Abstract
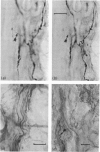
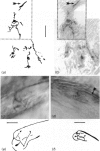
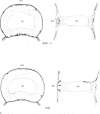
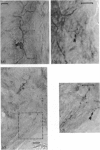
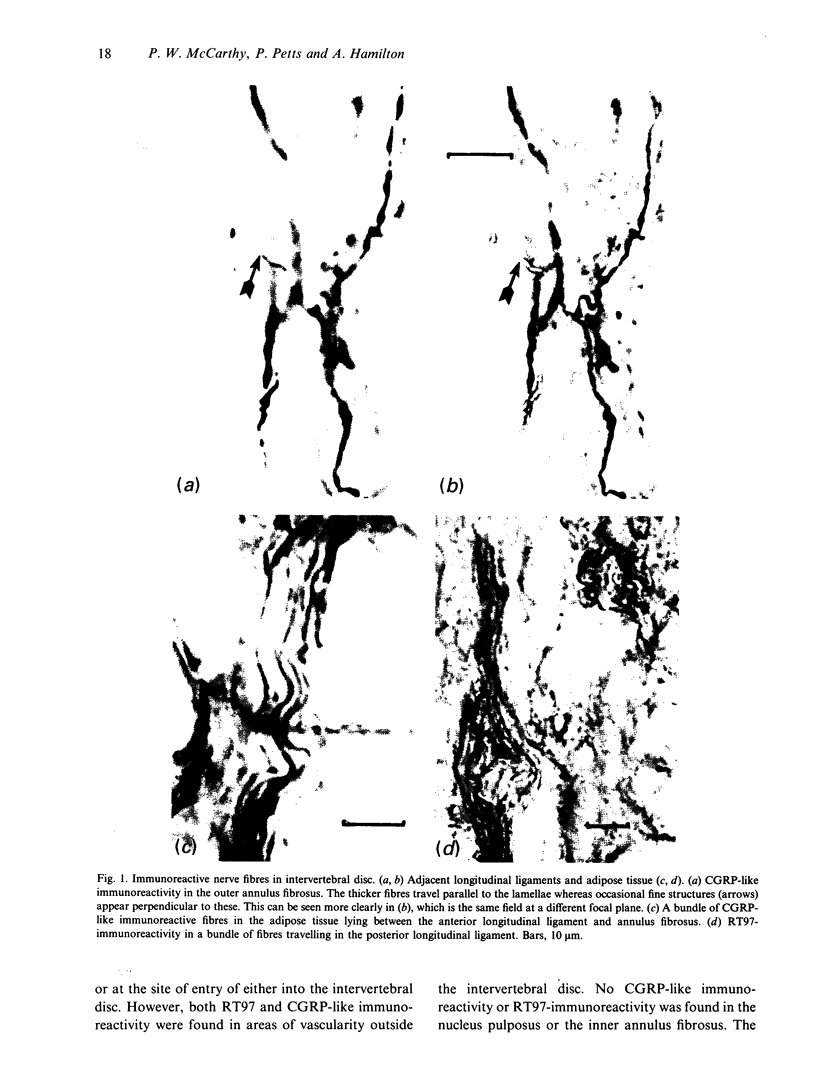
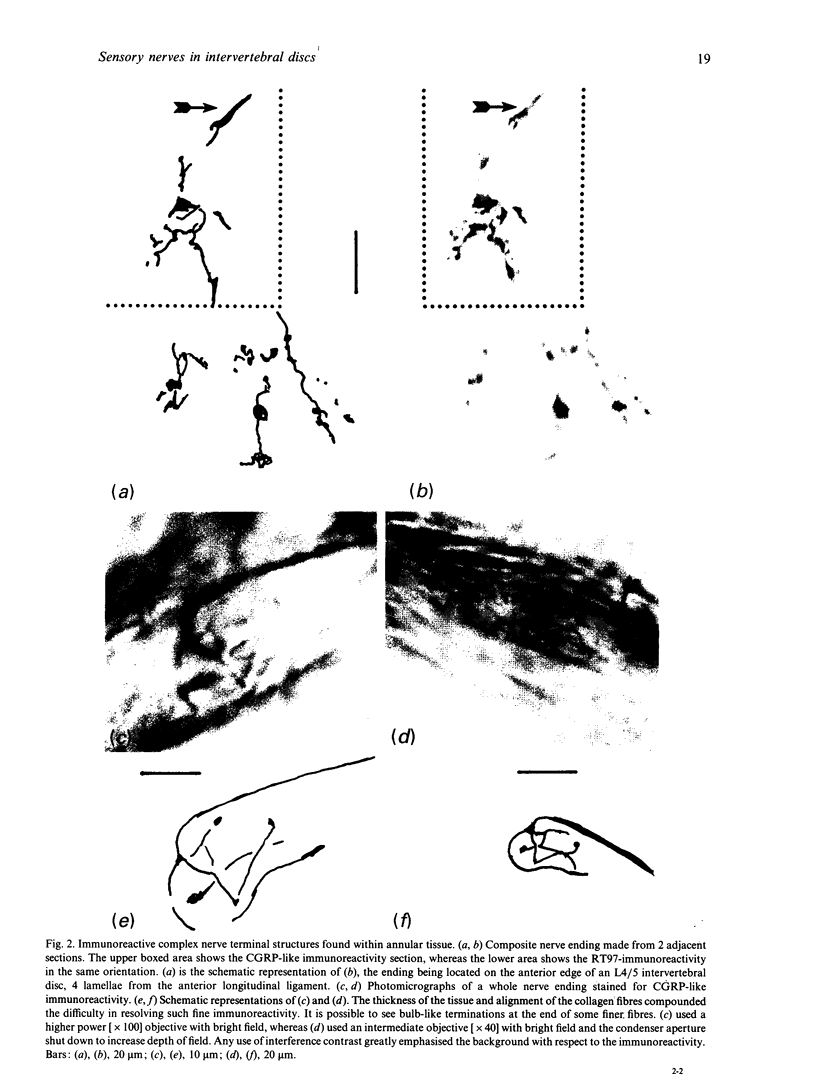
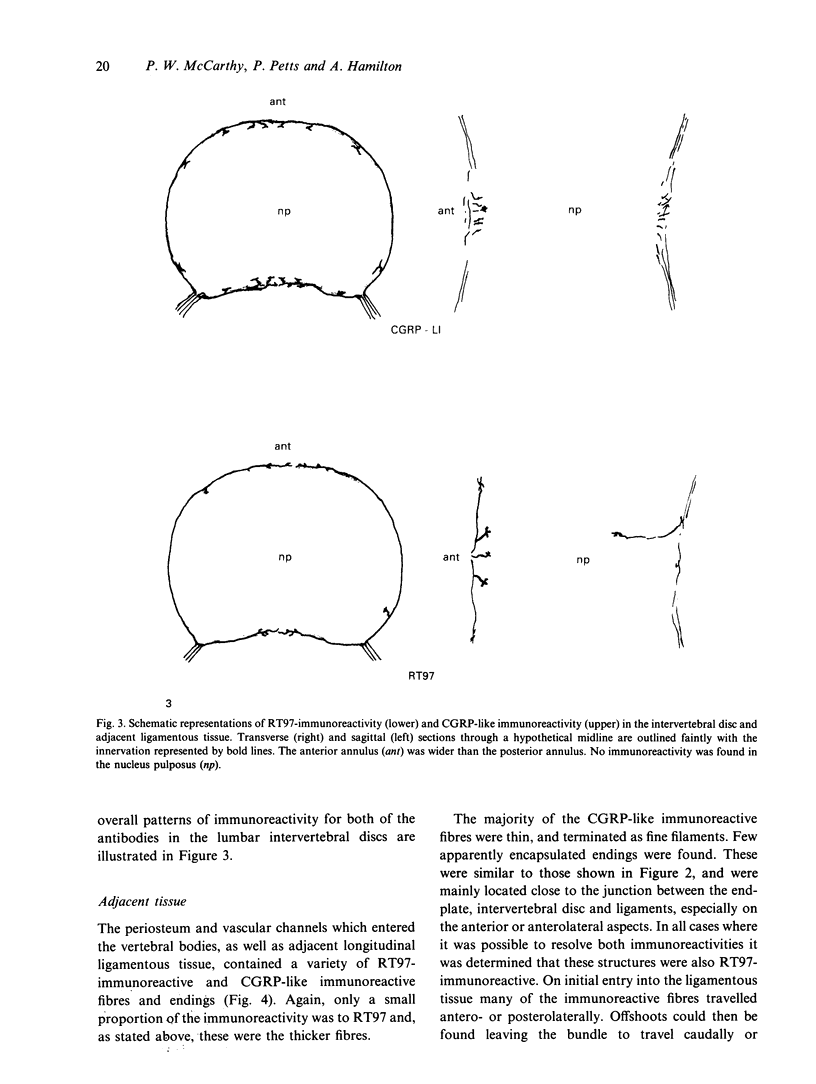
The innervation of rat intervertebral disc and adjacent ligamentous tissue has been investigated using 2 antibodies, RT97 and anti-calcitonin gene-related peptide. Immunoreactivity to the peptide was found in many fibres throughout the long ligaments around the intervertebral discs and in the periosteum, especially associated with vascular channels entering the vertebral bodies. Few of the immunoreactive fibres entered the annular lamellae of the disc tissue. Most of those which terminated did so as fine fibres which lay close to, or in, the interlamellar spaces of the outer annulus fibrosus. Calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity was also found in more complex endings in the longitudinal ligaments and rarely within the annulus fibrosus. RT97-immunoreactivity was also present in the complex endings and associated fibres. Conversely, RT97-immunoreactivity was apparent only in a few fine filamentous fibre endings. This suggested that the majority of fine filamentous, or free, nerve endings were of an unmyelinated sensory origin. Alternatively, those endings of a more complex nature, which were RT97-immunoreactive, were of a myelinated sensory origin. No immunoreactivity to either antibody was seen in the inner annular or nuclear tissue. It was therefore concluded that the sensory innervation of the rat intervertebral disc has both myelinated and unmyelinated components, the latter being more extensive. Both types of innervation appear to be restricted to the outermost rings of the annulus fibrosus.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard G. W., Shih C. The osteogenic stimulating effect of neuroactive calcitonin gene-related peptide. Peptides. 1990 Jul-Aug;11(4):625–632. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(90)90171-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjurholm A., Kreicbergs A., Brodin E., Schultzberg M. Substance P- and CGRP-immunoreactive nerves in bone. Peptides. 1988 Jan-Feb;9(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogduk N. The innervation of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1983 Apr;8(3):286–293. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198304000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogduk N., Tynan W., Wilson A. S. The nerve supply to the human lumbar intervertebral discs. J Anat. 1981 Jan;132(Pt 1):39–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain S. D., Williams T. J., Tippins J. R., Morris H. R., MacIntyre I. Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature. 1985 Jan 3;313(5997):54–56. doi: 10.1038/313054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner K., Frewein J. Untersuchungen der Vaskularisation der Disci intervertebrales des erwachsenen Hundes. Anat Histol Embryol. 1989 Mar;18(1):76–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0264.1989.tb00583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppes M. H., Marani E., Thomeer R. T., Oudega M., Groen G. J. Innervation of annulus fibrosis in low back pain. Lancet. 1990 Jul 21;336(8708):189–190. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91723-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard C. J., Björklund H., Jonsson C. E., Hermansson A., Dahl D. Distribution of neurofilament-immunoreactive nerve fibers in human skin. Histochemistry. 1984;81(2):111–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00490102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard C. J., Rydh M., Haegerstrand A. Cutaneous innervation in man visualized with protein gene product 9.5 (PGP 9.5) antibodies. Histochemistry. 1989;92(5):385–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00492495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson S. J., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Sabate I. M., Mulderry P. M., Ghatei M. A., McGregor G. P., Morrison J. F., Kelly J. S., Evans R. M. Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of man and of eight other species. J Neurosci. 1984 Dec;4(12):3101–3111. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-12-03101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönblad M., Korkala O., Konttinen Y. T., Nederström A., Hukkanen M., Tolvanen E., Polak J. M. Silver impregnation and immunohistochemical study of nerves in lumbar facet joint plical tissue. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1991 Jan;16(1):34–38. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199101000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillot M., Pionchon H., Pialat J., Bancel B., Galtier B. Etude de l'innervation des ligaments du rachis lombaire chez l'homme. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1988 Apr 1;55(5):421–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill E. L., Elde R. Calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive nerve fibers in mandibular periosteum of rat: evidence for primary afferent origin. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Feb 29;85(2):172–178. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90347-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P. Local effector functions of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve endings: involvement of tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and other neuropeptides. Neuroscience. 