Abstract
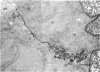
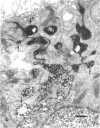
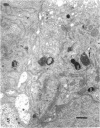
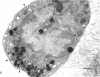
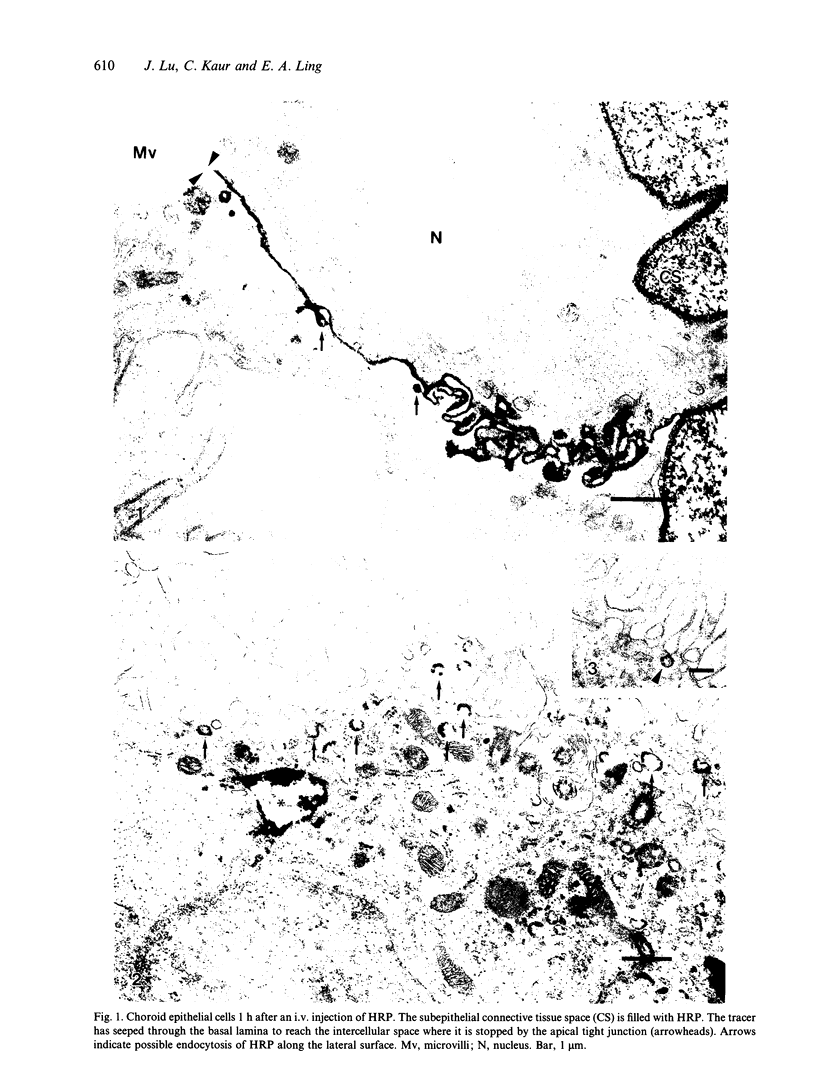
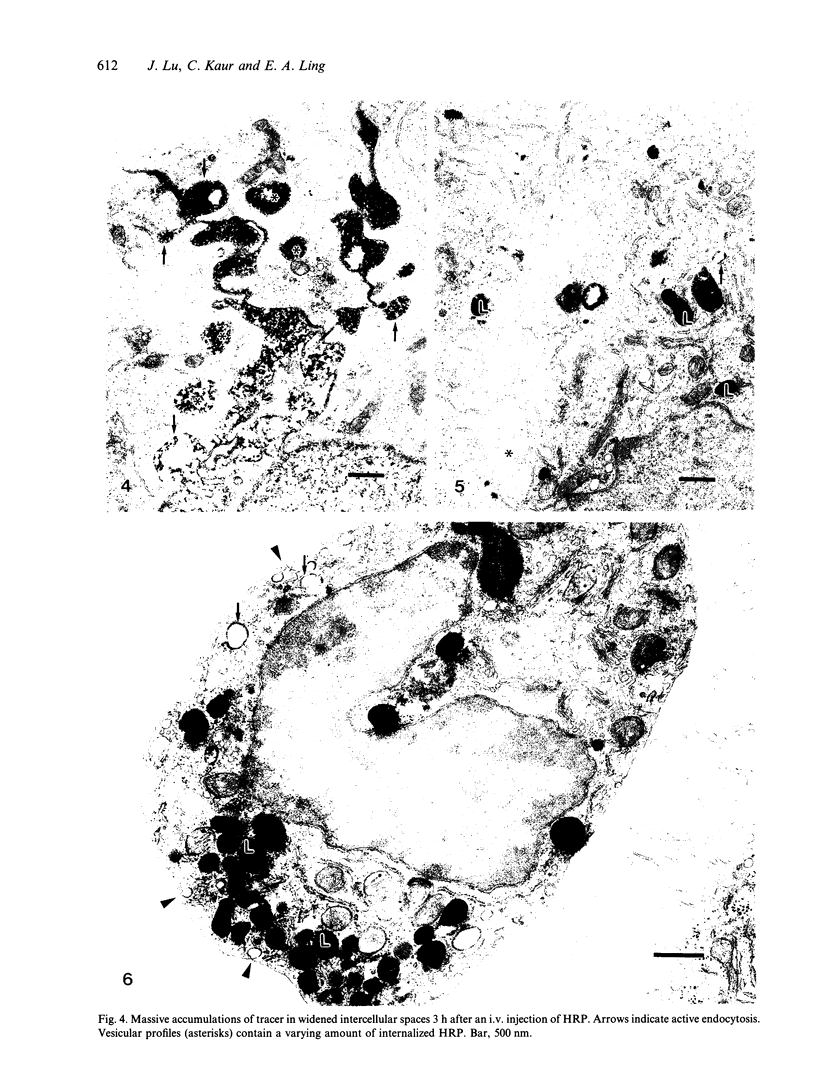
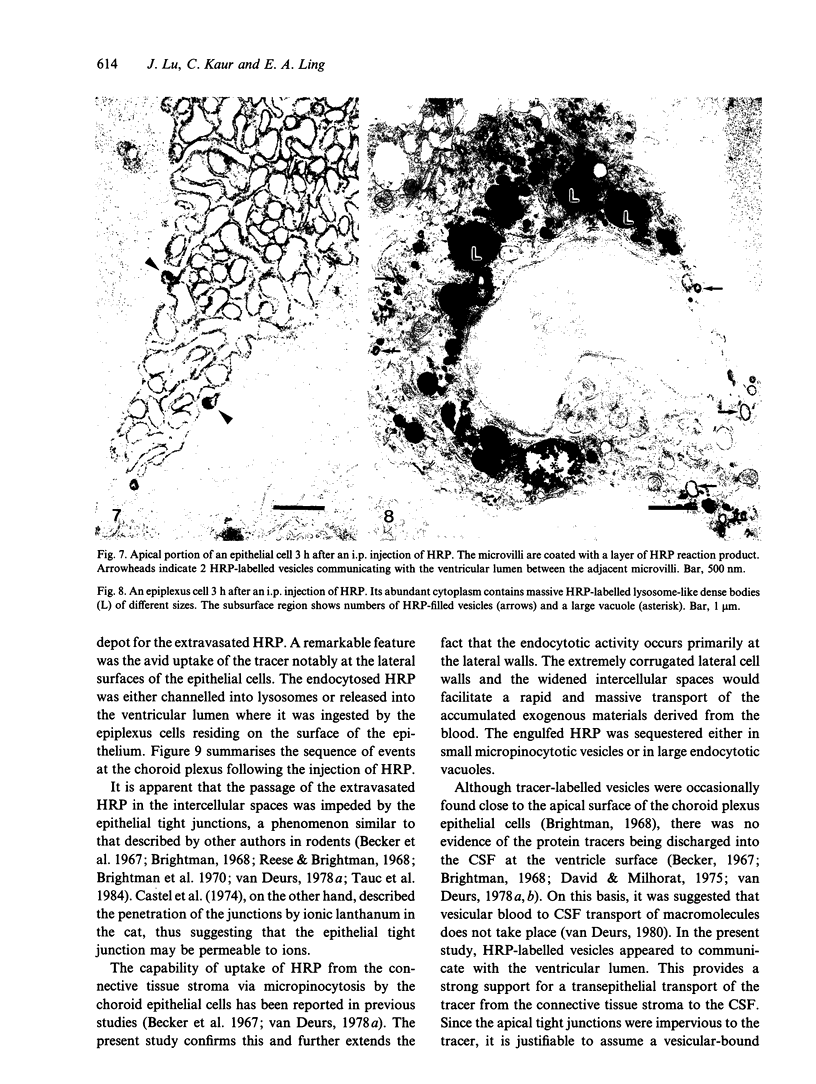
Rapid passage of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) from the blood circulation to the cerebrospinal fluid was demonstrated in postnatal rats. At 30 min-1 h after an intravenous (i.v.) injection of HRP, the extravasated tracer from the blood vessels entered the connective tissue of the choroid plexus to reach the epithelial intercellular spaces where it was retarded by the apical tight junctions. The HRP which accumulated in widened intercellular spaces was readily endocytosed by the epithelial cells, notably at their lateral surfaces. This was especially pronounced 3 h after the injection. The endocytosed HRP was either routed to lysosomes or discharged apically by exocytosis into the CSF via membrane-bound vesicles by the epithelial cells. After longer survival periods, i.e. 6 h after injection, the intercellular spaces were relatively clear of tracer. HRP-labelled vacuoles or vesicles had diminished with a concomitant increase in the number of lysosomes containing HRP reaction product. In the course of HRP injection, the epiplexus cells residing on the choroid epithelium progressively accumulated HRP by endocytosis so that in rats killed 6 h after injection, the cells were heavily loaded with HRP incorporated into massive lysosomes. The labelling pattern of epithelial and epiplexus cells in rats injected intraperitoneally followed that observed in those receiving i.v. injections. These results suggest that the epiplexus cells together with lysosomal activity by the choroid epithelial cells serve as a protective line of defence for the blood-CSF barrier which appears to be inefficient.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. J. Scanning electron microscopy of epiplexus macrophages (Kolmer cells) in the dog. J Comp Neurol. 1975 May 15;161(2):197–213. doi: 10.1002/cne.901610205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker N. H., Almazon R. Evidence for the functional polarization of micropinocytotic vesicles in the rat choroid plexus. