Abstract
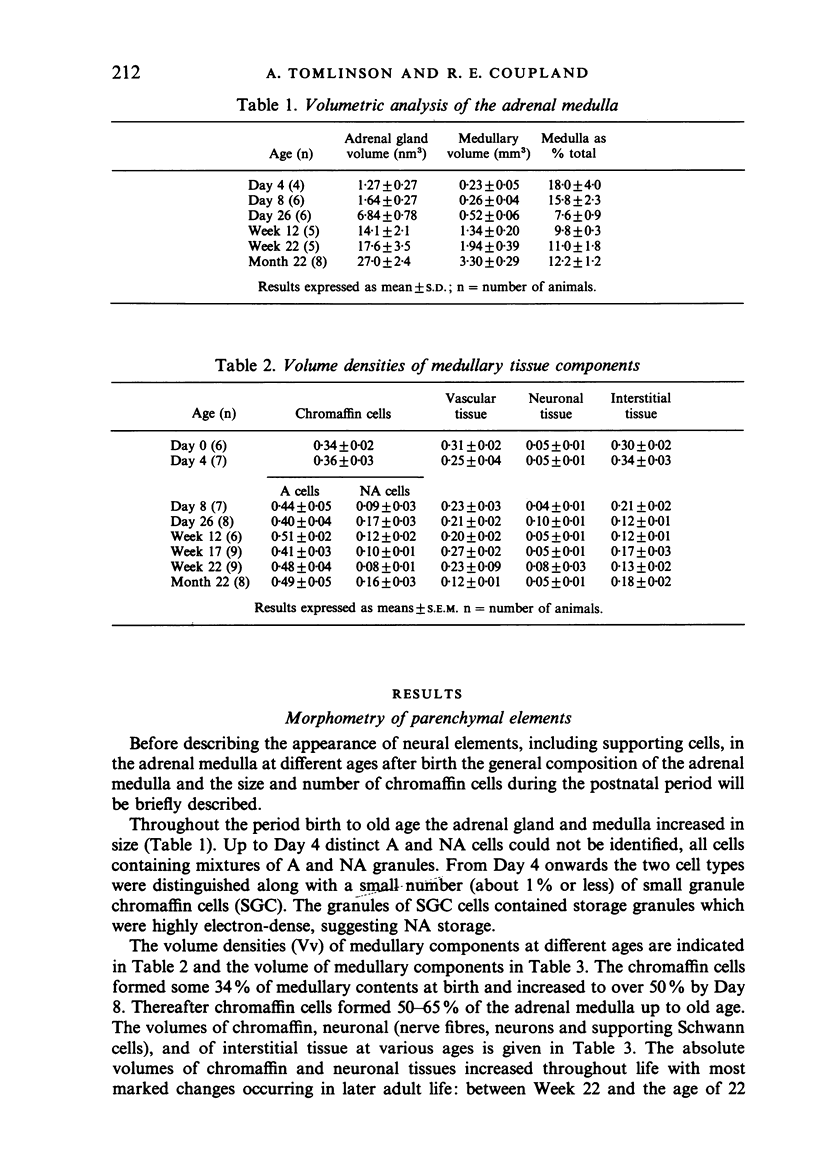
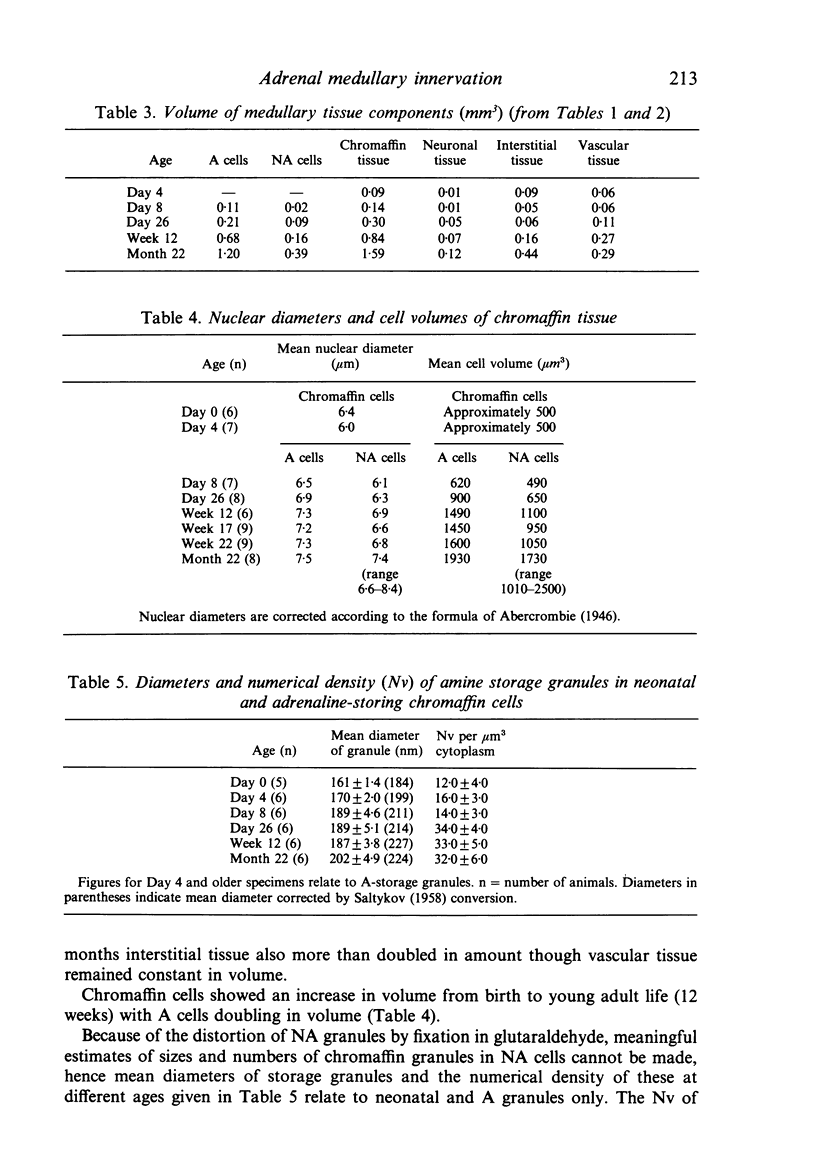
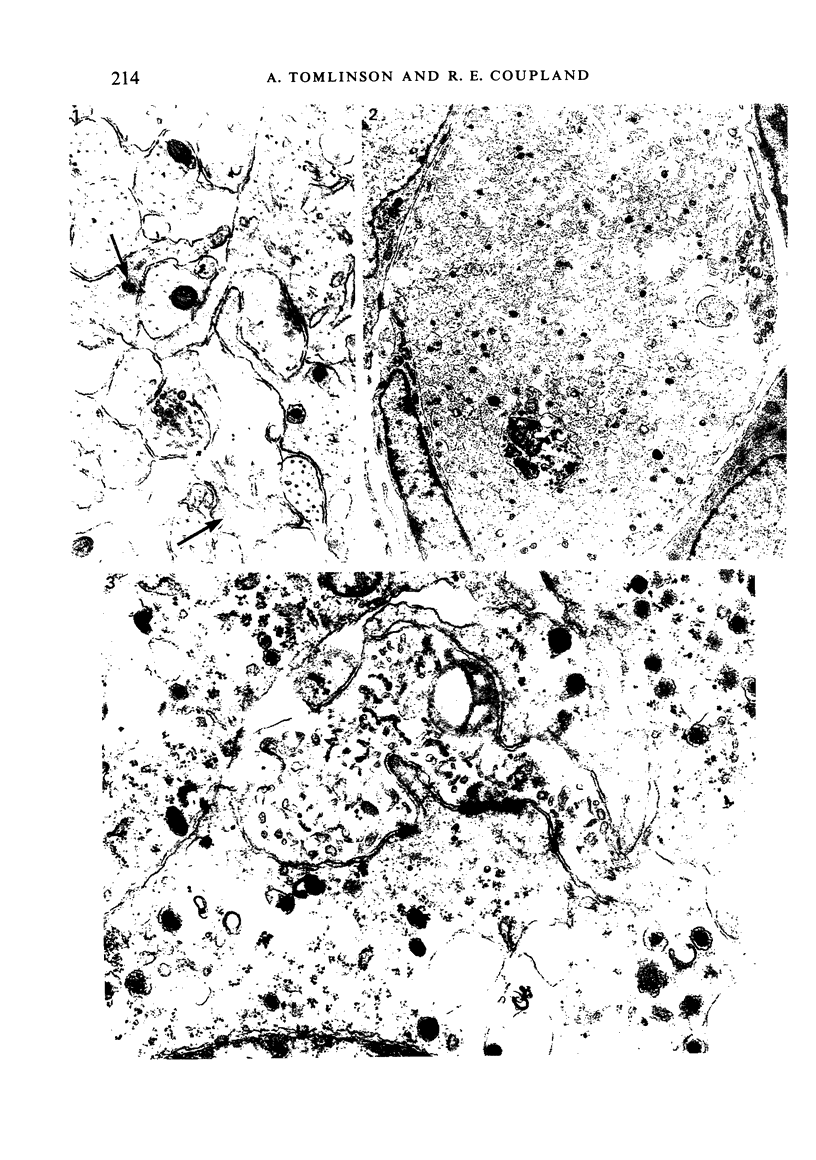
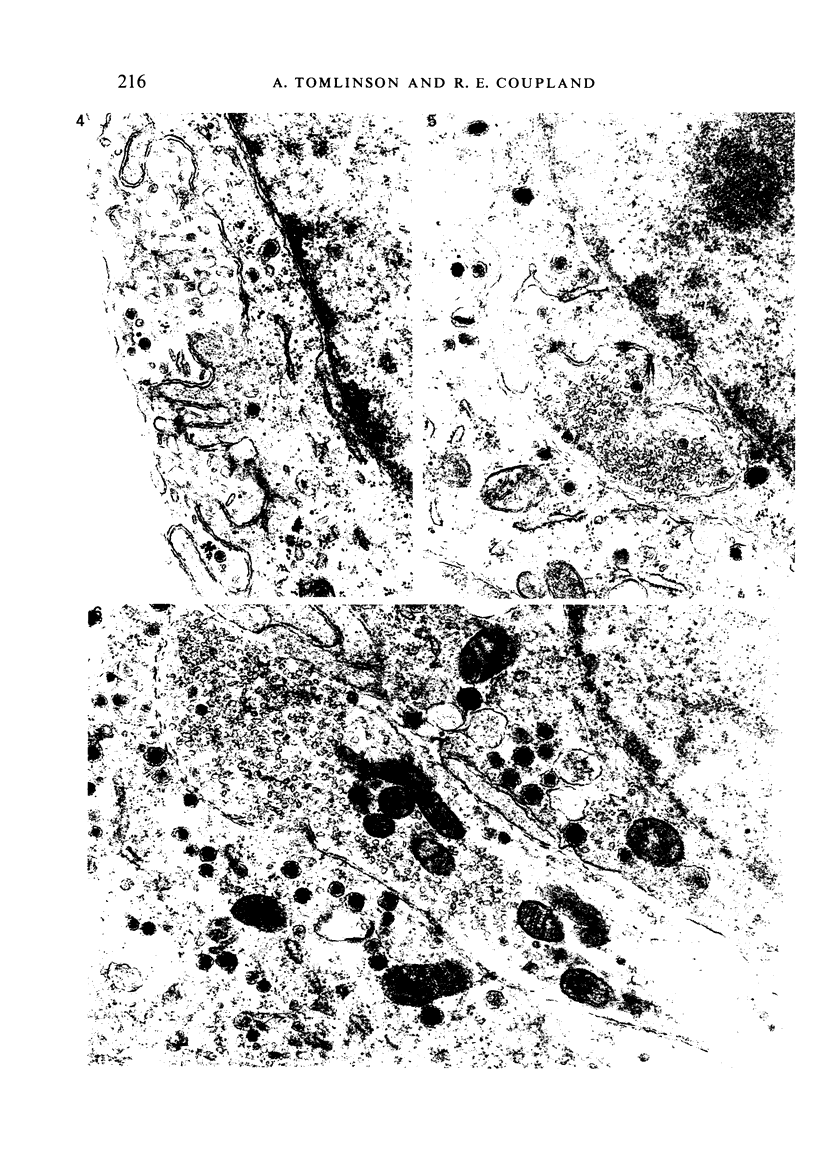
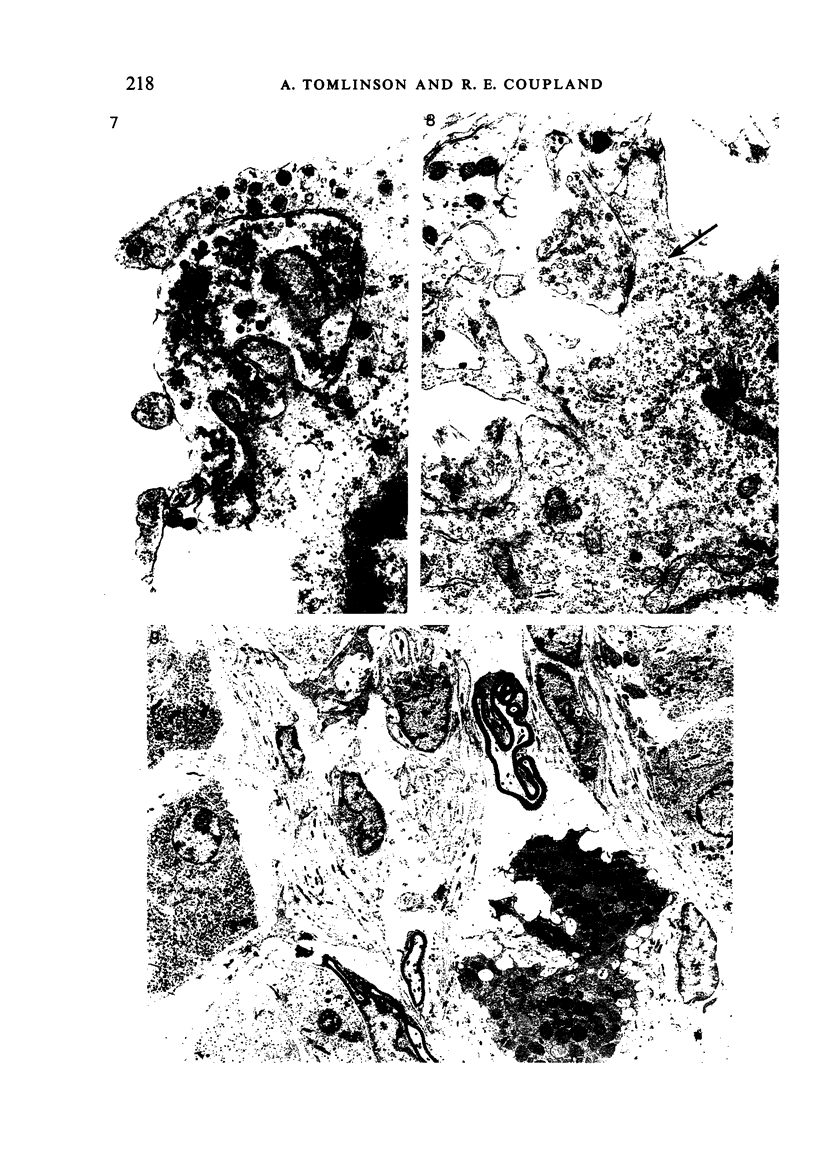
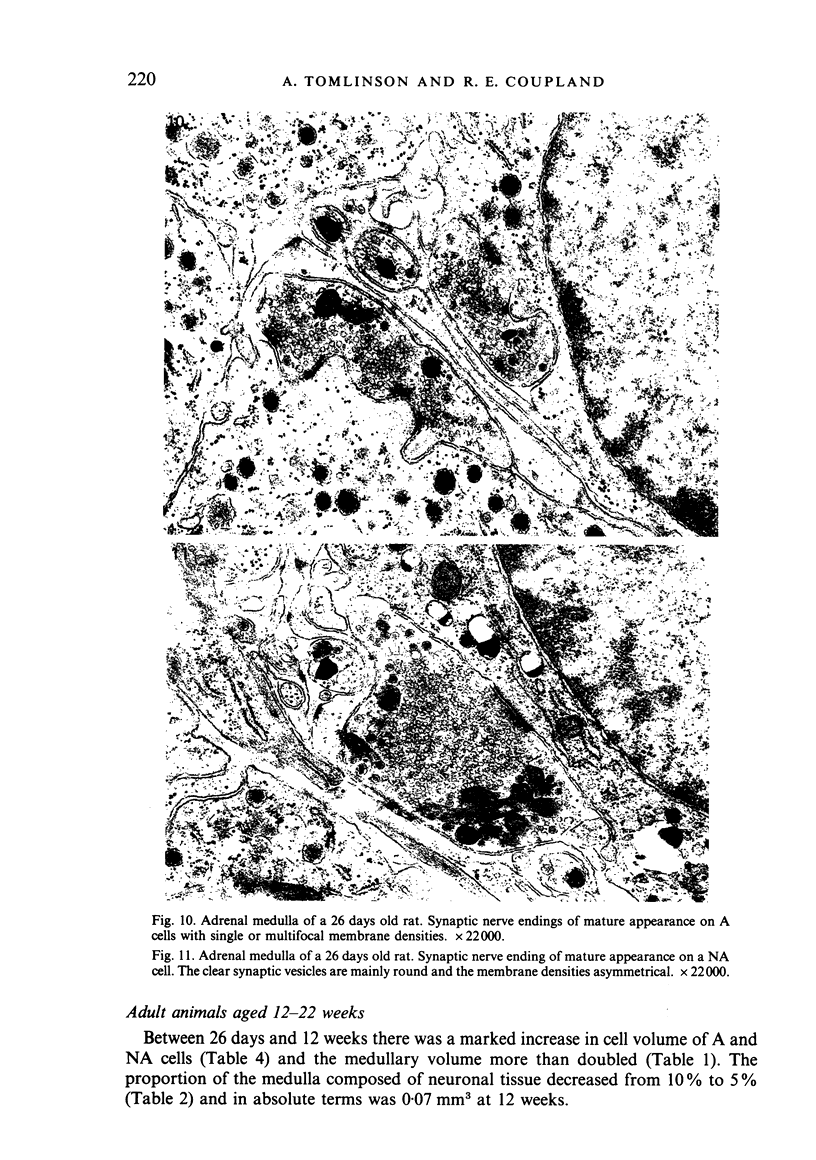
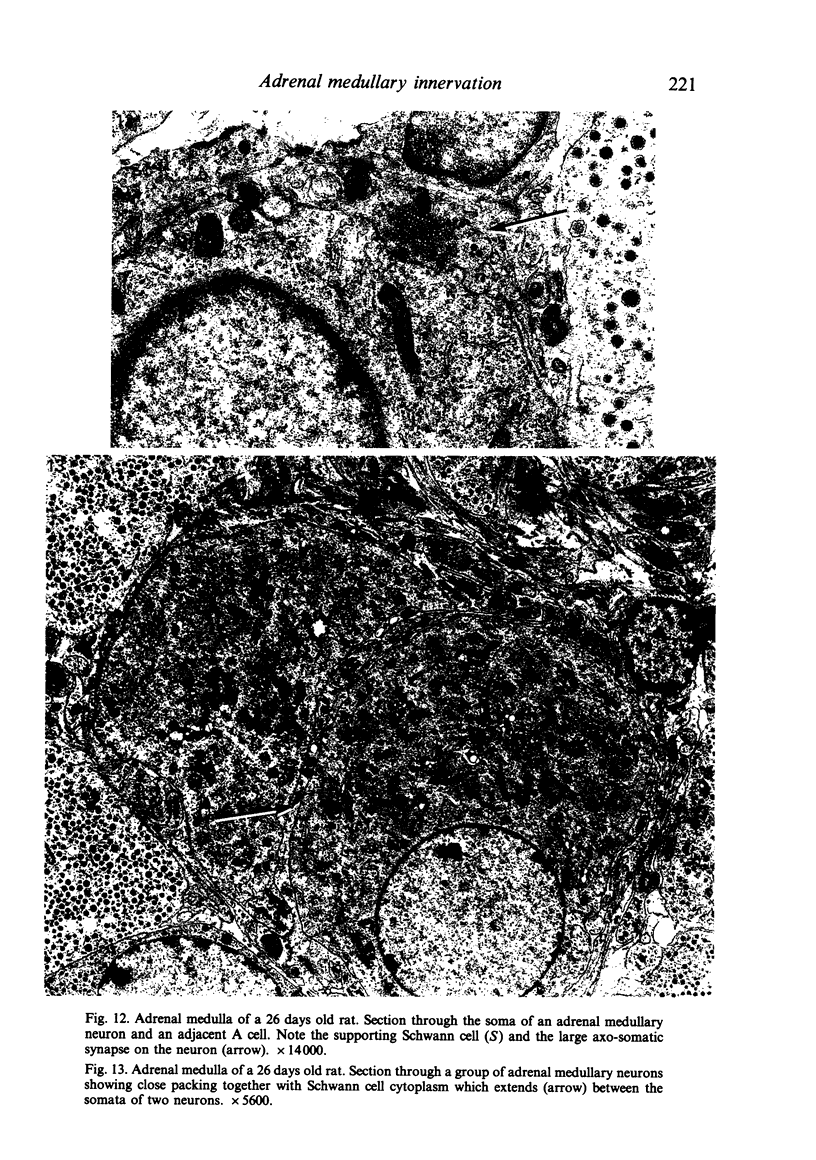
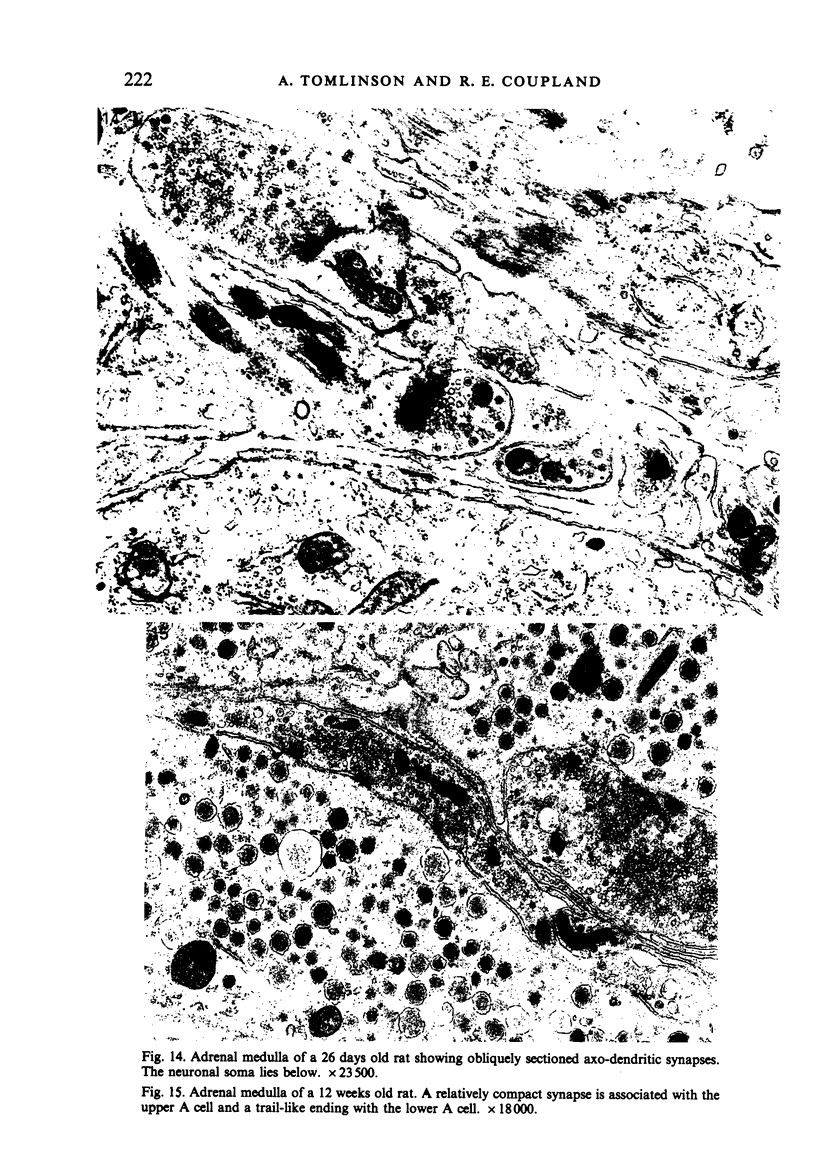
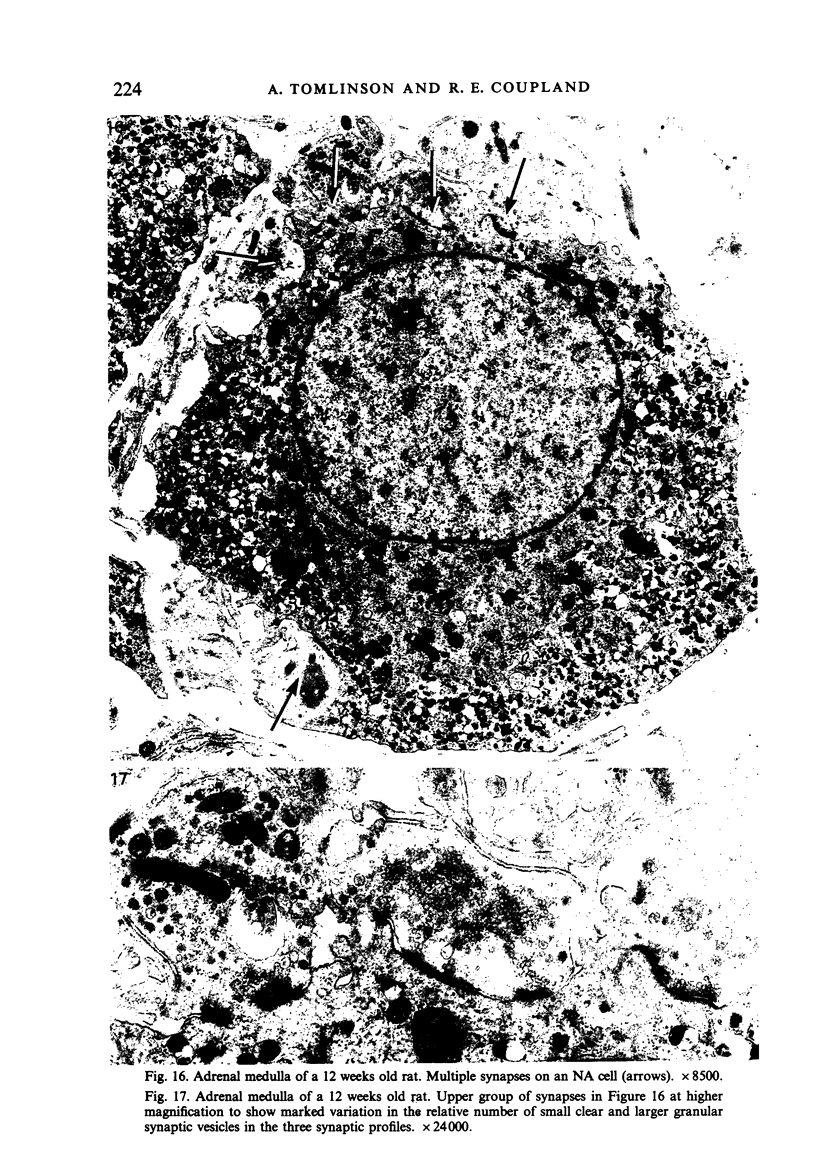
The innervation of the adrenal medulla has been investigated in normal Wistar rats from birth to old age and ultrastructural findings compared with biochemical markers of the cholinergic innervation of the adrenal gland and catecholamine storage. Morphological evidence of the immaturity of the innervation during the first postnatal week is provided and using quantitative morphometry the innervation of chromaffin cells is shown to reach a mean total of 5.4 synapses per chromaffin cell during the period 26 days to 12 weeks of age. The variation in contents of synaptic profiles is discussed in the light of recent work that demonstrates a major sensory as well as visceral efferent innervation of the gland. Adrenal medullary neurons usually occur in closely packed groups, intimately associated with Schwann cells. Axodendritic and axosomatic synapses on these neurons are described and the likely origin of axonal processes innervating the neurons discussed. In old age the density of innervation remains the same as in young adult animals even though the medulla shows evidence of hyperplasia and hypertrophy of individual chromaffin cells.