Abstract
The T-cell receptor (TCR) α locus is thought to undergo multiple cycles of secondary rearrangements that maximize the generation of αβ T cells. Taking advantage of the nucleotide sequence of the human Vα and Jα segments, we undertook a locus-wide analysis of TCRα gene rearrangements in human αβ T-cell clones. In most clones, VαJα rearrangements occurred on both homologous chromosomes and, remarkably, resulted in the use of two neighboring Jα segments. No such interallelic coincidence was found for the position of the two rearranged Vα segments, and there was only a loose correlation between the 5′ or 3′ chromosomal position of the Vα and Jα segments used in a given rearrangement. These observations question the occurrence of extensive rounds of secondary Vα→Jα rearrangements and of a coordinated and polarized usage of the Vα and Jα libraries. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of developing T cells in which TCRα rearrangements are taking place showed that the interallelic positional coincidence in Jα usage cannot be explained by the stable juxtaposition of homologous Jα clusters.
Keywords: DNA recombination/homologous chromosomal pairing/T cell/T-cell receptor/Vα repertoire
Introduction
As T cells develop in the thymus, they undergo site-specific DNA recombination reactions that result in the random recombination of variable (V) and joining (J) gene segments in TCRα genes, and of V, diversity (D) and J gene segments in TCRβ genes. V(D)J joining reactions may result either in productive rearrangements that maintain an open reading frame throughout the gene or in out-of-frame non-functional genes. This process would be expected frequently to generate T-cell clones expressing more than one TCRαβ chain combination. However, the expression of one productively rearranged TCRβ chain gene prevents further V→DJ rearrangements (Uematsu et al., 1988), suggesting the existence of a feedback inhibition mechanism, referred to as allelic exclusion, to ensure that most mature T-cell clones express one, and only one, TCRβ chain. The configuration of the TCRβ alleles in mature T cells further suggested that TCRβ genes follow a ‘regulated’ model of allelic exclusion similar to that proposed for immunoglobulin (Ig) genes (Alt et al., 1992). According to this model, TCRβ genes are first rearranged only on one allele and tested for the production of a TCRβ polypeptide before a cycle of V→DJ recombination is attempted on the second TCRβ allele. The TCRβ polypeptides resulting from productive rearrangements participate in the assembly of a molecular sensor, known as the pre-TCR, and thereby trigger not only allelic exclusion but also the progression to the CD4+CD8+ double-positive (DP) stage and the initiation of TCRα gene rearrangements (reviewed in von Boehmer et al., 1999). To be rescued from programmed cell death and to differentiate into CD4 or CD8 single-positive cells, DP thymocytes rely on a selection process that occurs only if their αβ TCR binds with low affinity to self-peptide– major histocompatibility complex (MHC) complexes expressed in the thymus. The antigenic specificity of a given T-cell clone is fixed by the irreversible shut-down of the V(D)J recombinase associated with this selection. It has been suggested, mostly on the basis of indirect evidence (reviewed in Malissen and Malissen, 1995), that a given TCRα locus undergoes multiple rounds of secondary rearrangements (i.e. Vα→Jα rearrangements involving Vα located 5′ and Jα located 3′ to the primary VαJα rearrangement) that permit the specificity of the complementarity-determining regions of a pre-existing TCRβ chain to be ‘assayed’ successively in the context of several distinct TCRα chains.
Most mouse peripheral αβ T cells carry VαJα rearrangements on both alleles, and a sizeable fraction of them (∼25%) show V–J junctions that had maintained a proper translational reading frame on both alleles (reviewed in Malissen et al., 1992). In studies comparing the chromosomal positions of the two Jα gene segments that are rearranged in most mature αβ T cell clones (one in each allelic Jα cluster), it was found that they tend to be contiguous within the 60 kb long Jα cluster (Hue et al., 1990; Rytkonen et al., 1994). This finding was inconsistent with the idea that simultaneous accessibility of the entire Jα cluster to the V(D)J recombinase would yield a random distribution of the two rearranged Jα segments. Several models have been put forward to account for the coincidence observed between the chromosomal location of the two rearranged Jα segments. The most prevalent, denoted as the ‘bi-directional and coordinated nibbling’ model, takes into account the fact that both TCRα alleles plausibly undergo multiple rounds of secondary rearrangements and confer a unique status to T early α (TEA), a cis-regulatory element located 5′ of the Jα cluster (Villey et al., 1996), in making it a primary ‘entry site’ for the V(D)J recombinase. According to this model, when a DP cell acquires the competence to rearrange its two TCRα alleles simultaneously, VαJα rearrangements always start at the 5′-most, TEA-controlled, Jα segments. In the event that one of the two primary rearrangements is not fixed by TCRαβ selection, successive secondary VαJα rearrangements proceed coordinately via small steps on both homologs. This results in the progressive and parallel utilization of both allelic Jα clusters until either the recombination process is halted via TCRαβ selection or the cell dies via programmed cell death (Petrie et al., 1993). The two rearranged Jα segments that are genetically fixed at the time of TCRαβ selection therefore tend to occupy a similar location within each Jα cluster. As a corollary, the postulated 5′ to 3′ polarized utilization of the Jα library may be coordinated with a 3′ to 5′ polarized utilization of the library of Vα gene segments. This ‘bi-directional and coordinated nibbling’ model, which is reminiscent of the associative DNA tracking model proposed for Ig genes (Wood and Tonegawa, 1983), should result in the preferential rearrangement of 3′-most Vα to 5′-most Jα and of 5′-most Vα to 3′-most Jα, and prevent the premature exhaustion of either gene segment library (Roth et al., 1991; Rytkonen et al., 1996; Jouvin-Marche et al., 1998; Huang and Kanagawa, 2001).
However, this model is based mainly on early studies which can be criticized on the following grounds. First, they involved the analysis of VαJα rearrangements of only a limited number of T-cell clones. Secondly, the location of the VαJα rearrangements affecting the TCRα locus was determined mostly via Southern blot analysis and therefore only reached a low degree of resolution (Rytkonen et al., 1996). Thirdly, these analyses were limited to mouse and it was therefore difficult to assess their generality. The data reported here address the above criticisms and constitute the most comprehensive analysis to date of TCRα gene rearrangement patterns in functional human and mouse αβ T-cell clones. The construction of this large database benefited from the availability of the complete human and mouse Jα cluster nucleotide sequences (Koop and Hood, 1994), and relied on PCR analysis to determine the configuration of rearranged TCRα alleles. Moreover, the availability of the human Vα cluster nucleotide sequence (Boysen et al., 1997) allowed us to determine whether any coincidence also exists in the chromosomal location of the rearranged Vα genes on both alleles of human αβ T cells, and to test whether Vα and Jα segments are used in an ordered and coordinated manner.
