Abstract
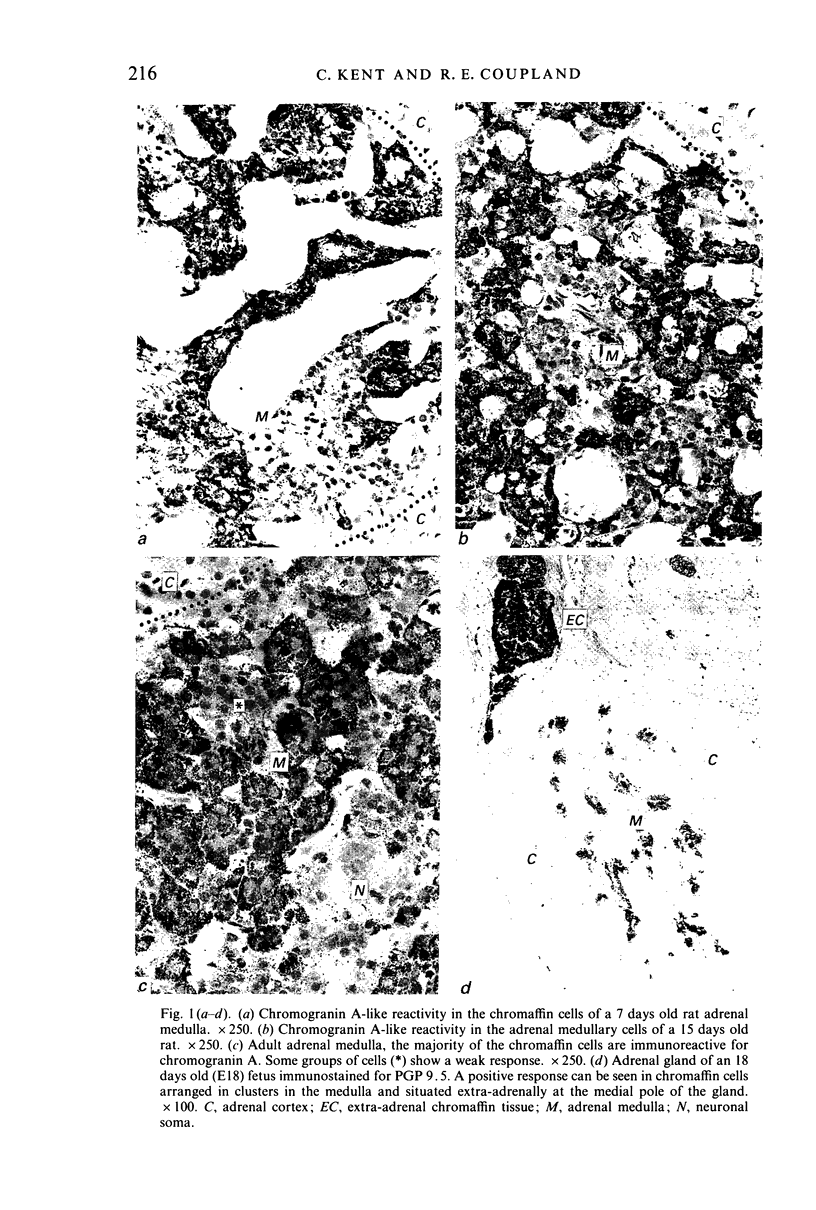
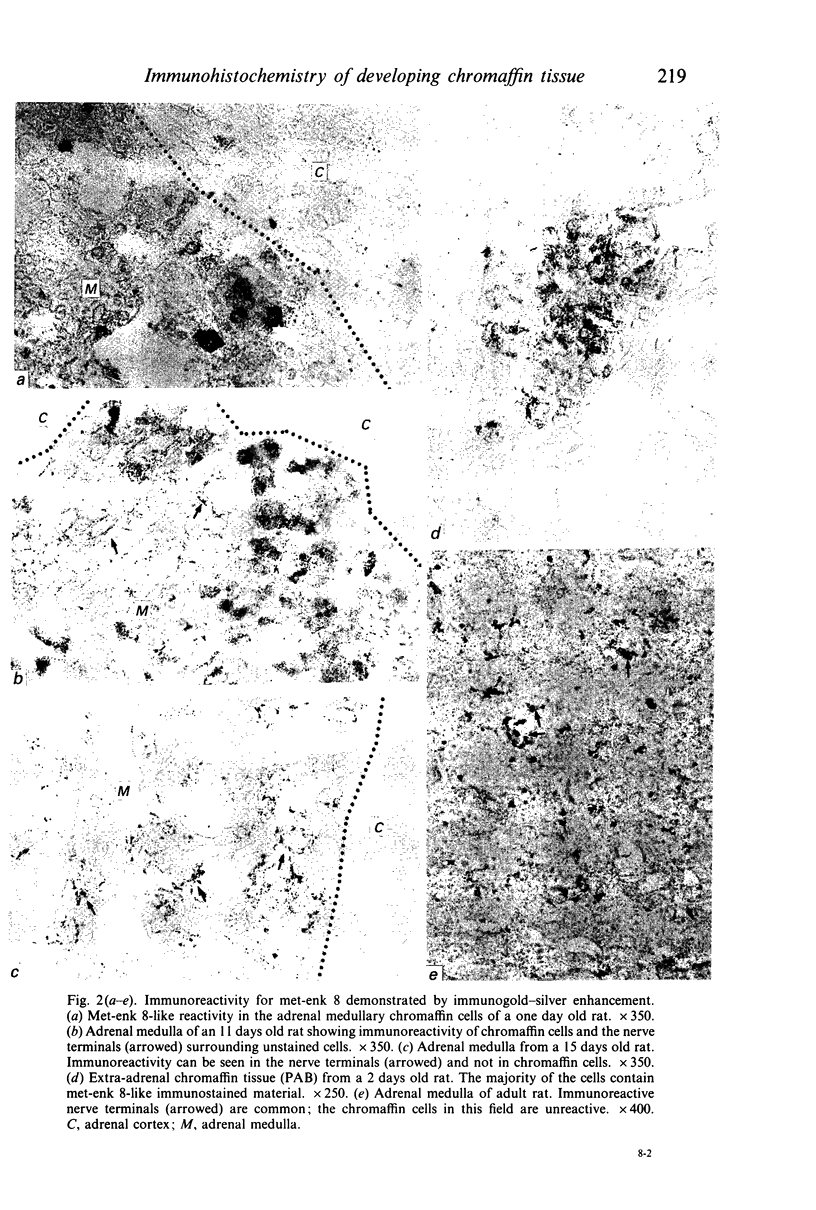
The localisation of chromogranins A and B, met-enkephalin-arg6-gly7-leu8 (met-enk 8) and protein gene product 9.5 (PGP 9.5) in the adrenal medulla and extra-adrenal chromaffin tissue has been studied in the developing rat by immunogold-silver staining. In the adult rat adrenal the cytoplasm of all medullary chromaffin cells showed a positive response with chromogranin A and B; in each case occasional groups of cells with a low reactivity that may have been NA cells were seen. Chromogranin A was first detected in adrenal medullary and extra-adrenal chromaffin cells at 18 days of gestation whilst chromogranin B was not detected in animals younger than 7 days. In 15 days old animals the adrenal medullary response to A and B was of the same intensity as that seen in the adult. Less than 1% of adult medullary chromaffin cells were responsive to met-enk 8 staining and medullary cells were unreactive in the fetus, with only extra-adrenal chromaffin tissue responding prenatally. During the first postnatal week immunoreactive cells appeared in the adrenal medulla in considerably greater proportions than in the adult gland. In contrast, positively stained nerve terminals associated with chromaffin cells and abundant in the adult adrenal were not detected during the first week of life. Immunoreactive nerve terminals were first seen early in the second week of life at a time when positive chromaffin cells were becoming less common. PGP 9.5 was located in all chromaffin cells of the adult adrenal and was readily detected in chromaffin cells in the adrenal and in extra-adrenal locations of the earliest stage examined (E16). Our findings suggest that the ontogenesis of the chromogranin-like immunostaining reflects the maturation of chromaffin granules and the PGP 9.5 immunostaining detected a protein common to cells of neuronal origin and expressed at an early stage of differentiation. The reciprocal relationship between the presence of enkephalins in chromaffin cells and in their presynaptic terminals merits further investigation.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bareis D. L., Slotkin T. A. Responses of heart ornithine decarboxylase and adrenal catecholamines to methadone and sympathetic stimulants in developing and adults rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Apr;205(1):164–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschko H., Comline R. S., Schneider F. H., Silver M., Smith A. D. Secretion of a chromaffin granule protein, chromogranin, from the adrenal gland after splanchnic stimulation. Nature. 1967 Jul 1;215(5096):58–59. doi: 10.1038/215058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundin T. Studies on the preaortal paraganglia of newborn rabbits. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1966;290:1–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Weakley B. S. Developing chromaffin tissue in the rabbit: an electron microscopic study. J Anat. 1968 Mar;102(Pt 3):425–455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Weakley B. S. Electron microscopic observation on the adrenal medulla and extra-adrenal chromaffin tissue of the postnatal rabbit. J Anat. 1970 Mar;106(Pt 2):213–231. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daikoku S., Kinutani M., Sako M. Development of the adrenal medullary cells in rats with reference to synaptogenesis. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Mar 30;179(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00278463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V. Adrenal medullary responses to splanchnic nerve stimulation in new-born calves. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:409–416. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Maghraby M., Lever J. D. Typification and differentiation of medullary cells in the developing rat adrenal. A histochemical and electron microscopic study. J Anat. 1980 Aug;131(Pt 1):103–120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elfvin L. G. The development of the secretory granules in the rat adrenal medulla. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Jan;17(1):45–62. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Frischenschlager I. Immunological characterization of secretory proteins of chromaffin granules: chromogranins A, chromogranins B, and enkephalin-containing peptides. J Neurochem. 1985 Jun;44(6):1854–1861. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Hagn C., Schober M. Chromogranins A, B, and C: widespread constituents of secretory vesicles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:120–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Lassmann H., Hagn C., Winkler H. Immunological studies on the distribution of chromogranin A and B in endocrine and nervous tissues. Neuroscience. 1985 Nov;16(3):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleminger G., Lahm H. W., Udenfriend S. Changes in rat adrenal catecholamines and proenkephalin metabolism after denervation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3587–3590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulbenkian S., Wharton J., Polak J. M. The visualisation of cardiovascular innervation in the guinea pig using an antiserum to protein gene product 9.5 (PGP 9.5). J Auton Nerv Syst. 1987 Mar;18(3):235–247. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(87)90122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hervonen A., Korkala O. The effect of hypoxia on the catecholamine content of human fetal abdominal paraganglia and adrenal medulla. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1972;51(1):17–24. doi: 10.3109/00016347209154963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hexum T. D., Yang H. Y., Costa E. Biochemical characterization of enkephalin-like immunoreactive peptides of adrenal glands. Life Sci. 1980 Sep 29;27(13):1211–1216. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90474-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y., Nakao K., Yoshimasa T., Yanaihara N., Numa S., Imura H. Existence of Met-enkephalin-Arg6-Gly7-Leu8 with Met-enkephalin, Leu-enkephalin and Met-enkephalin-Arg6-Phe7 in the brain of guinea pig, rat and golden hamster. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 30;107(2):656–662. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91541-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P., Thomson V. M., Thompson R. J. A comparison of the evolutionary distribution of the two neuroendocrine markers, neurone-specific enolase and protein gene product 9.5. J Neurochem. 