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COUPLAND R. E. (ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE RAT ADRENAL MEDULLA. I. THE ULTRASTRUCTURE AND ORGANIZATION OF CHROMAFFIN CELLS IN THE NORMAL ADRENAL MEDULLA.) J Anat. 1965 Apr;99:231–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUPLAND R. E., HOLMES R. L. The distribution of cholinesterase in the adrenal glands of the rat, cat and rabbit. J Physiol. 1958 Apr 3;141(1):97–106. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
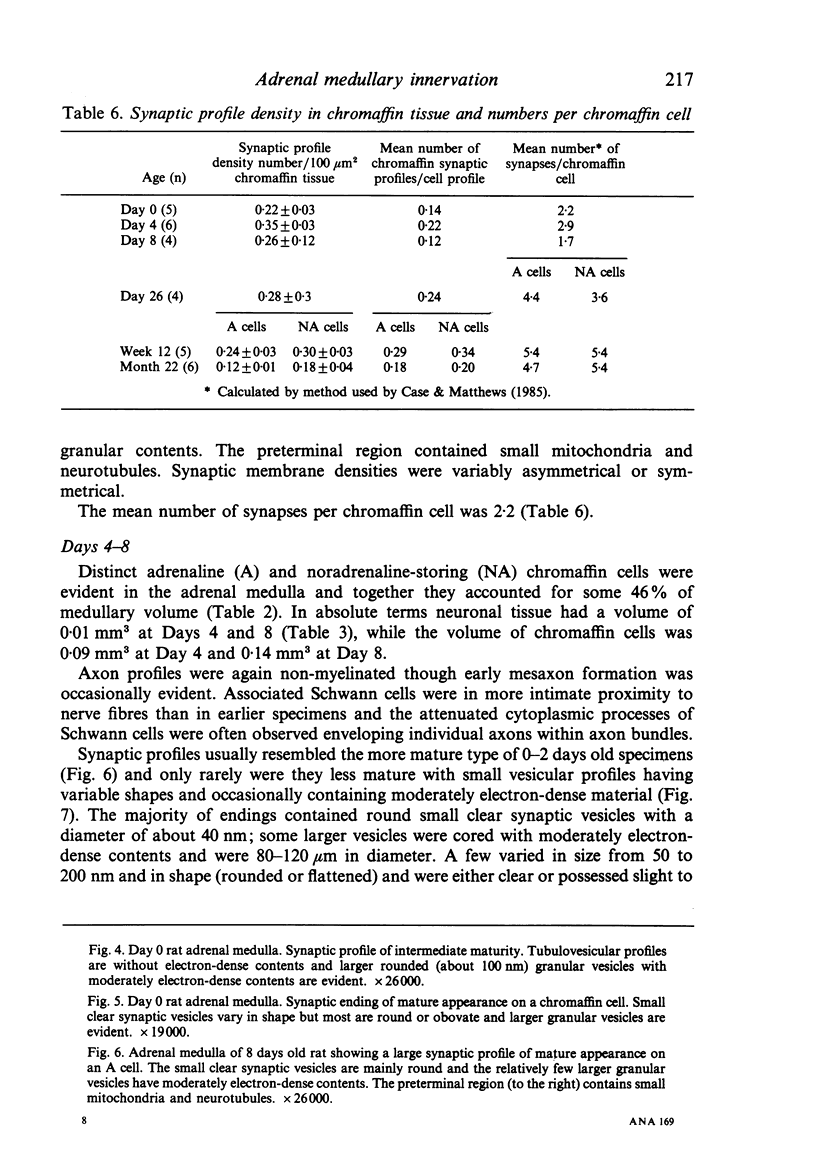
- Case C. P., Matthews M. R. A quantitative study of structural features, synapses and nearest-neighbour relationships of small, granule-containing cells in the rat superior cervical sympathetic ganglion at various adult stages. Neuroscience. 1985 May;15(1):237–282. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E. Electron microscopic observations on the structure of the rat adrenal medulla: II. Normal innervation. J Anat. 1965 Apr;99(Pt 2):255–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Parker T. L., Kesse W. K., Mohamed A. A. The innervation of the adrenal gland. III. Vagal innervation. J Anat. 1989 Apr;163:173–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Tomlinson A. The development and maturation of adrenal medullary chromaffin cells of the rat in vivo: a descriptive and quantitative study. