicin. Experientia. 1980 Jan 15;36(1):92–93. doi: 10.1007/BF02003993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel C. W., Byars T. D., Divers T. J., Murch O., DeAngelis D. Serum concentrations of trimethoprim and sulfadiazine following oral paste administration to the horse. Am J Vet Res. 1981 Nov;42(11):2002–2005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarda R. T., Muir W. W. Continuous caudal epidural and subarachnoid anesthesia in mares: a comparative study. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Dec;44(12):2290–2298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarda R. T., Muir W. W. Segmental thoracolumbar spinal (subarachnoid) analgesia in conscious horses. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Dec;43(12):2121–2128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh K. C., Kwan K. C. A comparison of numerical integrating algorithms by trapezoidal, Lagrange, and spline approximation. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Feb;6(1):79–98. doi: 10.1007/BF01066064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