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Apr;16(4):278–280. doi: 10.1177/16.4.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker N. H., Novikoff A. B., Zimmerman H. M. Fine structure observations of the uptake of intravenously injected peroxidase by the rat choroid plexus. J Histochem Cytochem. 1967 Mar;15(3):160–165. doi: 10.1177/15.3.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W., Klatzo I., Olsson Y., Reese T. S. The blood-brain barrier to proteins under normal and pathological conditions. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Mar;10(3):215–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W., Reese T. S. Junctions between intimately apposed cell membranes in the vertebrate brain. J Cell Biol. 1969 Mar;40(3):648–677. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W. The distribution within the brain of ferritin injected into cerebrospinal fluid compartments. I. Ependymal distribution. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jul;26(1):99–123. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W. The intracerebral movement of proteins injected into blood and cerebrospinal fluid of mice. Prog Brain Res. 1968;29:19–40. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S. J., McCarthy L. E., Borison H. L. Electron microscopic study of the epiplexus (Kolmer) cells of the cat choroid plexus. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;110(4):471–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00330099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castel M., Sahar A., Erlij D. The movement of lanthanum across diffusion barriers in the choroid plexus of the cat. Brain Res. 1974 Feb 15;67(1):178–184. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90311-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D. A., Milhorat T. H. The blood-brain barrier of the rat choroid plexus. Anat Rec. 1975 Apr;181(4):779–789. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091810409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deurs B. V. Horseradish peroxidase uptake into the rat choroid plexus epithelium, with special reference to the lysosomal system. J Ultrastruct Res. 1978 Feb;62(2):155–167. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(78)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deurs B. V. Microperoxidase uptake into the rat choroid plexus epithelium. J Ultrastruct Res. 1978 Feb;62(2):168–180. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(78)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoya Y., Fujita T. Scanning electron microscope observation of intraventricular macrophages (Kolmer cells) in the rat brain. Arch Histol Jpn. 1973 Jan;35(2):133–140. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.35.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPPERS J. A. Beitrag zur experimentellen Untersuchung von Funktion und Herkunft der Kolmerschen Zellen des Plexus chorioideus beim Axolotl und Meerschweinchen. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1953;117(1):1–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur C., Ling E. A., Gopalakrishnakone P., Wong W. C. Response of intraventricular macrophages to crotoxin-coated microcarrier beads injected into the lateral ventricle of postnatal rats. J Anat. 1990 Feb;168:63–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A., Gopalakrishnakone P., Tan C. K. Electron-microscopical study of the choroid plexus and epiplexus cells in cats following a cisternal injection of crotoxin complex. Acta Anat (Basel) 1988;131(3):241–248. doi: 10.1159/000146523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A., Tseng C. Y., Wong W. C. An electron microscopical study of epiplexus and supraependymal cells in the prenatal rat brain following a maternal injection of 6-aminonicotinamide. J Anat. 1985 Jan;140(Pt 1):119–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A. Ultrastruct and origin of epiplexus cells in the telencephalic choroid plexus of postnatal rats studied by intravenous injection of carbon particles. J Anat. 1979 Oct;129(Pt 3):479–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A. Ultrastructure and mode of formation of epiplexus cells in the choroid plexus in the lateral ventricles of the monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J Anat. 1981 Dec;133(Pt 4):555–569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J., Kaur C., Ling E. A. Intraventricular macrophages in the lateral ventricles with special reference to epiplexus cells: a quantitative analysis and their uptake of fluorescent tracer injected intraperitoneally in rats of