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1989;7(5):419–438. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(89)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Weakley B. S. Developing chromaffin tissue in the rabbit: an electron microscopic study. J Anat. 1968 Mar;102(Pt 3):425–455. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daikoku S., Kinutani M., Sako M. Development of the adrenal medullary cells in rats with reference to synaptogenesis. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Mar 30;179(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00278463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. R. The control of the suprarenal glands by the splanchnic nerves. J Physiol. 1912 Jul 15;44(5-6):374–409. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1912.sp001521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. R. The innervation of the adrenal glands. J Physiol. 1913 Jun 19;46(3):285–290. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1913.sp001591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Minz B., Tsudzimura H. The mechanism of the nervous discharge of adrenaline. J Physiol. 1934 Jun 9;81(3):286–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1934.sp003136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. A rapid radiochemical method for the determination of choline acetyltransferase. J Neurochem. 1975 Feb;24(2):407–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb11895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynszpan-Winograd O. Adrenaline and noradrenaline cells in the adrenal medulla of the hamster: a morphological study of their innervation. J Neurocytol. 1974 Aug;3(3):341–361. doi: 10.1007/BF01097918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen H. J., Osterby R. Optimizing sampling efficiency of stereological studies in biology: or 'do more less well!'. J Microsc. 1981 Jan;121(Pt 1):65–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1981.tb01199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hervonen A., Korkala O. The effect of hypoxia on the catecholamine content of human fetal abdominal paraganglia and adrenal medulla. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1972;51(1):17–24. doi: 10.3109/00016347209154963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzwarth M. A. The distribution of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the rat adrenal cortex and medulla. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1984 Nov;11(3):269–283. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(84)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Sato A., Sato Y., Suzuki H. Increases in adrenal catecholamine secretion and adrenal sympathetic nerve unitary activities with aging in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Sep 12;69(3):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90491-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. M., Black I. B. Expression and regulation of catecholaminergic traits in primary sensory neurons: relationship to target innervation in vivo. J Neurosci. 1986 Apr;6(4):983–989. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-04-00983.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent C., Coupland R. E. Localisation of chromogranin A and B, met-enkephalin-arg6-gly7-leu8 and PGP9.5-like immunoreactivity in the developing and adult rat adrenal medulla and extra-adrenal chromaffin tissue. J Anat. 1989 Oct;166:213–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesse W. K., Parker T. L., Coupland R. E. The innervation of the adrenal gland. I. The source of pre- and postganglionic nerve fibres to the rat adrenal gland. J Anat. 1988 Apr;157:33–41. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil Z., Livett B. G., Marley P. D. Sensory fibres modulate histamine-induced catecholamine secretion from the rat adrenal medulla and sympathetic nerves. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:511–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil Z., Livett B. G., Marley P. D. The role of sensory fibres in the rat splanchnic nerve in the regulation of adrenal medullary secretion during stress. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:201–215. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil Z., Marley P. D., Livett B. G. Neonatal capsaicin treatment prevents insulin-stress-induced adrenal catecholamine secretion in vivo: possible involvement of sensory nerves containing substance P. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Mar 9;45(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90330-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Coupland R. F. Two populations of microvesicles in the SGC (small granule chromaffin) cells of the mouse adrenal medulla. Arch Histol Jpn. 1977 Jun;40(3):251–259. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.40.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc G., Landis S. Development of choline acetyltransferase (CAT) in the sympathetic innervation of rat sweat glands. J Neurosci. 1986 Jan;6(1):260–265. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-01-00260.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. R., Shute C. C. An electron-microscopic study of cholinesterase distribution in the rat adrenal medulla. J Microsc. 