Abstract
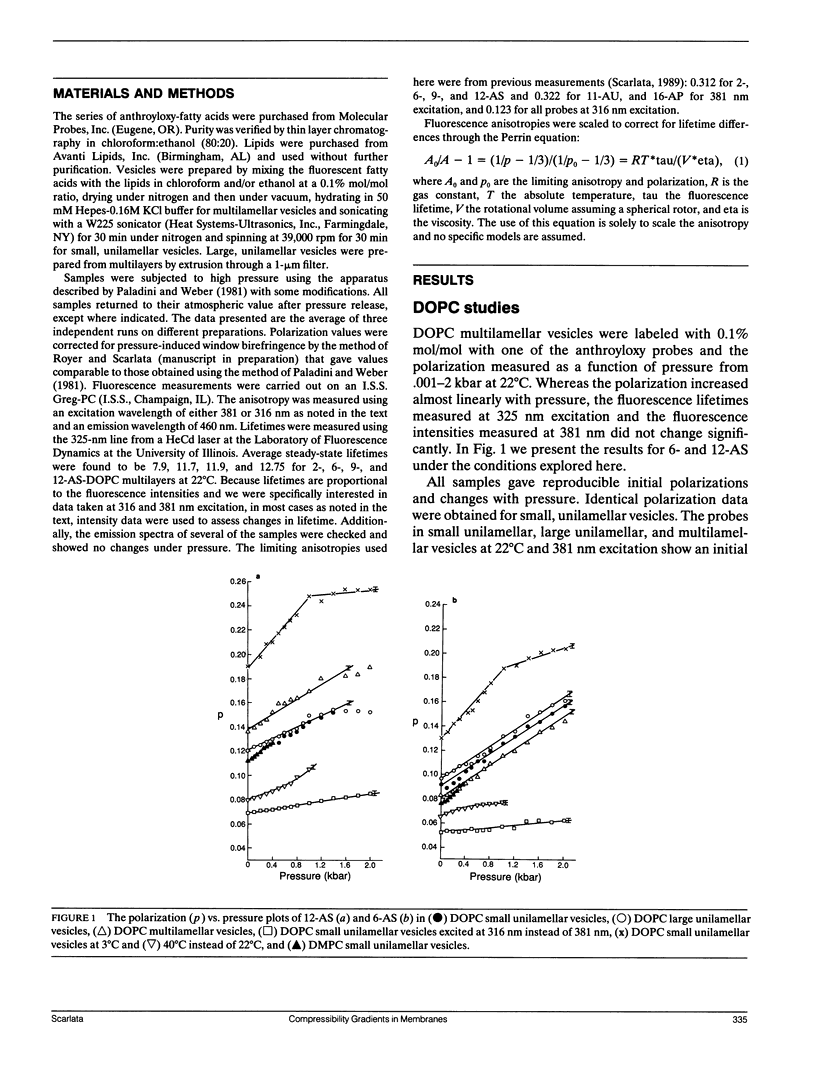
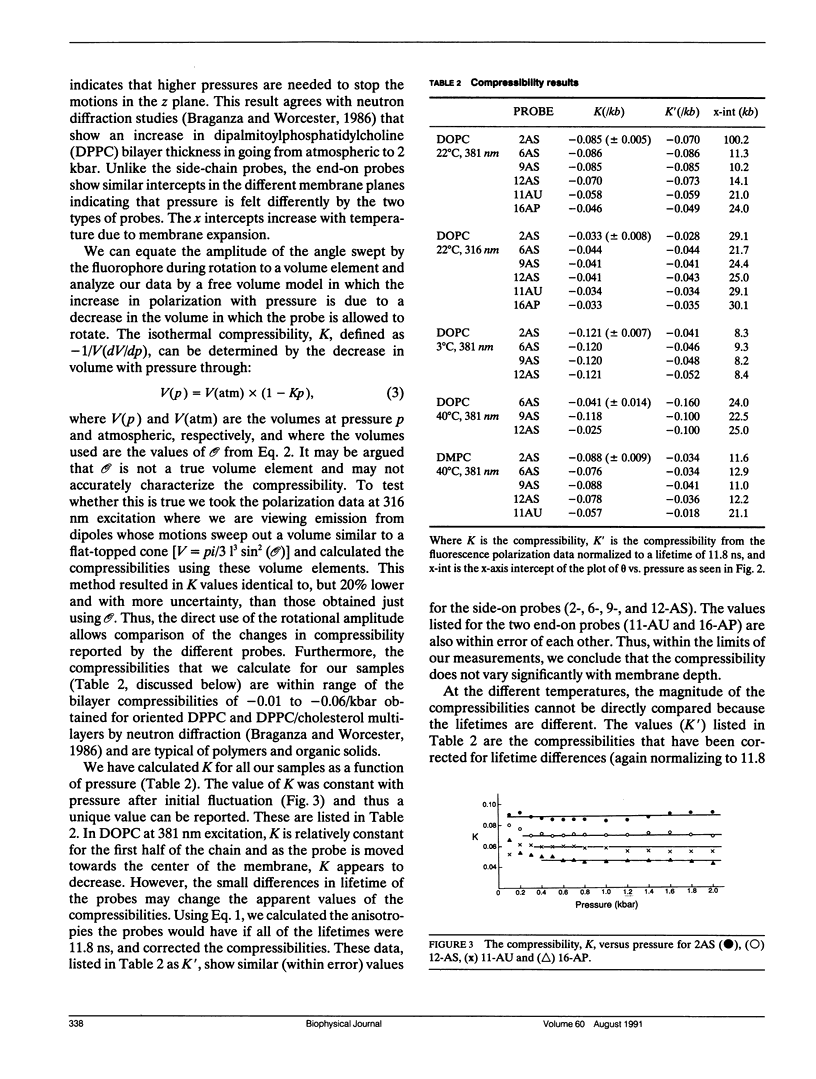
We have measured the microscopic isothermal compressibility of dioleoyl- and dimyristyl-phosphatidylcholine multilayers and bilayers as a function of membrane depth by the pressure dependence of the polarization of a series of anthroyloxy fatty acids. In both systems, within experimental error, the compressibility did not change with membrane depth. The magnitudes of the compressibilities matched those of organic solids and those reported for dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine multilayers from neutron diffraction measurements (Braganza, L. F., and D. L. Worcester. 1986. Biochemistry, 25:7484-7488). The bilayer compressibility decreased with temperature and this decrease was similar with membrane depth consistent with the isotropic thermal expansion of membranes previously observed (Scarlata, S. 1989. Biophys. J. 55:1215-1223). The vertical compressibility in the z direction is much lower than the horizontal (xy planes) for probes that lie parallel to the hydrocarbon chains which is consistent with an increase in bilayer thickness. The compressibility for probes that lie perpendicular to the hydrocarbon chains is more isotropic due to their limited spatial access to the z plane.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auger M., Jarrell H. C., Smith I. C., Siminovitch D. J., Mantsch H. H., Wong P. T. Effects of the local anesthetic tetracaine on the structural and dynamic properties of lipids in model membranes: a high-pressure Fourier transform infrared study. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 9;27(16):6086–6093. doi: 10.1021/bi00416a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braganza L. F., Worcester D. L. Structural changes in lipid bilayers and biological membranes caused hydrostatic pressure. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7484–7488. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong P. L. Effects of hydrostatic pressure on the location of PRODAN in lipid bilayers and cellular membranes. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):399–404. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckmann M., Haimovitz R., Shinitzky M. Selective release of integral proteins from human erythrocyte membranes by hydrostatic pressure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 5;821(2):334–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger J., Scarlata S. F. The lateral fluidity of erythrocyte membranes. Temperature and pressure dependence. Biophys Chem. 1987 Dec;28(3):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(87)80098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsey M. J., Wardley-Smith B. Pressure reversal of narocsis produced by anaesthetics, narcotics and tranquillisers. Nature. 1975 Oct 30;257(5529):811–813. doi: 10.1038/257811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heremans K. High pressure effects on proteins and other biomolecules. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1982;11:1–21. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.11.060182.