Abstract
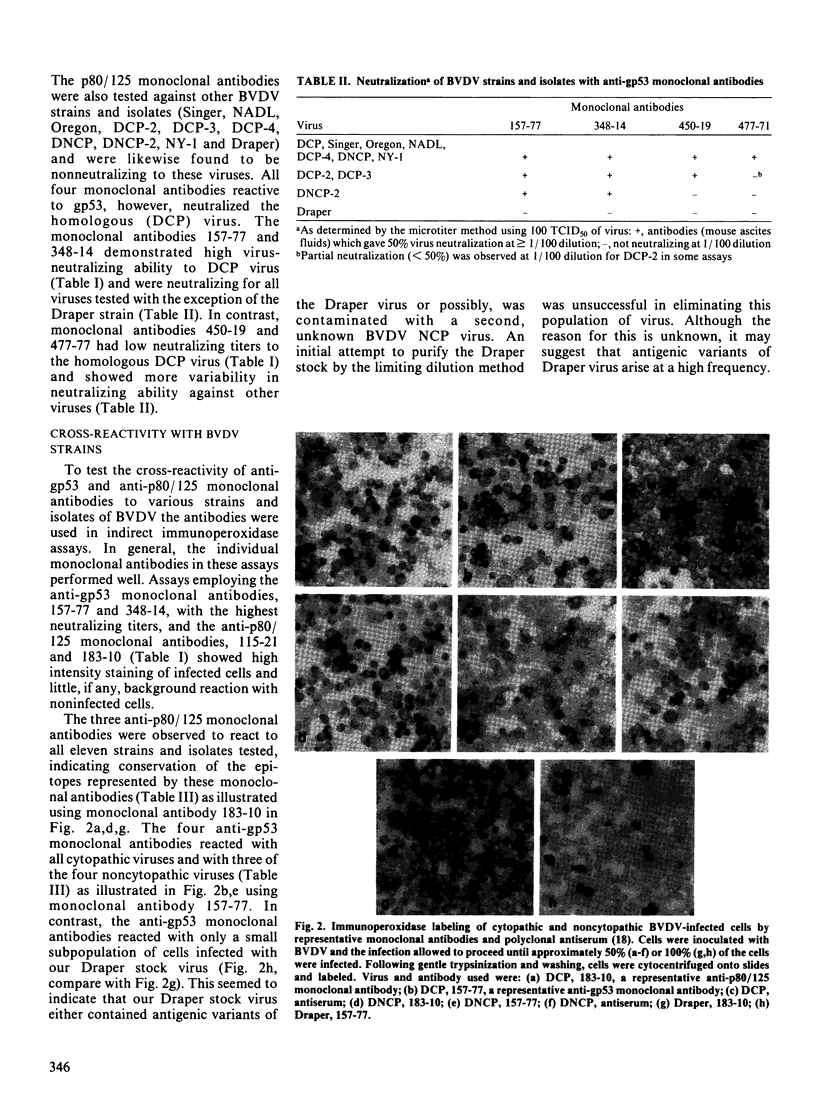
Monoclonal antibodies reactive to the bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) protein gp53 were produced and characterized. These antibodies and our panel of anti-p80/125 monoclonal antibodies were tested for their cross-reactivity with 11 different North American and European (Danish) BVDV strains and isolates including viruses of both cytopathic and noncytopathic biotypes. The four anti-gp53 monoclonal antibodies were neutralizing for the homologous Danish cytopathic isolate and cross-reacted with all BVDV strains examined except for the Draper strain. Further, anti-gp53 monoclonal antibodies neutralized the majority of BVDV strains examined. The anti-p80/125 monoclonal antibodies cross-reacted with all eleven strains and isolates tested. This indicated that various strains of BVDV have common epitopes. The broad cross-reactivities demonstrated by these monoclonal antibodies suggest that a pool of these antibodies may be used for detection of BVDV cellular contamination or for virus isolation, in place of polyclonal antiserum.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. C. Bovine viral diarrhea virus: a review. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1987 Jun 1;190(11):1449–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielefeldt Ohmann H. BVD virus antigens in tissues of persistently viraemic, clinically normal cattle: implications for the pathogenesis of clinically fatal disease. Acta Vet Scand. 1988;29(1):77–84. doi: 10.1186/BF03548395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielefeldt Ohmann H. Double-immunolabeling systems for phenotyping of immune cells harboring bovine viral diarrhea virus. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Jun;35(6):627–633. doi: 10.1177/35.6.3033062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolin S. R., McClurkin A. W., Cutlip R. C., Coria M. F. Response of cattle persistently infected with noncytopathic bovine viral diarrhea virus to vaccination for bovine viral diarrhea and to subsequent challenge exposure with cytopathic bovine viral diarrhea virus. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Dec;46(12):2467–2470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolin S. R., McClurkin A. W., Cutlip R. C., Coria M. F. Severe clinical disease induced in cattle persistently infected with noncytopathic bovine viral diarrhea virus by superinfection with cytopathic bovine viral diarrhea virus. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Mar;46(3):573–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolin S., Moennig V., Kelso Gourley N. E., Ridpath J. Monoclonal antibodies with neutralizing activity segregate isolates of bovine viral diarrhea virus into groups. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1988;99(1-2):117–123. doi: 10.1007/BF01311029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlie J., Clarke M. C., Howard C. J. Experimental production of fatal mucosal disease in cattle. Vet Rec. 1984 Jun 2;114(22):535–536. doi: 10.1136/vr.114.22.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianfriglia M., Armellini D., Massone A., Mariani M. Simple immunization protocol for high frequency production of soluble antigen-specific hybridomas. Hybridoma. 1983;2(4):451–457. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1983.2.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Larson R., Belzer S. K., Retzel E. Proteins encoded by bovine viral diarrhea virus: the genomic organization of a pestivirus. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):200–208. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90673-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Moennig V., Horzinek M. C. Recent advances in pestivirus research. J Gen Virol. 1989 Feb;70(Pt 2):253–266. