Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gale E. F., Epps H. M. Studies on bacterial amino-acid decarboxylases: 1. l(+)-lysine decarboxylase. Biochem J. 1944;38(3):232–242. doi: 10.1042/bj0380232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale E. F. Studies on bacterial amino-acid decarboxylases: 5. The use of specific decarboxylase preparations in the estimation of amino-acids and in protein analysis. Biochem J. 1945;39(1):46–52. doi: 10.1042/bj0390046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hills G. M. Ammonia production by pathogenic bacteria. Biochem J. 1940 Jul;34(7):1057–1069. doi: 10.1042/bj0341057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
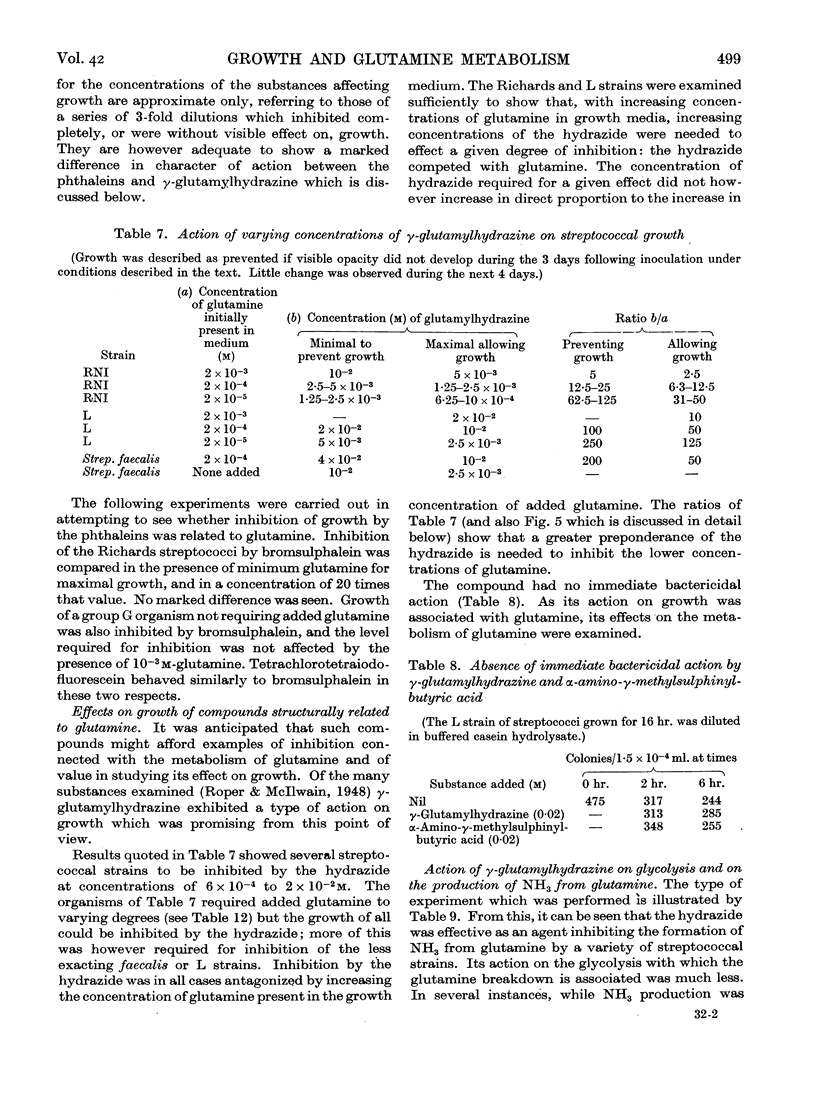