1985 Jul;45(1):185–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05491.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Jones B. N., Kojima K., Udenfriend S. Identification of the octapeptide [Met]enkephalin -Arg6-Gly7-Leu8 in extracts of bovine adrenal medulla. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):698–705. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90506-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby R. F., McCarty R. Ontogeny of functional sympathetic innervation to the heart and adrenal medulla in the preweanling rat. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1987 Apr;19(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(87)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo H., Kuramoto H., Iwanaga T. Immunohistochemical study on Met-enkephalin-Arg-Gly-Leu-like immunoreactive nerve fibers in the rat adrenal medulla. Brain Res. 1984 Sep 24;310(2):371–375. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo H., Kuramoto H., Wainer B. H., Yanaihara N. Evidence for the coexistence of acetylcholine and enkephalin in the sympathetic preganglionic neurons of rats. Brain Res. 1985 Jun 3;335(2):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90483-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Gamma E. F., Adler J. E. Development of transsynaptic regulation of adrenal enkephalin. Brain Res. 1988 Apr 1;467(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(88)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaGamma E. F., Adler J. E., Black I. B. Impulse activity differentially regulates [Leu]enkephalin and catecholamine characters in the adrenal medulla. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1102–1104. doi: 10.1126/science.6144183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaGamma E. F., White J. D., Adler J. E., Krause J. E., McKelvy J. F., Black I. B. Depolarization regulates adrenal preproenkephalin mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8252–8255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau C., Bartolome J. V., Bartolome M. B., Slotkin T. A. Central and sympatho-adrenal responses to insulin in adult and neonatal rats. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 1;433(2):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau C., Slotkin T. A. Accelerated development of rat sympathetic neurotransmission caused by neonatal triiodothyronine administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1979 Mar;208(3):485–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. V., Stern A. S., Kilpatrick D. L., Gerber L. D., Rossier J., Stein S., Udenfriend S. Marked increases in large enkephalin-containing polypeptides in the rat adrenal gland following denervation. J Neurosci. 1981 Jan;1(1):80–82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-01-00080.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnoila R. I., Diaugustine R. P., Hervonen A., Miller R. J. Distribution of [Met5]- and [Leu5]-enkephalin-, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide- and substance P-like immunoreactivities in human adrenal glands. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2247–2259. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Hirose T., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for bovine adrenal preproenkephalin. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):202–206. doi: 10.1038/295202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelto-Huikko M., Salminen T., Hervonen A. Localization of enkephalins in adrenaline cells and the nerves innervating adrenaline cells in rat adrenal medulla. Histochemistry. 1985;82(4):377–383. doi: 10.1007/BF00494067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schober M., Fischer-Colbrie R., Winkler H. Ontogenesis of chromogranin A and B and catecholamines in rat adrenal medulla. Brain Res. 1989 Jan 23;478(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91475-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Brandt J., Elde R. P., Goldstein M. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in gland cells and nerve terminals of the adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1978;3(12):1169–1186. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotkin T. A. Maturation of the adrenal medulla. II. Content and properties of catecholamine storage vesicles of the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Aug 15;22(16):2033–2044. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotkin T. A. Maturation of the adrenal medulla. III. Practical and theoretical considerations of age-dependent alterations in kinetics of incorporation of catecholamines and non-catecholamines. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Jan 1;24(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springall D. R., Hacker G. W., Grimelius L., Polak J. M. The potential of the immunogold-silver staining method for paraffin sections. Histochemistry. 1984;81(6):603–608. doi: 10.1007/BF00489542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. J., Doran J. F., Jackson P., Dhillon A. P., Rode J. PGP 9.5--a new marker for vertebrate neurons and neuroendocrine cells. Brain Res. 1983 Nov 14;278(1-2):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhofstad A. A., Coupland R. E., Parker T. R., Goldstein M. Immunohistochemical and biochemical study on the development of the noradrenaline- and adrenaline-storing cells of the adrenal medulla of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;242(2):233–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00214536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viveros O. H., Diliberto E. J., Jr, Hazum E., Chang K. J. Opiate-like materials in the adrenal medulla: evidence for storage and secretion with catecholamines. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(3):1101–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Apps D. K., Fischer-Colbrie R. The molecular function of adrenal chromaffin granules: established facts and unresolved topics. Neuroscience. 1986 Jun;18(2):261–290. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. The composition of adrenal chromaffin granules: an assessment of controversial results. Neuroscience. 1976;1(2):65–80. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoburn B. C., Franklin S. O., Calvano S. E., Inturrisi C. E. Regulation of rat adrenal medullary enkephalins by glucocorticoids. Life Sci. 1987 Jun 29;40(26):2495–2503. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]