1969;89(2):181–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1969.tb00664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed A. A., Parker T. L., Coupland R. E. The innervation of the adrenal gland. II. The source of spinal afferent nerve fibres to the guinea-pig adrenal gland. J Anat. 1988 Oct;160:51–58. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratzenhofer M., Müller O. Ultrastructure of adrenal medulla of the prenatal rat. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1967 Aug;18(1):13–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm L. P., Adair J. R., Stribling J. M., Gray L. P. Preganglionic innervation of the adrenal gland of the rat: a study using horseradish peroxidase. Exp Neurol. 1975 Nov;49(2):540–553. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(75)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. G., Evoniuk G., Poston C. W., Mills E. Relation between functional maturation of cervical sympathetic innervation and ontogeny of alpha-noradrenergic smooth muscle contraction in the rat. Neuroscience. 1983 Mar;8(3):609–616. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Mueller R. A., Axelrod J. Trans-synaptic induction of adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Oct;169(2):249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Durbin J., Coupland R. E. A quantitative analysis of rat adrenal chromaffin tissue: morphometric analysis at tissue and cellular level correlated with catecholamine content. Neuroscience. 1987 Mar;20(3):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90250-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson D. R., Moriarty R. J., Mayer J. H. Prevention and reversal of defective axonal transport and motor nerve conduction velocity in rats with experimental diabetes by treatment with the aldose reductase inhibitor Sorbinil. Diabetes. 1984 May;33(5):470–476. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.5.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhofstad A. A., Coupland R. E., Parker T. R., Goldstein M. Immunohistochemical and biochemical study on the development of the noradrenaline- and adrenaline-storing cells of the adrenal medulla of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;242(2):233–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00214536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Dalnok G. K., Menssen H. D. A quantitative electron microscopic study of the effect of glucocorticoids in vivo on the early postnatal differentiation of paraneuronal cells in the carotid body and the adrenal medulla of the rat. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1986;174(3):307–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00698781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]