Abstract
Retrograde tracers were injected in various parts of the neocortex of the porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). Labelled thalamic neurons were plotted in three-dimensional reconstructions. The lateral geniculate nucleus projects to the visually excitable part of the lateral gyrus. Ventral parts of the medial geniculate nucleus project to the auditory area of the suprasylvian gyrus, while dorsal medial geniculate projects to the 'secondary' auditory area of the ectosylvian gyrus and to the temporal operculum. The ventrobasal and ventropostero-inferior complex projects to cortex anterior to the suprasylvian auditory area, corresponding to somatosensory function. The main projection of the inferior pulvinar is to the suprasylvian gyrus, that of the medial pulvinar to the ectosylvian gyrus, and of the lateral pulvinar to the border of the lateral and suprasylvian gyri. The lateral and posterior complexes project to perisylvian cortex. Throughout the thalamus there is a rough topographic organisation. Lateral to medial through the thalamus represents progression from medial to lateral over the cortex from lateral gyrus to perisylvian cortex. Anterior in cortex is represented by anteroventral in thalamus, and posterior in cortex by posterodorsal in thalamus.
Full text
PDF



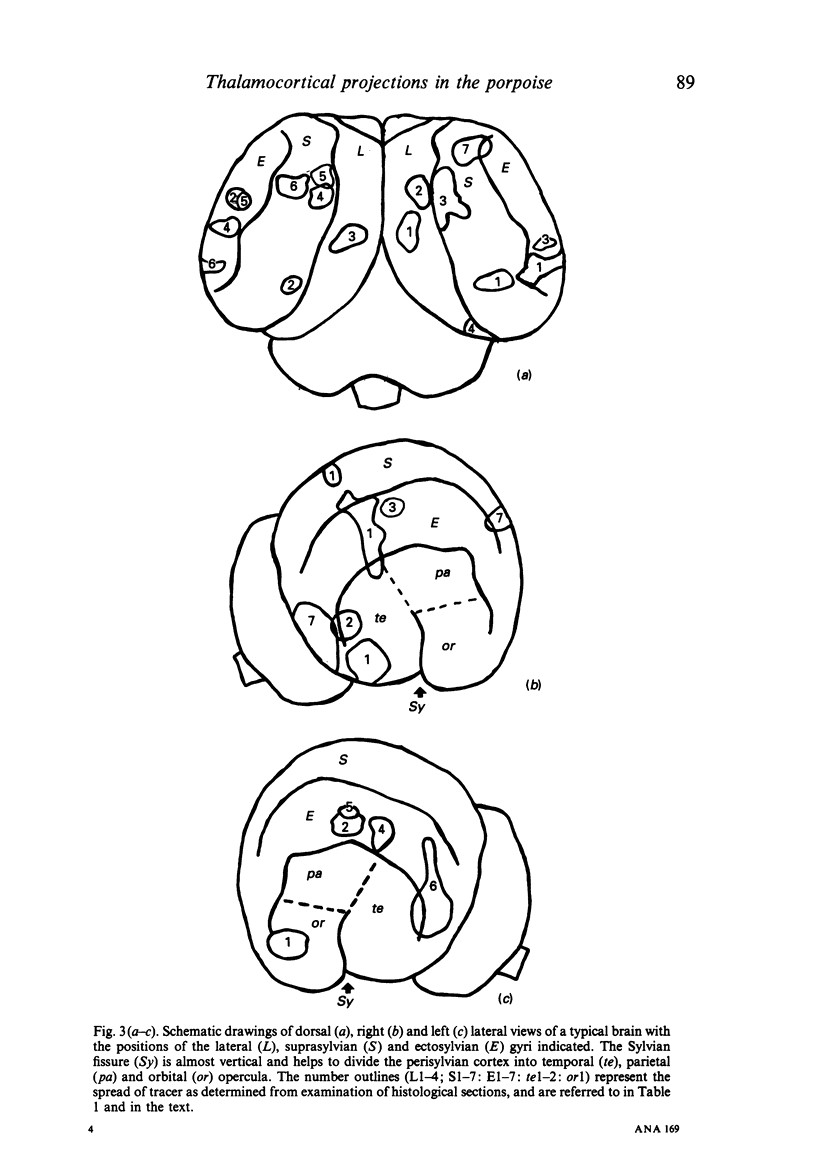




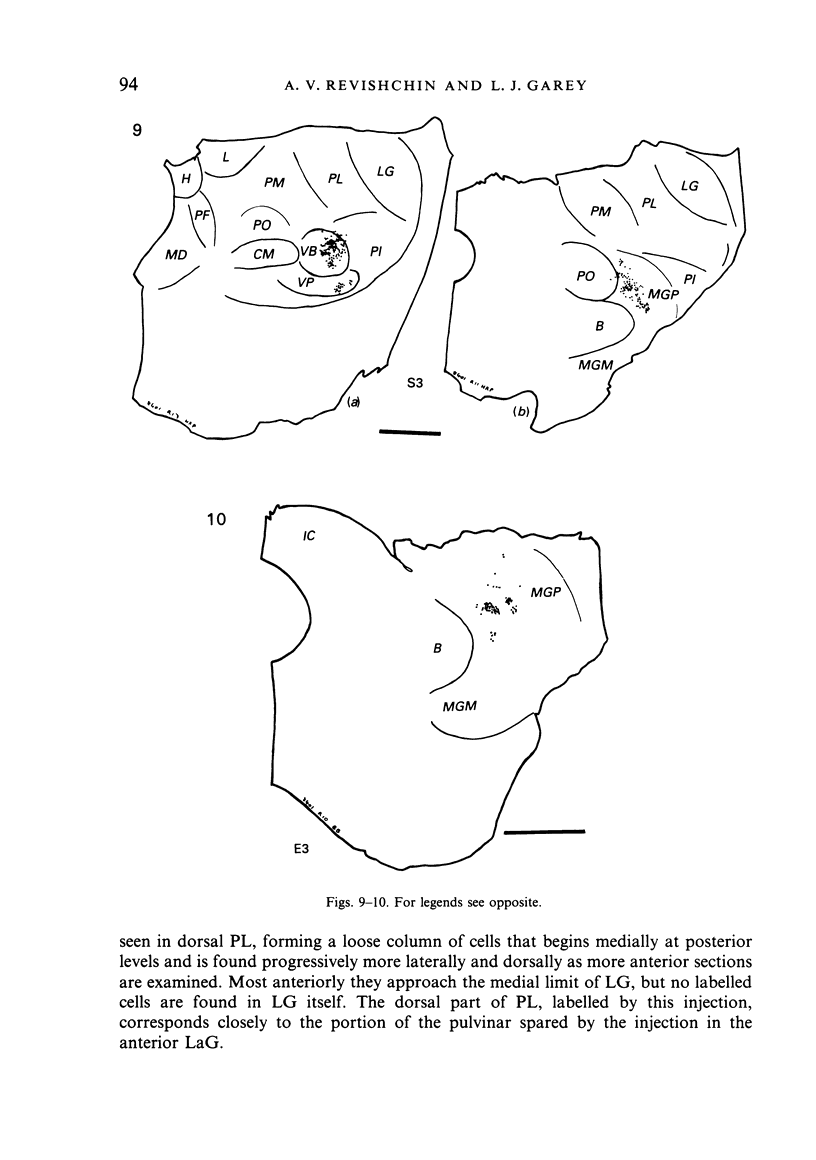
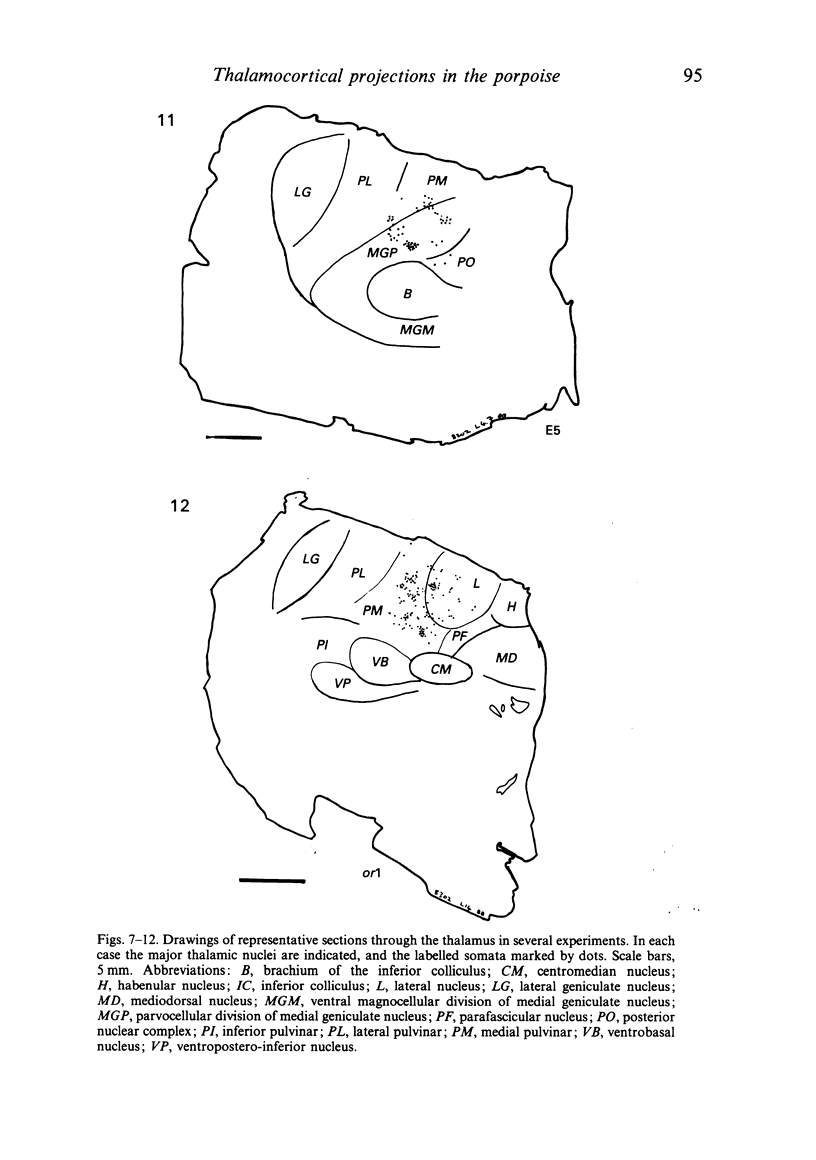







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C. Technical considerations on the use of horseradish peroxidase as a neuronal marker. Neuroscience. 1977;2(1):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(77)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen R. A., Knight P. L., Merzenich M. M. The thalamocortical and corticothalamic connections of AI, AII, and the anterior auditory field (AAF) in the cat: evidence for two largely segregated systems of connections. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Dec 1;194(3):663–701. doi: 10.1002/cne.901940312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock T. H. Comparative neuroscience holds promise for quiet revolutions. Science. 