Abstract
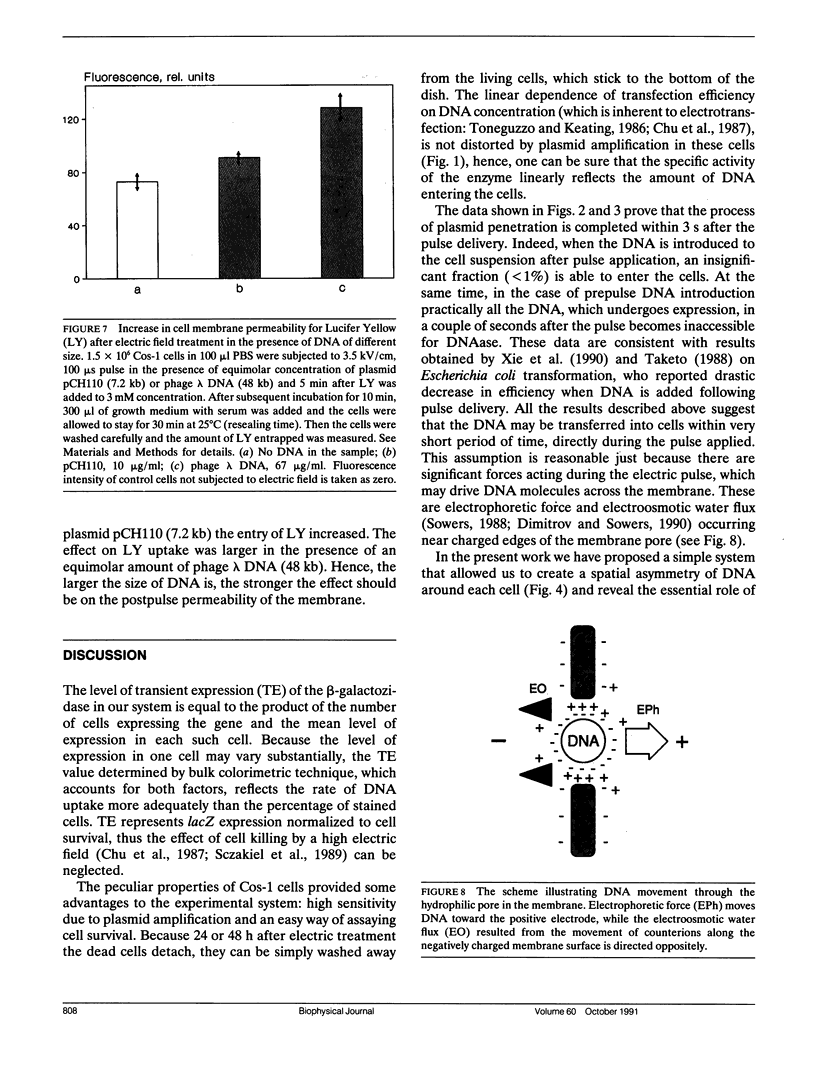
Simian Cos-1 cells were transfected electrically with the plasmid pCH110 carrying the beta-galactosidase gene. The efficiency of transfection was determined by a transient expression of this gene. When the plasmid was introduced into a cell suspension 2 s after pulse application, the transfection efficiency was shown to be less than 1% as compared with a prepulse addition of DNA. Addition of DNAase to suspension immediately after a pulse did not decrease transfection efficiency, thus the time of DNA translocation was estimated to be less than 3 s. The use of electric treatment medium, in which the postpulse colloid-osmotic cell swelling was prevented, did not affect the transfection efficiency. These results contradict both assumptions of free DNA diffusion into cell through the long-lived pores and of involvement of osmotic effects in DNA translocation. Transfection of cells in monolayer on a porous film allowed creation of the spatial asymmetry of cell-plasmid interaction along the direction of electric field applied. A pulse with a polarity inducing DNA electrophoresis toward the cells resulted in the 10-fold excess of transfection efficiency compared with a pulse with reverse polarity. Ficoll (10%) which increases medium viscosity or Mg2+ ions (10 mM) which decrease the effective charge of DNA, both reduced transfection efficiency 2-3-fold. These results prove a significant role of DNA electrophoresis in the phenomenon considered. The permeability of cell membranes for an indifferent dye was shown to increase noticeably if the cells were pulsed in the presence of DNA. This indicates a possible interaction of DNA translocated with the pores in an electric field, that results in pore expansion.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An G., Hidaka K., Siminovitch L. Expression of bacterial beta-galactosidase in animal cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1628–1632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreason G. L., Evans G. A. Optimization of electroporation for transfection of mammalian cell lines. Anal Biochem. 1989 Aug 1;180(2):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beliaev N. D., Budker V. G., Gorokhova O. E., Sokolov A. V. Mg2+-zavisimoe vzaimodeistvie DNK s éukarioticheskimi kletkami. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1988 Nov-Dec;22(6):1667–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. C., Reese T. S. Changes in membrane structure induced by electroporation as revealed by rapid-freezing electron microscopy. Biophys J. 1990 Jul;58(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82348-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernomordik L. V., Sokolov A. V., Budker V. G. Electrostimulated uptake of DNA by liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 9;1024(1):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90222-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S., Hillen W., Morgeneyer B., Wells R. D., Pörschke D. Orientation relaxation of DNA restriction fragments and the internal mobility of the double helix. Biophys Chem. 1982 Jul;15(4):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(82)80009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. S., Sowers A. E. Membrane electroporation--fast molecular exchange by electroosmosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Mar;1022(3):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90289-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escande-Géraud M. L., Rols M. P., Dupont M. A., Gas N., Teissié J. Reversible plasma membrane ultrastructural changes correlated with electropermeabilization in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 7;939(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Rhodes G. Gene therapeutics. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):351–352. doi: 10.1038/349351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gass G. V., Chernomordik L. V. Reversible large-scale deformations in the membranes of electrically-treated cells: electroinduced bleb formation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Mar 30;1023(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jastreboff M. M., Ito E., Bertino J. R., Narayanan R. Use of electroporation for high-molecular-weight DNA-mediated gene transfer. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Aug;171(2):513–517. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Tsong T. Y. Formation and resealing of pores of controlled sizes in human erythrocyte membrane. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):438–441. doi: 10.1038/268438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C., Yee D. Electroporation: parameters affecting transfer of DNA into mammalian cells. