Abstract
Fibre optic confocal imaging (FOCI) is a new type of microscopy which has been recently developed (Delaney et al. 1993). In contrast to conventional light microscopy, FOCI and other confocal techniques allow clear imaging of subsurface structures within translucent objects. However, unlike conventional confocal microscopes which are bulky (because of a need for accurate alignment of large components) FOCI allows the imaging end to be miniaturised and relatively mobile. FOCI is thus particularly suited for clear subsurface imaging of structures within living animals or subjects. The aim of the present study was to assess the suitability of using FOCI for imaging of subsurface structures within the colon, both in vitro (human and rat biopsies) and in vivo (in rats). Images were obtained in fluorescence mode (excitation 488 nm, detection above 515 nm) following topical application of fluorescein. By this technique the glandular structure of the colon was imaged. FOCI is thus suitable for subsurface imaging of the colon in vivo.
Full text
PDF
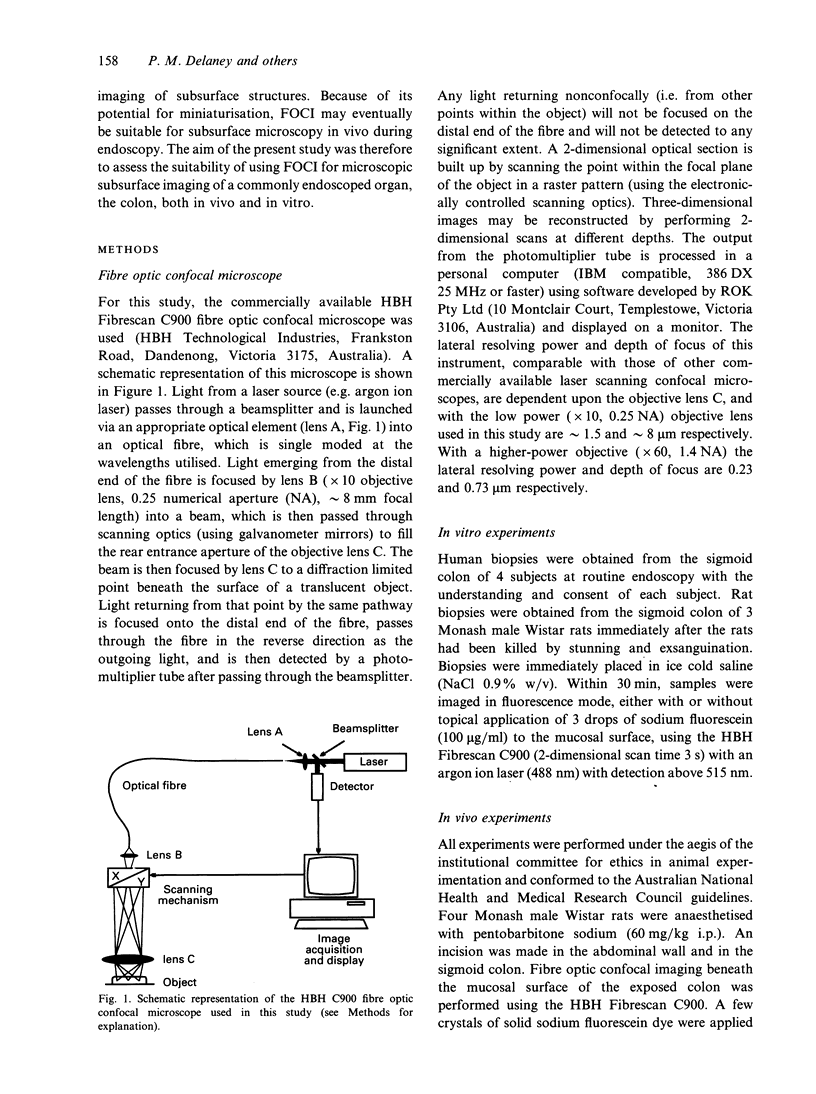
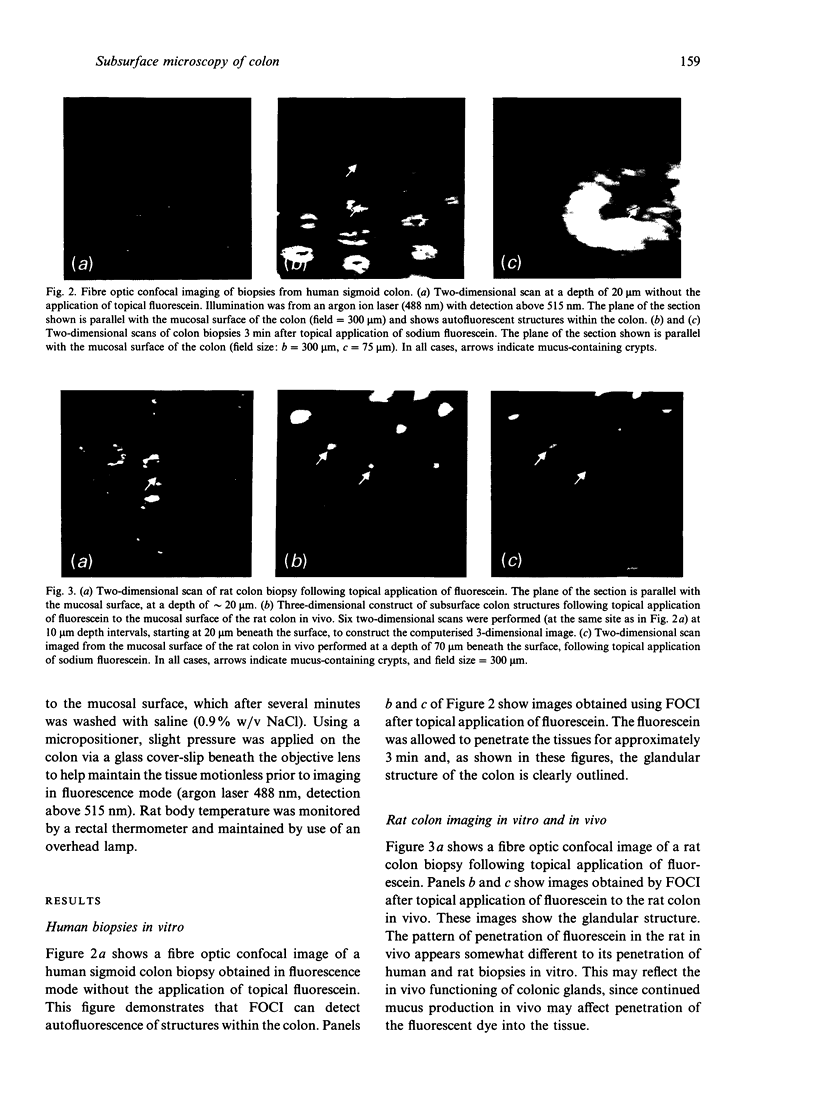

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Delaney P. M., Harris M. R., King R. G. Novel microscopy using fibre optic confocal imaging and its suitability for subsurface blood vessel imaging in vivo. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1993 Mar;20(3):197–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1993.tb01669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine A., Amos W. B., Durbin R. M., McNaughton P. A. Confocal microscopy: applications in neurobiology. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Aug;11(8):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paddock S. W. The laser-scanning confocal microscope in biomedical research. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1991 Dec;198(3):772–780. doi: 10.3181/00379727-198-43321b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G., Amos W. B., Fordham M. An evaluation of confocal versus conventional imaging of biological structures by fluorescence light microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):41–48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