1984 Aug 3;225(4661):473–478. doi: 10.1126/science.6740319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürsteler M. R., Blakemore C., Garey L. J. Uptake of horseradish peroxidase by geniculo-cortical axons in the golden hamster: analysis by computer reconstruction. Exp Brain Res. 1977 Sep 28;29(3-4):487–500. doi: 10.1007/BF00236186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias H., Schwartz D. Surface areas of the cerebral cortex of mammals determined by stereological methods. Science. 1969 Oct 3;166(3901):111–113. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3901.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entin T. I. Gistologicheskoe issledovanie kory zatylochnoi oblasti mozga del'fina. Arkh Anat Gistol Embriol. 1973 Dec;65(12):92–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer I., Perera M. Structure and nerve cell organisation in the cerebral cortex of the dolphin Stenella coeruleoalba a Golgi study. With special attention to the primary auditory area. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1988;178(2):161–173. doi: 10.1007/BF02463650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garey L. J., Leuba G. A quantitative study of neuronal and glial numerical density in the visual cortex of the bottlenose dolphin: evidence for a specialized subarea and changes with age. J Comp Neurol. 1986 May 22;247(4):491–496. doi: 10.1002/cne.902470408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garey L. J., Takács J., Revishchin A. V., Hámori J. Quantitative distribution of GABA-immunoreactive neurons in cetacean visual cortex is similar to that in land mammals. Brain Res. 1989 Apr 24;485(2):278–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90571-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garey L. J., Winkelmann E., Brauer K. Golgi and Nissl studies of the visual cortex of the bottlenose dolphin. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Oct 15;240(3):305–321. doi: 10.1002/cne.902400307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingerich P. D., Wells N. A., Russell D. E., Shah S. M. Origin of whales in epicontinental remnant seas: new evidence from the early eocene of pakistan. Science. 1983 Apr 22;220(4595):403–406. doi: 10.1126/science.220.4595.