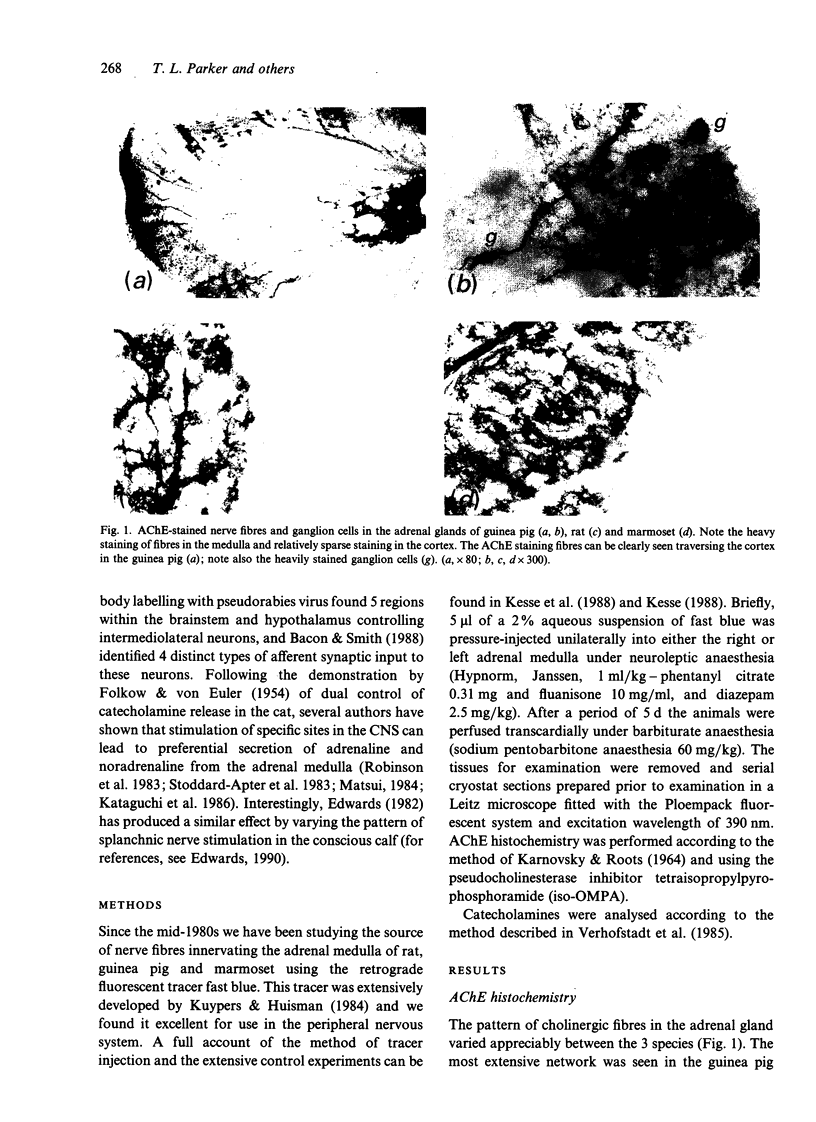
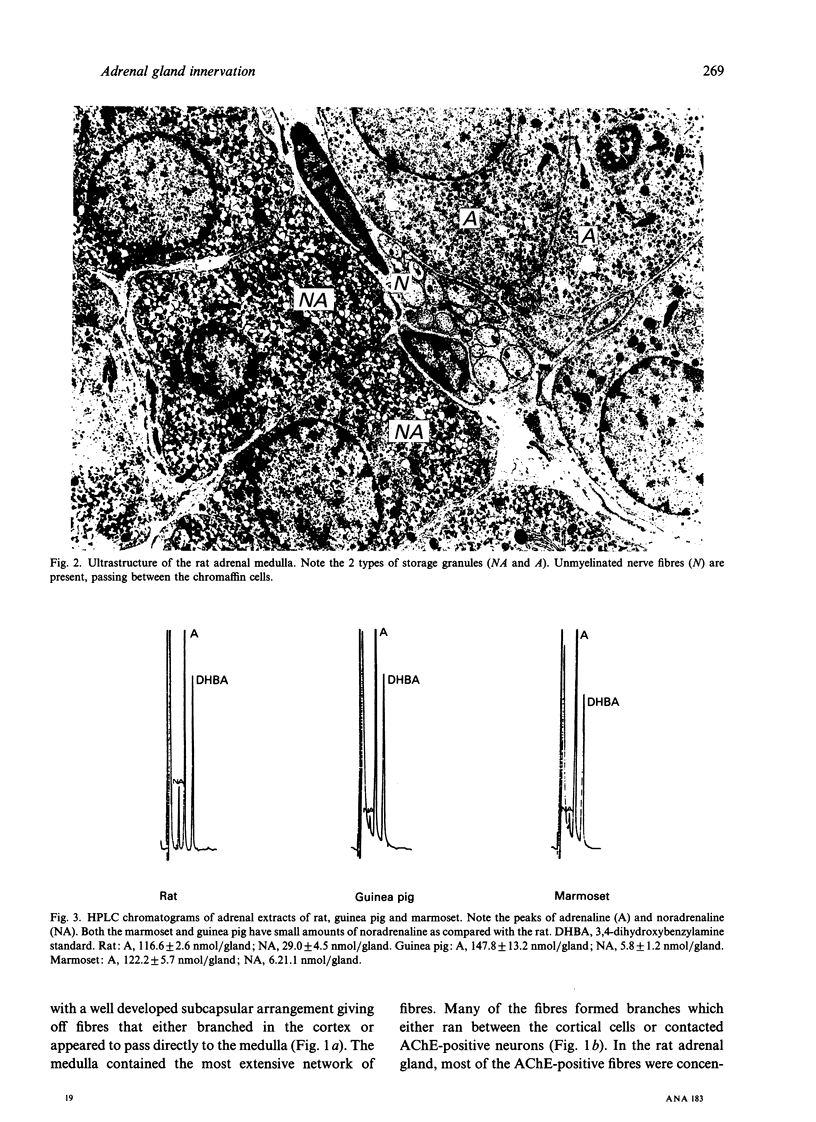
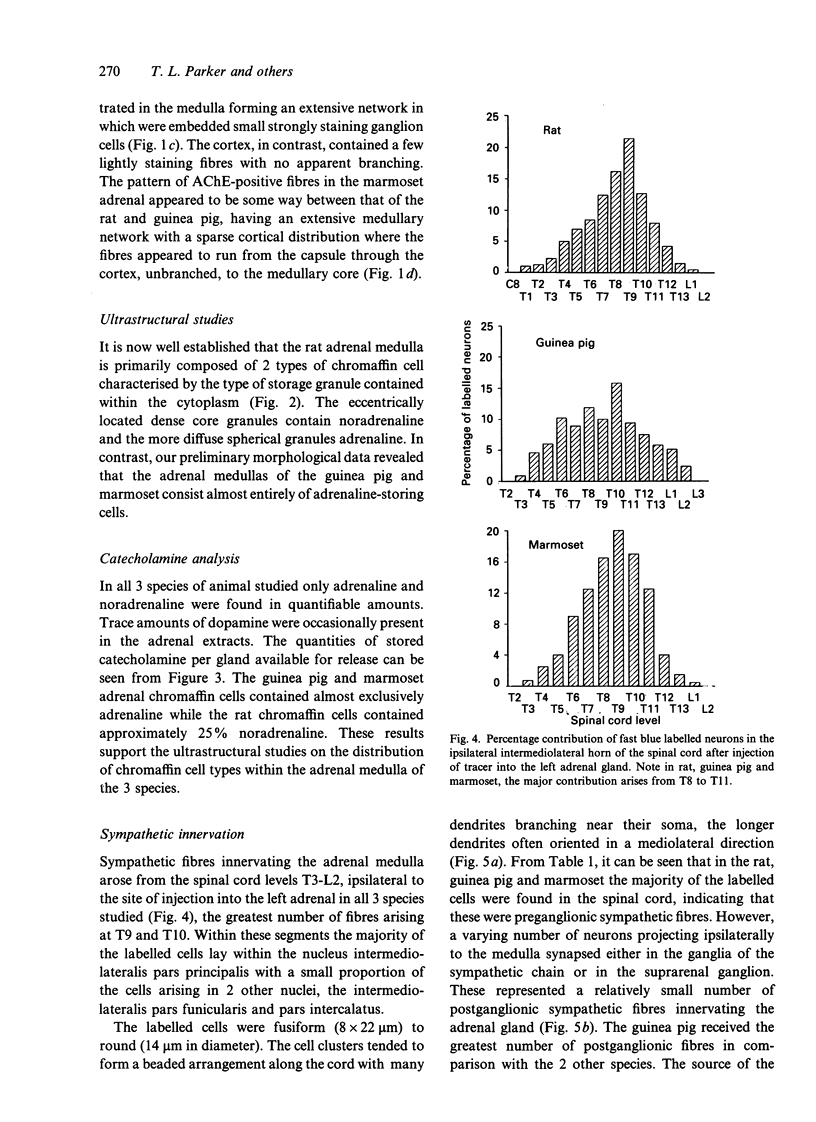
Abstract
Early conflicting reports and the lack of sensitive anatomical methods have led to an oversimplified view of adrenal gland innervation. It was not until the introduction of nerve fibre tracing techniques in the mid-1970s that the true complexity of adrenal innervation began to emerge. The first part of this article comprises a brief review of these and other relevant reports dealing with both medullary and cortical innervation. In the second part a detailed account is given of the work undertaken in Rex Coupland's Department relating to the innervation of the rodent and primate adrenal medulla using a retrograde fluorescent tracer technique. It was concluded that, in all 3 species studied, the adrenal medulla receives a sympathetic and parasympathetic efferent and an afferent innervation. The possible interrelationship between neural control of cortical and medullar secretions is discussed briefly.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacon S. J., Smith A. D. Preganglionic sympathetic neurones innervating the rat adrenal medulla: immunocytochemical evidence of synaptic input from nerve terminals containing substance P, GABA or 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988 Sep;24(1-2):97–122. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(88)90140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein S. R., Ehrhart-Bornstein M., Scherbaum W. A., Pfeiffer E. F., Holst J. J. Effects of splanchnic nerve stimulation on the adrenal cortex may be mediated by chromaffin cells in a paracrine manner. Endocrinology. 1990 Aug;127(2):900–906. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-2-900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck P., Gorgas K. Fine structure of baroreceptor terminals in the carotid sinus of guinea pigs and mice. Cell Tissue Res. 1976 Jul 20;170(1):95–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00220113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUPLAND R. E., HOLMES R. L. The distribution of cholinesterase in the adrenal glands of the rat, cat and rabbit. J Physiol. 1958 Apr 3;141(1):97–106. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson S., Skarphedinsson J. O., Delle M., Hoffman P., Thorén P. Reflex changes in post- and preganglionic sympathetic adrenal nerve activity and postganglionic sympathetic renal nerve activity upon arterial baroreceptor activation and during severe haemorrhage in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1992 Mar;144(3):317–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1992.tb09300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson S., Skarphedinsson J. O., Jennische E., Delle M., Thorén P. Neurophysiological evidence for and characterization of the post-ganglionic innervation of the adrenal gland in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1990 Dec;140(4):491–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1990.tb09025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celler B. G., Schramm L. P. Pre- and postganglionic sympathetic activity in splanchnic nerves of rats. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):R55–R61. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1981.241.1.R55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton B. G. Adrenal cortical innervation and glucocorticoid secretion. J Endocrinol. 