Results
Co-location of the Jα gene segments used on both alleles of mouse and human T cells
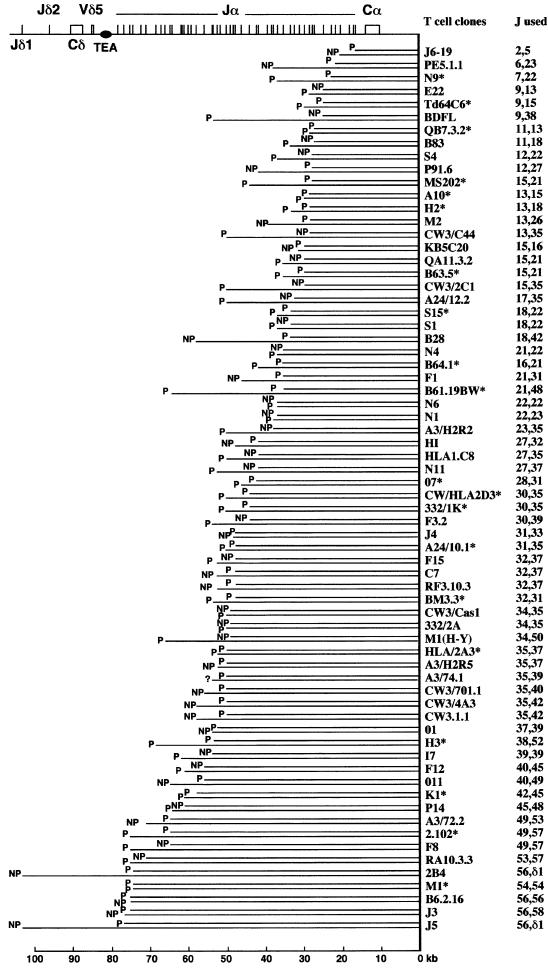
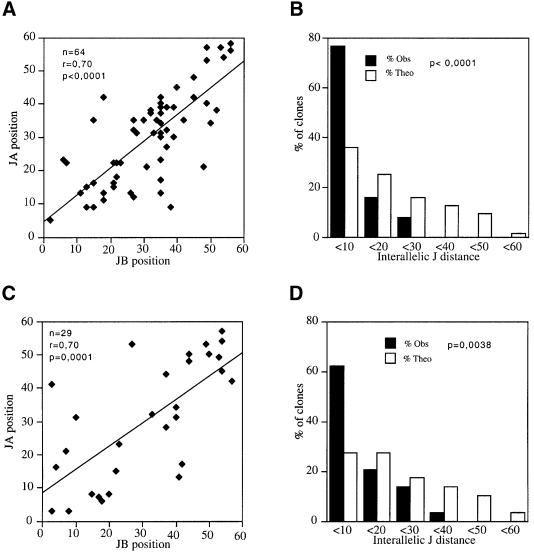
Figure 1 depicts the rearrangement status of both TCRα alleles in a set of 68 functional mouse T-cell clones and hybridomas (see Materials and methods). Several conclusions can be drawn from the analysis of this database. First, in most T cells, both α alleles have undergone Vα–Jα joining events. Only two T-cell clones (2B4 and J5) out of 68 have kept one Jα cluster in germline configuration, and in both instances this feature was associated with the presence on that allele of a non-productive VδDδJδ rearrangement. The single (productive) VαJα rearrangement found in both 2B4 and J5 T-cell clones involved one of the 5′-most Jα gene segments. Secondly, the 124 recombined Jα gene segments contained in the database are evenly distributed over the entire Jα cluster: in particular, there is no apparent recombination hot-spot and no under-representation in the usage of some Jα segments. Thirdly, when both homologs have undergone a VαJα recombination event, the two recombined Jα segments tend to occupy contiguous positions within the Jα cluster. This coincidence existing in interallelic Jα usage could be substantiated by (i) linear regression analysis (Figure 2A) and (ii) comparing the actual distribution of the distances existing between the two recombined Jα alleles in each of the 68 T-cell clones (a parameter denoted as the ‘interallelic distance’, see Figure 2) with the theoretical distribution of the interallelic distances that should take place if the two entire Jα clusters open at once and a random usage of the Jα segments occurs (Figure 2B).
Fig. 1. Analysis of the location of the Jα gene segments that are rearranged on both alleles of 68 functional mouse T cell clones and hybridomas. The genomic organization of the 3′ end of the mouse TCRα/δ locus is shown at the top. Constant (C) genes and the Vδ5 gene segment are shown as boxes. J gene segments are represented by vertical lines, and numbered 1–61, moving 3′ to 5′ along the Jα cluster (Koop and Hood, 1994). Also shown is the position of TEA, a cis-acting regulatory element thought to control the polarized utilization of the Jα cluster. The Vα library, not shown in the figure, is ∼1 Mb in length and located at the 5′ end of the TCRα/δ locus. The name of each T cell is indicated on the right, together with the number designating the Jα gene segment it used on each of its alleles. The productive (P) or non-productive (NP) status (when known) of each VαJα rearrangement is indicated on the left. In 19 T-cell clones (labeled with an asterisk), both α alleles are rearranged productively. The T-cell clones have been ordered according to the chromosomal position of their 3′-most Jα rearrangement.
Fig. 2. Coincidental Jα usage at both TCRα alleles of mouse and human T-cell clones. (A) Linear regression analysis of the position of the Jα segment rearranged on each of the two alleles (denoted A and B) of a given T-cell clone. The numbering of the Jα positions is as indicated in Figure 1. (B) The difference in the ranks of the two allelic Jα segments recombined in a given clone (denoted as the ‘interallelic distance’) may take any discrete values between 0 (if the two allelic VαJα rearrangements involve the same Jα gene segment) and 60 (if the 5′- and 3′-most Jα gene segments have been rearranged in a given clone). The values corresponding to the panel of 68 mouse T-cell clones reported in Figure 1 have been categorized in the six classes shown in the histogram. This actual distribution is compared with the theoretical one that should occur if the two entire Jα clusters open at once and there is a random utilization of the Jα segments by the V(D)J recombinase. (C) Linear regression analysis of the positions of the Jα segments that are rearranged on both alleles of a panel of 29 human T-cell clones. (D) Comparison of the distribution of the interallelic distance existing beetween the two Jα segments that are rearranged within each human T-cell clone to the theoretical distribution that should occur if there was a random utilization of the two Jα libraries.
To test the generality of these observations, we undertook a similar analysis of the VαJα rearrangements found in human αβ T-cell clones. In line with the data obtained in the mouse, analysis of a small panel of 29 T-cell clones (Table I) using a multiplex PCR approach (Couedel et al., 1999) indicated that each clone had undergone VαJα rearrangements on both alleles. Subsequent screening of a set of 250 αβ T-cell clones derived from lectin-stimulated peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) indicated that only five had kept one chromosomal copy of the TCRδ locus (data not shown), giving rise to a frequency in close agreement with that observed for mouse αβ T-cell clones (i.e. 2/68, see Figure 1). Reminiscent of the mouse data, the single VαJα rearrangement occurring in each of these rare clones involved a 5′ Jα, while the allele with a Jα cluster remaining in germline configuration carried either a partial DδJδ or a complete VδDδJδ TCRδ rearrangement (Table II). Particularly relevant to the data discussed below and as previously noted in the mouse, the two allelically rearranged Jα segments were co-located in most human T-cell clones. This was demonstrated both by the strong linear correlation existing between their chromosomal positions (Figure 2C) and by the non-random distribution of their interallelic distances (Figure 2D). Finally, the mean distance separating both rearranged Jα gene segments in each human T cells was very close to that observed in mouse T cells (mean values of 10.1 ± 9.4 Jα and 7.1 ± 6.7 Jα, respectively).
