Abstract
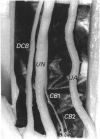
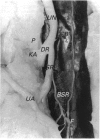
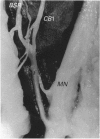
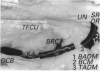
Branching of the ulnar nerve distal to the origin of the dorsal cutaneous branch was investigated in 25 hands in one of which an anatomical variation was observed. This finding may be of importance in the evaluation of certain entrapment phenomena of the ulnar nerve or unexplained sensory loss after trauma or surgical intervention in that particular area.
Full text
PDF
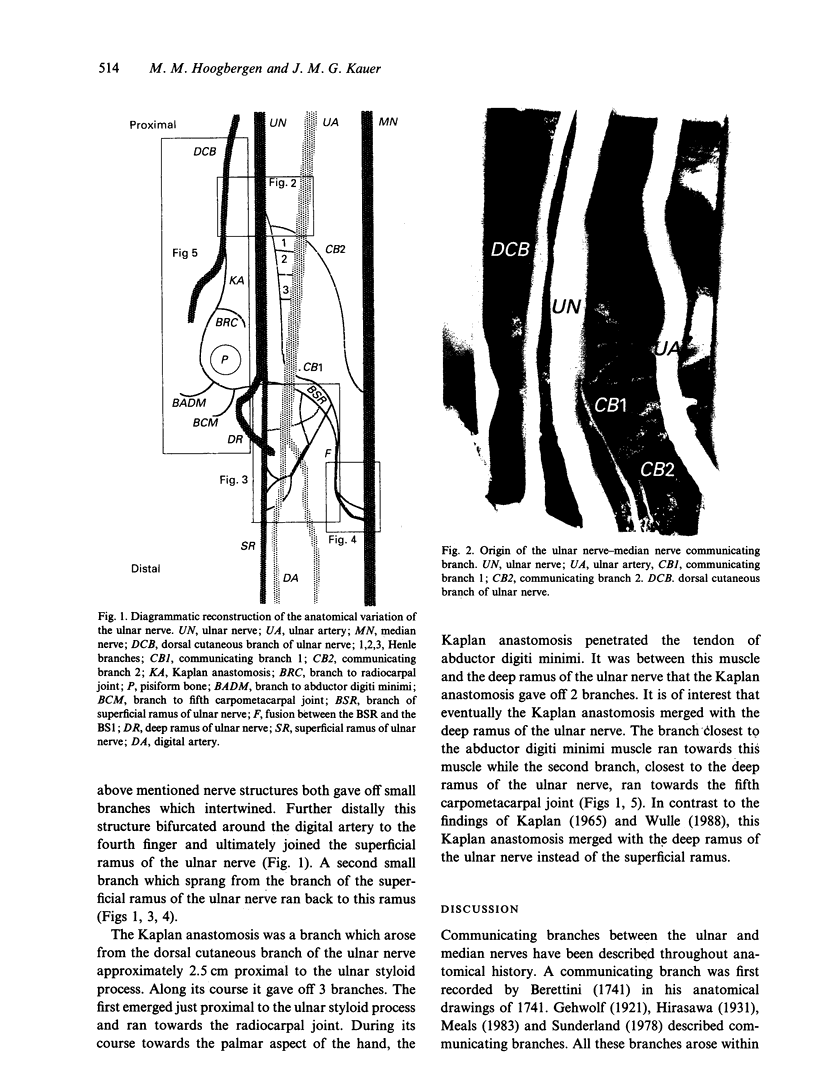


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- KAPLAN E. B. VARIATION OF THE ULNAR NERVE AT THE WRIST. Bull Hosp Joint Dis. 1963 Apr;24:85–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May J. W., Jr, Rosen H. Division of the sensory ramus communicans between the ulnar and median nerves: a complication following carpal tunnel release. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981 Jun;63(5):836–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meals R. A., Shaner M. Variations in digital sensory patterns: a study of the ulnar nerve-median nerve palmar communicating branch. J Hand Surg Am. 1983 Jul;8(4):411–414. doi: 10.1016/s0363-5023(83)80200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulle C. Die Kaplan-Anastomose am Kleinfinger. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 1988 Sep;20(5):285–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]