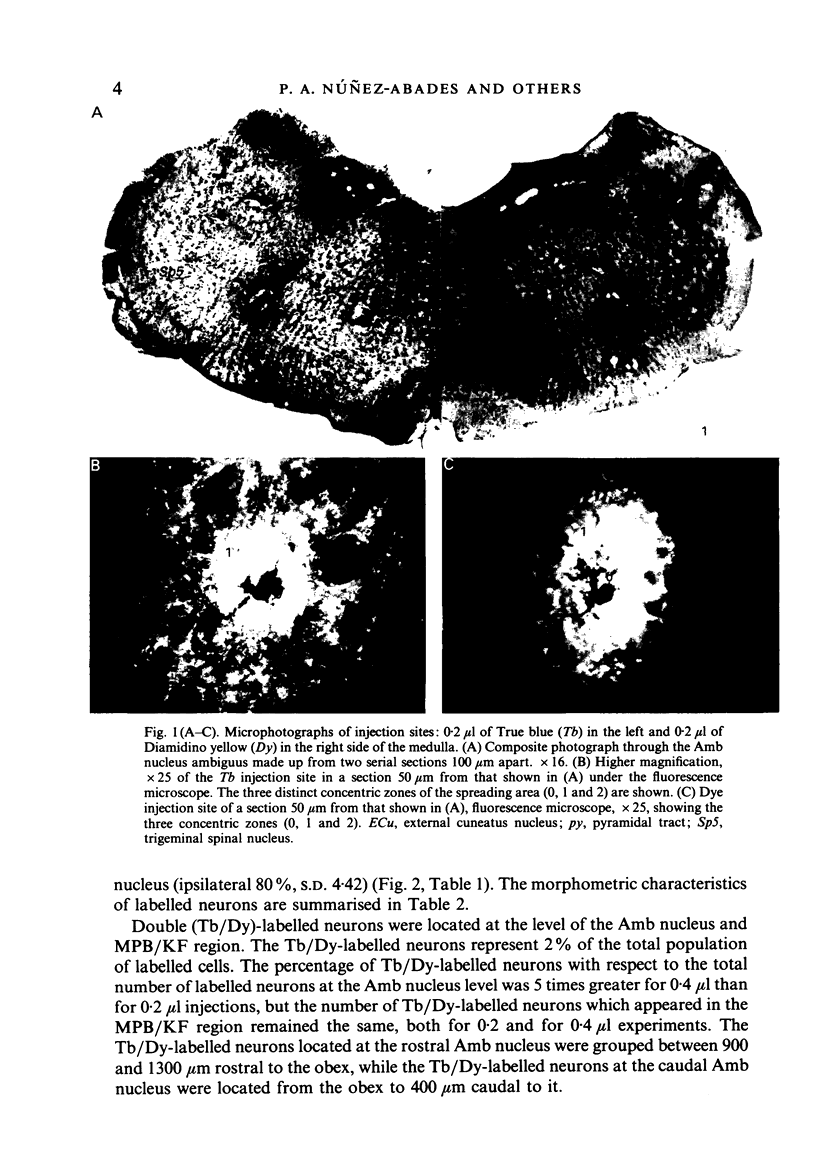
Abstract
The rat nucleus ambiguus (Amb nucleus) is composed mainly of laryngeal and pharyngeal motoneurons, and can be differentiated into three main subdivisions with respect to the morphology, distribution and physiological function of their neurons. The medial parabrachial and Kölliker-Fuse nuclei (MPB/KF), and the lateral nucleus of the solitary tract (SolL) play a modulator role over some of the physiological functions assigned to the Amb nucleus. The location and characteristics of labelled neurons in the MPB/KF, SolL and Amb nuclei have been studied following the simultaneous and bilateral injections of True blue and Diamidino yellow in each of the three subdivisions of the Amb nucleus. All of the identified axonal projections were mainly ipsilateral. Some of the described pathways also have collaterals which connect both sides of the Amb complex.
