Abstract
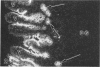
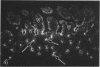
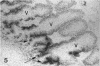
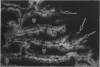
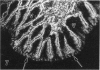
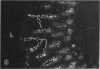
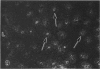
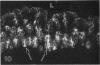
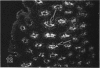
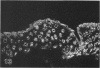
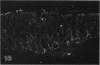
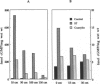
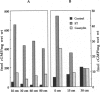
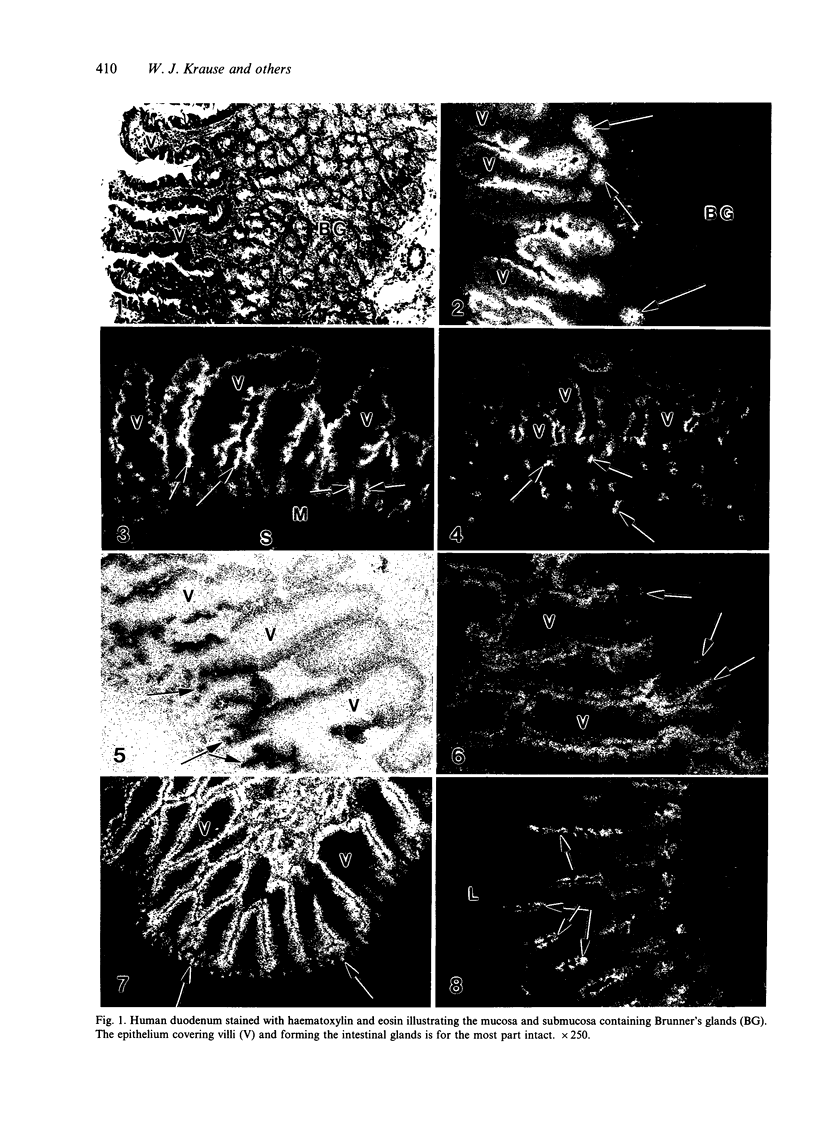
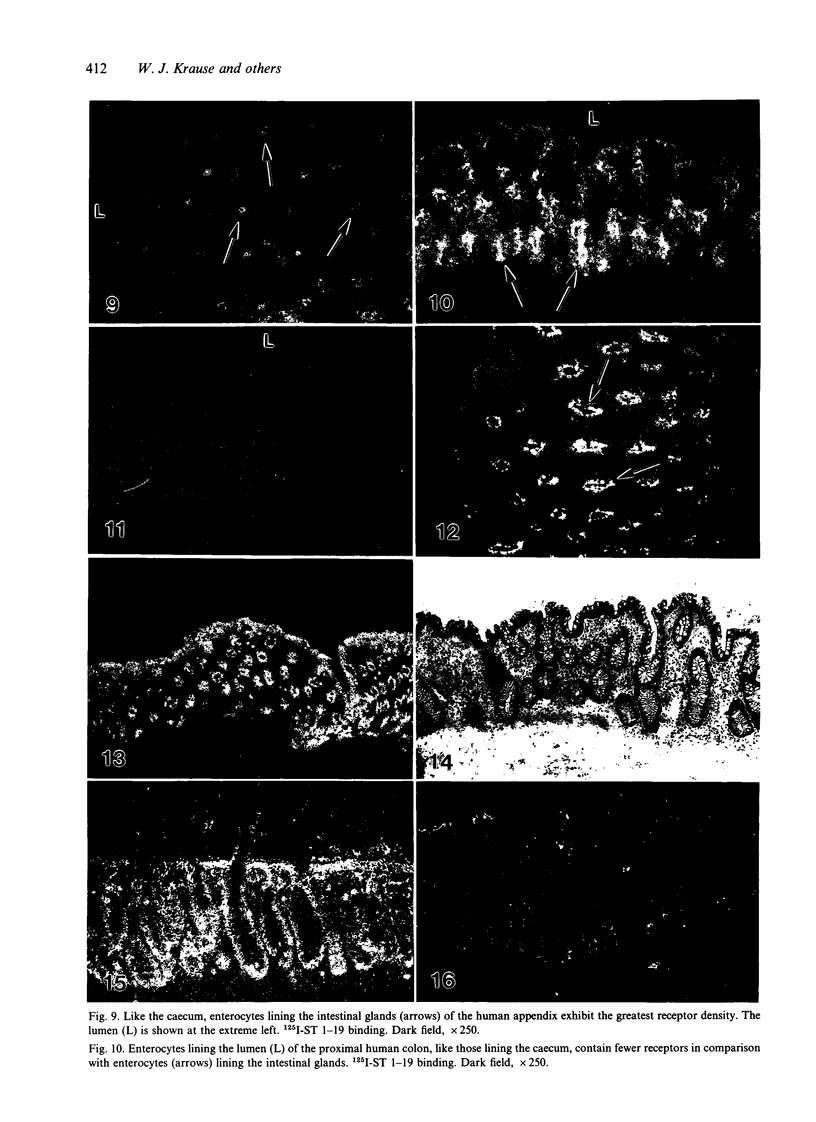
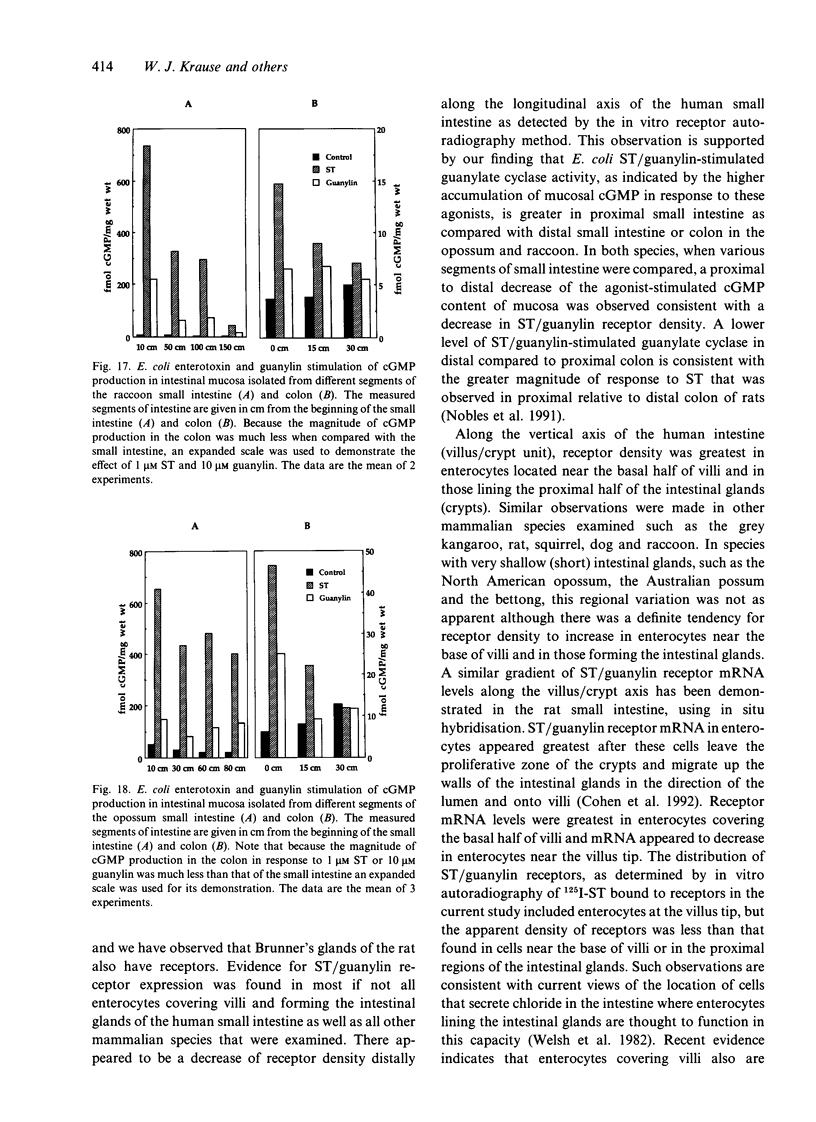
The human intestinal tract, as well as that of several eutherian and metatherian mammals, was examined for the distribution of heat-stable enterotoxin (ST)/guanylin receptors. These receptors were confined to the intestinal epithelium lining the lumen and forming the intestinal glands throughout the length of both the small intestine and colon of all species examined. In man and most other mammalian species, there appeared to be a decrease in receptor density distally along the longitudinal axis of the small intestine. ST/guanylin receptors were not observed in other strata forming the gut wall. Along the vertical axis of the human small intestine (villus/crypt unit), as well as that of most other mammals, receptor density was greatest in enterocytes located near the base of villi and in those forming the proximal portion of the intestinal glands. ST/guanylin receptors were for the most part confined to the region of the plasmalemma forming the microvillus border. In the colon of man and the other species examined, receptor density was greatest in enterocytes forming the proximal region of the intestinal glands. Receptors were present in the intestinal epithelium lining the lumen of the colon, but generally were fewer in number. The distribution of cellular cGMP accumulation responses to E. coli ST and guanylin in the opossum (Didelphis virginiana) and raccoon (Procyon lotor) revealed that proximal small intestine had greater magnitudes of cGMP responses than did the distal small intestine. Proximal colon had greater cGMP responses than distal colon, which had no significant cGMP responses to either ST or guanylin.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black R. E., Brown K. H., Becker S., Alim A. R., Huq I. Longitudinal studies of infectious diseases and physical growth of children in rural Bangladesh. II. Incidence of diarrhea and association with known pathogens. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Mar;115(3):315–324. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Brown K. H., Becker S., Yunus M. Longitudinal studies of infectious diseases and physical growth of children in rural Bangladesh. I. Patterns of morbidity. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Mar;115(3):305–314. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess M. N., Bywater R. J., Cowley C. M., Mullan N. A., Newsome P. M. Biological evaluation of a methanol-soluble, heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin in infant mice, pigs, rabbits, and calves. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.526-531.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. B., Guarino A., Shukla R., Giannella R. A. Age-related differences in receptors for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin in the small and large intestine of children. Gastroenterology. 