Abstract
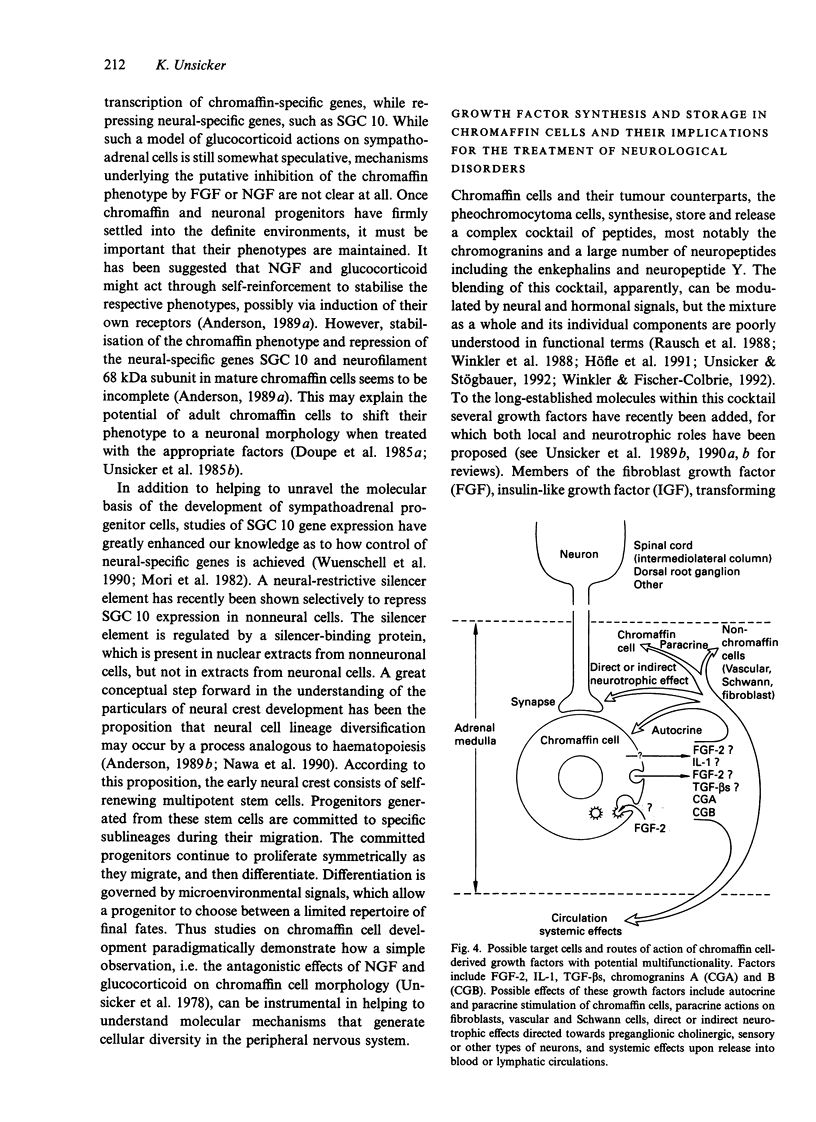
This article reviews the chromaffin cell in relation to studies that have elucidated fundamental phenomena in cell biology (the molecular anatomy of exocytosis) and developmental neuroscience (the principle of neuropoiesis in the development of the sympathoadrenal cell lineage). A final section addresses growth factor synthesis and storage in chromaffin cells and their implications for the treatment of neurological disorders, such as Parkinson's disease.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Weller U., Dauzenroth M. E., Habermann E., Gratzl M. The tetanus toxin light chain inhibits exocytosis. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):245–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80478-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. M., Geisow M. J., Burgoyne R. D. A role for calpactin in calcium-dependent exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):313–315. doi: 10.1038/340313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Axel R. A bipotential neuroendocrine precursor whose choice of cell fate is determined by NGF and glucocorticoids. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90823-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Carnahan J. F., Michelsohn A., Patterson P. H. Antibody markers identify a common progenitor to sympathetic neurons and chromaffin cells in vivo and reveal the timing of commitment to neuronal differentiation in the sympathoadrenal lineage. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3507–3519. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03507.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J. The neural crest cell lineage problem: neuropoiesis? Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson C., Svenson S. B., Van Deventer S., Cerami A., Bartfai T. Interleukin-1 alpha expression is inducible by cholinergic stimulation in the rat adrenal gland. Neuroscience. 1992;47(2):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90262-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader M. F., Thiersé D., Aunis D., Ahnert-Hilger G., Gratzl M. Characterization of hormone and protein release from alpha-toxin-permeabilized chromaffin cells in primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5777–5783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Knight D. E. High-voltage techniques for gaining access to the interior of cells: application to the study of exocytosis and membrane turnover. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:28–37. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballesta J. J., Palmero M., Hidalgo M. J., Gutierrez L. M., Reig J. A., Viniegra S., Garcia A. G. Separate binding and functional sites for omega-conotoxin and nitrendipine suggest two types of calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1050–1056. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birren S. J., Anderson D. J. A v-myc-immortalized sympathoadrenal progenitor cell line in which neuronal differentiation is initiated by FGF but not NGF. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90094-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blottner Dieter, Unsicker Klaus. Maintenance of Intermediolateral Spinal Cord Neurons by Fibroblast Growth Factor Administered to the Medullectomized Rat Adrenal Gland: Dependence on Intact Adrenal Innervation and Cellular Organization of Implants. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(4):378–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blottner Dieter, Westermann Reiner, Grothe Claudia, Böhlen Peter, Unsicker Klaus. Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor in the Adrenal Gland. Eur J Neurosci. 1989 Sep;1(5):471–478. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Cheek T. R. Cytoskeleton: role of fodrin in secretion. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):448–448. doi: 10.1038/326448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Cheek T. R., Morgan A., O'Sullivan A. J., Moreton R. B., Berridge M. J., Mata A. M., Colyer J., Lee A. G., East J. M. Distribution of two distinct Ca2+-ATPase-like proteins and their relationships to the agonist-sensitive calcium store in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):72–74. doi: 10.1038/342072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D. Control of exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 22;1071(2):174–202. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90024-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnahan J. F., Patterson P. H. Isolation of the progenitor cells of the sympathoadrenal lineage from embryonic sympathetic ganglia with the SA monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3520–3530. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03520.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnahan J. F., Patterson P. H. The generation of monoclonal antibodies that bind preferentially to adrenal chromaffin cells and the cells of embryonic sympathetic ganglia. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3493–3506. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03493.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron J., Drouin J. Glucocorticoid inhibition of transcription from episomal proopiomelanocortin gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8903–8907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Jackson T. R., O'Sullivan A. J., Moreton R. B., Berridge M. J., Burgoyne R. D. Simultaneous measurements of cytosolic calcium and secretion in single bovine adrenal chromaffin cells by fluorescent imaging of fura-2 in cocultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1219–1227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Tempst P., Yankner B. A. Secretogranin I/chromogranin B is a heparin-binding adhesive protein. J Neurochem. 