Full text
PDF
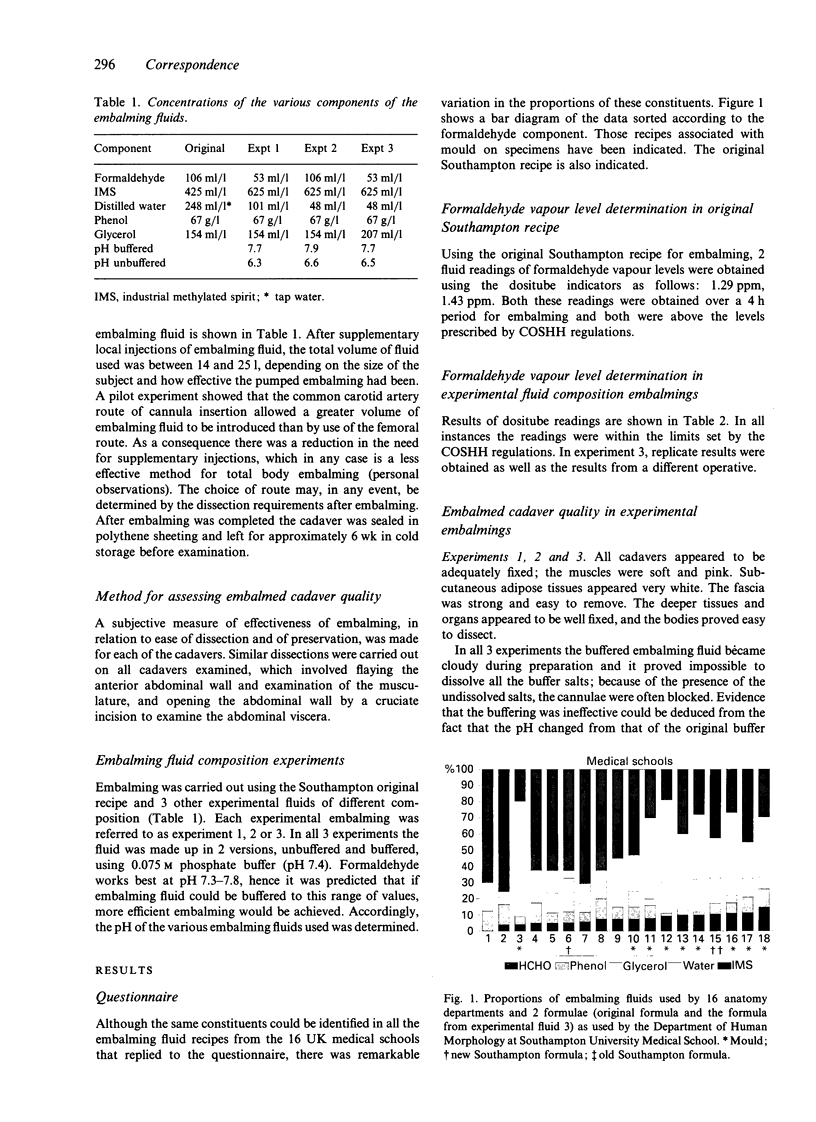

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Frølich K. W., Andersen L. M., Knutsen A., Flood P. R. Phenoxyethanol as a nontoxic substitute for formaldehyde in long-term preservation of human anatomical specimens for dissection and demonstration purposes. Anat Rec. 1984 Feb;208(2):271–278. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092080214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes R. B., Blair A., Stewart P. A., Herrick R. F., Mahar H. Mortality of U.S. embalmers and funeral directors. Am J Ind Med. 1990;18(6):641–652. doi: 10.1002/ajim.4700180603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst R. Exposure to formaldehyde in anatomy: an occupational health hazard? Anat Rec. 1987 Oct;219(2):109–112. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092190202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