1988 Feb;94(2):367–373. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90423-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. B., Mann E. A., Lau C., Henning S. J., Giannella R. A. A gradient in expression of the Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin receptor exists along the villus-to-crypt axis of rat small intestine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 15;186(1):483–490. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80833-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie M. G., Fok K. F., Kato J., Moore R. J., Hamra F. K., Duffin K. L., Smith C. E. Guanylin: an endogenous activator of intestinal guanylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):947–951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Wallace R. B., Whipp S. C., Olarte J. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and diarrheal disease in Mexican children. J Infect Dis. 1977 Mar;135(3):482–485. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.3.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Robertson D. C. Solubilization and partial characterization of the intestinal receptor for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):537–543. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.537-543.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte L. R., Eber S. L., Turner J. T., Freeman R. H., Fok K. F., Currie M. G. Guanylin stimulation of Cl- secretion in human intestinal T84 cells via cyclic guanosine monophosphate. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2423–2428. doi: 10.1172/JCI116476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte L. R., Krause W. J., Freeman R. H. Escherichia coli enterotoxin receptors: localization in opossum kidney, intestine, and testis. Am J Physiol. 1989 Nov;257(5 Pt 2):F874–F881. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.5.F874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte L. R., Krause W. J., Freeman R. H. Guanylin bioactivity in human intestinal and opossum kidney cells. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1993;28:133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte L. R., Krause W. J., Freeman R. H. Receptors and cGMP signalling mechanism for E. coli enterotoxin in opossum kidney. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 2):F1040–F1046. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.5.F1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte L. R., Thorne P. K., Eber S. L., Krause W. J., Freeman R. H., Francis S. H., Corbin J. D. Stimulation of intestinal Cl- transport by heat-stable enterotoxin: activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase by cGMP. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 1):C607–C615. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.3.C607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz J. C., Jaso-Friedman L., Robertson D. C. Binding of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin to rat intestinal cells and brush border membranes. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):622–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.622-630.