Full text
PDF


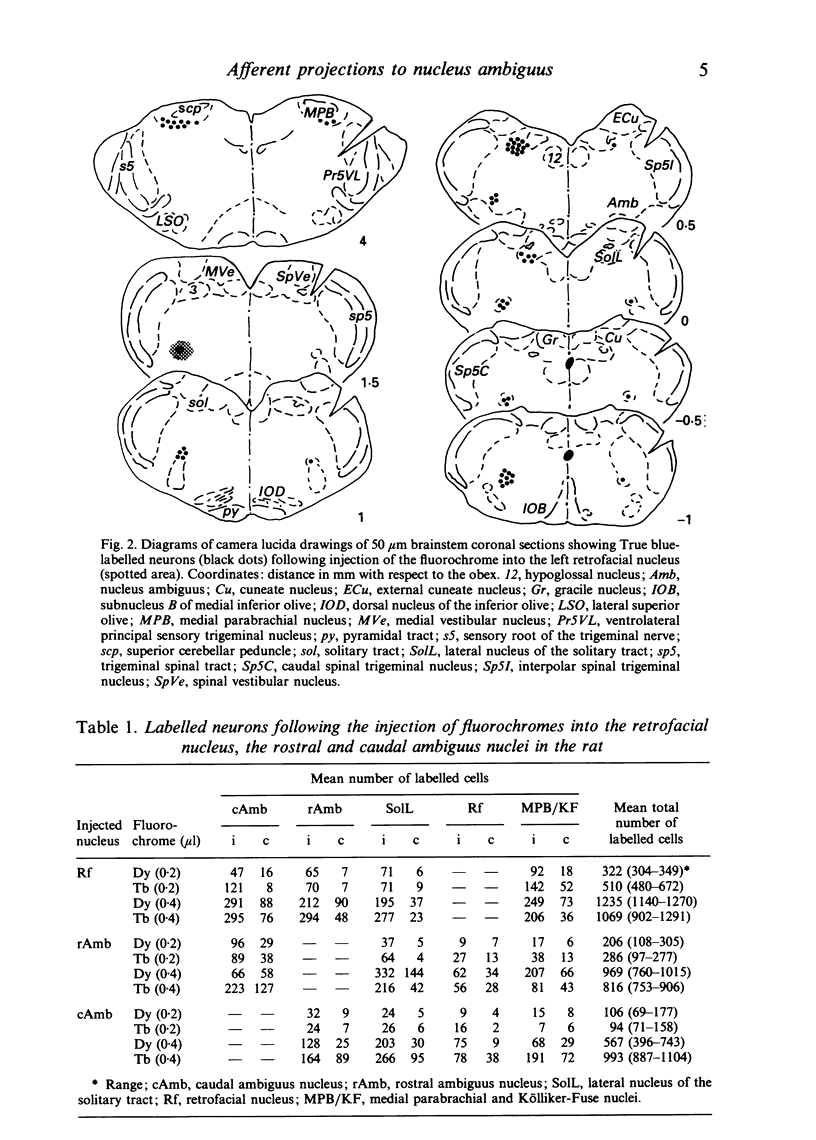
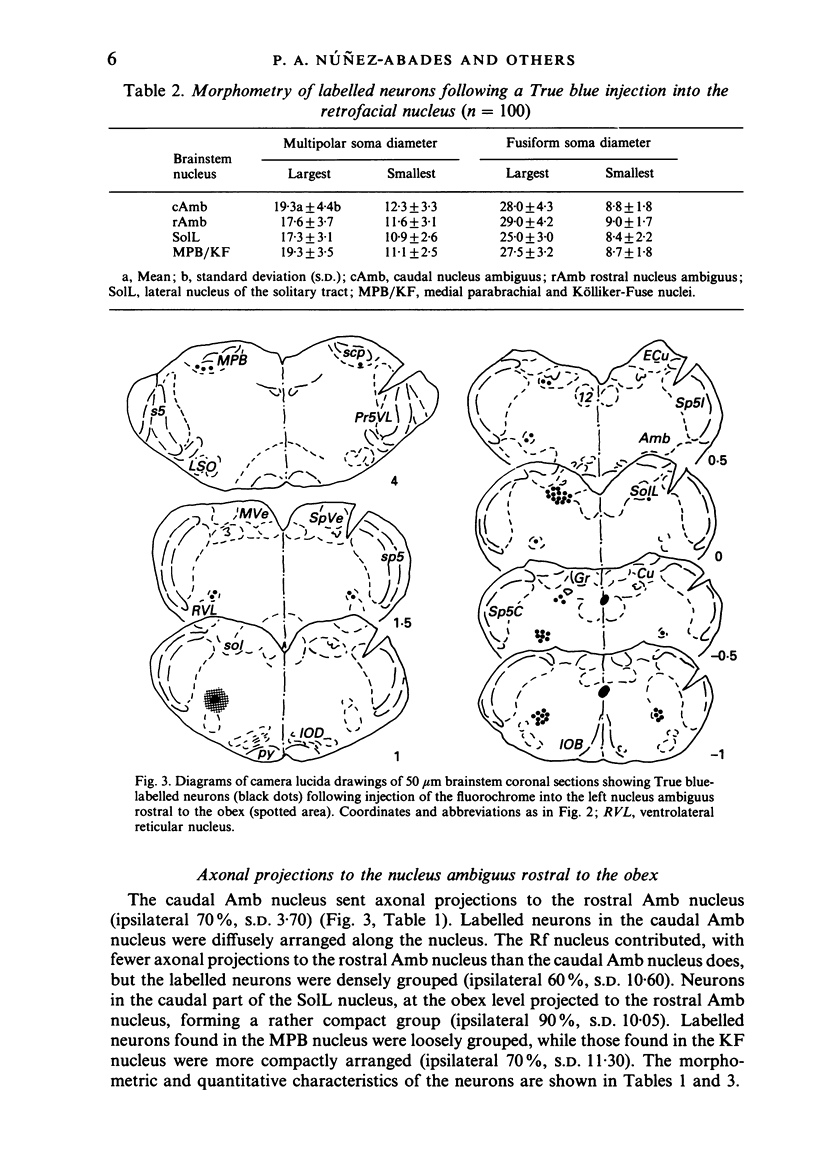
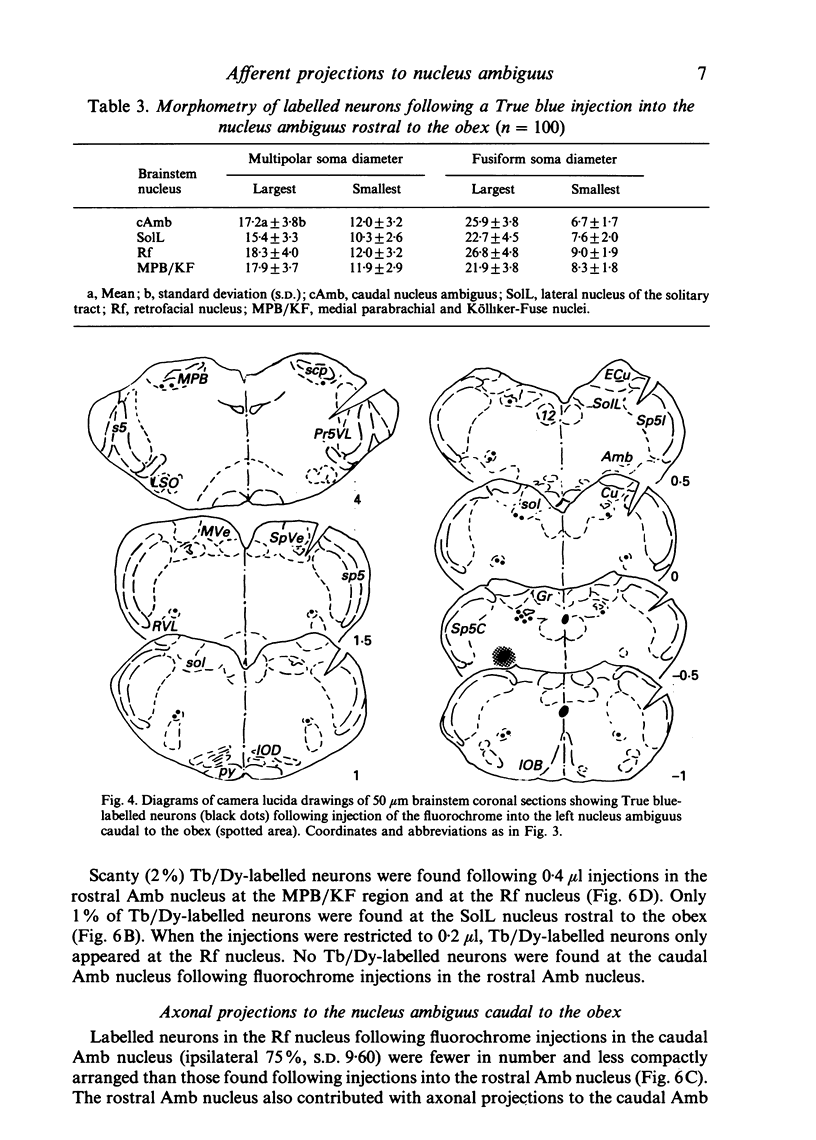

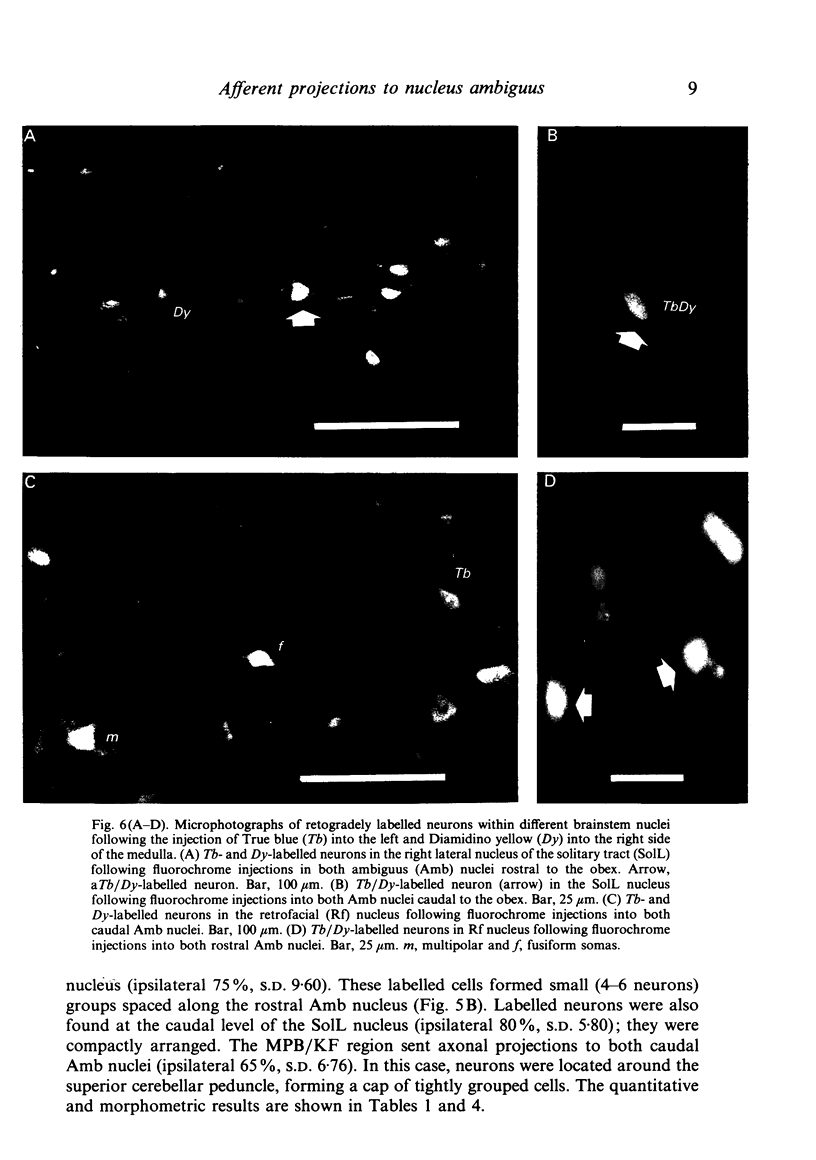






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianchi A. L., Barillot J. C. Respiratory neurons in the region of the retrofacial nucleus: pontile, medullary, spinal and vagal projections. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Aug 31;31(3):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi A. L. Localisation et étude des neurones respiratoires bulbaires. Mise en jeu antidromique par stimulation spinale ou vagale. J Physiol (Paris) 1971 Jan-Feb;63(1):5–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi A. L., St John W. M. Pontile axonal projections of medullary respiratory neurons. Respir Physiol. 1981 Aug;45(2):167–183. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(81)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieger D., Hopkins D. A. Viscerotopic representation of the upper alimentary tract in the medulla oblongata in the rat: the nucleus ambiguus. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Aug 22;262(4):546–562. doi: 10.1002/cne.902620408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bystrzycka E. K. Afferent projections to the dorsal and ventral respiratory nuclei in the medulla oblongata of the cat studied by the horseradish peroxidase technique. Brain Res. 1980 Mar 3;185(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90670-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coil J. D., Norgren R. Cells of origin of motor axons in the subdiaphragmatic vagus of the rat. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1979 Dec;1(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(79)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condé F. Further studies on the use of the fluorescent tracers fast blue and diamidino yellow: effective uptake area and cellular storage sites. J Neurosci Methods. 1987 Sep;21(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(87)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R. J., Gomez M. M., Norgren R. Central origins of cranial nerve parasympathetic neurons in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Mar 15;190(2):373–394. doi: 10.1002/cne.901900211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dampney