- McIlwain H., Fildes P., Gladstone G. P., Knight B. C. Glutamine and the growth of Streptococcus haemolyticus. Biochem J. 1939 Feb;33(2):223–229. doi: 10.1042/bj0330223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlwain H., Hughes D. E. Biochemical characterization of the actions of chemotherapeutic agents: 2. A reaction of haemolytic streptococci, involving pantothenate-usage, inhibited by pantoyltaurine, and associated with carbohydrate metabolism. Biochem J. 1944;38(2):187–195. doi: 10.1042/bj0380187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
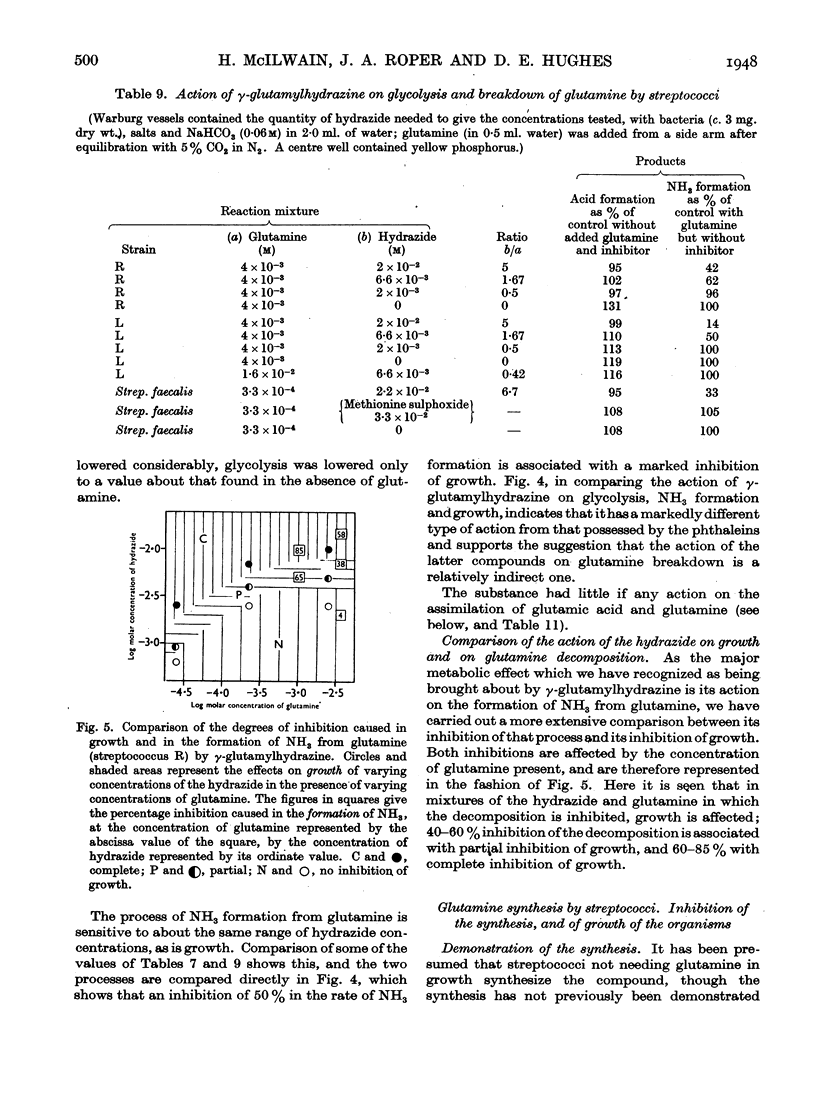
- McIlwain H. The metabolism and functioning of vitamin-like compounds: 1. Ammonia formation from glutamine by haemolytic streptococci; its reciprocal connexion with glycolysis. Biochem J. 1946;40(1):67–78. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
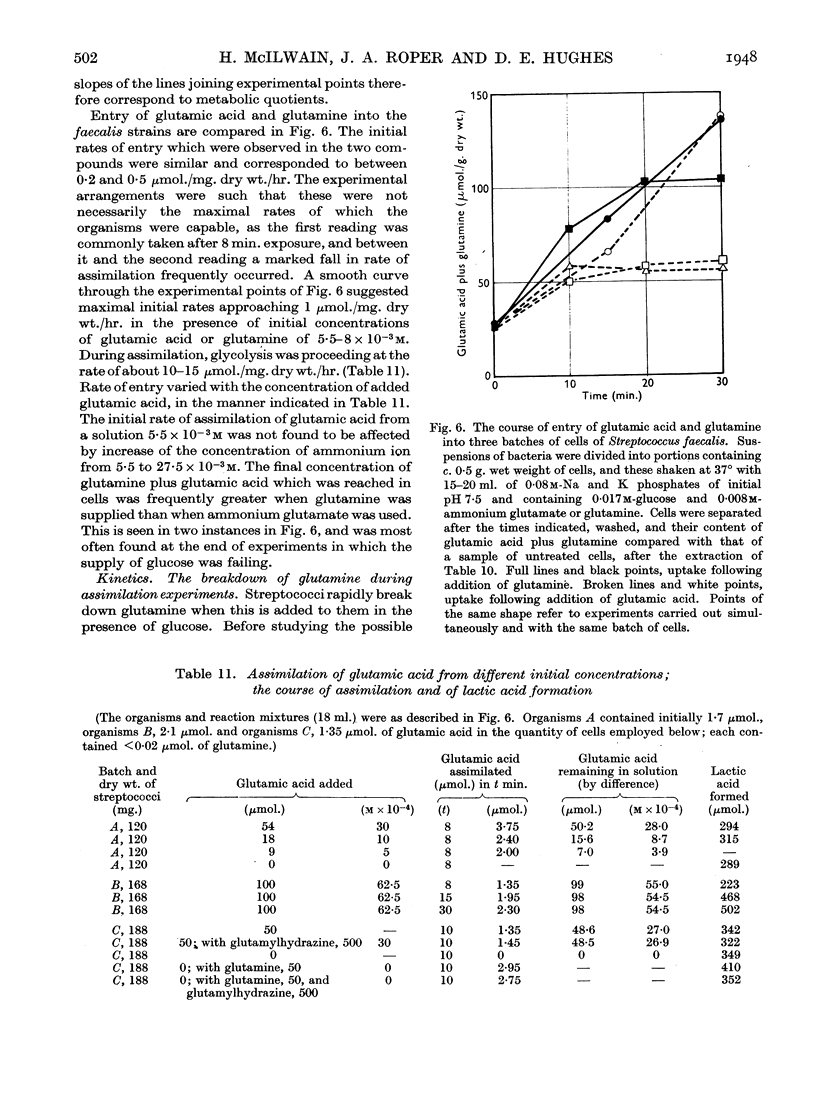