Table I. Listing of human peripheral T-cell clones whose VαJα rearrangements have been characterized on both alleles.
| Clone | Allele a |
Allele b |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCR Vα | TCR Vα rank | TCR Jα | Status | TCR Vα | TCR Vα rank | TCR Jα | Status | |
| Asm8.19 | 19S1 | 29 | 57 | + | 29S1 | 41 | 42 | – |
| 1.10 | 19S1 | 29 | 54 | + | 26S2 | 46 | 45 | + |
| 14.7 | 14S1 | 21 | 54 | + | 9S2 | 22 | 54 | + |
| A5.23 | 26S1 | 37 | 54 | – | 36S1 | 49 | 57 | + |
| A22.28 | 16S1 | 26 | 53 | – | 101S1 | 34 | 27 | + |
| A22.18 | 9S2 | 22 | 53 | + | 26S1 | 37 | 49 | – |
| 4V12 | 16S1 | 26 | 53 | – | 17S1 | 27 | 49 | + |
| D25.12 | 12S1 | 13 | 50 | + | 38S2 | 52 | 44 | + |
| Asm8.20 | 25S1 | 36 | 50 | – | 35S1 | 48 | 50 | + |
| 2.4 | 13S1 | 16 | 44 | + | 14S1 | 21 | 48 | + |
| D25.13 | 25S1 | 35 | 41 | + | 38S2 | 52 | 13 | – |
| Asm8.18 | 4S1 | 5 | 40 | – | 101S1 | 34 | 31 | + |
| DP1 | 4S1 | 5 | 40 | – | 23S1 | 33 | 34 | + |
| A13.6 | 13S2 | 20 | 37 | – | 35S1 | 48 | 44 | + |
| 17.12 | 10S1 | 11 | 32 | – | 9S2 | 22 | 33 | + |
| 2IV9 | 20S1 | 30 | 31 | + | 29S1 | 41 | 10 | + |
| 22.15 | 20S1 | 30 | 28 | + | 22S1 | 32 | 37 | – |
| A22.19 | 22S1 | 32 | 23 | + | 36S1 | 49 | 23 | + |
| 2.22 | 1S2 | 2 | 21 | + | 14S1 | 21 | 7 | – |
| DN25.5 | 10S1 | 11 | 18 | + | 16S1 | 26 | 6 | – |
| 1.9 | 19S1 | 29 | 17 | + | 23S1 | 33 | 7 | + |
| TM15 | 21S1 | 31 | 17 | + | 38S2 | 52 | 42 | + |
| 2.2 | 2S1 | 3 | 16 | + | 13S1 | 16 | 4 | – |
| DP3 | 9S2 | 22 | 15 | + | 16S1 | 26 | 22 | – |
| 2.15 | 1S1 | 1 | 8 | + | 6S1 | 7 | 3 | – |
| D25.10 | 6S1 | 7 | 8 | + | 8S6 | 25 | 15 | + |
| 19.15 | 19S1 | 29 | 8 | + | 23S1 | 33 | 20 | – |
| D25.20 | 6S1 | 7 | 3 | – | 13S1 | 16 | 3 | + |
| D25.1 | 13S1 | 16 | 3 | + | 26S1 | 37 | 41 | + |
The nomenclature and relative chromosomal position of the Vα are as indicated in Boysen et al. (1997). The Jα nomenclature is as indicated in Koop et al. (1994). The productive (+) and non-productive (–) status of each VαJα rearrangement is indicated.
Table II. Status of the single rearranged TCRα allele found in the rare human αβ T-cell clones that have kept one Jα cluster in germline configuration.
| Clone | Allele a |
Allele b |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCR Vα | TCR Vα rank | TCR Jα | TCRδ configuration | |
| 4VII13 | 35S1 | 48 | 31 | Dδ Jδ |
| 4I15 | 12S2 | 17 | 44 | VδDδJδ |
| 4I4 | 30S1 | 42 | 52 | VδDδJδ |
| 4V17 | 26S1 | 37 | 39 | DδJδ |
| 4VIII2 | 26S2 | 46 | 45 | VδDδJδ |
See legend of Figure 3 for the nomenclature and numbering of Vα and Jα segments. The allele with a Jα cluster kept in germline configuration is denoted arbitrarily as allele b, and carried a TCRδ locus with either a partial DδJδ or a complete VδDδJδ configuration.
Usage of human Vα does not show a tight interallelic positional coincidence
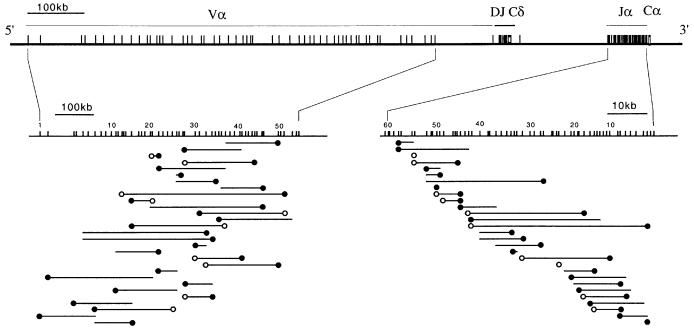
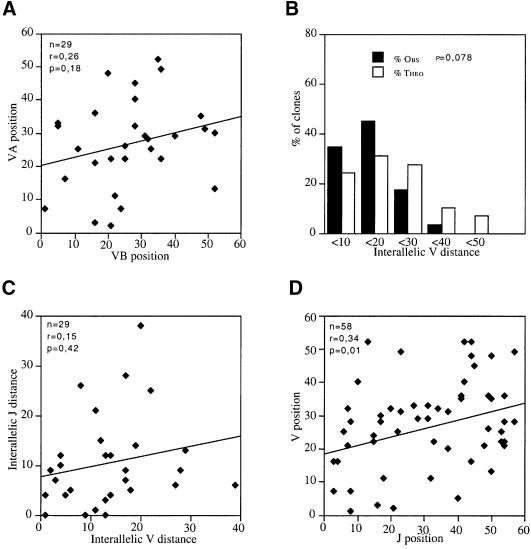
The symmetrical usage of the Vα and Jα libraries postulated by the ‘bi-directional and coordinated nibbling’ model (see Introduction) should result in the existence of a tight correlation (i) between the chromosomal positions of the Vα and Jα segments that are rearranged on a given allele and (ii) between the interallelic distances separating the two Vα segments and the two Jα segments that are found rearranged in a given T-cell clone. Furthermore, provided they derive from DP cells that experienced TCRαβ selection after a single or a few early Vα→Jα rearrangement attempts, the rare αβ T cells containing a single VαJα rearrangement should have recombined exclusively 3′-most Vα and 5′-most Jα gene segments. The complexity of the mouse Vα locus is such that members of a given Vα subfamily are not grouped in discrete units along the chromosome but are largely interspersed with members of other subfamilies (Jouvin-Marche et al., 1990). This does not facilitate the precise chromosomal localization of the Vα segments that have been fixed at the time of positive selection. Considering that the human Vα locus presents a simpler organization (Figure 3), we subsequently focused on human T cells and determined whether both rearranged Vα segments in a given T cell belong to the same section of the Vα locus. Analysis of the VαJα rearrangements on both alleles of 29 human αβ T-cell clones (Figure 3) showed that (i) there was no correlation between the positions of the two rearranged allelic Vα segments (Figure 4A) and (ii) that the observed interallelic Vα distances did not differ significantly from a random distribution (Figure 4B). Moreover, the interallelic distances of the two Vα and two Jα segments rearranged in each T-cell clone were not correlated (Figure 4C). Taken together, this analysis indicates that the coincidence previously noted in the chromosomal location of the two Jα segments rearranged in a given T cell does not extend symmetrically to the usage of the two Vα partners. Consistent with the above observations, the 5′ Jα used by the rare T-cell clones that have kept one Jα cluster in germline configuration were found rearranged with Vα gene segments that are not located exclusively in the 3′ end of the Vα library (Table II).
Fig. 3. Mapping of the Vα and Jα segments used on both alleles of 29 human T-cell clones. The two VαJα rearrangements that occurred in each T cell (one on each allele) are depicted by two lines whose ends correspond to the location of the two rearranged Vα (left line) and of the two rearranged Jα segments (right line) (see Table I for a listing of the corresponding VαJα rearrangements). For clones carrying a single productive VαJα rearrangement, the Vα and Jα segments accounting for the productive rearrangement are marked by a closed circle. In the case of clones with two productive VαJα rearrangements, open and closed circles allow the VαJα combination used by each of them to be specified. T-cell clones were ranked according to the chromosomal position of their 5′-most Jα rearrangement. In 10 T-cell clones, both α alleles are rearranged productively. The relative position and numbering of the Vα and Jα gene segments are as described by Boysen et al. (1997) and Koop et al. (1994) for the Vα and Jα libraries, respectively. The Jα segments are numbered 1–61, moving 3′ to 5′, whereas Vα segments are numbered 1–58, moving 5′ to 3′ along the Vα library. Note that the Vα and Jα libraries are not represented at the same scale.