R. A., Goodchild A. K., Robertson L. G., Montgomery W. Role of ventrolateral medulla in vasomotor regulation: a correlative anatomical and physiological study. Brain Res. 1982 Oct 14;249(2):223–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. J., Nail B. S. On the location and size of laryngeal motoneurons in the cat and rabbit. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Nov 20;230(1):13–32. doi: 10.1002/cne.902300103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezure K., Manabe M., Yamada H. Distribution of medullary respiratory neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1988 Jul 12;455(2):262–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorko L., Merrill E. G. Axonal projections from the rostral expiratory neurones of the Bötzinger complex to medulla and spinal cord in the cat. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:487–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman J. L., Speck D. F. Interactions among inspiratory neurons in dorsal and ventral respiratory groups in cat medulla. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Feb;49(2):472–490. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.49.2.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulwiler C. E., Saper C. B. Subnuclear organization of the efferent connections of the parabrachial nucleus in the rat. Brain Res. 1984 Aug;319(3):229–259. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilaire G., Monteau R., Bianchi A. L. A cross-correlation study of interactions among respiratory neurons of dorsal, ventral and retrofacial groups in cat medulla. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 4;302(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91281-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikawa K., Powell E. W. Comparison of techniques for retrograde labeling using the rat's facial nucleus. J Neurosci Methods. 1986 Sep;17(4):287–296. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(86)90129-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. R., Tabatabai M. Localization of the medullary respiratory neurons in rats by microelectrode recording. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Nov;39(5):812–817. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Sullivan J. M. Brainstem projections of sensory and motor components of the vagus nerve in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Nov 1;211(3):248–265. doi: 10.1002/cne.902110304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karczewski W. A., Gromysz H. The significance of species differences in respiratory neurophysiology-the split-brainstem preparation. Experientia. 1982 Jul 15;38(7):826–827. doi: 10.1007/BF01972295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keizer K., Kuypers H. G., Huisman A. M., Dann O. Diamidino yellow dihydrochloride (DY . 2HCl); a new fluorescent retrograde neuronal tracer, which migrates only very slowly out of the cell. Exp Brain Res. 1983;51(2):179–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00237193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers H. G., Bentivoglio M., Catsman-Berrevoets C. E., Bharos A. T. Double retrograde neuronal labeling through divergent axon collaterals, using two fluorescent tracers with the same excitation wavelength which label different features of the cell. Exp Brain Res. 1980;40(4):383–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00236147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey B. G., Segers L. S., Shannon R. Functional associations among simultaneously monitored lateral medullary respiratory neurons in the cat. II. Evidence for inhibitory actions of expiratory neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Apr;57(4):1101–1117. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.4.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewy A. D. Descending pathways to sympathetic and parasympathetic preganglionic neurons. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1981 Apr;3(2-4):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(81)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. E., Duffin J. The medullary respiratory neurons: a review. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1984 Feb;62(2):161–182. doi: 10.1139/y84-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill E. G. The lateral respiratory neurones of the medulla: their associations with nucleus ambiguus, nucleus retroambigualis, the spinal accessory nucleus and the spinal cord. Brain Res. 1970 Nov 11;24(1):11–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill E. G. Where are the real respiratory neurons? Fed Proc. 1981 Jul;40(9):2389–2394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgren R. Projections from the nucleus of the solitary tract in the rat. Neuroscience. 