Abstract
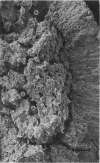
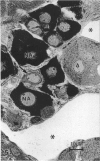
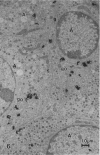
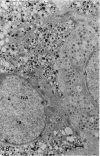
The morphological aspects of chromaffin tissue are reviewed, based mainly on our studies on the mouse adrenal gland. Particular attention was focused on the differential fixation of adrenaline and noradrenaline, and on the uptake and storage of [3H]dopa, [3H]dopamine and related substances in the adrenaline-storing (A) and noradrenaline-storing (NA) cells. Scanning electron microscopy combined with the NaOH-maceration method was useful for demonstrating the 3-dimensional organisation of nerve terminals, chromaffin cells, glial elements and vascular elements. In transmission electron microscopy, 3 types of chromaffin cell were distinguished. They were A, NA and SGC (small granule chromaffin) cells. After glutaraldehyde fixation followed by postosmication, A cell granules showed lower electron density, whereas NA cell granules were solid and dark. This difference in appearance between A and NA cells was first explained by the hypothesis that, after glutaraldehyde fixation, most of the adrenaline dissolved, whereas noradrenaline was precipitated in situ. Later, this hypothesis was supported by a series of autoradiographic and radioisotopic assay studies using [3H]dopa, [3H]dopamine and related substances; when [3H]adrenaline occurred, radioactivity in A cells mostly disappeared in the specimen, whereas that in the NA cells remained. At 15-60 min after an i.p. injection of [3H]dopa or [3H]dopamine, the concentration of radioactivity in A cells was higher than that in NA cells. However, in hypophysectomised mice, the radioactivity was low and evenly distributed in these 2 types of chromaffin cell. It was deduced that the carrier activities for extracellular dopa and dopamine were made greater in the A cells than in the NA cells by the pituitary gland. The hypophysectomy effects were restored by i.p. administration of ACTH.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee D. K., Lutz R. A., Levine M. A., Rodbard D., Pollard H. B. Uptake of norepinephrine and related catecholamines by cultured chromaffin cells: characterization of cocaine-sensitive and -insensitive plasma membrane transport sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1749–1753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benchimol S., Cantin M. Ultrastructural radioautography of synthesis and migration of proteins and catecholamines in the rat adrenal medulla. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;225(2):293–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00214683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benchimol S., Cantin M. Ultrastructural radioautography of the incorporation of tritiated leucine by the rat adrenal medulla in vivo. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Oct 17;193(2):179–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00209033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUPLAND R. E., PYPER A. S., HOPWOOD D. A METHOD FOR DIFFERENTIATING BETWEEN NORADRENALINE- AND ADRENALINE-STORING CELLS IN THE LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. Nature. 1964 Mar 21;201:1240–1242. doi: 10.1038/2011240b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Hopwood D. The mechanism of the differential staining reaction for adrenaline-and noreadrenaline-storing granules in tissues fixed in glutaraldehyde. J Anat. 1966 Apr;100(Pt 2):227–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Kobayashi S., Crowe J. On the fixation of catecholamines including adrenaline in tissue sections. J Anat. 1976 Nov;122(Pt 2):403–413. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Kobayashi S., Kent C. Observations on the localization of recently synthesized catecholamines in chromaffin cells after the injection of L-(2,5,6-3H)dopa. J Endocrinol. 1976 Apr;69(1):139–148. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0690139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Selby J. E. The blood supply of the mammalian adrenal medulla: a comparative study. J Anat. 1976 Dec;122(Pt 3):539–551. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLARP N. A., HOKFELT B. Histochemical demonstration of noradrenaline and adrenaline in the adrenal medulla. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 Jan;3(1):1–5. doi: 10.1177/3.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Kobayashi S., Kent C., Coupland R. E. Autoradiographic demonstration of a zonal distribution of 3H-dopamine-derived radioactivity in the mouse adrenal medulla perfusion-fixed with glutaraldehyde. Arch Histol Jpn. 1977 Mar;40(2):107–119. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.40.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Kobayashi S. Stress effects on the localization of exogenous [3H]dopamine in the mouse adrenal medulla. Brain Res. 1980 Jun 16;192(1):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Kobayashi S. The effects of hypophysectomy on the uptake and distribution of 3H-dopamine in the mouse adrenal medulla: an autoradiographic study. Arch Histol Jpn. 1978 Nov;41(5):401–410. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.41.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T. Neural regulation of adrenal chromaffin cell function in the mouse--stress effect on the distribution of [3H]dopamine in denervated adrenal medulla. Brain Res. 1982 Apr 22;238(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90769-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T. Neural regulation of adrenal chromaffin cell function in the mouse: fate and distribution of [3H]dopamine in denervated adrenal medulla. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1986 Apr;15(4):285–295. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(86)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent C., Coupland R. E. On the uptake of exogenous catecholamines by adrenal chromaffin cells and nerve endings. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;221(2):371–383. doi: 10.1007/BF00216741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesse W. K., Parker T. L., Coupland R. E. The innervation of the adrenal gland. I. The source of pre- and postganglionic nerve fibres to the rat adrenal gland. J Anat. 1988 Apr;157:33–41. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuta A., Murakami T. Microcirculation of the rat adrenal gland: a scanning electron microscope study of vascular casts. Am J Anat. 1982 May;164(1):19–28. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001640103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuta A., Murakami T. Relationship between chromaffin cells and blood vessels in the rat adrenal medulla: a transmission electron microscopic study combined with blood vessel reconstructions. Am J Anat. 1984 May;170(1):73–81. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001700106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuta A., Ohtani O., Murakami T. Three-dimensional organization of the collagen fibrillar framework in the rat adrenal gland. Arch Histol Cytol. 1991 May;54(2):133–144. doi: 10.1679/aohc.54.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Coupland R. F. Two populations of microvesicles in the SGC (small granule chromaffin) cells of the mouse adrenal medulla. Arch Histol Jpn. 1977 Jun;40(3):251–259. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.40.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Furness J. B., Smith T. K., Pompolo S. Histological identification of the interstitial cells of Cajal in the guinea-pig small intestine. Arch Histol Cytol. 1989 Jul;52(3):267–286. doi: 10.1679/aohc.52.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Goto K., Kano K. Disappearance of the difference between adrenal A and NA cells in the level of radioactivity after 3H-dopa injection in the hypophysectomized mouse. Arch Histol Jpn. 1978 Jun;41(3):285–290. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.41.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Kent C., Coupland R. E. Observations on the localization of labelled amino acid in mouse adrenal chromaffin cells after the injection of L-[4,5-3H] leucine. J Endocrinol. 1978 Jul;78(1):21–29. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0780021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Miyabayashi T., Uchida T., Yanaihara N. Met-enkephalin-Arg6-Gly7-Leu8 in large-cored vesicles of splanchnic nerve terminals innervating guinea pig adrenal chromaffin cells. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Feb 4;53(3):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90545-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo H. Immunohistochemical analysis of the localization of neuropeptides in the adrenal gland. Arch Histol Jpn. 1985 Dec;48(5):453–481. doi: 10.1679/aohc.48.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassmann H. Ein dritter Zelltyp im Nebennierenmark der Maus? Verh Anat Ges. 1974;68:641–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami T. Application of the scanning electron microscope to the study of the fine distribution of the blood vessels. Arch Histol Jpn. 1971 Feb;32(5):445–454. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.32.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani O. Three-dimensional organization of the connective tissue fibers of the human pancreas: a scanning electron microscopic study of NaOH treated-tissues. Arch Histol Jpn. 1987 Dec;50(5):557–566. doi: 10.1679/aohc.50.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Role L. W., Perlman R. L. Catecholamine uptake into isolated adrenal chromaffin cells: inhibition of uptake by acetylcholine. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):987–996. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Brandt J., Elde R. P., Goldstein M. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in gland cells and nerve terminals of the adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1978;3(12):1169–1186. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAGI K., KASUYA Y., WATANABE K. STUDIES ON THE DRUGS FOR PEPTIC ULCER. A RELIABLE METHOD FOR PRODUCING STRESS ULCER IN RATS. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1964 Apr;12:465–472. doi: 10.1248/cpb.12.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAMEZZANI J. H., CHIOCCHIO S., WASSERMANN G. F. A TECHNIQUE FOR LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC IDENTIFICATION OF ADRENALIN- AND NORADRENALIN-STORING CELLS. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Dec;12:890–899. doi: 10.1177/12.12.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi K., Okabe S. The effects of drugs on the production and recovery processes of the stress ulcer. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1968 Mar;18(1):9–18. doi: 10.1254/jjp.18.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi-Iwanaga H., Fujita T. Application of an NaOH maceration method to a scanning electron microscopic observation of Ito cells in the rat liver. Arch Histol Jpn. 1986 Aug;49(3):349–357. doi: 10.1679/aohc.49.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Coupland R. E. The innervation of the adrenal gland. IV. Innervation of the rat adrenal medulla from birth to old age. A descriptive and quantitative morphometric and biochemical study of the innervation of chromaffin cells and adrenal medullary neurons in Wistar rats. J Anat. 1990 Apr;169:209–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K. Chromaffin, small granule-containing and ganglion cells in the adrenal gland of reptiles: A comparative ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res. 1976 Jan 28;165(4):477–508. doi: 10.1007/BF00224477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K. Fine structure and innervation of the avian adrenal gland. I. Fine structure of adrenal chromaffin cells and ganglion cells. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Dec 6;145(3):389–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00307164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Habura-Flüh O., Zwarg U. Different types of small granule-containing cells and neurons in the guinea-pig adrenal medulla. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 May 18;189(1):109–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00223124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD J. G., BARRNETT R. J. HISTOCHEMICAL DEMONSTRATION OF NOREPINEPHRINE AT A FINE STRUCTURAL LEVEL. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Mar;12:197–209. doi: 10.1177/12.3.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD J. G. Identification of and observations on epinephrine and norepinephrine containing cells in the adrenal medulla. Am J Anat. 1963 May;112:285–303. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001120302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Fischer-Colbrie R. The chromogranins A and B: the first 25 years and future perspectives. Neuroscience. 1992 Aug;49(3):497–528. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90222-N. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]