Fig. 4. Vα usage at both TCRα alleles of 29 human αβ T-cell clones. (A) Linear regression analysis of the positions of the Vα segments that are rearranged on both alleles (denoted A and B) of a panel of 29 human T-cell clones. (B) Comparison of the distribution of the interallelic distance existing between the two Vα segments that are rearranged within each T-cell clone with the theoretical distribution that should occur if there was a random utilization of the two Vα libraries. (C) Linear regression analysis of the interallelic Vα and Jα distances observed in each of the 29 human T-cell clones. (D) Linear regression analysis of the position of the Vα and Jα segments that are used by each of the 58 alleles probed in the panel of 29 T-cell clones. The position and numbering of the human Vα and Jα segments are as described in the legend of Figure 3.
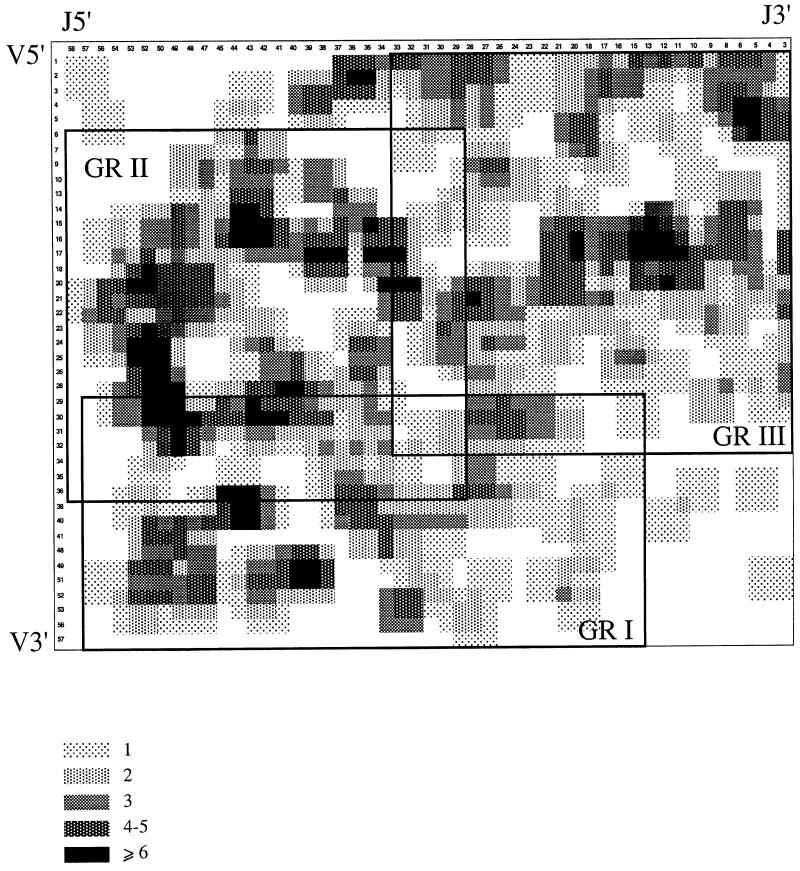
Considering that the VαJα gene sample probed by our first panel of T-cell clones is rather small when compared with the large number of potential VαJα combinations, we further analyzed a second panel of 394 independent human VαJα rearrangements derived from published TCRα sequences and from our laboratory. This last set of VαJα combinations was subjected to correspondence analysis (see Materials and methods), and the results plotted onto a bi-dimensional matrix (Figure 5). Both the upper left and the lower right corners of the matrix are almost empty, an attribute that corresponds to the paucity of rearrangements involving 5′-most Vα with 5′-most Jα, and 3′-most Vα with 3′-most Jα, respectively. Further statistical analysis unequivocally identified three subsets of preferential VαJα rearrangements. The first subset (GRI, n = 90) is centered on the Vα44 and Jα36 segments, and encompasses Vα29–Vα57 and Jα57–Jα16. It roughly corresponds to rearrangements involving Jα elements located in the 5′ half and the mid-section of the Jα cluster with Vα elements located in the 3′ half of the Vα library. The second subset (GRII, n = 155) is centered on the Vα21 and Jα44 segments and encompasses Vα5–Vα45 and Jα58–Jα29. This subset overlaps with GRI, and involves 5′ Jα elements and Vα elements that are widely distributed over the whole Vα library. The third subset (GRIII, n = 149) is centered on the Vα14 and Jα16 segments and encompasses Vα1–Vα32 and Jα33–Jα1. It corresponds to rearrangements involving Jα segments located in the 3′ half of the Jα cluster and Vα segments located in the 5′ half of the Vα library. Finally, this panel of 394 human VαJα rearrangements also shows that there is no under-representation in the utilization of the 5′-most Vα segments and of the 3′-most Jα segments (Figure 6). Therefore, these results do not support the fine-tuned utilization of Vα and Jα libraries postulated by the ‘bi-directional and coordinated nibbling’ model. However, Figures 4D and 5 both suggest that there still exists a loose correlation between the chromosomal position of the Vα and Jα elements that are found rearranged on a given allele.
Fig. 5. Representation of the contingency table (Vα versus Jα positions) of 394 human VαJα rearrangements and positioning of the groups of preferential rearrangements as defined by correspondence analysis (CA). The x-axis corresponds to the positions of functional Jα elements, moving from 5′ to 3′, whereas the y-axis corresponds to the positions of functional Vα elements moving from 5′ to 3′. Given the small size of the sample (n = 394) compared with the large number of VαJα rearrangement modalities (n = 1960), we used for graphical representation a moving average to smooth the results. Groups of preferential rearrangements defined by CA are represented by rectangles centered on the mean position of the Vα and Jα elements defining the group. The sides of the rectangle correspond to the confidence intervals for the Vα and Jα positions. For group I: n = 90, J mean = 36.9 (confidence interval: 16.1–57.8), V mean = 44.5 (28.6–60.3); for group II: n = 155, J mean = 44.2 (29.3–59.4), V mean = 20.9 (4.9–36.8); and for group III: n = 149, J mean = 16.2 (0–33.5), V mean = 14.5 (0–32.9).