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofman M. A. Size and shape of the cerebral cortex in mammals. I. The cortical surface. Brain Behav Evol. 1985;27(1):28–40. doi: 10.1159/000118718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. S., Galaburda A. M., McFarland W. L., Morgane P. J. The insular formations of the dolphin brain: quantitative cytoarchitectonic studies of the insular component of the limbic lobe. J Comp Neurol. 1984 May 20;225(3):396–432. doi: 10.1002/cne.902250307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M. S., Morgane P. J., McFarland W. L. Degeneration of visual pathways in the bottlenose dolphin. Brain Res. 1975 May 2;88(2):346–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90397-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesarev V. S., Malofeyeva L. I., Trykova O. V. Ecological specificity of cetacean neocortex. J Hirnforsch. 1977;18(6):447–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnoshchekova E. I., Figurina I. I. Korkovye proektsii medial'nogo kolenchatogo tela mozga del'fina. Arkh Anat Gistol Embriol. 1980 Apr;78(4):19–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers H. G., Bentivoglio M., van der Kooy D., Catsman-Berrevoets C. E. Retrograde transport of bisbenzimide and propidium iodide through axons to their parent cell bodies. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Apr;12(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)91471-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladygina T. F., Mass A. M., Supin A. Ia. Mnozhestvennye sensornye proektsii v kore bol'shikh polusharii del'fina. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 1978 Sep-Oct;28(5):1047–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lende R. A., Welker W. I. An unusual sensory area in the cerebral neocortex of the bottlenose dolphin, Tursiops truncatus. Brain Res. 1972 Oct 27;45(2):555–560. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90482-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M. Tetramethyl benzidine for horseradish peroxidase neurohistochemistry: a non-carcinogenic blue reaction product with superior sensitivity for visualizing neural afferents and efferents. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Feb;26(2):106–117. doi: 10.1177/26.2.24068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgane P. J., Jacobs M. S., Galaburda A. Conservative features of neocortical evolution in dolphin brain. Brain Behav Evol. 1985;26(3-4):176–184. doi: 10.1159/000118774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGEL E. L., MORGANE P. J., MCFARLAND W. L. ANESTHESIA FOR THE BOTTLENOSE DOLPHIN, TURSIOPS TRUNCATUS. Science. 1964 Dec 18;146(3651):1591–1593. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3651.1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilleri G., Kraus C., Gihr M. The structure of the cerebral cortex of the Ganges dolphin Susu (Plactanista) gangetia Lebeck 1801. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch. 1968;79(2):373–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway S. H., McCormick J. G. Anesthetization of porpoises for major surgery. Science. 1967 Oct 27;158(3800):510–512. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3800.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saini K. D., Garey L. J. Morphology of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the monkey. A Golgi study. Exp Brain Res. 1981;42(3-4):235–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00237491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmued L. C., Fallon J. H. Fluoro-Gold: a new fluorescent retrograde axonal tracer with numerous unique properties. Brain Res. 1986 Jul 2;377(1):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91199-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolov V. E., Ladygina T. F., Supin A. Ia. Lokalizatsiia sensornykh zon v kore golovnogo mozga del'fina. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1972 Jan 11;202(2):490–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanegas H., Hollander H., Distel H. Early stages of uptake and transport of horseradish-peroxidase by cortical structures, and its use for the study of local neurons and their processes. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Jan 15;177(2):193–211. doi: 10.1002/cne.901770203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Courten C., Garey L. J. Morphology of the neurons in the human lateral geniculate nucleus and their normal development. A Golgi study. Exp Brain Res. 1982;47(2):159–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00239375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]