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corapi W. V., Donis R. O., Dubovi E. J. Monoclonal antibody analyses of cytopathic and noncytopathic viruses from fatal bovine viral diarrhea virus infections. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2823–2827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2823-2827.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deregt D., Babiuk L. A. Monoclonal antibodies to bovine coronavirus: characteristics and topographical mapping of neutralizing epitopes on the E2 and E3 glycoproteins. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):410–420. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90134-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deregt D., Sabara M., Babiuk L. A. Structural proteins of bovine coronavirus and their intracellular processing. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2863–2877. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis R. O., Corapi W., Dubovi E. J. Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to bovine viral diarrhoea virus bind to the 56K to 58K glycoprotein. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):77–86. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Brownlie J., Clarke M. C. Comparison by the neutralisation assay of pairs of non-cytopathogenic and cytopathogenic strains of bovine virus diarrhoea virus isolated from cases of mucosal disease. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Apr;13(4):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. A., Harkness J. W. Viral contamination of foetal bovine serum. Vet Rec. 1975 Jul 5;97(1):16–16. doi: 10.1136/vr.97.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kniazeff A. J., Wopschall L. J., Hopps H. E., Morris C. S. Detection of bovine viruses in fetal bovine serum used in cell culture. In Vitro. 1975 Nov-Dec;11(6):400–403. doi: 10.1007/BF02616377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magar R., Minocha H. C., Lecomte J. Bovine viral diarrhea virus proteins: heterogeneity of cytopathogenic and non-cytopathogenic strains and evidence of a 53K glycoprotein neutralization epitope. Vet Microbiol. 1988 Apr;16(4):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(88)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmann H. B., Jensen M. H., Sørensen K. J., Dalsgaard K. Experimental fetal infection with bovine viral diarrhea virus. I. Virological and serological studies. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Oct;46(4):357–362. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters W., Greiser-Wilke I., Moennig V., Liess B. Preliminary serological characterization of bovine viral diarrhoea virus strains using monoclonal antibodies. Vet Microbiol. 1986 Sep;12(3):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(86)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu M., Satou K., Nishioka N., Yoshino T., Momotani E., Ishikawa Y. Serological characterization of viruses isolated from experimental mucosal disease. Vet Microbiol. 1989 Jan;19(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(89)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland E., Thiel H. J., Hess G., Weiland F. Development of monoclonal neutralizing antibodies against bovine viral diarrhea virus after pretreatment of mice with normal bovine cells and cyclophosphamide. J Virol Methods. 1989 Apr-May;24(1-2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(89)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G., Brinton M. A., Gaidamovich SYa, Horzinek M. C., Igarashi A., Käriäinen L., Lvov D. K., Porterfield J. S., Russell P. K., Trent D. W. Togaviridae. Intervirology. 1985;24(3):125–139. doi: 10.1159/000149632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Babiuk L. A. Synthesis and processing of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoproteins. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):401–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.401-410.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]