different ages. J Anat. 1993 Oct;183(Pt 2):405–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell W. L., Hardy I. G., Watt C., McGadey J., Graham D. I., Adams J. H., Gennarelli T. A. Changes in the choroid plexus, responses by intrinsic epiplexus cells and recruitment from monocytes after experimental head acceleration injury in the non-human primate. Acta Neuropathol. 1992;84(1):78–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00427218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merker G. Einige Feinstrukturbefunde an den Plexus chorioidei von Affen. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;134(4):565–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. A developmental study of epiplexus cells and supraependymal cells and their possible relationship to microglia. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1978 Sep-Oct;4(5):307–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1978.tb01345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. A light microscopic and scanning electron microscopic study of intraventricular macrophages in the brains of aged mice. J Anat. 1983 Jun;136(Pt 4):761–771. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturrock R. R. A semithin light microscopic, transmission electron microscopic and scanning electron microscopic study of macrophages in the lateral ventricle of mice from embryonic to adult life. J Anat. 1979 Aug;129(Pt 1):31–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauc M., Vignon X., Bouchaud C. Evidence for the effectiveness of the blood--CSF barrier in the fetal rat choroid plexus. A freeze-fracture and peroxidase diffusion study. Tissue Cell. 1984;16(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(84)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B. Choroid plexus absorption of horseradish peroxidase from the cerebral ventricles. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Jun;55(3):400–416. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B. Structural aspects of brain barriers, with special reference to the permeability of the cerebral endothelium and choroidal epithelium. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;65:117–191. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61960-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]