1992 May;58(5):1691–1698. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claude P., Parada I. M., Gordon K. A., D'Amore P. A., Wagner J. A. Acidic fibroblast growth factor stimulates adrenal chromaffin cells to proliferate and to extend neurites, but is not a long-term survival factor. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):783–790. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham E. T., Jr, Wada E., Carter D. B., Tracey D. E., Battey J. F., De Souza E. B. In situ histochemical localization of type I interleukin-1 receptor messenger RNA in the central nervous system, pituitary, and adrenal gland of the mouse. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):1101–1114. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-01101.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmer M. K., Hart P. M., Perlman R. L. Insulin-like growth factor-I enhances tyrosine hydroxylase activation in bovine chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1347–1353. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmer M. K., Perlman R. L. Bovine chromaffin cells have insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptors: IGF-I enhances catecholamine secretion. J Neurochem. 1988 Jul;51(1):321–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb04873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Aldrich T. H., Valenzuela D. M., Wong V. V., Furth M. E., Squinto S. P., Yancopoulos G. D. The receptor for ciliary neurotrophic factor. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.1648265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCicco-Bloom E., Black I. B. Insulin growth factors regulate the mitotic cycle in cultured rat sympathetic neuroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4066–4070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Landis S. C., Patterson P. H. Environmental influences in the development of neural crest derivatives: glucocorticoids, growth factors, and chromaffin cell plasticity. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2119–2142. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Patterson P. H., Landis S. C. Small intensely fluorescent cells in culture: role of glucocorticoids and growth factors in their development and interconversions with other neural crest derivatives. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2143–2160. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drust D. S., Creutz C. E. Aggregation of chromaffin granules by calpactin at micromolar levels of calcium. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):88–91. doi: 10.1038/331088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn L. A., Holz R. W. Catecholamine secretion from digitonin-treated adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4989–4993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engele J., Bohn M. C. The neurotrophic effects of fibroblast growth factors on dopaminergic neurons in vitro are mediated by mesencephalic glia. J Neurosci. 1991 Oct;11(10):3070–3078. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-10-03070.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanders K. C., Lüdecke G., Engels S., Cissel D. S., Roberts A. B., Kondaiah P., Lafyatis R., Sporn M. B., Unsicker K. Localization and actions of transforming growth factor-beta s in the embryonic nervous system. Development. 1991 Sep;113(1):183–191. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaris N., Tischler A. S. Substrate dependency of neurite outgrowth from adult human chromaffin cells. Inhibitory effects of human brain tissue. Lab Invest. 1990 Apr;62(4):493–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed W. J., Morihisa J. M., Spoor E., Hoffer B. J., Olson L., Seiger A., Wyatt R. J. Transplanted adrenal chromaffin cells in rat brain reduce lesion-induced rotational behaviour. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):351–352. doi: 10.1038/292351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed W. J., Poltorak M., Becker J. B. Intracerebral adrenal medulla grafts: a review. Exp Neurol. 1990 Nov;110(2):139–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(90)90026-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage F. H., Fisher L. J. Intracerebral grafting: a tool for the neurobiologist. Neuron. 1991 Jan;6(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90116-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz C. G., Olanow C. W., Koller W. C., Penn R. D., Cahill D., Morantz R., Stebbins G., Tanner C. M., Klawans H. L., Shannon K. M. Multicenter study of autologous adrenal medullary transplantation to the corpus striatum in patients with advanced Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):337–341. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Salminen A., Walworth N. C., Novick P. J. A GTP-binding protein required for secretion rapidly associates with secretory vesicles and the plasma membrane in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):753–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grothe C., Unsicker K. Immunocytochemical localization of basic fibroblast growth factor in bovine adrenal gland, ovary, and pituitary. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Dec;37(12):1877–1883. doi: 10.1177/37.12.2685112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grothe C., Unsicker K. Immunocytochemical mapping of basic fibroblast growth factor in the developing and adult rat adrenal gland. Histochemistry. 1990;94(2):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF02440180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han V. K., D'Ercole A. J., Lund P. K. Cellular localization of somatomedin (insulin-like growth factor) messenger RNA in the human fetus. Science. 1987 Apr 10;236(4798):193–197. doi: 10.1126/science.3563497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper G. P., Pearce F. L., Vernon C. A. Production of nerve growth factor by the mouse adrenal medulla. Nature. 1976 May 20;261(5557):251–253. doi: 10.1038/261251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbacher G. K., Irminger J. C., Zapf J., Ziegler W. H., Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factor II in human adrenal pheochromocytomas and Wilms tumors: expression at the mRNA and protein level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1104–1106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfle G., Weiler R., Fischer-Colbrie R., Humpel C., Laslop A., Wohlfarter T., Hogue-Angeletti R., Saria A., Fleming P. J., Winkler H. Stimulation of rat adrenal medulla can induce differential changes in the peptide and mRNA levels of chromogranins, neuropeptides and other constituents of chromaffin granules. Regul Pept. 1991 Feb 26;32(3):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(91)90025-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillien L. E., Claude P. Nerve growth factor is a mitogen for cultured chromaffin cells. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):632–634. doi: 10.1038/317632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindau M., Gomperts B. D. Techniques and concepts in exocytosis: focus on mast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 12;1071(4):429–471. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90006-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindvall O. Transplantation into the human brain: present status and future possibilities. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989 Jun;Suppl:39–54. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.52.suppl.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahanthappa N. K., Gage F. H., Patterson P. H. Adrenal chromaffin cells as multipotential neurons for autografts. Prog Brain Res. 1990;82:33–39. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62587-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelsohn A. M., Anderson D. J. Changes in competence determine the timing of two sequential glucocorticoid effects on sympathoadrenal progenitors. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):589–604. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90285-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Burgoyne R. D. Exo1 and Exo2 proteins stimulate calcium-dependent exocytosis in permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1992 Feb 27;355(6363):833–836. doi: 10.1038/355833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Schoenherr C., Vandenbergh D. J., Anderson D. J. A common silencer element in the SCG10 and type II Na+ channel genes binds a factor present in nonneuronal cells but not in neuronal cells. Neuron. 1992 Jul;9(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata T., Hirokawa N. Organization of cortical cytoskeleton of cultured chromaffin cells and involvement in secretion as revealed by quick-freeze, deep-etching, and double-label immunoelectron microscopy. J Neurosci. 1992 Jun;12(6):2186–2197. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-06-02186.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata T., Sobue K., Hirokawa N. Conformational change and localization of calpactin I complex involved in exocytosis as revealed by quick-freeze, deep-etch electron microscopy and immunocytochemistry. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):13–25. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Yamamori T., Le T., Patterson P. H. Generation of neuronal diversity: analogies and homologies with hematopoiesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:247–253. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Marty A. Discrete changes of cell membrane capacitance observed under conditions of enhanced secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6712–6716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen F. C., Gammeltoft S. Insulin-like growth factors are mitogens for rat pheochromocytoma PC 12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):1018–1023. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notter M. F., Gupta M., Gash D. M. Neuronal properties of monkey adrenal medulla in vitro. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;244(1):69–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00218383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notter M. F., Hansen J. T., Okawara S., Gash D. M. Rodent and primate adrenal medullary cells in vitro: phenotypic plasticity in response to coculture with C6 glioma cells or NGF. Exp Brain Res. 1989;76(1):38–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00253621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L. Fluorescence histochemical evidence for axonal growth and secretion from transplanted adrenal medullary tissue. Histochemie. 1970;22(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00310543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto D., Unsicker K. Basic FGF reverses chemical and morphological deficits in the nigrostriatal system of MPTP-treated mice. J Neurosci. 