The homologous Jα clusters are not paired in DP thymocytes
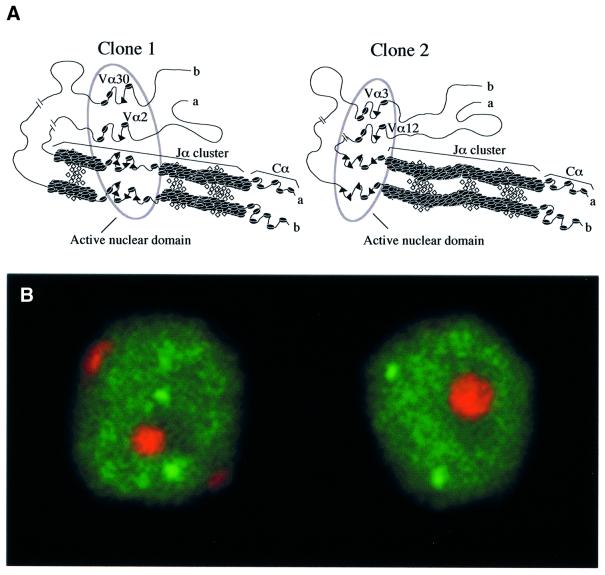
One possible mechanism for the coincident usage of the two homologous Jα clusters may be their physical linkage at the time of TCRα gene rearrangement. In Drosophila, pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs in somatic cells and is responsible for trans-sensing effects, where the status of one allele affects the other, homologous allele (reviewed in Henikoff and Comai, 1998). Trans-sensing-like effects have also been described in mammalian cells (Ashe et al., 1997). The ‘trans-sensing’ model shown in Figure 7A suggests that following pairing of the two homologous TCRα loci, the same, randomly chosen section of the two Jα clusters may be co-localized to a dedicated subnuclear compartment and coordinately made available to the V(D)J recombinase. To test this possibility, sorted DP thymocytes were subjected to fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis using cosmid or bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clones covering the 3′ portion of the TCRα locus and methods previously shown to preserve nuclear structure and organization (see Materials and methods). As shown in Figure 7B, and summarized in Table III, the two TCRα alleles were clearly separated from each other in the great majority of DP thymocytes. Similar results were obtained using DP thymocytes isolated from wild-type adult mice (Experiment 1 in Table III), and from MHC class I/MHC class II doubly deficient mice at embryonic day 17 (Experiment 2 in Table III). The latter mice were used to ensure that most DP cells are actively rearranging their TCRα locus and are not inhibited via MHC ligation of their TCR (Merkenschlager et al., 1997). Furthermore, when subjected to the same FISH analysis, DN and lymph node T cells that do not rearrange their TCRα genes showed patterns of TCRα hybridization that are comparable with DP thymocytes. These data argue strongly against a model in which the interallelic coincidence of Jα usage is achieved via the stable juxtaposition of the homologous Jα clusters.
Fig. 7. The interallelic positional coincidence noted in Jα usage is not due to the pairing of the two homologous Jα clusters. (A) A ‘trans-sensing’ model accounting for coincident substrate choice at both Jα alleles. In each of the two depicted clones, following homologous pairing of the chromosomal segment harboring the Jα clusters, a randomly chosen section of the paired Jα clusters that approximates 10 Jα segments (a value that corresponds to the mean interallelic Jα distance observed in mouse and human T cells, see Results) become accessible to the V(D)J recombinase. A similar repositioning process may occur simultaneously at the level of the Vα libraries. However, the plausible presence of repeated sequences and/or the high degree of homology existing between the Vα segments may lead to misalignment in the pairing of the Vα libraries and account for the loose coincidence noticed in the position of the two allelic Vα segments that are rearranged in most T cells. Two independent synaptic complexes are present within the active nuclear domain, allowing the recombination to proceed between recombination signal sequences (shown as a triangle) located on the same allele and via a deletional mechanism. The open diamonds are intended to depict the putative proteins involved in the pairing of the homologous chromosomal segments. (B) Confocal image showing the position of the TCRα genes (green) relative to each other and to γ-satellite sequences (red) in resting DP cells sorted from MHC-deficient mice thymi at embryonic day 17.
Table III. The two TCRα alleles are not paired in DP thymocytes that are actively undergoing rearrangement of TCRα genes.
| Positioning of TCRα genesa | Percentage of cells with the designated type of nuclear TCRα gene position |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| DN | DP | Lymph node T cellsb | |
| Experiment 1c | |||
| Two separate spots | 79 | 71 | 73 |
| One doublet (two spots | |||
| right next to or on top | 7 | 4 | 4 |
| of each other) | |||
| Two separate spots plus | 9 | 16 | 13 |
| one doublet | |||
| Two doublets | 1 | 6 | 5 |
| One spot only | 4 | 3 | 5 |
| Experiment 2d | |||
| Two separate spots | ND | 87 | 92 |
| One doublet | ND | 7 | 6 |
| One spot only | ND | 5 | 2 |
| No signal | ND | 1 | 0 |
aIn experiment 1, the ‘one doublet’ population could represent cells with either one replicated locus and with the other allele undetected by FISH analysis, or two unreplicated TCRα loci that are co-localized. In experiment 2, cells in S and G2/M phase of the cell cycle were excluded from the analysis on the basis of the number and structure of centromeric clusters, the size of the nucleus, the degree of chromatin condensation and the occurrence of two doublets in a single nucleus. Since hybridization efficiency was high in experiment 2, the ‘one doublet’ population most probably corresponds to cells with two unreplicated TCRα loci that are co-localized.
bIn experiment 2, lymph node T cells were activated for 3 days by culture with antibodies directed against the TCR and CD28.
cMore than 200 nuclei were scored for each cell type.
dA total of 100 nuclei were scored for each cell type.
Discussion
DP thymocytes are generally assumed to undergo extensive cycles of secondary Vα→Jα rearrangements that involve their two TCRα alleles, thereby increasing their probability of being positively selected on a per cell basis. It has even been suggested that the rate of secondary rearrangements that DP cells experience per allele is so high, and the efficiency of positive selection so low, that exhaustion of the Vα and Jα libraries is frequent and thus accounts for the short DP lifespan (Petrie et al., 1993, 1995). Along this line, the unexpected coincidence in the chromosomal position of the two rearranged allelic Jα segments in most mouse αβ T cells might be accounted for by extensive secondary rearrangements that proceed on both Jα clusters in a 5′ to 3′ polarized and synchronized mode. In the present study, we show a similar positional coincidence of Jα usage in human αβ T-cell clones. In contrast, there exists only a loose correlation between the chromosomal position of the Vα and Jα elements on a given rearranged allele. There is also no interallelic coincidence in the chromosomal position of the two rearranged Vα elements in most human αβ T-cell clones (this study) and in NK1.1 T cells (Shimamura et al., 1997). This erratic usage of the allelic Vα libraries appears inconsistent with the ‘bi-directional and coordinated nibbling’ model (see Introduction and Figure 8A).
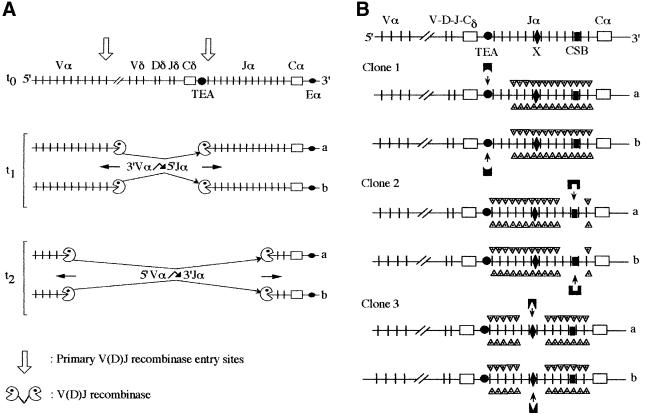
Fig. 8. Two models accounting for coincident substrate choice at both Jα alleles. The large database assembled in this study provides an observed value (∼2%) for the frequency of αβ T cells in which only one TCRα chain gene has been rearranged. This low frequency distinguishes TCRα from TCRβ genes and suggests that VαJα rearrangements are attempted quasi-simultaneously on both alleles. (A) The ‘bi-directional and coordinated nibbling’ model postulates the existence of two preferential V(D)J recombinase entry sites (each labeled with an arrow) localized at the 3′ end of the Vα library and at the 5′ end of the Jα cluster. Secondary rearrangements occur on both alleles (denoted a and b) at a high rate and in a polarized and synchronous mode. Successive secondary rearrangements involve preferentially the Vα and Jα gene segments which directly flank those used in the last cycle of VαJα rearrangement [i.e. the V(D)J recombinase is not retargeted directly from a 5′ Jα substrate to a 3′ Jα substrate]. Such preference for the nearest Jα neighbors may result from interactions between the promoter of the rearranged Vα gene and the TCRα enhancer (Eα) downstream of Cα. In contrast to the model depicted in (B), this model predicts the existence of a tight relationship between the stage of development reached by a DP cell (denoted t0, t1 and t2) and the section of the Jα cluster it is in the process of using. As proposed by Villey et al. (1996), TEA may mark the postulated 3′ recombinase entry site in that it possesses a rearrangement-focusing activity that targets the V(D)J recombinase to the nine 5′-most Jα segments. (B) The ‘coincident windows’ model postulates that in each DP cell only a narrow block of Jα segments is accessible to the recombination process. The position of this block differs from cell to cell, but is identical on both TCRα alleles of a given cell. This coincidental positioning is controlled by cis-regulatory sequences among which three have been depicted and tentatively denoted as TEA, X and CSB (for conserved sequence block). Note that the Jα cluster contains several evolutionary CSBs (Koop and Hood, 1994) that additionally may control local Jα accessibility. Once specifically bound by extrinsic factors that are postulated to be produced differentially by stromal cell niches, these sequences direct the opening of accessibility windows located 5′ (TEA), at the center (X) or 3′ (CSB) of the Jα cluster. Consistent with the existence of discrete windows of accessibility, the deletion of TEA or of CSB locally impairs the utilization of the flanking Jα (Villey et al., 1996; Riegert and Gilfillan, 1999).
