Abstract
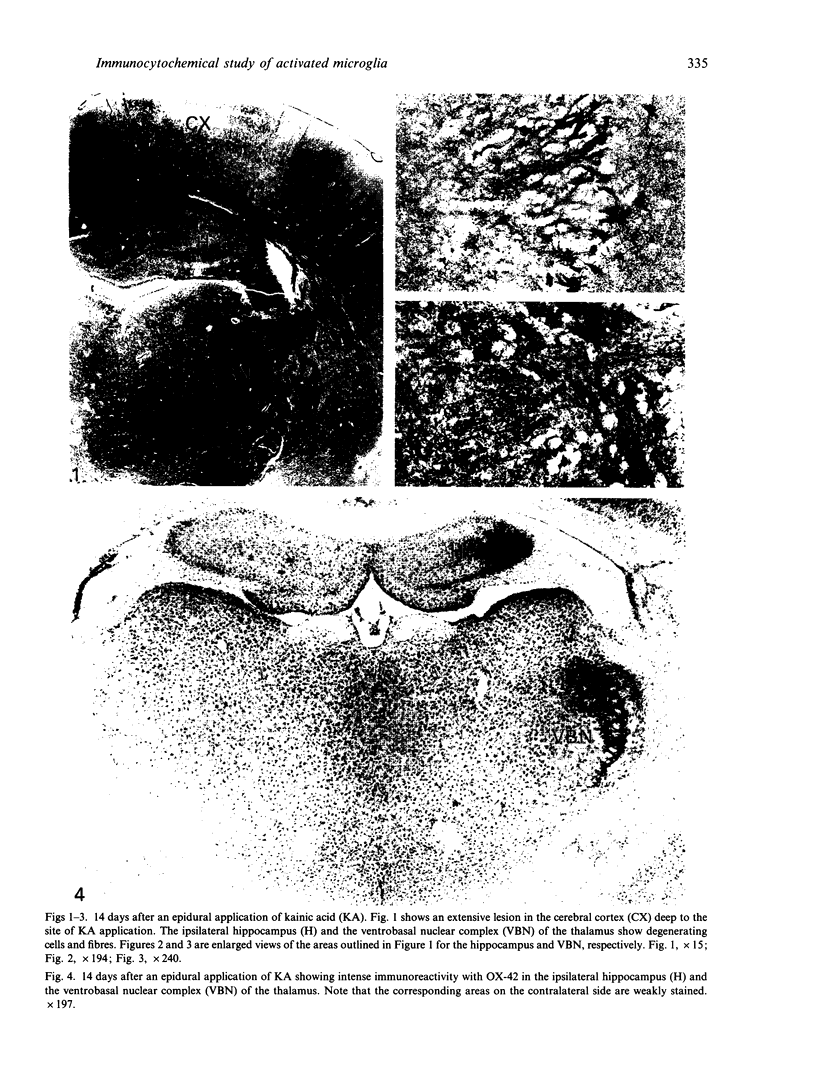
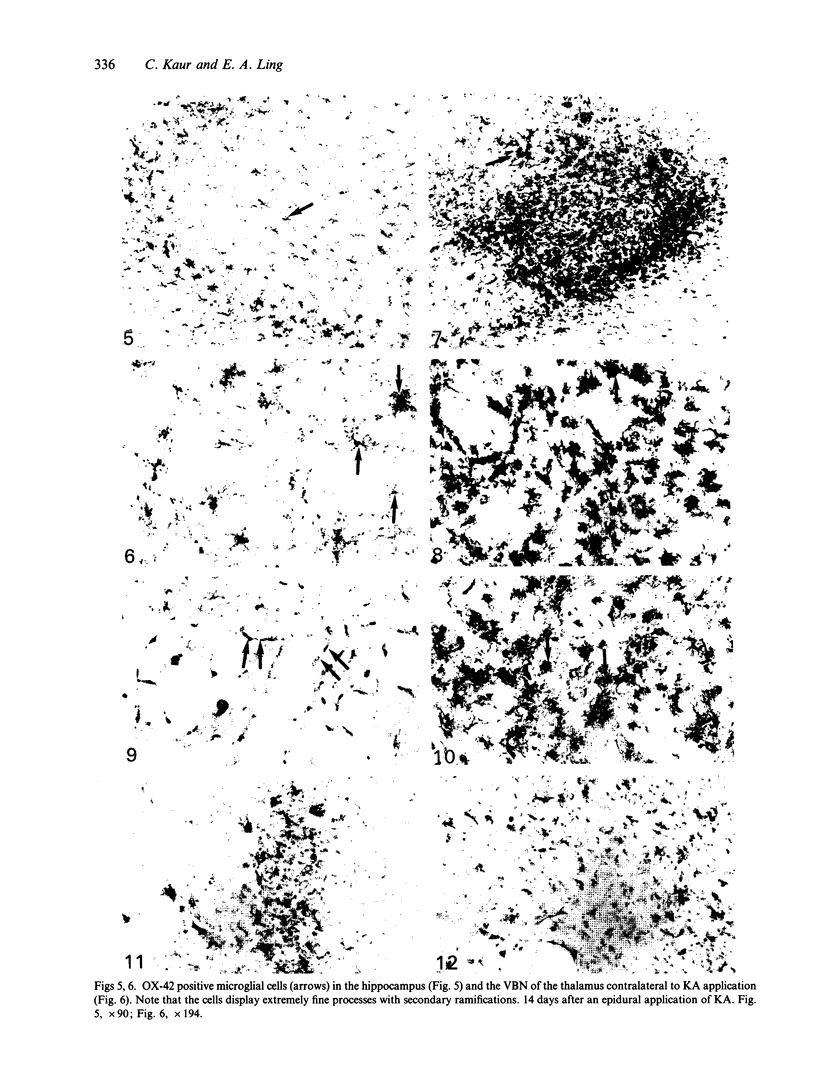
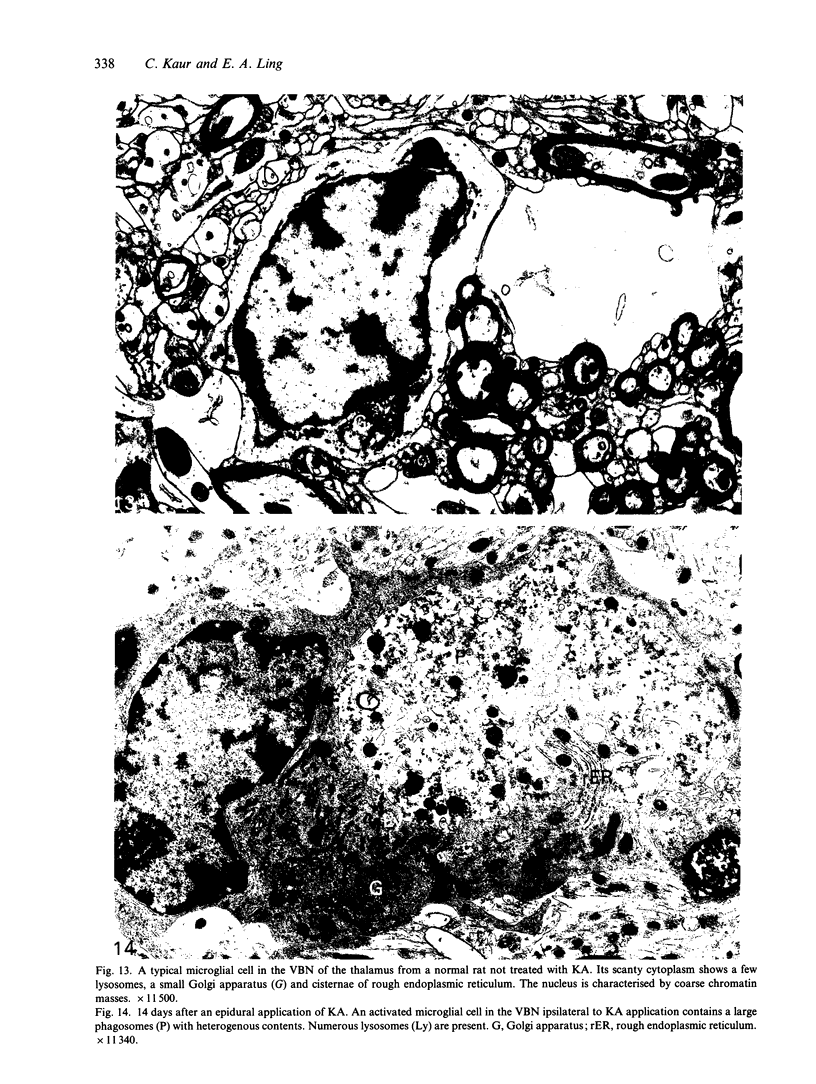
Following an epidural application of kainic acid over the sensorimotor cortex in rats, the ipsilateral hippocampus and the ventrobasal nuclear complex of the thalamus showed extensive neural degeneration. The neuronal death, either as a result of direct neurotoxic destruction or wallerian and retrograde degeneration, elicited a dramatic expression of immunoreactivity on numerous cells bearing the external morphology of microglia. Thus, with the monoclonal antibody OX-42, many amoeboid immunoreactive cells bearing stout processes were observed in the above-mentioned lesioned sites. The present electron microscopic immunocytochemical study confirmed that these OX-42 positive cells were activated microglia characterised by an abundant cytoplasm containing a variable number of lysosomes and phagosomes. The surfaces of these activated microglial cells were thrown into pseudopodial processes engaged in the phagocytosis of cellular debris. Immunoreactivity was also observed in these cells with the monoclonal antibodies OX-18 and OX-6, although in the latter the immunoreactive cells were fewer and less intensely stained. With OX-42, the corresponding areas on the contralateral side showed some widely scattered typical microglial cells bearing extremely fine processes. They were not stained with either OX-18 or OX-6. It was concluded from this study that neural degeneration induced the expression of CR3 receptors (marked by OX-42) and MHC encoded antigens (marked by OX-18 and OX-6) in microglia. The elevation of the former antigen was related to their active phagocytic activity. The latter, on the other hand, would facilitate the capability of interaction between the activated microglia and T lymphocytes in a possible immune response.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama H., Itagaki S., McGeer P. L. Major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on rat microglia following epidural kainic acid lesions. J Neurosci Res. 1988;20(2):147–157. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490200202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama H., McGeer P. L. Microglial response to 6-hydroxydopamine-induced substantia nigra lesions. Brain Res. 1989 Jun 12;489(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90857-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink R. P., Heimer L. Two methods for selective silver impregnation of degenerating axons and their synaptic endings in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 1967 Apr;4(4):369–374. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(67)90166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeber M. B., Streit W. J., Kreutzberg G. W. Axotomy of the rat facial nerve leads to increased CR3 complement receptor expression by activated microglial cells. J Neurosci Res. 1988 Sep;21(1):18–24. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490210104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldin W. O., Markowitsch H. J. Epidural kainate, but not ibotenate, produces lesions in local and distant regions of the brain. A comparison of the intracerebral actions of kainic acid and ibotenic acid. J Neurosci Methods. 1982 Jan;5(1-2):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(82)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey W. F., Kimura H. Graft-vs.-host disease elicits expression of class I and class II histocompatibility antigens and the presence of scattered T lymphocytes in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2082–2086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno H., Yamamoto T., Iwasaki Y., Saitoh T., Suzuki H., Terunuma H. Ia-expressing microglial cells in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;77(5):472–479. doi: 10.1007/BF00687248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A., Kaur C., Wong W. C. Expression of major histocompatibility complex antigens and CR3 complement receptors in activated microglia following an injection of ricin into the sciatic nerve in rats. Histol Histopathol. 1992 Jan;7(1):93–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A., Kaur L. C., Yick T. Y., Wong W. C. Immunocytochemical localization of CR3 complement receptors with OX-42 in amoeboid microglia in postnatal rats. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1990;182(5):481–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00178913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A., Wen C. Y., Shieh J. Y., Yick T. Y., Leong S. K. Neuroglial response to neuron injury. A study using intraneural injection of ricinus communis agglutinin-60. J Anat. 1989 Jun;164:201–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Fujiwara M. Absence of donor-type major histocompatibility complex class I antigen-bearing microglia in the rat central nervous system of radiation bone marrow chimeras. J Neuroimmunol. 1987 Dec;17(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(87)90032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Fujiwara M. In situ detection of class I and II major histocompatibility complex antigens in the rat central nervous system during experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. An immunohistochemical study. J Neuroimmunol. 1986 Oct;12(4):265–277. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(86)90033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Hume D. A., Gordon S. Immunohistochemical localization of macrophages and microglia in the adult and developing mouse brain. Neuroscience. 1985 Jun;15(2):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. P., White T. M., Mason D. W. Macrophage heterogeneity in the rat as delineated by two monoclonal antibodies MRC OX-41 and MRC OX-42, the latter recognizing complement receptor type 3. Immunology. 1986 Feb;57(2):239–247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J., Scherer J. Microglial cell responses in the rabbit retina following transection of the optic nerve. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Dec 22;302(4):779–791. doi: 10.1002/cne.903020410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. A., Perry V. H., Mellanby J. Tetanus toxin-induced seizures cause microglial activation in rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Nov 27;120(1):66–69. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90169-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streit W. J., Graeber M. B., Kreutzberg G. W. Functional plasticity of microglia: a review. Glia. 1988;1(5):301–307. doi: 10.1002/glia.440010502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. L., Walker D. G., Akiyama H., McGeer P. L. Herpes simplex virus type I infection of the CNS induces major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on rat microglia. J Neurosci Res. 1990 May;26(1):55–65. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490260107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]