1990 Jun;10(6):1912–1921. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-06-01912.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappas G. D., Sagen J. The fine structure of chromaffin cell implants in the pain modulatory regions of the rat periaqueductal gray and spinal cord. Prog Brain Res. 1988;78:513–520. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson P. H. Control of cell fate in a vertebrate neurogenic lineage. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1035–1038. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90379-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson P. H. The molecular basis of phenotypic choices in the sympathoadrenal lineage. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:20–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzak A., Winkler H. Exocytotic exposure and recycling of membrane antigens of chromaffin granules: ultrastructural evaluation after immunolabeling. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):510–515. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhoat A., Naville D., Jaillard C., Chatelain P. G., Saez J. M. Hormonal regulation of insulin-like growth factor I secretion by bovine adrenal cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6858–6862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perin M. S., Brose N., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Domain structure of synaptotagmin (p65) J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):623–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin D., Langley O. K., Aunis D. Anti-alpha-fodrin inhibits secretion from permeabilized chromaffin cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):498–501. doi: 10.1038/326498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petroski R. E., Grierson J. P., Choi-Kwon S., Geller H. M. Basic fibroblast growth factor regulates the ability of astrocytes to support hypothalamic neuronal survival in vitro. Dev Biol. 1991 Sep;147(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(05)80002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzoli G., Fahn S., Dwork A., Truong D. D., de Yebenes J. G., Jackson-Lewis V., Herbert J., Cadet J. L. Non-chromaffin tissue plus nerve growth factor reduces experimental parkinsonism in aged rats. Brain Res. 1988 Sep 6;459(2):398–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90659-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Ornberg R., Levine M., Kelner K., Morita K., Levine R., Forsberg E., Brocklehurst K. W., Duong L., Lelkes P. I. Hormone secretion by exocytosis with emphasis on information from the chromaffin cell system. Vitam Horm. 1985;42:109–196. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Rifkin D. B. Immunoreactive basic fibroblast growth factor-like proteins in chromaffin granules. J Neurochem. 1991 Mar;56(3):1087–1088. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausch D. M., Iacangelo A. L., Eiden L. E. Glucocorticoid- and nerve growth factor-induced changes in chromogranin A expression define two different neuronal phenotypes in PC12 cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Oct;2(10):921–927. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-10-921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer H., Thoenen H. Relationship between differentiation and terminal mitosis: chick sensory and ciliary neurons differentiate after terminal mitosis of precursor cells, whereas sympathetic neurons continue to divide after differentiation. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3739–3748. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03739.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagen J., Pappas G. D. Morphological and functional correlates of chromaffin cell transplants in CNS pain modulatory regions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;495:306–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb23683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Andersson C., Undén A., Troye-Blomberg M., Svenson S. B., Bartfai T. Interleukin-1 in adrenal chromaffin cells. Neuroscience. 1989;30(3):805–810. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer F. E., Schäfer T., Tapparelli C., Grob M., Karli U. O., Heumann R., Thoenen H., Bookman R. J., Burger M. M. Inhibition of exocytosis by intracellularly applied antibodies against a chromaffin granule-binding protein. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):709–712. doi: 10.1038/339709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidl K., Unsicker K. Survival and neuritic growth of sympathoadrenal (chromaffin) precursor cells in vitro. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1989;7(5):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(89)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidl K., Unsicker K. The determination of the adrenal medullary cell fate during embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1989 Dec;136(2):481–490. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90273-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serck-Hanssen G., Søvik O., Lie R. T. Characterization of specific insulin binding sites on chromaffin cells from bovine adrenal medulla. Int J Biochem. 