Although a differential scanning of the Jα and of the Vα libraries (ordered for Jα, erratic for Vα) can be readily incorporated into a revised version of the ‘bi-directional and coordinated nibbling’ model, it should be emphasized that kinetic constraints may also restrict the extent of secondary VαJα rearrangements occurring in a given DP cell. For instance, the time between two successive secondary rearrangements should be longer than that elapsing between the transcription of a VαJαCα unit encoding a selectable TCRα chain and its fixing in the genome by the negative feedback loop that renders TCRα alleles inaccessible to further V(D)J recombination. If secondary Vα→Jα rearrangements occur faster than the speed at which this negative feedback loop operates, rearranging T cells may experience the deletion of a primary VαJα rearrangement whose product was perhaps being tested successfully. Restrictions on the rate of secondary rearrangements may be more relevant for TCRαβ selection than for TCRβ selection. First, the TCRα locus differs from the TCRβ locus in that it has the potential for multiple secondary rearrangements. Secondly, TCRαβ selection depends on the specificity of the TCRαβ heterodimer, whereas TCRβ selection relies on a prompt cell-autonomous process, not constrained by the need to interact specifically with extracellular ligands (Saint-Ruf et al., 2000). In a pre-T cell, only a couple of hours might elapse between the onset of a newly assembled VβDβJβCβ transcription unit and the incorporation of TCRβ chains into a pre-TCR complex capable of autonomously activating the negative feedback loop, rendering the TCRβ locus inaccessible to rearrangement. If the same kinetics hold true for TCRαβ selection, DP cells, the half-life of which approximates 3 days, should have ample time to scan the entire Vα and Jα loci via polarized and coordinated secondary rearrangements (Figure 8A). However, a few considerations make the above time base difficult to apply to TCRαβ selection. First, VαJα rearrangements involving the 5′ portion of the Jα cluster will result in transcriptional units of ∼60 kb. The length of time required for their transcription may significantly delay the expression of the resulting TCRα protein at the cell surface. Secondly, once displayed on the cell surface, the resulting, clonally distributed, TCRαβ heterodimers may not be checked immediately for their binding specificity owing to the existence of only a limited number of stromal cell niches capable of supporting positive selection (discussed in Merkenschlager et al., 1997). Therefore, in comparison with TCRβ selection, the process of TCRαβ selection may be slower and may require allotment of a generous time margin to DP cells before they embark on the next cycle of secondary rearrangements, and therefore irreversibly erase the VαJα transcription unit whose product was being tested.
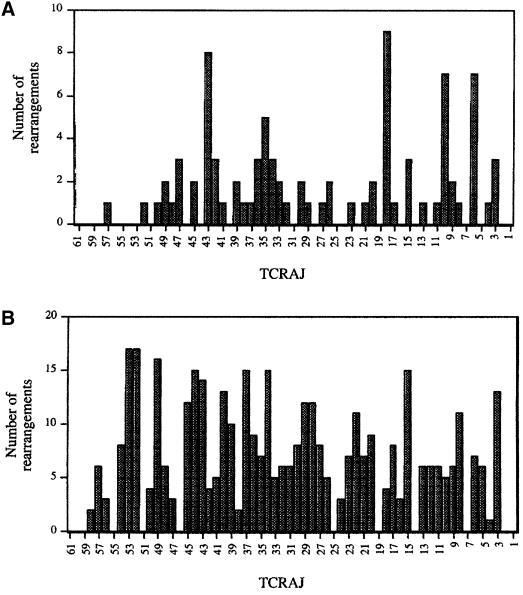
These plausible kinetic constraints question the existence of a high rate of secondary Vα→Jα rearrangements per allele. When considered together with the non-coordinated usage of the Vα and Jα libraries documented herein, they challenge the prevalent ‘bi-directional and coordinated nibbling’ model. However, consistent with recent analysis of a limited number of mouse Vα subfamilies (Aude-Garcia et al., 2001; Huang and Kanagawa, 2001), the present observations are still compatible with the view that the accessibility of the 5′ and 3′ halves of the Vα and Jα libraries is coordinately regulated. For instance, the first and third subsets of VαJα rearrangements individualized via correspondence analysis (Figure 5) support the existence of a loose correlation between the chromosomal location of Vα and Jα segments and their utilization by the V(D)J recombinase. Conversely, VαJα rearrangements belonging to the second subset (Figure 5) are more difficult to interpret in the frame of a position-dependent VαJα usage model. However, it is possible that they originate from alleles that have experienced a primary V→DδJδ rearrangement at an earlier time point (Wilson et al., 1996). Some Vα gene segments are capable of rearranging to DδJδ. Therefore, if the Vα involved in the primary V→DδJδ rearrangement is located in the middle of the Vα locus, 5′ Jα segments will be forced to rearrange with a 5′ Vα gene segment. Our data also impact on two additional issues. First, considering the broad specification of Vα segments capable of rearranging with a given Jα (Figures 4D and 5), each Jα has the potential to rearrange with a larger repertoire of Vα segments than postulated actually to be accessible by the ‘bi-directional and coordinated nibbling’ model. Secondly, according to the ‘bi-directional and coordinated nibbling’ model, the 3′-most Jα segments should have a lower frequency of utilization than the more proximal 5′ Jα segments. Data obtained for the usage of both mouse (Figure 1) and human (Figure 6) Jα segments, however, show that they are utilized equally in polyclonal T-cell populations, a result that is inconsistent with the above prediction.
Fig. 6. Jα usage in human T cells. (A) Distribution over the Jα cluster of the Jα gene segments used in 87 VαJα rearrangements involving the Vα24 gene segment (53 rearrangements were characterized in our laboratory and 34 derived from public databases). (B) Distribution over the Jα cluster of the Jα gene segments used in 394 VαJα rearrangements involving random Vα gene segments. These rearrangements were collated from public databases (n = 339) and from our laboratory (n = 55).