1988 Mar;24(3):739–768. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa H., Wakisaka S., Matsuo S., Akai M. Peptidergic innervation of the temporomandibular disk in the rat. Experientia. 1989 Mar 15;45(3):303–304. doi: 10.1007/BF01951817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson H. C., 2nd, Winkelmann R. K., Bickel W. H. Nerve endings in the human lumbar spinal column and related structures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1966 Oct;48(7):1272–1281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd B. L., Mapp P. I., Blake D. R., Gibson S. J., Polak J. M. Neurogenic influences in arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Aug;49(8):649–652. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.8.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima Y., Maeda T., Arai R., Shichikawa K. Nerve supply to the posterior longitudinal ligament and the intervertebral disc of the rat vertebral column as studied by acetylcholinesterase histochemistry. I. Distribution in the lumbar region. J Anat. 1990 Apr;169:237–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima Y., Maeda T., Arai R., Shichikawa K. Nerve supply to the posterior longitudinal ligament and the intervertebral disc of the rat vertebral column as studied by acetylcholinesterase histochemistry. II. Regional differences in the distribution of the nerve fibres and their origins. J Anat. 1990 Apr;169:247–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korkala O., Grönblad M., Liesi P., Karaharju E. Immunohistochemical demonstration of nociceptors in the ligamentous structures of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1985 Mar;10(2):156–157. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198503000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson S. N., Harper A. A., Harper E. I., Garson J. A., Anderton B. H. A monoclonal antibody against neurofilament protein specifically labels a subpopulation of rat sensory neurones. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Sep 10;228(2):263–272. doi: 10.1002/cne.902280211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y., Takami K., Kawai Y., Girgis S., Hillyard C. J., MacIntyre I., Emson P. C., Tohyama M. Distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the rat peripheral nervous system with reference to its coexistence with substance P. Neuroscience. 1985 Aug;15(4):1227–1237. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALINSKY J. The ontogenetic development of nerve terminations in the intervertebral discs of man. (Histology of intervertebral discs, 11th communication). Acta Anat (Basel) 1959;38:96–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapp P. I., Kidd B. L., Gibson S. J., Terry J. M., Revell P. A., Ibrahim N. B., Blake D. R., Polak J. M. Substance P-, calcitonin gene-related peptide- and C-flanking peptide of neuropeptide Y-immunoreactive fibres are present in normal synovium but depleted in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Neuroscience. 