1990 Jul;126(1):5–8. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1260005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Parker T. L., Kesse W. K., Mohamed A. A. The innervation of the adrenal gland. III. Vagal innervation. J Anat. 1989 Apr;163:173–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupland R. E., Selby J. E. The blood supply of the mammalian adrenal medulla: a comparative study. J Anat. 1976 Dec;122(Pt 3):539–551. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Poisner A. M. Preferential release of adrenaline from the adrenal medulla by muscarine and pilocarpine. Nature. 1965 Dec 11;208(5015):1102–1103. doi: 10.1038/2081102a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V. Adrenal catecholamine output in response to stimulation of the splanchnic nerve in bursts in the conscious calf. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:409–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. R. The innervation of the adrenal glands. J Physiol. 1913 Jun 19;46(3):285–290. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1913.sp001591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison J. P., Clark M. G. Retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase in peripheral autonomic nerves. J Comp Neurol. 1975 May 1;161(1):103–113. doi: 10.1002/cne.901610108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B., VON EULER U. S. Selective activation of noradrenaline and adrenaline producing cells in the cat's adrenal gland by hypothalamic stimulation. Circ Res. 1954 May;2(3):191–195. doi: 10.1161/01.res.2.3.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Minz B., Tsudzimura H. The mechanism of the nervous discharge of adrenaline. J Physiol. 1934 Jun 9;81(3):286–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1934.sp003136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goadsby P. J. Brainstem activation of the adrenal medulla in the cat. Brain Res. 1985 Feb 18;327(1-2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91517-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorgas K., Reinecke M., Weihe E., Forssmann W. G. Neurotensin and substance P immunoreactive nerve endings in the guinea pig carotid sinus and their ultrastructural counterparts. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1983;167(3):347–354. doi: 10.1007/BF00315672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görne R. C., Pfister C., Rathsack R., Oehme P. Zur zellulären Verteilung von Substanz P im Nebennierenmark der Ratte. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1984;43(1):135–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase P., Contestabile A., Flumerfelt B. A. Preganglionic innervation of the adrenal gland of the rat using horseradish peroxidase. Exp Neurol. 1982 Oct;78(1):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(82)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holets V., Elde R. The differential distribution and relationship of serotoninergic and peptidergic fibers to sympathoadrenal neurons in the intermediolateral cell column of the rat: a combined retrograde axonal transport and immunofluorescence study. Neuroscience. 1982 May;7(5):1155–1174. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)91123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzwarth M. A., Cunningham L. A., Kleitman N. The role of adrenal nerves in the regulation of adrenocortical functions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;512:449–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb24980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzwarth M. A. The distribution of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the rat adrenal cortex and medulla. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1984 Nov;11(3):269–283. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(84)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Lundberg J. M., Schultzberg M., Fahrenkrug J. Immunohistochemical evidence for a local VIP-ergic neuron system in the adrenal gland of the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Dec;113(4):575–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06944.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Sato A., Shimamura K., Swenson R. S. Reflex changes in sympatho-adrenal medullary functions in response to baroreceptor stimulation in anesthetized rats. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1984 May-Jun;10(3-4):295–303. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(84)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Edwards A. V. Muscarinic adrenal responses to acetylcholine in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:605–614. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J., ROOTS L. A "DIRECT-COLORING" THIOCHOLINE METHOD FOR CHOLINESTERASES. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Mar;12:219–221. doi: 10.1177/12.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISS T. Experimentell-morphologische Analyse der Nebenniereninnervation. Acta Anat (Basel) 1951;13(1-2):81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katafuchi T., Yoshimatsu H., Oomura Y., Sato A. Responses of adrenal catecholamine secretion to lateral hypothalamic stimulation and lesion in rats. Brain Res. 1986 Jan 15;363(1):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90666-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesse W. K., Parker T. L., Coupland R. E. The innervation of the adrenal gland. I. The source of pre- and postganglionic nerve fibres to the rat adrenal gland. J Anat. 1988 Apr;157:33–41. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalil Z., Livett B. G., Marley P. D. The role of sensory fibres in the rat splanchnic nerve in the regulation of adrenal medullary secretion during stress. J Physiol. 1986 Jan;370:201–215. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuta A., Murakami T. Microcirculation of the rat adrenal gland: a scanning electron microscope study of vascular casts. Am J Anat. 1982 May;164(1):19–28. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001640103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuta A., Murakami T. Relationship between chromaffin cells and blood vessels in the rat adrenal medulla: a transmission electron microscopic study combined with blood vessel reconstructions. Am J Anat. 1984 May;170(1):73–81. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001700106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleitman N., Holzwarth M. A. Catecholaminergic innervation of the rat adrenal cortex. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;241(1):139–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00214635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. Observations on the muscarinic activation of catecholamine secretion in the chicken adrenal. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):357–366. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Miyabayashi T., Uchida T., Yanaihara N. Met-enkephalin-Arg6-Gly7-Leu8 in large-cored vesicles of splanchnic nerve terminals innervating guinea pig adrenal chromaffin cells. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Feb 4;53(3):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90545-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo H., Kuramoto H., Fujita T. An immuno-electron-microscopic study of the localization of VIP-like immunoreactivity in the adrenal gland of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;245(3):531–538. doi: 10.1007/BF00218554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. R., Shute C. C. An electron-microscopic study of cholinesterase distribution in the rat adrenal medulla. J Microsc. 1969;89(2):181–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1969.tb00664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang B. T., Perlman R. L. Catecholamine secretion by hamster adrenal cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Mar;32(3):927–933. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G., Marley P. D., Wan D. C., Zhou X. F. Peptide regulation of adrenal medullary function. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1990;29:77–89. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9050-0_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMEJAC J. ACTIVITY OF THE ADRENAL MEDULLA AND ITS REGULATION. Physiol Rev. 1964 Apr;44:186–218. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1964.44.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley P. D., Bunn S. J., Wan D. C., Allen A. M., Mendelsohn F. A. Localization of angiotensin II binding sites in the bovine adrenal medulla using a labelled specific antagonist. Neuroscience. 1989;28(3):777–787. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley P., Livett B. G. Neuropeptides in the autonomic nervous system. CRC Crit Rev Clin Neurobiol. 1985;1(3):201–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui H. Adrenal medullary secretion in response to diencephalic stimulation in the rat. Neuroendocrinology. 1984 Feb;38(2):164–168. doi: 10.1159/000123885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maubert E., Tramu G., Croix D., Beauvillain J. C., Dupouy J. P. Co-localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and neuropeptide Y immunoreactivities in the nerve fibers of the rat adrenal gland. Neurosci Lett. 1990 May 31;113(2):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90290-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migally N. The innervation of the mouse adrenal cortex. Anat Rec. 1979 May;194(1):105–111. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091940107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed A. A., Parker T. L., Coupland R. E. The innervation of the adrenal gland. II. The source of spinal afferent nerve fibres to the guinea-pig adrenal gland. J Anat. 1988 Oct;160:51–58. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niijima A., Winter D. L. The effect of catecholamines on unit activity in afferent nerves from the adrenal glands. J Physiol. 1968 Apr;195(3):647–656. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oomori Y., Okuno S., Fujisawa H., Ono K. Immunoelectron microscopic study of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive nerve fibers and ganglion cells in the rat adrenal gland. Anat Rec. 1991 Mar;229(3):407–414. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092290313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelto-Huikko M., Salminen T., Hervonen A. Localization of enkephalins in adrenaline cells and the nerves innervating adrenaline cells in rat adrenal medulla. Histochemistry. 1985;82(4):377–383. doi: 10.1007/BF00494067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister C., Görne R. C. Substanz-P-Immunofluorescenz im Nebennierenmark der Ratte. Acta Histochem. 1983;72(1):127–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice F. D., Wood J. G. Adrenergic innervation of cat adrenal medulla. Anat Rec. 1975 Apr;181(4):689–703. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091810402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. M., Perry R. A., Hardy K. J., Coghlan J. P., Scoggins B. A. The innervation of the adrenal cortex in the sheep, Ovis ovis. J Anat. 1977 Sep;124(Pt 1):117–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson R. L., Culberson J. L., Carmichael S. W. Influence of hypothalamic stimulation on the secretion of adrenal medullary catecholamines. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 May;8(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Role L. W., Perlman R. L. Both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors mediate catecholamine secretion by isolated guinea-pig chromaffin cells. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):979–985. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90236-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. P., Miele E. A study of the differential secretion of epinephrine and norepinephrine from the perfused cat adrenal gland. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Nov;164(1):115–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm L. P., Adair J. R., Stribling J. M., Gray L. P. Preganglionic innervation of the adrenal gland of the rat: a study using horseradish peroxidase. Exp Neurol. 1975 Nov;49(2):540–553. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(75)90107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Brandt J., Elde R. P., Goldstein M. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in gland cells and nerve terminals of the adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1978;3(12):1169–1186. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Nishida S. The innervation of the adrenal cortex. Arch Histol Jpn. 1967 Feb;28(1):23–43. doi: 10.1679/aohc1950.28.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow R. A., Coupland R. E. Blood flow to the adrenal gland of the rat: its distribution between the cortex and the medulla before and after haemorrhage. J Anat. 1987 Dec;155:51–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoddard-Apter S. L., Siegel A., Levin B. E. Plasma catecholamine and cardiovascular responses following hypothalamic stimulation in the awake cat. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1983 Aug;8(4):343–360. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(83)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strack A. M., Sawyer W. B., Marubio L. M., Loewy A. D. Spinal origin of sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1988 Jul 5;455(1):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strack A. M., Sawyer W. B., Platt K. B., Loewy A. D. CNS cell groups regulating the sympathetic outflow to adrenal gland as revealed by transneuronal cell body labeling with pseudorabies virus. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 10;491(2):274–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson A., Coupland R. E. The innervation of the adrenal gland. IV. Innervation of the rat adrenal medulla from birth to old age. A descriptive and quantitative morphometric and biochemical study of the innervation of chromaffin cells and adrenal medullary neurons in Wistar rats. J Anat. 1990 Apr;169:209–236. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Habura-Flüh O., Zwarg U. Different types of small granule-containing cells and neurons in the guinea-pig adrenal medulla. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 May 18;189(1):109–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00223124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K. On the innervation of the rat and pig adrenal cortex. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;116(1):151–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00332863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varndell I. M., Polak J. M., Allen J. M., Terenghi G., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide tyrosine (NPY) immunoreactivity in norepinephrine-containing cells and nerves of the mammalian adrenal gland. Endocrinology. 1984 Apr;114(4):1460–1462. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-4-1460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhofstad A. A., Coupland R. E., Parker T. R., Goldstein M. Immunohistochemical and biochemical study on the development of the noradrenaline- and adrenaline-storing cells of the adrenal medulla of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;242(2):233–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00214536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakade A. R., Wakade T. D. Contribution of nicotinic and muscarinic receptors in the secretion of catecholamines evoked by endogenous and exogenous acetylcholine. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):973–978. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Hiramatsu K., Ohmori Y., Paik Y. K. Histo- and cytochemical studies on the distribution of acetylcholinesterase-positive nerve fibers in the goat adrenal gland. Anat Histol Embryol. 1990 Sep;19(3):245–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0264.1990.tb00886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesselingh S. L., Li Y. W., Blessing W. W. PNMT-containing neurons in the rostral medulla oblongata (C1, C3 groups) are transneuronally labelled after injection of herpes simplex virus type 1 into the adrenal gland. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Nov 20;106(1-2):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. Z. Partial degeneration of the nerve supply of the adrenal. A study in autonomic innervation. J Anat. 1939 Jul;73(Pt 4):540–550.1. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X. F., Livett B. G. Substance P increases catecholamine secretion from perfused rat adrenal glands evoked by prolonged field stimulation. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:321–334. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X. F., Oldfield B. J., Livett B. G. Substance P-containing sensory neurons in the rat dorsal root ganglia innervate the adrenal medulla. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1991 May;33(3):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(91)90025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]