Other models not relying on polarized DNA tracking and on a high rate of secondary Vα→Jα rearrangements per allele can also account for the interallelic positional coincidence noted in Jα usage. For instance, as outlined in Figure 8B, the coincidence of Jα usage on each homolog of a given T cell could result from mechanisms similar to those operating in B cells during Ig class switch recombination, a process that changes the Ig class and involves Ig switch region (S) sequences that are located 5′ of each constant Ig gene except Cδ (reviewed in Kinoshita et al., 1999). Importantly, in a given B cell, class switch recombination is usually directed to the same S region on both homologous chromosomes and involves both productively and non-productively rearranged IgH loci (Gu et al., 1993). This is due to the fact that the transcription/accessibility of each S region is under the control of a specific cytokine secreted in the germinal center environment. Likewise, a few cis-acting regulatory elements, akin to TEA (Villey et al., 1996) or the constant sequence block (CSB; Kuo et al., 1998; Riegert and Gilfillan, 1999), might be distributed evenly over the entire Jα cluster, thereby differentially activating a region of accessibility in each T cell in response to factors produced by specific stromal cell niches (Figure 8B). As a result, the block of Jα gene segments flanking the targeted cis-acting regulatory sequence on both homologs might become available simultaneously to the V(D)J recombinase [see also Rytkonen et al. (1994) for a model invoking a role for environmental influence on the accessibility of Jα gene segments]. Since a polyclonal T-cell population utilizes all Jα gene segments equally (see Figures 1 and 6), the postulated windows of accessibility are likely to be both evenly distributed over the whole Jα cluster and used with an equal probability in the T-cell population.
Considering that our data do not support the ‘trans-sensing’ model depicted in Figure 7A, the parallel usage of the allelic Jα segments still requires an explanation. A locus-wide analysis of human TCRα gene rearrangements led us to question the occurrence of extensive rounds of secondary Vα→Jα rearrangements per allele leading to a polarized and coordinated usage of the Vα and Jα libraries. As an alternative, we propose that the striking interallelic positional coincidence noted in human and mouse Jα usage may result from the fact that, at a given time, the same restricted block of Jα segments becomes accessible simultaneously to the action of the V(D)J recombinase on both homologs and only allows a limited number of secondary Vα→Jα rearrangements.
Materials and methods
Characterization of mouse TCRα gene rearrangements
The structure of the TCRα gene rearrangements was determined by cloning and sequencing the corresponding genomic fragments or by RNA PCR amplification with a panel of oligonucleotides specific for each of the known Vα gene segments (Casanova et al., 1991). The references for each of the individual T cells shown in Figure 1 are available upon request.
Characterization of human TCRα rearrangements
RNA from 5 × 106 T cells was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Gibco-BRL) according to the supplier’s instructions and dissolved in a final volume of 40 µl of water. Reverse transcription was performed in a final volume of 12.5 µl for 30 min at 45°C in a mix containing 2.5 µl of the RNA solution, 50 mM Tris–HCl pH 8.3, 75 mM KCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 10 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), 10 U of rRNasin (Promega), 1 mM each dNTP, 100 U of M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Gibco-BRL) and 25 pM Cα-specific reverse primer (5′-TGAAGTCCATAGACCTCATGTC-3′). For each T-cell clone, five independent reverse transcription reactions were performed (one for each multiplex PCR). Each reverse transcription reaction was completed to 50 µl with a mix containing Taq DNA polymerase (Pharmacia), 10 mM Tris–HCl pH 9, 50 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 1.25 U of Taq DNA polymerase and 25 pM of a set of Vα primers (Couedel et al., 1999). Amplification was performed on a 96-well thermocycler (PTC-100™; MJ Research, Inc.) with the following cycles: one cycle of 5 min at 94°C, one cycle of 30 s at 45°C, one cycle of 72°C, 30 cycles consisting of 1 min at 94°C, one cycle of 1.5 min at 45°C and one cycle of 1 min at 72°C. PCR products were migrated on a 2% agarose gel. Bands of interest were cut out and incubated overnight in 0.5 ml of buffered phenol. A 50 µl aliquot of TE 10/1 was added to each tube and the tubes were then centrifuged at 13 000 r.p.m. in a microcentrifuge for 1 h. The aqueous phase was recovered, extracted once with phenol: chloroform (1:1) and ethanol precipitated. DNA pellets were resuspended in 10 µl of 1× Sequenase reaction buffer (Amersham) containing 1 mM sequencing primer (5′-CTTTGTGACACATTTGTTTGAG-3′). Sequences of the purified PCR products were determined with Sequenase (Amersham) following a modified version of the supplier’s protocol. Denaturation and annealing steps were performed by heating at 95°C for 5 min and cooling immediately in a dry ice–ethanol bath. For labeling, we used a sequencing primer, positioned just in front of a sequence rich in T but lacking G, to favor incorporation of [35S]adenosine using dCTP, dTTP and dATP labeling mixes, and to limit elongation at the first C encountered on the Cα sequence.
Statistical analyses
Correlative analyses. The positions of the Vα (or Jα) elements correspond to their relative chromosomal location (see legend of Figure 4). The interallelic distance corresponds to the number of Vα (or Jα) elements separating the two V (or J) elements that are found rearranged (one on each homolog) in a given T-cell clone. To prevent biases in V/J position correlation studies, assignments of V or J elements to one or the other allele were randomized using a uniform function. All correlation analyses were performed using a Spearman test and SAS Institute Inc. (Cary, NC) software.
Comparisons between observed and randomized distributions of interallelic Vα or Jα distances. Random distributions of V (or J) interallelic distances were generated using a uniform function, taking into account only the functional Vα or Jα elements. Comparisons between the observed distribution of interallelic V or J distances of our panel of 68 mouse and 29 human T-cell clones and the theoretical distribution of 68 and 29 V/V or J/J pairs was estimated by Fisher’s exact test. Robustness of the test was validated by comparison of the observed values with 50 independent random samplings. The distribution of P-values of Fisher’s exact test was evaluated and we retained as the theoretical distribution the one whose P-value was the closest to the modal class.
Correspondence analyses. VαJα rearrangements drawn from public data banks were obtained using BLAST search software. We searched for sequences homologous to each Jα element and retained only those for which a Vα element could be determined unambiguously as a rearrangement partner. The 421 unique rearrangements characterized with this approach were pooled with 108 novel VαJα rearrangements, the sequences of which were determined in the course of the present study. To avoid any bias in the selection of our panel of VαJα rearrangements, we systematically discarded redundant rearrangements derived from the same study. We also removed from the panel of rearrangements those derived from the same T-cell clone. A total of 394 rearrangements remained in this second panel. Correspondence analyses were performed using Spad.N software (Cisia, St Mandé 94, France) on each panel of rearrangements (n = 528 and n = 394). In both cases, splitting of the contingency table (V position versus J position) into three groups was the most satisfactory way to allow a maximal separation of the groups (65.5% intergroup inertia), while keeping a good individual distribution homogeneity in each group (inertia: GRI, 11%; GRII, 9%; GRIII, 14%). These three groups are centered on very similar V/J positions in the two panels of rearrangements analyzed.
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH)
Thymocytes and lymph node cells were labeled with anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 monoclonal antibodies and sorted. In Figure 7 and Table III (Experiment 2), simultaneous localization of TCRα genes and of centromeric γ-satellite domains was performed essentially as described (Brown et al., 1997, 1999). The γ-satellite probe was labeled directly with fluoroRED (Amersham) and the biotinylated TCRα probe prepared by nick translation from cosmid 32.1W7 (Malissen et al., 1988). In Table III (Experiment 1), the FISH protocol of Brown et al. (1997) was modified as described (Chen et al., 2000).
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgements
We thank P.Golstein, P.Bongrand, E.Jouvin-Marche and J.P.de Villartay for discussion. This work was supported by grants from the CNRS, INSERM and the ARC.
