Full text
PDF

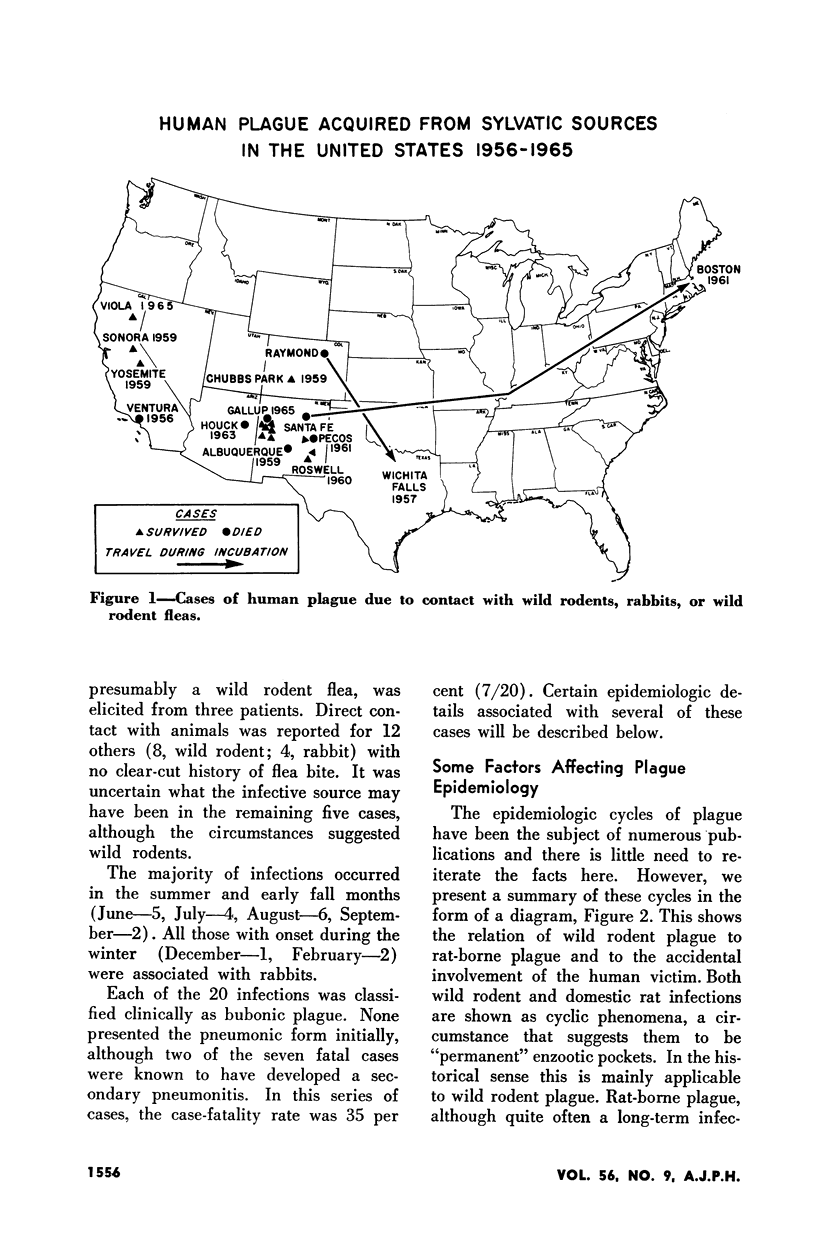
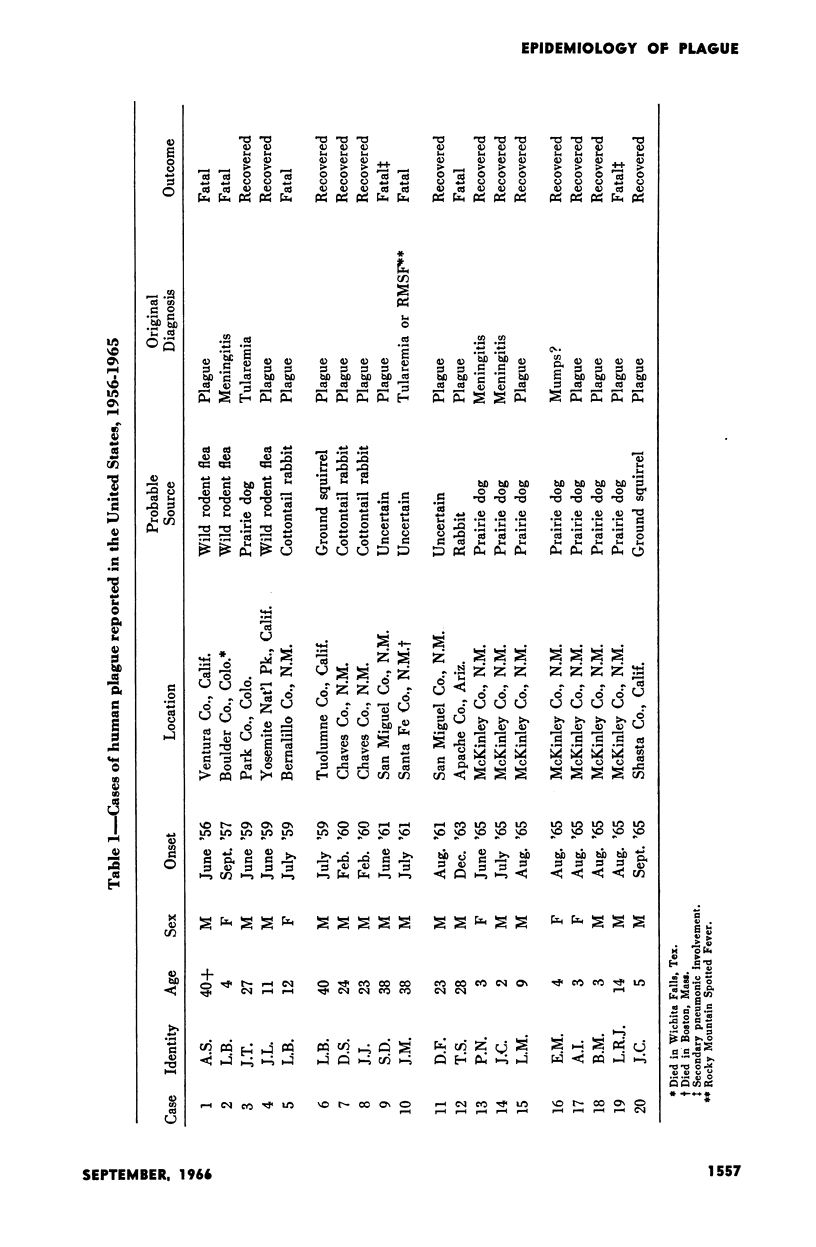
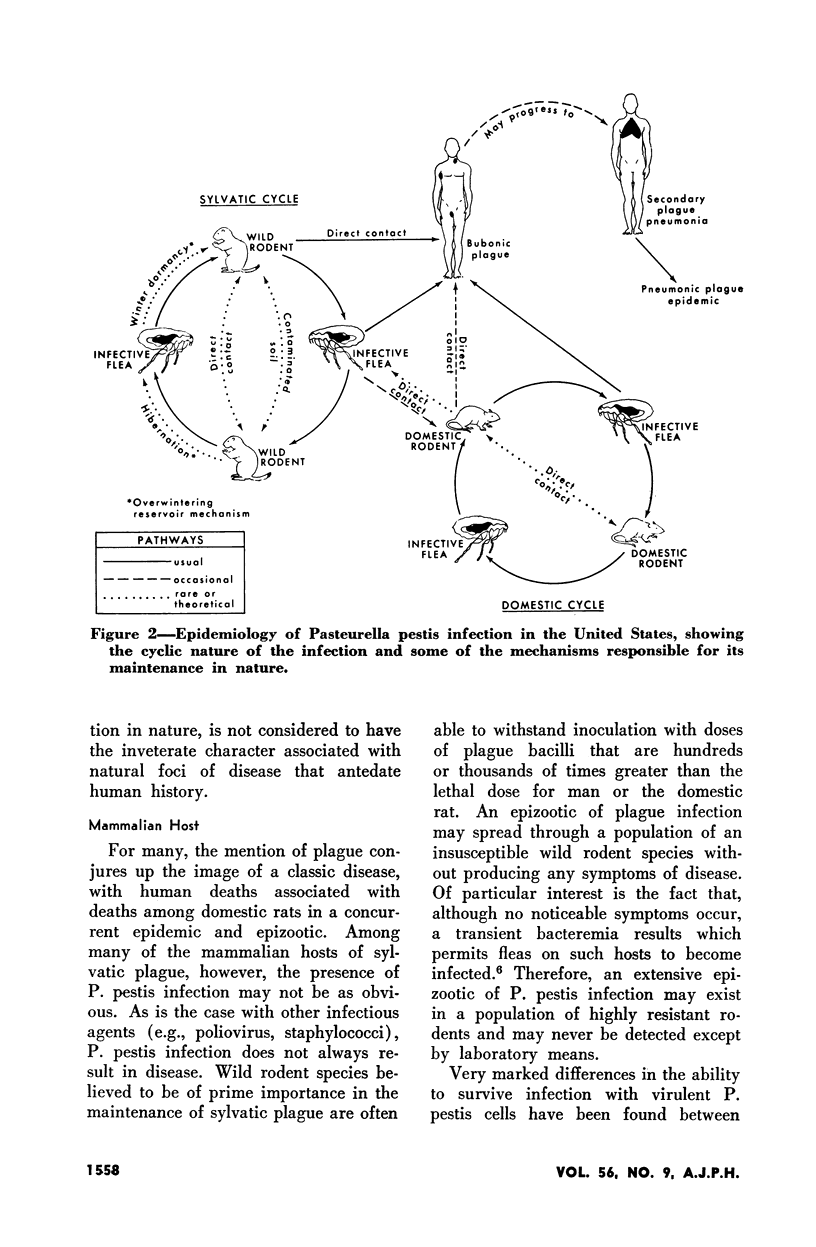











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACON G. A., BURROWS T. W. The basis of virulence in Pasteurella pestis: an antigen determining virulence. Br J Exp Pathol. 1956 Oct;37(5):481–493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAKER E. E., SOMMER H., FOSTER L. E., MEYER E., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. I. The isolation and characterization of the soluble antigen of Pasteurella pestis. J Immunol. 1952 Feb;68(2):131–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTAZARD M., KARIMI Y., EFTEKHARI M., CHAMSA M., MOLLARET H. H. LA CONSERVATION INTER'EPIZOOTIQUE DE LA PESTE EN FOYER INV'ET'ER'E. HYPOTH'ESES DE TRAVAIL. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1963 Nov-Dec;56:1230–1245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDENBERG M. I., QUAN S. F., HUDSON B. W. THE DETECTION OF INAPPARENT INFECTIONS WITH PASTEURELLA PESTIS IN A MICROTUS CALIFORNICUS POPULATION IN THE SAN FRANCISCO BAY AREA. Zoonoses Res. 1964 Apr;3:1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTWELL W. V., SCOTT K. G., KARTMAN L. Observations on flea transfer between hosts; a mechanism in the spread on bubonic plague. Science. 1958 Apr 11;127(3302):814–814. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3302.814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDENRIED R., QUAN S. F. Susceptibility of New Mexico rodents to experimental plague. Public Health Rep. 1956 Oct;71(10):979–984. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUDSON B. W., QUAN S. F., GOLDENBERG M. I. SERUM ANTIBODY RESPONSES IN A POPULATION OF MICROTUS CALIFORNICUS AND ASSOCIATED RODENT SPECIES DURING AND AFTER PASTEURELLA PESTIS EPIZOOTICS IN THE SAN FRANCISCO BAY AREA. Zoonoses Res. 1964 Apr;3:15–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALABUKHOV N. I. [On the problem of the structure and dynamics of natural foci of plague]. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1961 May;32:81–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L., PRINCE F. M., QUAN S. F., STARK H. E. New knowledge on the ecology of sylvatic plague. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Jun 3;70(3):668–711. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb35421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L., PRINCE F. M. Studies on Pasteurella pestis in fleas. V. The experimental plague-vector efficiency of wild rodent fleas compared with Xenopsylla cheopis, together with observations on the influence of temperature. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1956 Nov;5(6):1058–1070. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1956.5.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L., QUAN S. F., LECHLEITNER R. R. Die-off of a Gunnison's prairie dog colony in central Colorado. II. Retrospective determination of plague infection in flea vectors, rodents, and man. Zoonoses Res. 1962 May 20;1:201–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L., QUAN S. F., MILES V. I. Ecological studies of wild rodent plague in the San Francisco Bay area of Californa. V. The distribution of naturally infected fleas during an epizootic in relation to their infection rates. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1960 Jan;9:96–100. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1960.9.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARTMAN L., QUAN S. F., STARK H. E. Ecological studies of wild rodent plague in the San Francisco Bay Area of California. VII. Effects of plague in nature on Microtus californicus and other wild rodents. Zoonoses Res. 1962 Jan 5;1:99–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHETTE N. J., BUSHMAN J. B., PARKER D. D., JOHNSON E. E. Studies on infectious diseases in wild animals in Utah. IV. A wild rodent (Peromyscus spp.) plague focus in Utah. Zoonoses Res. 1962 Dec 31;1:341–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCHETTE N. J., LUNDGREN D. L., NICHOLES P. S., BUSHMAN J. B., VEST D. Studies on infectious diseases in wild animals in Utah. II. Susceptibility of wild mammals to experimental plague. Zoonoses Res. 1962 Sep 20;1:225–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAYNE F. E., LARSON A., FOSTER W. L., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. IX. The effect of cortisone on mouse resistance to attenuated strains of Pasteurella pestis. J Infect Dis. 1955 Mar-Apr;96(2):168–173. doi: 10.1093/infdis/96.2.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAN S. F., KARTMAN L. Ecological studies of wild rodent plague in the San Francisco Bay Area of California. VIII. Susceptibility of wild rodents to experimental plague infection. Zoonoses Res. 1962 Jan 5;1:121–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUAN S. F., KNAPP W., GOLDENBERG M. I., HUDSON B. W., LAWTON W. D., CHEN T. H., KARTMAN L. ISOLATION OF A STRAIN OF PASTEURELLA PSEUDOTUBERCULOSIS FROM ALASKA IDENTIFIED AS PASTEURELLA PESTIS: AN IMMUNOFLUORESCENT FALSE POSITIVE. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1965 May;14:424–432. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1965.14.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL' Iu M., FEDOROV V. N. [On the problem of the physiological evaluation of rodents as carriers of plague and the onehost concept of its natural foci]. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1960 Feb;31:29–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUST J. H., Jr, CAVANAUGH D. C., KADIS S., AJL S. J. PLAGUE TOXIN: ITS EFFECT IN VITRO AND IN VIVO. Science. 1963 Oct 18;142(3590):408–409. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3590.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surgalla M. J. Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis information as background for understanding plague. Public Health Rep. 1965 Sep;80(9):825–828. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORPE B. D., MARCHETTE N. J., BUSHMAN J. B. Virulence studies of Pasteurella pestis isolates from the Great Salt Lake Desert. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1963 Mar;12:219–222. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1963.12.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER C. C., CHERRY W. B., MOODY M. D. An unusual strain of Pasteurella pestis isolated from a fatal human case of plague. Bull World Health Organ. 1960;23:408–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