1990;37(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90199-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy P. W., Lawson S. N. Cell type and conduction velocity of rat primary sensory neurons with calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity. Neuroscience. 1990;34(3):623–632. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon S. B., Koltzenburg M. Novel classes of nociceptors: beyond Sherrington. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jun;13(6):199–201. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molander C., Ygge J., Dalsgaard C. J. Substance P-, somatostatin- and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity and fluoride resistant acid phosphatase-activity in relation to retrogradely labeled cutaneous, muscular and visceral primary sensory neurons in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Feb 10;74(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachemson A. Towards a better understanding of low-back pain: a review of the mechanics of the lumbar disc. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1975 Aug;14(3):129–143. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/14.3.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEACOCK A. Observations on the postnatal structure of the intervertebral disc in man. J Anat. 1952 Apr;86(2):162–179. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman J. D., Kruger L. Calcitonin-gene-related-peptide-immunoreactive innervation of the rat head with emphasis on specialized sensory structures. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Feb 8;280(2):303–330. doi: 10.1002/cne.902800211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanini M., De Martino C., Zamboni L. Fixation of ejaculated spermatozoa for electron microscopy. Nature. 1967 Oct 14;216(5111):173–174. doi: 10.1038/216173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein J., Claverie W., Gibson S. The pain of discography. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1988 Dec;13(12):1344–1348. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198812000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahia L. H., Newman N., Rivard C. H. Neurohistology of lumbar spine ligaments. Acta Orthop Scand. 1988 Oct;59(5):508–512. doi: 10.3109/17453678809148773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa H., O'Brien J. P., Smith W. T., Trumper M. The neuropathology of intervertebral discs removed for low-back pain. J Pathol. 1980 Oct;132(2):95–104. doi: 10.1002/path.1711320202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]