References
- Ashe H.L., Monks,J., Wijgerde,M., Fraser,P. and Proudfoot,N.J. (1997) Intergenic transcription and transinduction of the human β-globin locus. Genes Dev., 11, 2494–2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aude-Garcia C., Gallagher,M., Marche,P.N. and Jouvin-Marche,E. (2001) Preferential ADV–AJ association during recombination in the mouse T-cell receptor α/δ locus. Immunogenetics, 52, 224–230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F.W., Oltz,E.M., Young,F., Gorman,J., Taccioli,G. and Chen,J. (1992) VDJ recombination. Immunol. Today, 13, 306–314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boysen C., Simon,M.I. and Hood,L. (1997) Analysis of the 1.1-Mb human α/δ T-cell receptor locus with bacterial artificial chromosome clones. Genome Res., 7, 330–338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K.E., Guest,S.G., Smale,S.T., Hahm,K., Merkenschlager,M. and Fisher,A.G. (1997) Association of transcriptionally silent genes with Ikaros complexes at centromeric heterochromatin. Cell, 91, 845–854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J.L., Romero,P., Widmann,C., Kourilsky,P. and Maryanski,J.L. (1991) T cell receptor genes in a series of class I major histocompatibility complex-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones specific for a Plasmodium berghei nonapeptide: implications for T cell allelic exclusion and antigen-specific repertoire. J. Exp. Med., 174, 1371–1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H.T. et al. (2000) Response to RAG-mediated V(D)J cleavage by NBS1 and γ-H2AX. Science, 290, 1962–1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couedel C., Bodinier,M., Peyrat,M.A., Bonneville,M., Davodeau,F. and Lang,F. (1999) Selection and long-term persistence of reactive CTL clones during an EBV chronic response are determined by avidity, CD8 variable contribution compensating for differences in TCR affinities. J. Immunol., 162, 6351–6358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu H., Zou,Y.R. and Rajewsky,K. (1993) Independent control of immunoglobulin switch recombination at individual switch regions evidenced through Cre–loxP-mediated gene targeting. Cell, 73, 1155–1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. and Comai,L. (1998) Trans-sensing effects: the ups and downs of being together. Cell, 93, 329–332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C.Y. and Kanagawa,O. (2001) Ordered and coordinated rearrangement of the TCRα locus: role of secondary rearrangement in thymic selection. J. Immunol., 166, 2597–2601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hue I., Trucy,J., Mc Coy,C., Couez,D., Malissen,B. and Malissen,M. (1990) A novel type of aberrant T cell receptor α-chain gene rearrangement. J. Immunol., 144, 4410–4419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvin-Marche E., Hue,I., Marche,P.N., Liebe-Gris,C., Marolleau,J.P., Malissen,B., Cazenave,P.A. and Malissen,M. (1990) Genomic organization of the mouse T cell receptor Vα family. EMBO J., 9, 2141–2150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvin-Marche E., Aude-Garcia,C., Candeias,S., Borel,E., Hachemi-Rachedi,S., Gahery-Segard,H., Cazenave,P.A. and Marche,P.N. (1998) Differential chronology of TCRADV2 gene use by α and δ chains of the mouse TCR. Eur. J. Immunol., 28, 818–827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita K., Lee,C.G., Tashiro,J., Muramatsu,M., Chen,X.-C., Yoshikawa,K. and Honjo,T. (1999) Molecular mechanism of immunoglobulin class switch recombination. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol., 64, 217–226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop B.F. and Hood,L. (1994) Striking sequence similarity over almost 100 kilobases of human and mouse T-cell receptor DNA. Nature Genet., 7, 48–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop B.F. et al. (1994) The human T-cell receptor TCRAC/TCRDC (Cα/Cδ) region: organization, sequence and evolution of 97.6 kb of DNA. Genomics, 19, 478–493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C.L., Chen,M.L., Wang,K., Chou,C.K., Vernooij,B., Seto,D., Koop,B.F. and Hood,L. (1998) A conserved sequence block in murine and human T cell receptor (TCR) Jα region is a composite element that enhances TCRα enhancer activity and binds multiple nuclear factors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 95, 3839–3844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen B. and Malissen,M. (1995) Allelic exclusion of T cell antigen receptor genes in T cell receptors. In Bell,J.I., Owen,M.J. and Simpson,E. (eds), T Cell Receptors. Oxford University Press, New York, NY, pp. 352–368.
- Malissen M., Trucy,J., Jouvin-Marche,E., Cazenave,P.A., Scollay,R. and Malissen,B. (1992) Regulation of TCRα and β gene allelic exclusion during T-cell development. Immunol. Today, 13, 315–322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Trucy,J., Letourneur,F., Rebaï,N., Dunn,D.E., Fitch,F.W., Hood,L. and Malissen,B. (1988) A T cell clone expresses two T cell receptor α genes but uses one αβ heterodimer for allorecognition and self MHC-restricted antigen recognition. Cell, 55, 49–59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkenschlager M., Graf,D., Lovatt,M., Bommhardt,U., Zamoyska,R. and Fisher,A.G. (1997) How many thymocytes audition for selection? J. Exp. Med., 186, 1149–1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrie H.T., Livak,F., Schatz,D.G., Strasser,A., Crispe,I.N. and Shortman,K. (1993) Multiple rearrangements in T cell receptor α chain genes maximize the production of useful thymocytes. J. Exp. Med., 178, 615–622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrie H.T., Livak,F., Burtrum,D. and Mazel,S. (1995) T cell receptor gene recombination patterns and mechanisms: cell death, rescue and T cell production. J. Exp. Med., 182, 121–127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riegert P. and Gilfillan,S. (1999) A conserved sequence block in the murine and human TCR Jα region: assessment of regulatory function in vivo. J. Immunol., 162, 3471–3480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M.E., Holman,P.O. and Kranz,D.M. (1991) Nonrandom use of Jα gene segments. Influence of Vα and Jα gene location. J. Immunol., 147, 1075–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytkonen M., Hurwitz,J.L., Tolonen,K. and Pelkonen,J. (1994) Evidence for recombinatorial hot spots at the T cell receptor Jα locus. Eur. J. Immunol., 24, 107–115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytkonen M.A., Hurwitz,J.L., Thompson,S.D. and Pelkonen,J. (1996) Restricted onset of T cell receptor α gene rearrangement in fetal and neonatal thymocytes. Eur. J. Immunol., 26, 1892–1896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saint-Ruf C., Panigada,M., Azogui,O., Debey,P., Von Boehmer,H. and Grassi,F. (2000) Different initiation of pre-TCR and γδTCR signalling. Nature, 406, 524–527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura M., Ohteki,T., Beutner,U. and MacDonald,H.R. (1997) Lack of directed Vα14–Jα281 rearrangements in NK1+ T cells. Eur. J. Immunol., 27, 1576–1579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uematsu Y., Ryser,S., Dembic,Z., Borgulya,P., Krimpenfort,P., Berns,A., von Boehmer,H. and Steinmetz,M. (1988) In transgenic mice the introduced functional T cell receptor β gene prevents expression of endogenous β genes. Cell, 52, 831–841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villey I., Caillol,D., Selz,F., Ferrier,P. and de Villartay,J.P. (1996) Defect in rearrangement of the most 5′ TCR-Jα following targeted deletion of T early α (TEA): implications for TCRα locus accessibility. Immunity, 5, 331–342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Boehmer H., Aifantis,I., Fenberg,J., Lechner,O., Saint-Ruf,C., Walter,U., Buer,J. and Azogui,O. (1999) Pleiotropic changes controlled by the pre-T-cell receptor. Curr. Opin. Immunol., 11, 135–142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A., de Villartay,J.P. and MacDonald,H.R. (1996) T cell receptor δ gene rearrangement and T early α (TEA) expression in immature αβ lineage thymocytes: implications for αβ/γδ lineage commitment. Immunity, 4, 37–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. and Tonegawa,S. (1983) Diversity and joining segments of mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain genes are closely linked and in the same orientation: implications for the joining mechanism. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 80, 3030–3034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]