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawato S., Kinosita K., Jr, Ikegami A. Dynamic structure of lipid bilayers studied by nanosecond fluorescence techniques. Biochemistry. 1977 May 31;16(11):2319–2324. doi: 10.1021/bi00630a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever M. J., Miller K. W., Paton W. D., Smith E. B. Pressure reversal of anaesthesia. Nature. 1971 Jun 11;231(5302):368–371. doi: 10.1038/231368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald A. G. The effects of pressure on the molecular structure and physiological functions of cell membranes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Jan 7;304(1118):47–68. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller C. P., Shinitzky M. Passive shedding of erythrocyte antigens induced by membrane rigidification. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Nov;136(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wilkinson D. A. Lecithin bilayers. Density measurement and molecular interactions. Biophys J. 1978 Aug;23(2):159–175. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85441-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlata S. F. Evaluation of the thermal coefficient of the resistance to fluorophore rotation in model membranes. Biophys J. 1989 Jun;55(6):1215–1223. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82917-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thulborn K. R., Sawyer W. H. Properties and the locations of a set of fluorescent probes sensitive to the fluidity gradient of the lipid bilayer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 4;511(2):125–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley L., Thulborn K. R., Sawyer W. H. An assessment of the fluidity gradient of the lipid bilayer as determined by a set of n-(9-anthroyloxy) fatty acids (n = 2, 6, 9, 12, 16). J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2592–2594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Blitterswijk W. J., Van Hoeven R. P., Van der Meer B. W. Lipid structural order parameters (reciprocal of fluidity) in biomembranes derived from steady-state fluorescence polarization measurements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 22;644(2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90390-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent M., de Foresta B., Gallay J., Alfsen A. Nanosecond fluorescence anisotropy decays of n-(9-anthroyloxy) fatty acids in dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles with regard to isotropic solvents. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 16;21(4):708–716. doi: 10.1021/bi00533a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. T., Mantsch H. H. Reorientational and conformational ordering processes at elevated pressures in 1,2-dioleoyl phosphatidylcholine: a Raman and infrared spectroscopic study. Biophys J. 1988 Nov;54(5):781–790. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83016-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakim D., Wong P. T. A high-pressure, infrared spectroscopic study of the solvation of bilirubin in lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 27;29(8):2003–2007. doi: 10.1021/bi00460a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