1988;20(12):1435–1441. doi: 10.1016/s0020-711x(98)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. L., Reichardt L. F. Expression of the beta-nerve growth factor gene correlates with the density of sympathetic innervation in effector organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7951–7955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silani V., Pizzuti A., Falini A., Borsani G., Rugarli E. I., Melo C. A., Sidoli A., Villani F., Baralle F., Scarlato G. Beta-nerve growth factor (beta-NGF) mRNA expression in the parkinsonian adrenal gland. Exp Neurol. 1991 Aug;113(2):166–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(91)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemple D. L., Mahanthappa N. K., Anderson D. J. Basic FGF induces neuronal differentiation, cell division, and NGF dependence in chromaffin cells: a sequence of events in sympathetic development. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömberg I., Ebendal T., Olson L., Hoffer B. Chromaffin grafts: survival and nerve fiber formation as a function of donor age, nerve growth factor and host sympathetic denervation. Prog Brain Res. 1990;82:87–94. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62594-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terbush D. R., Holz R. W. Activation of protein kinase C is not required for exocytosis from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. The effects of protein kinase C(19-31), Ca/CaM kinase II(291-317), and staurosporine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21179–21184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., DeLellis R. A., Biales B., Nunnemacher G., Carabba V., Wolfe H. J. Nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth from normal human chromaffin cells. Lab Invest. 1980 Nov;43(5):399–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., Perlman R. L., Nunnemacher G., Morse G. M., DeLellis R. A., Wolfe H. J., Sheard B. E. Long-term effects of dexamethasone and nerve growth factor on adrenal medullary cells cultured from young adult rats. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;225(3):525–542. doi: 10.1007/BF00214802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Krisch B., Otten U., Thoenen H. Nerve growth factor-induced fiber outgrowth from isolated rat adrenal chromaffin cells: impairment by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3498–3502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Seidl K., Hofmann H. D. The neuro-endocrine ambiguity of sympathoadrenal cells. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1989;7(5):413–417. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(89)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Skaper S. D., Varon S. Developmental changes in the responses of rat chromaffin cells to neuronotrophic and neurite-promoting factors. Dev Biol. 1985 Oct;111(2):425–433. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90495-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Stahnke G., Müller T. H. Survival, morphology, and catecholamine storage of chromaffin cells in serum-free culture: evidence for a survival and differentiation promoting activity in medium conditioned by purified chromaffin cells. Neurochem Res. 1987 Nov;12(11):995–1003. doi: 10.1007/BF00970928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Stögbauer F. Screening of adrenal medullary neuropeptides for putative neurotrophic effects. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1992 Apr;10(2):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(92)90044-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Vey J., Hofmann H. D., Müller T. H., Wilson A. J. C6 glioma cell-conditioned medium induces neurite outgrowth and survival of rat chromaffin cells in vitro: comparison with the effects of nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2242–2246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Westermann R. Basic fibroblast growth factor promotes transmitter storage and synthesis in cultured chromaffin cells. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1992 Feb 21;65(2):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(92)90181-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigé X., Costa E., Wise B. C. Mechanism of nerve growth factor mRNA regulation by interleukin-1 and basic fibroblast growth factor in primary cultures of rat astrocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermann R., Grothe C., Unsicker K. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), a multifunctional growth factor for neuroectodermal cells. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1990;13:97–117. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1990.supplement_13.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermann R., Johannsen M., Unsicker K., Grothe C. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) immunoreactivity is present in chromaffin granules. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):285–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Fischer-Colbrie R. The chromogranins A and B: the first 25 years and future perspectives. Neuroscience. 1992 Aug;49(3):497–528. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90222-N. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuenschell C. W., Mori N., Anderson D. J. Analysis of SCG10 gene expression in transgenic mice reveals that neural specificity is achieved through selective derepression. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90117-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Gage F. H. Cooperative regulation of nerve growth factor synthesis and secretion in fibroblasts and astrocytes by fibroblast growth factor and other cytokines. Brain Res. 1992 Jan 8;569(1):14–25. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90364-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