1978;3(2):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ONDINA D. M., YAMAMOTO W. S., MASLAND W. S. Respiratory centers in the albino rat. Am J Physiol. 1960 Feb;198:389–392. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.2.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otake K., Sasaki H., Ezure K., Manabe M. Axonal projections from Bötzinger expiratory neurons to contralateral ventral and dorsal respiratory groups in the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1988;72(1):167–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00248512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otake K., Sasaki H., Mannen H., Ezure K. Morphology of expiratory neurons of the Bötzinger complex: an HRP study in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Apr 22;258(4):565–579. doi: 10.1002/cne.902580407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portillo F., Pásaro R. Location of bulbospinal neurons and of laryngeal motoneurons within the nucleus ambiguus of the rat and cat by means of retrograde fluorescent labelling. J Anat. 1988 Aug;159:11–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portillo F., Pásaro R. Location of motoneurons supplying the intrinsic laryngeal muscles of rats. Horseradish peroxidase and fluorescence double-labeling study. Brain Behav Evol. 1988;32(4):220–225. doi: 10.1159/000116549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pásaro R., Lobera B., González-Barón S., Delgado-García J. M. Cytoarchitectonic organization of laryngeal motoneurons within the nucleus ambiguus of the cat. Exp Neurol. 1983 Dec;82(3):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(83)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. W., Camerer H., Meesmann M., Röhrig N. Studies on the synaptic interconnection between bulbar respiratory neurones of cats. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Jul;380(3):245–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00582903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Ruggiero D. A., Reis D. J. Projections from the nucleus tractus solitarii to the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Dec 22;242(4):511–534. doi: 10.1002/cne.902420405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saether K., Hilaire G., Monteau R. Dorsal and ventral respiratory groups of neurons in the medulla of the rat. Brain Res. 1987 Sep 1;419(1-2):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90571-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saper C. B., Loewy A. D. Efferent connections of the parabrachial nucleus in the rat. Brain Res. 1980 Sep 22;197(2):291–317. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segers L. S., Shannon R., Lindsey B. G. Interactions between rostral pontine and ventral medullary respiratory neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Aug;54(2):318–334. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.2.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segers L. S., Shannon R., Saporta S., Lindsey B. G. Functional associations among simultaneously monitored lateral medullary respiratory neurons in the cat. I. Evidence for excitatory and inhibitory actions of inspiratory neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Apr;57(4):1078–1100. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.4.1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi Y., Uemura M., Matsuda K., Matsushima R., Mizuno N. Parabrachial nucleus neurons projecting to the lower brain stem and the spinal cord. A study in the cat by the Fink-Heimer and the horseradish peroxidase methods. Exp Neurol. 1980 Nov;70(2):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(80)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers J. B., Norgren R. Afferent projections to the oral motor nuclei in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Nov 1;220(3):280–298. doi: 10.1002/cne.902200303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Ezure K., Manabe M. Efferent projections of inspiratory neurons of the ventral respiratory group. A dual labeling study in the rat. Brain Res. 1988 Jul 12;455(2):283–294. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Horst G. J., Luiten P. G., Kuipers F. Descending pathways from hypothalamus to dorsal motor vagus and ambiguus nuclei in the rat. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1984 Jul;11(1):59–75. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(84)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]