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbers D. L. Guanylate cyclase, a cell surface receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9103–9106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Luttrell M., Thompson M. Binding of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin to receptors on rat intestinal cells. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):G492–G498. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.4.G492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Pathogenesis of acute bacterial diarrheal disorders. Annu Rev Med. 1981;32:341–357. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.32.020181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guandalini S., Rao M. C., Smith P. L., Field M. cGMP modulation of ileal ion transport: in vitro effects of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):G36–G41. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.243.1.G36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino A., Cohen M. B., Overmann G., Thompson M. R., Giannella R. A. Binding of E. coli heat-stable enterotoxin to rat intestinal brush borders and to basolateral membranes. Dig Dis Sci. 1987 Sep;32(9):1017–1026. doi: 10.1007/BF01297193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino A., Cohen M., Thompson M., Dharmsathaphorn K., Giannella R. T84 cell receptor binding and guanyl cyclase activation by Escherichia coli heat-stable toxin. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):G775–G780. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.6.G775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Hughes J. M., Chang B., Robertson D. C., Murad F. Activation of intestinal guanylate cyclase by heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: studies of tissue specificity, potential receptors, and intermediates. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):220–228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamra F. K., Forte L. R., Eber S. L., Pidhorodeckyj N. V., Krause W. J., Freeman R. H., Chin D. T., Tompkins J. A., Fok K. F., Smith C. E. Uroguanylin: structure and activity of a second endogenous peptide that stimulates intestinal guanylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10464–10468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause W. J., Freeman R. H., Fort L. R. Autoradiographic demonstration of specific binding sites for E. coli enterotoxin in various epithelia of the North American opossum. Cell Tissue Res. 1990 May;260(2):387–394. doi: 10.1007/BF00318641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köckerling A., Sorgenfrei D., Fromm M. Electrogenic Na+ absorption of rat distal colon is confined to surface epithelium: a voltage-scanning study. Am J Physiol. 1993 May;264(5 Pt 1):C1285–C1293. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.5.C1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann E. A., Cohen M. B., Giannella R. A. Comparison of receptors for Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin: novel receptor present in IEC-6 cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 1):G172–G178. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1993.264.1.G172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezoff A. G., Giannella R. A., Eade M. N., Cohen M. B. Escherichia coli enterotoxin (STa) binds to receptors, stimulates guanyl cyclase, and impairs absorption in rat colon. Gastroenterology. 1992 Mar;102(3):816–822. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90163-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobles M., Diener M., Rummel W. Segment-specific effects of the heat-stable enterotoxin of E. coli on electrolyte transport in the rat colon. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 17;202(2):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki H., Sato T., Kubota H., Hata Y., Katsube Y., Shimonishi Y. Molecular structure of the toxin domain of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a pathogenic strain of Escherichia coli. A putative binding site for a binding protein on rat intestinal epithelial cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5934–5941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potten C. S., Loeffler M. Stem cells: attributes, cycles, spirals, pitfalls and uncertainties. Lessons for and from the crypt. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1001–1020. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. C., Orellana S. A., Field M., Robertson D. C., Giannella R. A. Comparison of the biological actions of three purified heat-stable enterotoxins: effects on ion transport and guanylate cyclase activity in rabbit ileum in vitro. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):165–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.165-170.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Merson M. H., Wells J. G., Sack R. B., Morris G. K. Diarrhoea associated with heat-stable enterotoxin-producing strains of Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1975 Aug 9;2(7928):239–241. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90958-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz S., Green C. K., Yuen P. S., Garbers D. L. Guanylyl cyclase is a heat-stable enterotoxin receptor. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):941–948. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90497-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S., Lowe D. G., Thorpe D. S., Rodriguez H., Kuang W. J., Dangott L. J., Chinkers M., Goeddel D. V., Garbers D. L. Membrane guanylate cyclase is a cell-surface receptor with homology to protein kinases. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):708–712. doi: 10.1038/334708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaandrager A. B., Bot A. G., De Vente J., De Jonge H. R. Atriopeptins and Escherichia coli enterotoxin STa have different sites of action in mammalian intestine. Gastroenterology. 1992 Apr;102(4 Pt 1):1161–1169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Murad F. Cyclic GMP synthesis and function. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Sep;39(3):163–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Smith P. L., Fromm M., Frizzell R. A. Crypts are the site of intestinal fluid and electrolyte secretion. Science. 1982 Dec 17;218(4578):1219–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.6293054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand R. C., Kato J., Huang M. D., Fok K. F., Kachur J. F., Currie M. G. Human guanylin: cDNA isolation, structure, and activity. FEBS Lett. 1992 Oct 19;311(2):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81387-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. K., Garbers D. L. Receptor guanylyl cyclases. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):299–305. doi: 10.1172/JCI115862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]