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jul;164(1):44–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90365-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubiniec R. T., Liang H., Hui S. W. Effects of pulse length and pulse strength on transfection by electroporation. Biotechniques. 1990 Jan;8(1):16–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Yokota T., Otsuka T., Gemmell L., Larson N., Luh J., Arai K., Rennick D. Isolation of cDNA for a human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by functional expression in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4360–4364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann E., Schaefer-Ridder M., Wang Y., Hofschneider P. H. Gene transfer into mouse lyoma cells by electroporation in high electric fields. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):841–845. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter H. Electroporation in biology: methods, applications, and instrumentation. Anal Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;174(2):361–373. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presse F., Quillet A., Mir L., Marchiol-Fournigault C., Feunteun J., Fradelizi D. An improved electrotransfection method using square shaped electric impulsions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 30;151(3):982–990. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwister K., Deuticke B. Formation and properties of aqueous leaks induced in human erythrocytes by electrical breakdown. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 27;816(2):332–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90501-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sczakiel G., Döffinger R., Pawlita M. Testing for electrotransfection parameters by use of the fluorescent dye lucifer yellow CH. Anal Biochem. 1989 Sep;181(2):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90248-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers A. E. Fusion events and nonfusion contents mixing events induced in erythrocyte ghosts by an electric pulse. Biophys J. 1988 Oct;54(4):619–626. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82997-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowers A. E., Lieber M. R. Electropore diameters, lifetimes, numbers, and locations in individual erythrocyte ghosts. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 15;205(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80893-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stopper H., Jones H., Zimmermann U. Large scale transfection of mouse L-cells by electropermeabilization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 12;900(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukharev S. I., Bandrina I. N., Barbul A. I., Fedorova L. I., Abidor I. G., Zelenin A. V. Electrofusion of fibroblasts on the porous membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 16;1034(2):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(90)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketo A. DNA transfection of Escherichia coli by electroporation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Mar 31;949(3):318–324. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketo A. Properties of electroporation-mediated DNA transfer in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1989 May;105(5):813–817. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titomirov A. V., Sukharev S., Kistanova E. In vivo electroporation and stable transformation of skin cells of newborn mice by plasmid DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 17;1088(1):131–134. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90162-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Keating A. Stable expression of selectable genes introduced into human hematopoietic stem cells by electric field-mediated DNA transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3496–3499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourne D. J., Thomas S., Hermon-Taylor J., Hussain I., Johnstone A. P. Electric shock-mediated transfection of cells. Characterization and optimization of electrical parameters. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 15;251(2):427–434. doi: 10.1042/bj2510427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. K., Neumann E. Electric field mediated gene transfer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 30;107(2):584–587. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91531-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie T. D., Sun L., Tsong T. Y. Study of mechanisms of electric field-induced DNA transfection. I. DNA entry by surface binding and diffusion through membrane pores. Biophys J. 1990 Jul;58(1):13–19. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82349-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann U., Pilwat G., Holzapfel C., Rosenheck K. Electrical hemolysis of human and bovine red blood cells. J Membr Biol. 1976 Dec 28;30(2):135–152. doi: 10.1007/BF01869664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