- McIlwain H. The metabolism and functioning of vitamin-like compounds: 3. Products of the decomposition of glutamine during streptococcal glycolysis. Biochem J. 1946;40(4):460–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
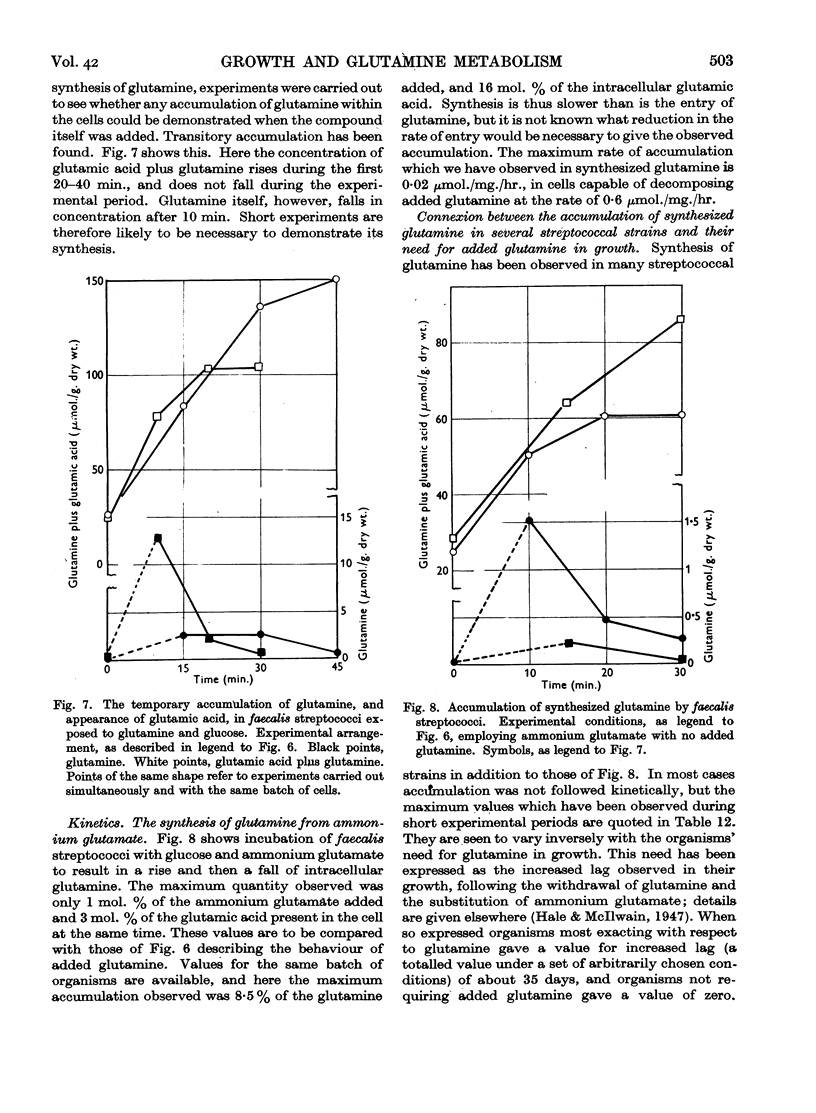
- Melville J. Labile glutamine peptides, and their bearing on the origin of the ammonia set free during the enzymic digestion of proteins. Biochem J. 1935;29(1):179–186. doi: 10.1042/bj0290179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roper J. A., McIlwain H. Preparation and antibacterial action of some compounds structurally related to glutamic acid. Their application in microbiological determination of small quantities of glutamine. Biochem J. 1948;42(4):485–492. doi: 10.1042/bj0420485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


