Abstract
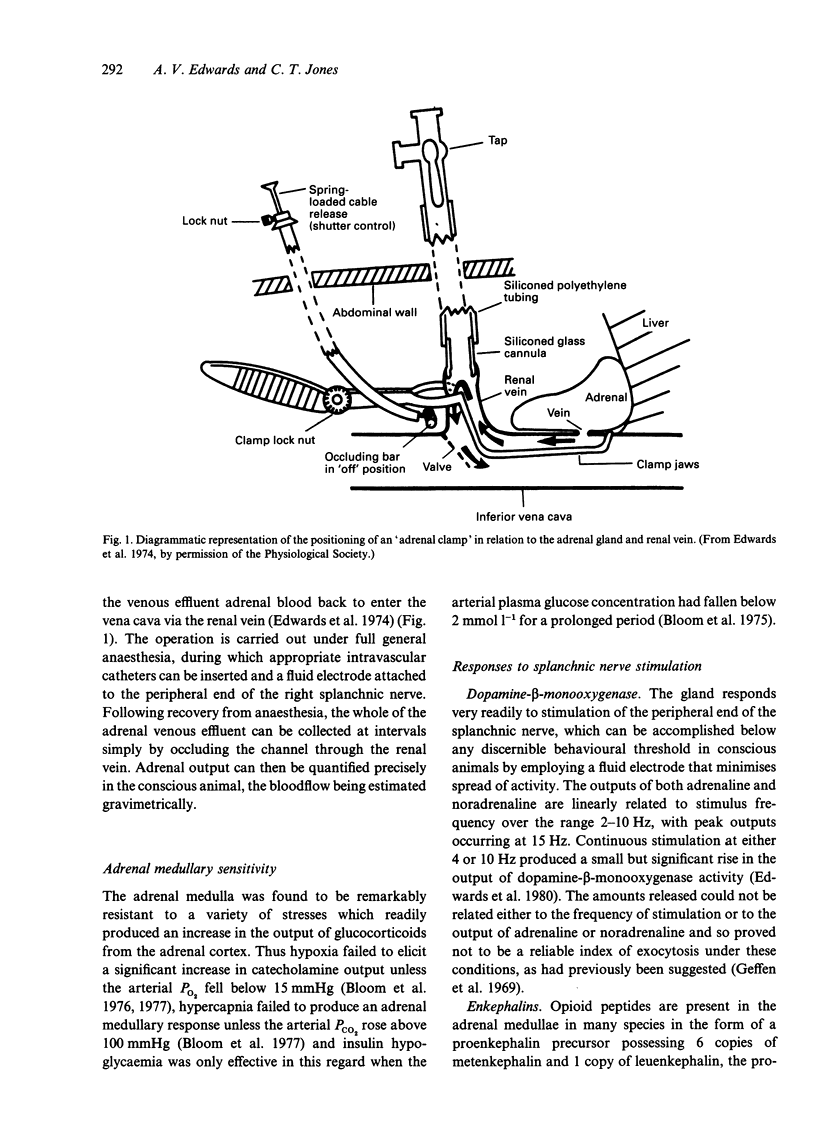
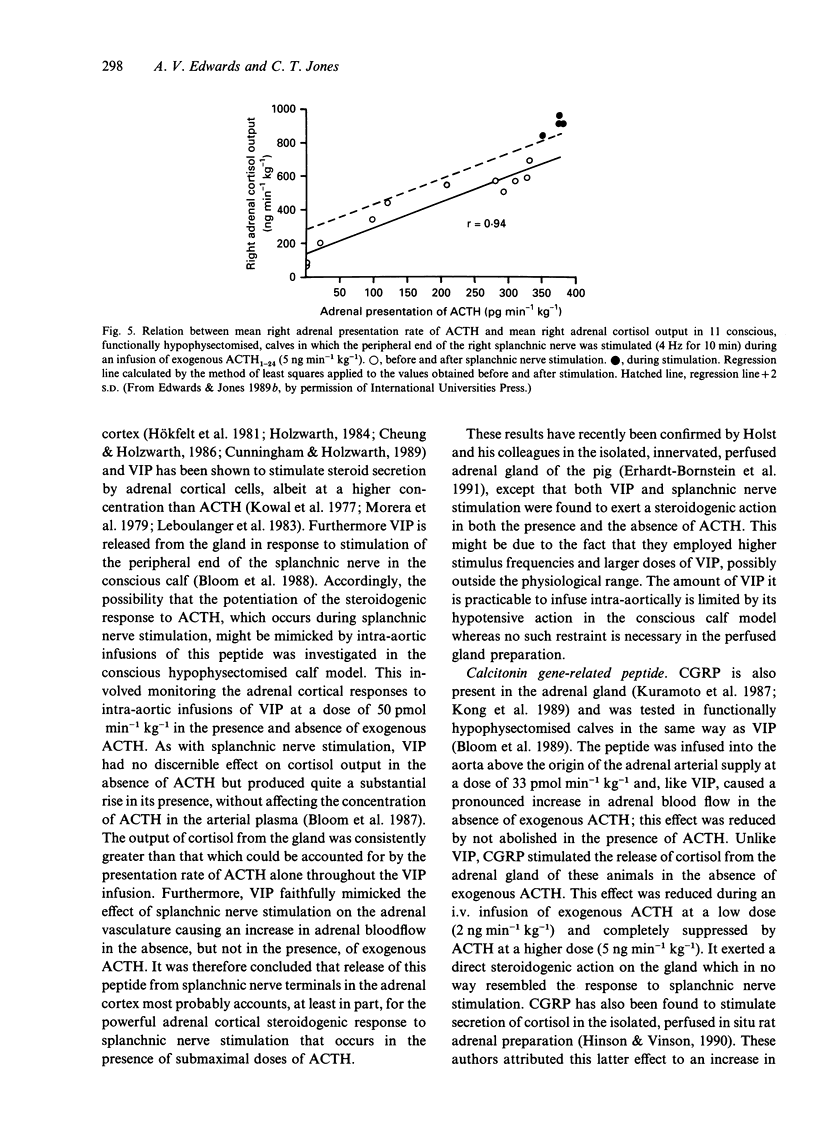
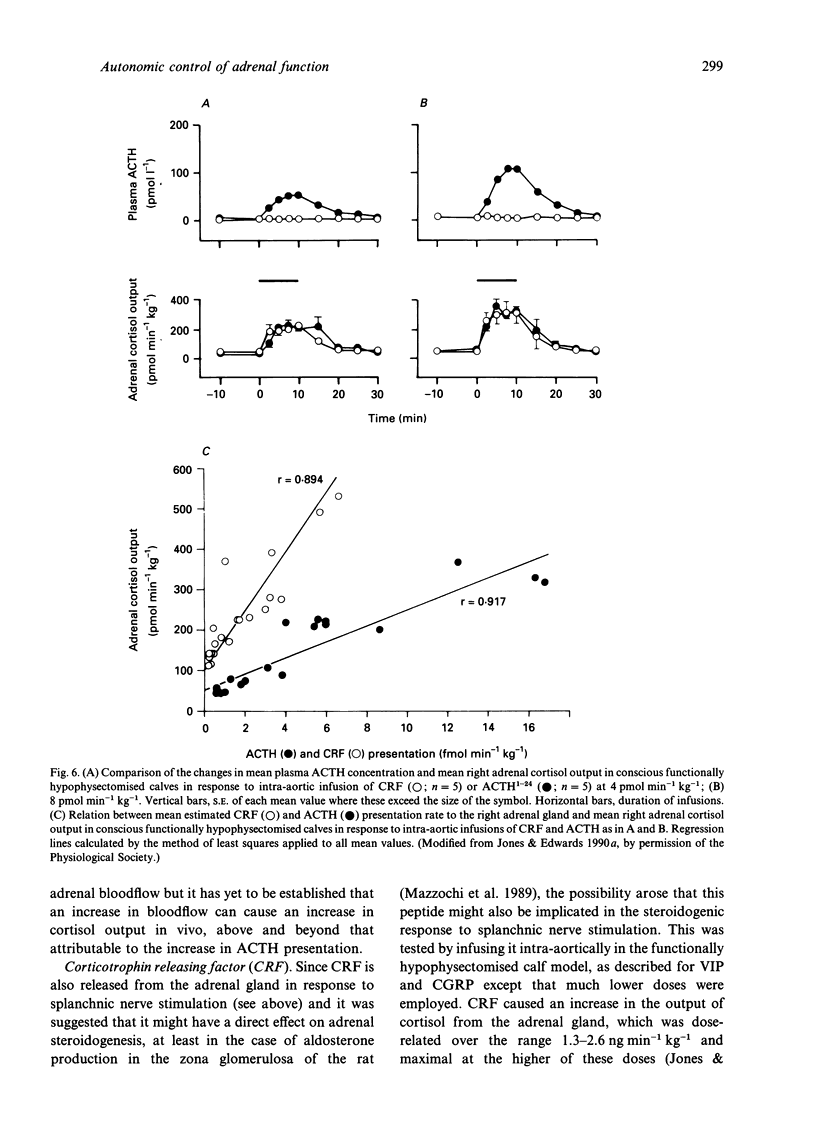
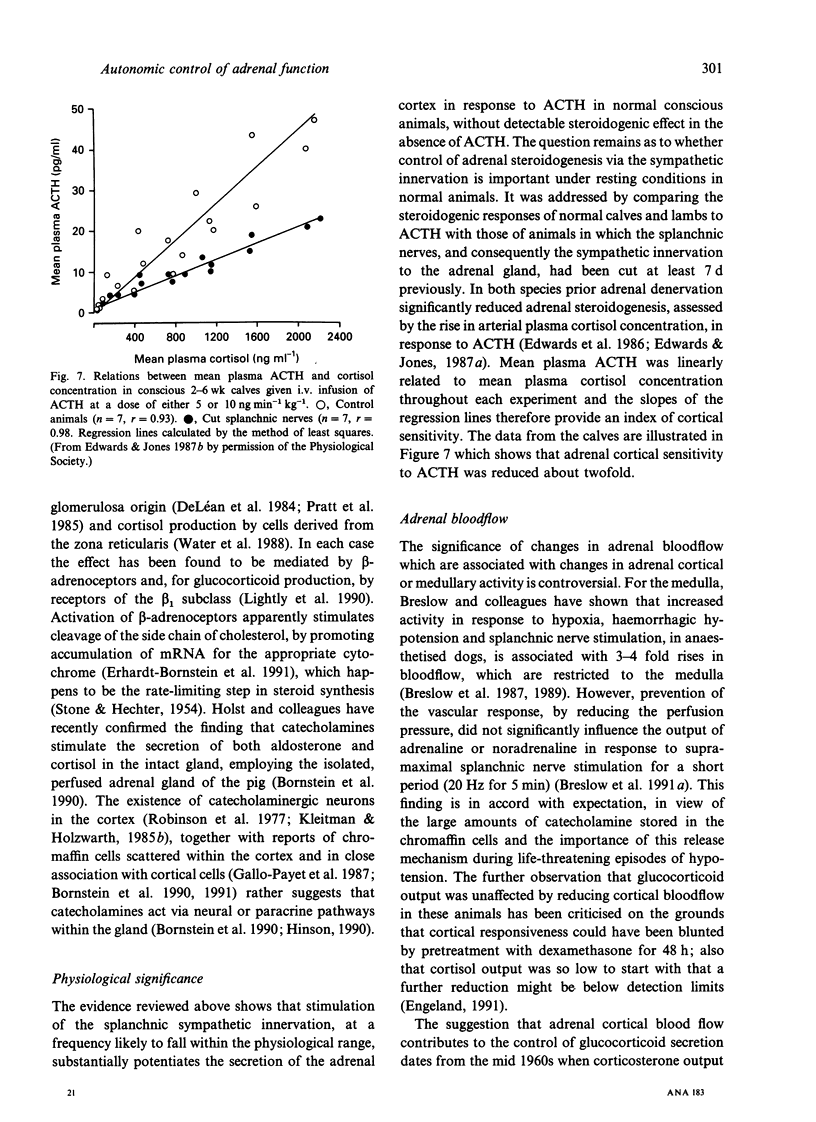
Recent studies of adrenal function in conscious calves are reviewed. These have involved collecting the whole of the adrenal effluent blood from the right adrenal gland at intervals and, where necessary, prior functional hypophysectomy by destruction of the pituitary stalk under general halothane anaesthesia 3 d previously. The adrenal medulla was found to release numerous neuropeptides, in addition to catecholamines, in response to stimulation of the peripheral end of the right splanchnic nerve, which was carried out below behavioural threshold. Many of these responses were enhanced by stimulating intermittently at a relatively high frequency. Intra-aortic infusions of a relatively low dose of acetylcholine (4.5 nmol min-1 kg-1) elicited similar responses. In the adrenal cortex, agonists which either potentiated the steroidogenic response to ACTH or exerted a direct steroidogenic action included VIP, CGRP, CRF and ACh acting via muscarinic receptors. Stimulation of the peripheral end of the right splanchnic nerve strongly potentiated the steroidogenic response to ACTH and there is compelling evidence that the innervation normally plays an important part in cortisol secretion.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANICHKOV S. V., MALYGHINA E. I., POSKALENKO A. N., RYZHENKOV V. E. Reflexes from carotid bodies upon the adrenals. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1960 Dec 1;129:156–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson P. O., Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Järhult J. Effects of stimulation of the chorda tympani in bursts on submaxillary responses in the cat. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:469–483. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreis P. G., Neri G., Nussdorfer G. G. Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) directly stimulates corticosterone secretion by the rat adrenal gland. Endocrinology. 1991 Feb;128(2):1198–1200. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-2-1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALFOUR W. E. Changes in the hormone output of the adrenal cortex of the young calf. J Physiol. 1953;122(Suppl):59–60P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballesta J. J., Borges R., García A. G., Hidalgo M. J. Secretory and radioligand binding studies on muscarinic receptors in bovine and feline chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1989 Nov;418:411–426. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyamina M., Leboulenger F., Lirhmann I., Delarue C., Feuilloley M., Vaudry H. Acetylcholine stimulates steroidogenesis in isolated frog adrenal gland through muscarinic receptors: evidence for a desensitization mechanism. J Endocrinol. 1987 Jun;113(3):339–348. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1130339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Hardy R. N. Adrenal and pancreatic endocrine responses to hypoxia and hypercapnia in the calf. J Physiol. 1977 Jul;269(1):131–154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Hardy R. N., Malinowska K. W., Silver M. Endocrine responses to insulin hypoglycaemia in the young calf. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(3):783–803. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Hardy R. N., Silver M. Adrenal and pancreatic endocrine responses to hypoxia in the conscious calf. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(2):271–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
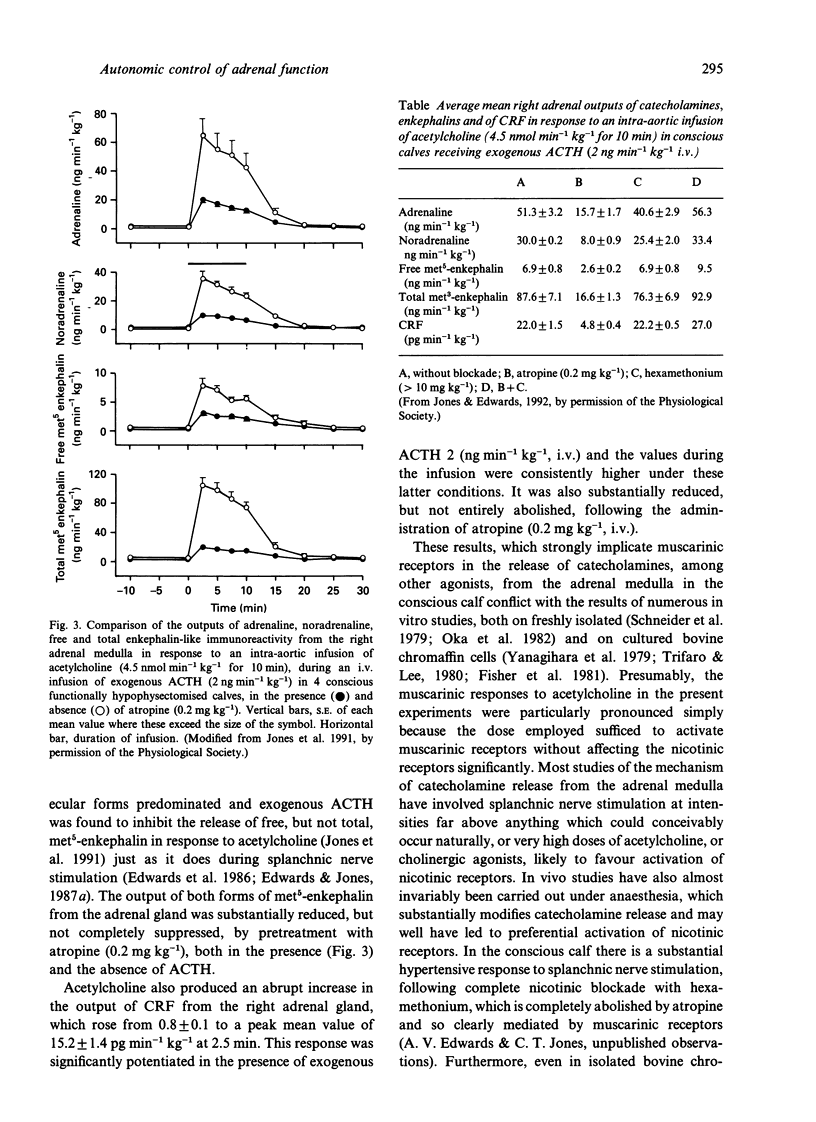
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Jones C. T. Adrenal cortical responses to vasoactive intestinal peptide in conscious hypophysectomized calves. J Physiol. 1987 Oct;391:441–450. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Jones C. T. Adrenal responses to calcitonin gene-related peptide in conscious hypophysectomized calves. J Physiol. 1989 Feb;409:29–41. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
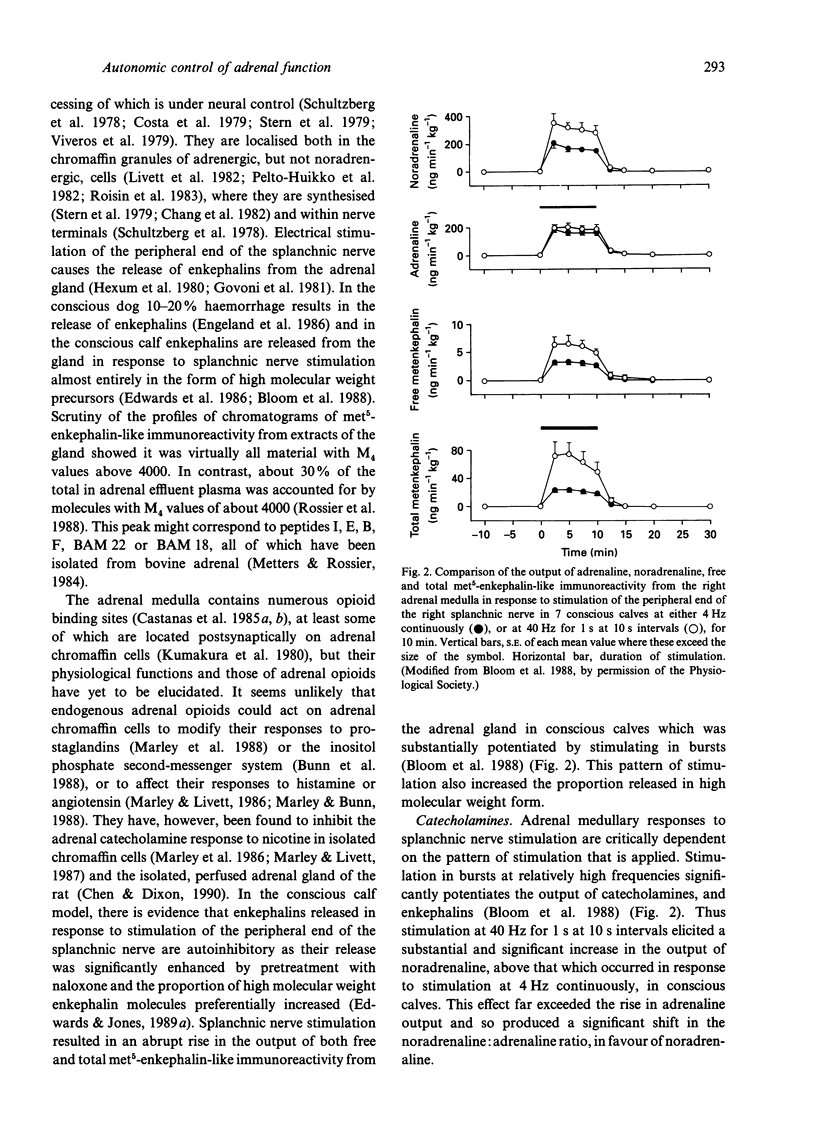
- Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V., Jones C. T. The adrenal contribution to the neuroendocrine responses to splanchnic nerve stimulation in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:513–526. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein S. R., Ehrhart-Bornstein M., Scherbaum W. A., Pfeiffer E. F., Holst J. J. Effects of splanchnic nerve stimulation on the adrenal cortex may be mediated by chromaffin cells in a paracrine manner. Endocrinology. 1990 Aug;127(2):900–906. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-2-900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein S. R., Ehrhart-Bornstein M., Usadel H., Böckmann M., Scherbaum W. A. Morphological evidence for a close interaction of chromaffin cells with cortical cells within the adrenal gland. Cell Tissue Res. 1991 Jul;265(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00318133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow M. J., Ball T. D., Miller C. F., Raff H., Traystman R. J. Adrenal blood flow and secretory relationships during hypoxia in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):H1458–H1465. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.5.H1458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow M. J., Jordan D. A., Thellman S. T., Traystman R. J. Neural control of adrenal medullary and cortical blood flow during hemorrhage. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 2):H521–H528. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.252.3.H521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn T. O., Engeland W. C., Anthony E. L., Gann D. S., Jackson I. M. Corticotropin-releasing factor in the dog adrenal medulla is secreted in response to hemorrhage. Endocrinology. 1987 Jan;120(1):25–33. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn S. J., Marley P. D., Livett B. G. Effects of opioid compounds on basal and muscarinic induced accumulation of inositol phosphates in cultured bovine chromaffin cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 1;37(3):395–399. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90205-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRONE C. THE SECRETION OF ADRENAL MEDULLARY HORMONES DURING HYPOGLYCEMIA IN INTACT, DECEREBRATE AND SPINAL SHEEP. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Mar;63:213–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton B. G. Adrenal cortical innervation and glucocorticoid secretion. J Endocrinol. 1990 Jul;126(1):5–8. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1260005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlton B. G., Nkomazana O. F., McGadey J., Neal D. E. A preliminary study of acetylcholinesterase-positive innervation in the human adrenal cortex. J Anat. 1991 Jun;176:99–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Dixon W. R. The effect of etorphine on nicotine- and muscarine-induced catecholamine secretion from perfused rat adrenal glands. Life Sci. 1990;46(16):1167–1173. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90453-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung C. Y., Holzwarth M. A. Fetal adrenal VIP: distribution and effect on medullary catecholamine secretion. Peptides. 1986 May-Jun;7(3):413–418. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(86)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley J. A., Ellis P., Ungar A. The reflex release of adrenaline and noradrenaline from the adrenal glands of cats and dogs. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:71–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham L. A., Holzwarth M. A. Autoradiographic distribution of 125I-VIP binding in the rat adrenal cortex. Peptides. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):1105–1108. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90196-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNER H. The effect of insulin hypoglycemia on the secretion of adrenaline and noradrenaline from the suprarenal of cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1954 Oct 20;32(1):63–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1954.tb01155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman M. F., Engeland W. C., Shinsako J. Compensatory adrenal growth: a neurally mediated reflex. Am J Physiol. 1976 Aug;231(2):408–414. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.2.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Léan A., Racz K., McNicoll N., Desrosiers M. L. Direct beta-adrenergic stimulation of aldosterone secretion in cultured bovine adrenal subcapsular cells. Endocrinology. 1984 Aug;115(2):485–492. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-2-485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempsher D. P., Gann D. S. Increased cortisol secretion after small hemorrhage is not attributable to changes in adrenocorticotropin. Endocrinology. 1983 Jul;113(1):86–93. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-1-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorovini-Zis K., Zis A. P. Innervation of the zona fasciculata of the adult human adrenal cortex: a light and electron microscopic study. J Neural Transm Gen Sect. 1991;84(1-2):75–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01249111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Kanno T., Sampson S. R. Effects of acetylcholine and other medullary secretagogues and antagonists on the membrane potential of adrenal chromaffin cells: an analysis employing techniques of tissue culture. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(1):107–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Poisner A. M. Preferential release of adrenaline from the adrenal medulla by muscarine and pilocarpine. Nature. 1965 Dec 11;208(5015):1102–1103. doi: 10.1038/2081102a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Furness P. N., Helle K. B. Adrenal medullary responses to stimulation of the splanchnic nerve in the conscious calf. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:15–27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Hansell D., Jones C. T. Effects of synthetic adrenocorticotrophin on adrenal medullary responses to splanchnic nerve stimulation in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:1–16. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Hardy R. N., Malinowska K. W. The sensitivity of adrenal responses to synthetic adrenocorticotrophin in the conscious unrestrained calf. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;245(3):639–653. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Jones C. T. Adrenal responses to splanchnic nerve stimulation in conscious calves given naloxone. J Physiol. 1989 Nov;418:339–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Jones C. T., Bloom S. R. Reduced adrenal cortical sensitivity to ACTH in lambs with cut splanchnic nerves. J Endocrinol. 1986 Jul;110(1):81–85. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1100081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Jones C. T. Secretion of corticotrophin releasing factor from the adrenal during splanchnic nerve stimulation in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:89–100. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Jones C. T. The effect of splanchnic nerve section on the sensitivity of the adrenal cortex to adrenocorticotrophin in the calf. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:23–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
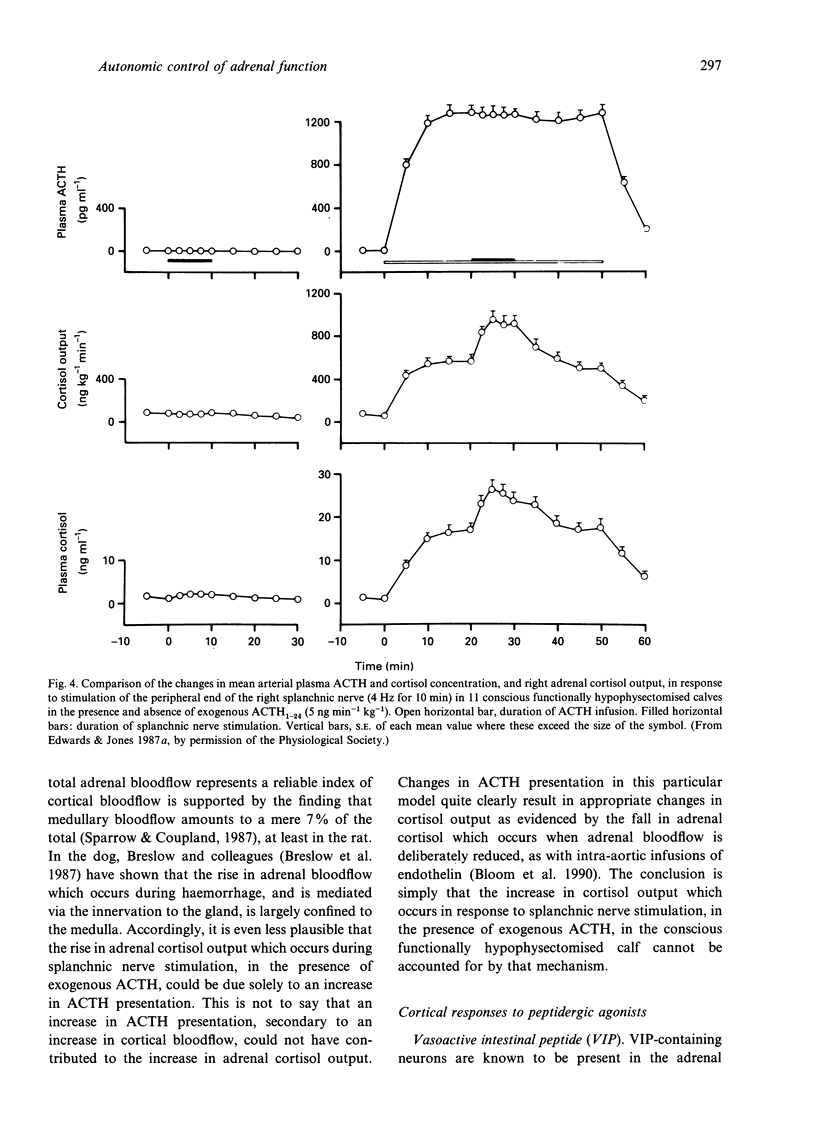
- Edwards A. V., Jones C. T. The effect of splanchnic nerve stimulation on adrenocortical activity in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1987 Jan;382:385–396. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhart-Bornstein M., Bornstein S. R., Scherbaum W. A., Pfeiffer E. F., Holst J. J. Role of the vasoactive intestinal peptide in a neuroendocrine regulation of the adrenal cortex. Neuroendocrinology. 1991 Dec;54(6):623–628. doi: 10.1159/000125969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engeland W. C., Bereiter D. F., Gann D. S. Sympathetic control of adrenal secretion of enkephalins after hemorrhage in awake dogs. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 2):R341–R348. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1986.251.2.R341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engeland W. C., Byrnes G. J., Presnell K., Gann D. S. Adrenocortical sensitivity to adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) in awake dogs changes as a function of the time of observation and after hemorrhage independently of changes in ACTH. Endocrinology. 1981 Jun;108(6):2149–2153. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-6-2149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engeland W. C., Dallman M. F. Neural mediation of compensatory adrenal growth. Endocrinology. 1976 Dec;99(6):1659–1662. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-6-1659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engeland W. C., Gann D. S. Splanchnic nerve stimulation modulates steroid secretion in hypophysectomized dogs. Neuroendocrinology. 1989 Aug;50(2):124–131. doi: 10.1159/000125211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B., VON EULER U. S. Selective activation of noradrenaline and adrenaline producing cells in the cat's adrenal gland by hypothalamic stimulation. Circ Res. 1954 May;2(3):191–195. doi: 10.1161/01.res.2.3.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Minz B., Tsudzimura H. The mechanism of the nervous discharge of adrenaline. J Physiol. 1934 Jun 9;81(3):286–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1934.sp003136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. K., Holz R. W., Agranoff B. W. Muscarinic receptors in chromaffin cell cultures mediate enhanced phospholipid labeling but not catecholamine secretion. J Neurochem. 