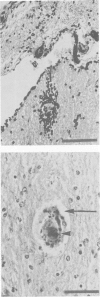
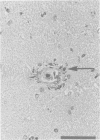
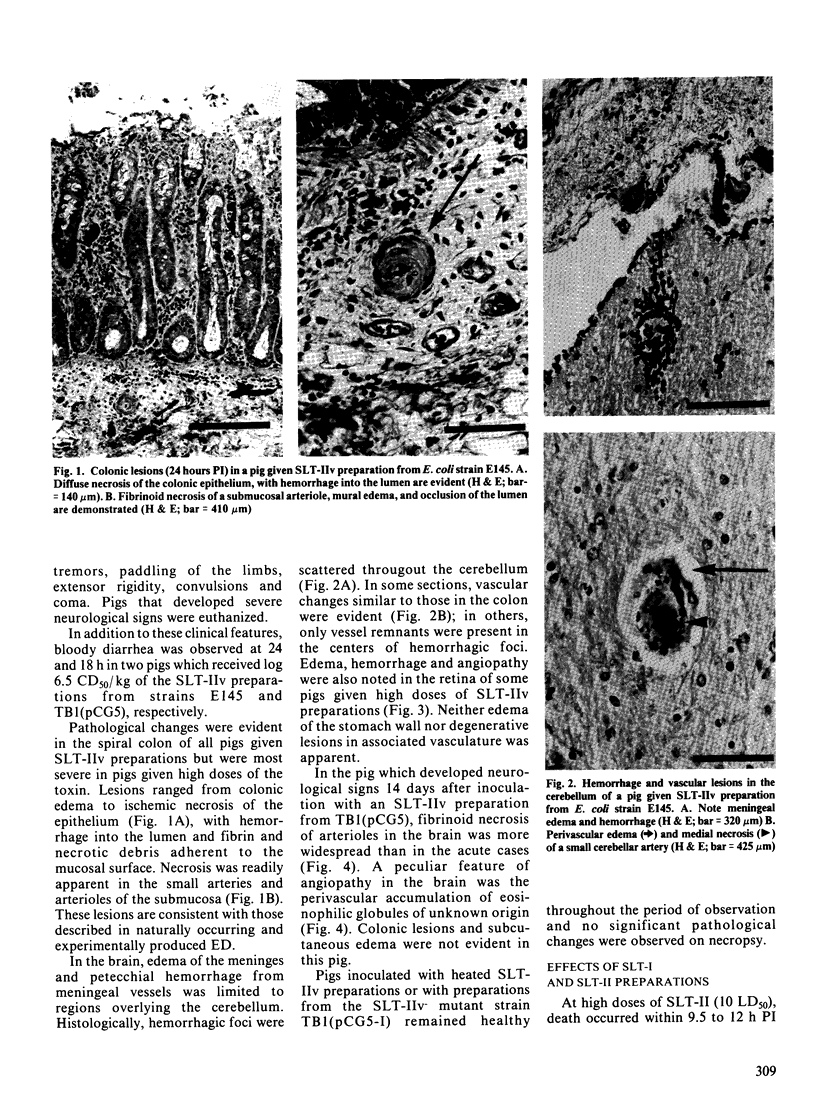
Abstract
Escherichia coli K12 strains TB1(pCG5), with the genes for Shiga-like toxin IIv from an edema disease isolate of E. coli and TB1(pCG5-1), with the toxin genes inactivated by transposon mutagenesis, were used to test the hypothesis that Shiga-like toxin IIv was the same as edema disease principle. Ammonium sulfate precipitated culture supernatants from the pair of E. coli K12 strains and from a wild edema disease isolate of E. coli (E145) were tested for their ability to induce signs and lesions of edema disease in intravenously inoculated weaned pigs. Similar preparations from E. coli which produce Shiga-like toxins I and II were also tested. Preparations from E. coli TB1 (pCG5) and E145 contained high levels of Shiga-like toxin IIv and induced signs and lesions similar to those seen in edema disease, whereas preparations from E. coli TB1 (pCG5-1) failed to induce signs or lesions of edema disease. All Shiga-like toxin preparations produced delayed neurological signs, fibrinoid necrosis of arterioles and hemorrhages in the cerebellum of pigs. High doses of Shiga-like toxin IIv were associated with superficial necrosis of the colonic epithelium and vasculitis. Shiga-like toxins I and II resulted in kidney lesions but no enteric pathology. Shiga-like toxin II preparations had the lowest median lethal dose for pigs, Shiga-like toxin IIv was intermediate and Shiga-like toxin I was the least toxic.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi S., Dinari G., Zevulunov A., Nitzan M. Convulsions in childhood shigellosis. Clinical and laboratory features in 153 children. Am J Dis Child. 1987 Feb;141(2):208–210. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1987.04460020098036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAIN M. C., DACIE J. V., HOURIHANE D. O. Microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia: the possible role of vascular lesions in pathogenesis. Br J Haematol. 1962 Oct;8:358–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1962.tb06541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIDGWATER F. A., MORGAN R. S., ROWSON K. E., WRIGHT G. P. The neurotoxin of Shigella shigae: morphological and functional lesions produced in the central nervous system of rabbits. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Oct;36(5):447–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAGH J. B., HOWARD J. G., WHITBY J. L. The neurotoxin of Shigella shigae; a comparative study of the effects produced in various laboratory animals. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Jun;37(3):272–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clugston R. E., Nielsen N. O. Experimental edema disease of swine (E. coli enterotoxemia). I. Dectection and preparation of an active principle. Can J Comp Med. 1974 Jan;38(1):22–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clugston R. E., Nielsen N. O., Smith D. L. Experimental edema disease of swine (E. coli enterotoxemia). 3. Pathology and pathogenesis. Can J Comp Med. 1974 Jan;38(1):34–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrescu L. New biological effect of edema disease principle (Escherichia coli-neurotoxin) and its use as an in vitro for this toxin. Am J Vet Res. 1983 Jan;44(1):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGORY D. W. Experimental edema disease (hemolytic Escherichia coli toxemia) in pigs and in mice. Am J Vet Res. 1960 Jan;21:88–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon V. P., Gyles C. L., Friendship R. W. Characteristics of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli from pigs. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Jul;52(3):331–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., De Grandis S. A., MacKenzie C., Brunton J. L. Cloning and nucleotide sequence analysis of the genes determining verocytotoxin production in a porcine edema disease isolate of Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1988 Dec;5(6):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H., Bezanson G. S. Cytotoxic Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with haemorrhagic colitis in Canada. Lancet. 1983 Jan 1;1(8314-5):76–76. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91616-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan B. S., Drummond K. N. The hemolytic-uremic syndrome is a syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 27;298(17):964–966. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804272981710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Steele B. T., Petric M., Lim C. Sporadic cases of haemolytic-uraemic syndrome associated with faecal cytotoxin and cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in stools. Lancet. 1983 Mar 19;1(8325):619–620. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keusch G. T., Jacewicz M., Donohue-Rolfe A. Pathogenesis of shigella diarrhea: evidence for an N-linked glycoprotein shigella toxin receptor and receptor modulation by beta-galactosidase. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):238–248. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konowalchuk J., Speirs J. I., Stavric S. Vero response to a cytotoxin of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.775-779.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F., Levin J., Walker L., Tung K. S., Gilman R. H., Rahaman M. M., Majid M. A., Islam S., Williams R. C., Jr Hemolytic-uremic syndrome after shigellosis. Relation to endotoxemia and circulating immune complexes. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 27;298(17):927–933. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804272981702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz H. J., Bergeland M. E., Barnes D. M. Pathologic changes in edema disease of swine. Am J Vet Res. 1969 May;30(5):791–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel A. F., Chabbert Y. A. Taxonomy and epidemiology of gram-negative bacterial plasmids studied by DNA-DNA filter hybridization in formamide. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):269–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheth K. J., Swick H. M., Haworth N. Neurological involvement in hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jan;19(1):90–93. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Green P., Parsell Z. Vero cell toxins in Escherichia coli and related bacteria: transfer by phage and conjugation and toxic action in laboratory animals, chickens and pigs. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3121–3137. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strockbine N. A., Marques L. R., Newland J. W., Smith H. W., Holmes R. K., O'Brien A. D. Two toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain 933 encode antigenically distinct toxins with similar biologic activities. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.135-140.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMLINSON J. R., BUXTON A. Anaphylaxis in pigs and its relationship to the pathogenesis of oedema disease and gastro-enteritis associated with Escherichia coli. Immunology. 1963 Mar;6:126–139. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIMONEY J. F. Oedema disease of swine. Vet Rec. 1950 Dec 9;62(49):748–756. doi: 10.1136/vr.62.49.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J., Lupski J. R. The use of transposon Tn5 mutagenesis in the rapid generation of correlated physical and genetic maps of DNA segments cloned into multicopy plasmids--a review. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]