1981 Aug;37(2):491–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg E. J., Rojas E., Pollard H. B. Muscarinic receptor enhancement of nicotine-induced catecholamine secretion may be mediated by phosphoinositide metabolism in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4915–4920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDFIEN A., GANONG W. F. Adrenal medullary and adrenal cortical response to stimulation of diencephalon. Am J Physiol. 1962 Feb;202:205–211. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.2.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANT J. K., FORREST A. P., SYMINGTON T. The secretion of cortisol and corticosterone by the human adrenal cortex. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1957 Oct;26(2):195–203. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0260195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo-Payet N., Pothier P., Isler H. On the presence of chromaffin cells in the adrenal cortex: their possible role in adrenocortical function. Biochem Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;65(6):588–592. doi: 10.1139/o87-076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffen L. B., Livett B. G., Rush R. A. Immunological localization of chromogranins in sheep sympathetic neurones, and their release by nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(2):58P–59P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govoni S., Hanbauer I., Hexum T. D., Yang H. Y., Kelly G. D., Costa E. In vivo characterization of the mechanisms that secrete enkephalin-like peptides stored in dog adrenal medulla. Neuropharmacology. 1981 Jul;20(7):639–645. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(81)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTMAN F. A., BROWNELL K. A., LIU T. Y. Blood flow through the dog adrenal. Am J Physiol. 1955 Feb;180(2):375–377. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.180.2.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZBAUER M., VOGT M. Functional changes produced in the adrenal cortex of the rat by administration or by release of corticotrophin. J Physiol. 1957 Oct 30;138(3):449–459. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjian A. J., Guidicelli C., Chambaz E. M. Cholinergic muscarinic stimulation of steroidogenesis in bovine adrenal cortex fasciculata cell suspensions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 12;714(1):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Murakami K., Hattori T., Niimi M., Fujino K., Ota Z. Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)-like immunoreactivity in the adrenal medulla. Peptides. 1984 Jul-Aug;5(4):707–711. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinson J. P., Kapas S., Teja R., Vinson G. P. Effect of the endothelins on aldosterone secretion by rat zona glomerulosa cells in vitro. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;40(1-3):437–439. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90213-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinson J. P. Paracrine control of adrenocortical function: a new role for the medulla? J Endocrinol. 1990 Jan;124(1):7–9. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1240007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinson J. P., Vinson G. P. Calcitonin gene-related peptide stimulates adrenocortical function in the isolated perfused rat adrenal gland in situ. Neuropeptides. 1990 Jul;16(3):129–133. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(90)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinson J. P., Vinson G. P., Kapas S., Teja R. The relationship between adrenal vascular events and steroid secretion: the role of mast cells and endothelin. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;40(1-3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90205-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinson J. P., Vinson G. P., Kapas S., Teja R. The role of endothelin in the control of adrenocortical function: stimulation of endothelin release by ACTH and the effects of endothelin-1 and endothelin-3 on steroidogenesis in rat and human adrenocortical cells. J Endocrinol. 1991 Feb;128(2):275–280. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1280275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinson J. P., Vinson G. P., Pudney J., Whitehouse B. J. Adrenal mast cells modulate vascular and secretory responses in the intact adrenal gland of the rat. J Endocrinol. 1989 May;121(2):253–260. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1210253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinson J. P., Vinson G. P., Whitehouse B. J., Price G. M. Effects of stimulation on steroid output and perfusion medium flow rate in the isolated perfused rat adrenal gland in situ. J Endocrinol. 1986 May;109(2):279–285. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1090279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzwarth M. A., Cunningham L. A., Kleitman N. The role of adrenal nerves in the regulation of adrenocortical functions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;512:449–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb24980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzwarth M. A. The distribution of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the rat adrenal cortex and medulla. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1984 Nov;11(3):269–283. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(84)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Lundberg J. M., Schultzberg M., Fahrenkrug J. Immunohistochemical evidence for a local VIP-ergic neuron system in the adrenal gland of the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Dec;113(4):575–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06944.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Zigmond R. E. Pattern of presynaptic nerve activity can determine the type of neurotransmitter regulating a postsynaptic event. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):472–474. doi: 10.1038/311472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Edwards A. V. Adrenal responses to corticotrophin-releasing factor in conscious hypophysectomized calves. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:25–36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Edwards A. V., Bloom S. R. Endocrine responses to intra-aortic infusions of acetylcholine in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1991 Aug;439:481–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Edwards A. V., Bloom S. R. The effect of changes in adrenal blood flow on adrenal cortical responses to adrenocorticotrophin in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:377–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Edwards A. V., Bloom S. R. The effect of changes in adrenal blood flow on adrenal cortical responses to adrenocorticotrophin in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:377–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Edwards A. V. Muscarinic adrenal responses to acetylcholine in conscious calves. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:605–614. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Edwards A. V. Release of adrenocorticotrophin from the adrenal gland in the conscious calf. J Physiol. 1990 Jul;426:397–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEPPING J. Modalités sécretoires de la médullosurrénale en fonction de la fréquence de stimulation du nerf splanchnique. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1956 Sep 10;150(4):705–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko M., Kaneko K., Shinsako J., Dallman M. F. Adrenal sensitivity to adrenocorticotropin varies diurnally. Endocrinology. 1981 Jul;109(1):70–75. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-1-70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesse W. K., Parker T. L., Coupland R. E. The innervation of the adrenal gland. I. The source of pre- and postganglionic nerve fibres to the rat adrenal gland. J Anat. 1988 Apr;157:33–41. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpekar S. M., Prat J. C., Schiavone M. T. Effect of muscarine on release of catecholamines from the perfused adrenal gland of the cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;77(3):455–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09318.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleitman N., Holzwarth M. A. Catecholaminergic innervation of the rat adrenal cortex. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;241(1):139–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00214635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleitman N., Holzwarth M. A. Compensatory adrenal cortical growth is inhibited by sympathectomy. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 1):E261–E263. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.2.E261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. Observations on the muscarinic activation of catecholamine secretion in the chicken adrenal. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):357–366. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong J. Y., Thureson-Klein A., Klein R. L. Differential distribution of neuropeptides and serotonin in pig adrenal glands. Neuroscience. 1989;28(3):765–775. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal J., Horst I., Pensky J., Alfonzo M. A comparison of the effects of ACTH, vasoactive intestinal peptide, and cholera toxin on adrenal cAMP and steroid synthesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Oct 28;297:314–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb41863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumakura K., Karoum F., Guidotti A., Costa E. Modulation of nicotinic receptors by opiate receptor agonists in cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):489–492. doi: 10.1038/283489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramoto H., Kondo H., Fujita T. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-like immunoreactivity in scattered chromaffin cells and nerve fibers in the adrenal gland of rats. Cell Tissue Res. 1987 Feb;247(2):309–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00218312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'age M., Gonzalez-Luque A., Yates F. E. Adrenal blood flow dependence of cortisol secretion rate in unanesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1970 Aug;219(2):281–287. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leboulenger F., Leroux P., Delarue C., Tonon M. C., Charnay Y., Dubois P. M., Coy D. H., Vaudry H. Co-localization of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and enkephalins in chromaffin cells of the adrenal gland of amphibia. Stimulation of corticosteroid production by VIP. Life Sci. 1983 Jan 24;32(4):375–383. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter F. H., Kirshner N. Studies of chick adrenal medulla in organ culture. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 May 1;24(9):967–974. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. L., Trendelenburg U. Muscarinic transmission of preganglionic impulses to the adrenal medulla of the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Oct;158(1):73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightly E. R., Walker S. W., Bird I. M., Williams B. C. Subclassification of beta-adrenoceptors responsible for steroidogenesis in primary cultures of bovine adrenocortical zona fasciculata/reticularis cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;99(4):709–712. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12993.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G., Day R., Elde R. P., Howe P. R. Co-storage of enkephalins and adrenaline in the bovine adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1982 May;7(5):1323–1332. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)91138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMEJAC J. ACTIVITY OF THE ADRENAL MEDULLA AND ITS REGULATION. Physiol Rev. 1964 Apr;44:186–218. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1964.44.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R., Staehelin M. Adrenal responses to corticotrophin in the presence of an inhibitor of protein synthesis. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1968 Aug;58(4):619–629. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0580619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley P. D., Bunn S. J. Lack of effect of opioid compounds on angiotensin II responses of bovine adrenal medullary cells. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Aug 1;90(3):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley P. D., Bunn S. J., Livett B. G. Prostanoid responses of bovine adrenal medullary cells: lack of effect of opioids. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 12;145(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley P. D., Livett B. G. Effects of opioid compounds on desensitization of the nicotinic response of isolated bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 15;36(18):2937–2944. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley P. D., Mitchelhill K. I., Livett B. G. Effects of opioid peptides containing the sequence of Met5-enkephalin or Leu5-enkephalin on nicotine-induced secretion from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1986 Jan;46(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb12918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley P. D., Mitchelhill K. I., Livett B. G. Metorphamide, a novel endogenous adrenal opioid peptide, inhibits nicotine-induced secretion from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Brain Res. 1986 Jan 15;363(1):10–17. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90653-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzocchi G., Rebuffat P., Meneghelli V., Nussdorfer G. G. Effects of the infusion with ACTH or CRH on the secretory activity of rat adrenal cortex. J Steroid Biochem. 1989 Jun;32(6):841–843. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(89)90461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morera A. M., Cathiard A. M., Laburthe M., Saez J. M. Interaction of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) with a mouse adrenal cell line (Y-1): specific binding and biological effects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):78–85. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91592-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenweller J. E., Meier A. H. Adrenal innervation may be an extrapituitary mechanism able to regulate adrenocortical rhythmicity in rats. Endocrinology. 1982 Oct;111(4):1334–1338. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-4-1334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenweller J. E., Meier A. H., Ferrell B. R., Horseman N. D., Proctor A. Extrapituitary regulation of the circadian rhythm of plasma corticosteroid concentration in rats. Endocrinology. 1978 Nov;103(5):1875–1879. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-5-1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelto-Huikko M., Salminen T., Hervonen A. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity is restricted to the adrenaline cells in the hamster adrenal medulla. Histochemistry. 1982;73(4):493–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00493363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter I. D., Whitehouse B. J., Taylor A. H., Nussey S. S. Effect of arginine vasopressin and oxytocin on acetylcholine-stimulation of corticosteroid and catecholamine secretion from the rat adrenal gland perfused in situ. Neuropeptides. 1988 Nov-Dec;12(4):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(88)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt J. H., Turner D. A., McAteer J. A., Henry D. P. Beta-adrenergic stimulation of aldosterone production by rat adrenal capsular explants. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):1189–1194. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-1189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPELA C. E., COVIAN M. R. Fréquence de stimulation des nerfs splanchniques et sécrétion surrénale d'adrénaline et de noradrénaline. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1954 Oct;148(19-20):1667–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPELA C. E. Differential secretion of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1956;6(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REDGATE E. S., GELLHORN E. Nature of sympathetico-adrenal discharge under conditions of excitation of central autonomic structures. Am J Physiol. 1953 Sep;174(3):475–480. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.174.3.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENFELD G. Stimulative effect of acetylcholine on the adrenocortical function of isolated perfused calf adrenals. Am J Physiol. 1955 Nov;183(2):272–278. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.183.2.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. M., Perry R. A., Hardy K. J., Coghlan J. P., Scoggins B. A. The innervation of the adrenal cortex in the sheep, Ovis ovis. J Anat. 1977 Sep;124(Pt 1):117–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roisin M. P., Artola A., Henry J. P., Rossier J. Enkephalins are associated with adrenergic granules in bovine adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1983 Sep;10(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Role L. W., Perlman R. L. Both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors mediate catecholamine secretion by isolated guinea-pig chromaffin cells. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):979–985. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90236-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAPIRSTEIN L. A., GOLDMAN H. Adrenal blood flow in the albino rat. Am J Physiol. 1959 Jan;196(1):159–162. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.196.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STONE D., HECHTER O. Studies on ACTH action in perfused bovine adrenals: the site of action of ACTH in corticosteroidogenesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1954 Aug;51(2):457–469. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(54)90501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakima N. T., Breslow M. J., Raff H., Traystman R. J. Lack of coupling between adrenal cortical metabolic activity and blood flow in anesthetized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 2):H410–H415. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.2.H410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider A. S., Cline H. T., Lemaire S. Rapid rise in cyclic GMP accompanies catecholamine secretion in suspensions of isolated adrenal chromaffin cells. Life Sci. 1979 Apr 9;24(15):1389–1394. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Brandt J., Elde R. P., Goldstein M. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in gland cells and nerve terminals of the adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1978;3(12):1169–1186. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow R. A., Coupland R. E. Blood flow to the adrenal gland of the rat: its distribution between the cortex and the medulla before and after haemorrhage. J Anat. 1987 Dec;155:51–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A. K., Meier A. H. Daily variation in concentration of cortisol in plasma in intact and hypophysectomized gulf killifish. Science. 1972 Jul 14;177(4044):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4044.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark E., Varga B., Acs Z., Papp M. Adrenal blood flow response to adrenocorticotrophic hormone and other stimuli in the dog. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1965 Sep 15;285(4):296–301. doi: 10.1007/BF00363229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A. S., Lewis R. V., Kimura S., Rossier J., Gerber L. D., Brink L., Stein S., Udenfriend S. Isolation of the opioid heptapeptide Met-enkephalin [Arg6,Phe7] from bovine adrenal medullary granules and striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6680–6683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Stjärne E., Msghina M., Bao J. X. K+ and Ca2+ channel blockers may enhance or depress sympathetic transmitter release via a Ca(2+)-dependent mechanism "upstream" of the release site. Neuroscience. 1991;44(3):673–692. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Tomori N., Tozawa F., Mouri T., Demura H., Shizume K. Distribution and characterization of immunoreactive corticotropin-releasing factor in human tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Nov;59(5):861–866. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-5-861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifaró J. M., Lee R. W. Morphological characteristics and stimulus-secretion coupling in bovine adcrenal chromaffin cell cultures. Neuroscience. 1980;5(9):1533–1546. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urquhart J. Adrenal blood flow and the adrenocortical response to corticotropin. Am J Physiol. 1965 Dec;209(6):1162–1168. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.6.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S., FOLKOW B. Einfluss verschiedener afferenter Nervenreize auf die Zusammensetzung des Nebennierenmarkinkretes bei der Katze. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1953;219(3):242–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson G. P., Pudney J. A., Whitehouse B. J. The mammalian adrenal circulation and the relationship between adrenal blood flow and steroidogenesis. J Endocrinol. 1985 May;105(2):285–294. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1050285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viveros O. H., Diliberto E. J., Jr, Hazum E., Chang K. J. Opiate-like materials in the adrenal medulla: evidence for storage and secretion with catecholamines. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(3):1101–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT R. D. Blood flow through the adrenal gland. Endocrinology. 1963 Mar;72:418–428. doi: 10.1210/endo-72-3-418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakade A. R., Wakade T. D. Contribution of nicotinic and muscarinic receptors in the secretion of catecholamines evoked by endogenous and exogenous acetylcholine. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):973–978. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. W., Lightly E. R., Milner S. W., Williams B. C. Catecholamine stimulation of cortisol secretion by 3-day primary cultures of purified zona fasciculata/reticularis cells isolated from bovine adrenal cortex. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1988 May;57(1-2):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(88)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. E., Shinsako J., Dallman M. F. Comparison of canine corticosteroid responses to mean and phasic increases in ACTH. Am J Physiol. 1982 Feb;242(2):E102–E108. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.242.2.E102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. E., Shinsako J., Keil L. C., Ramsay D. J., Dallman M. F. Apparent dissociation of adrenocorticotropin and corticosteroid responses to 15 ml/kg hemorrhage in conscious dogs. Endocrinology. 1982 Apr;110(4):1416–1421. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-4-1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara N., Isosaki M., Ohuchi T., Oka M. Muscarinic receptor-mediated increase in cyclic GMP level in isolated bovine adrenal medullary cells. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 15;105(2):296–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80633-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


