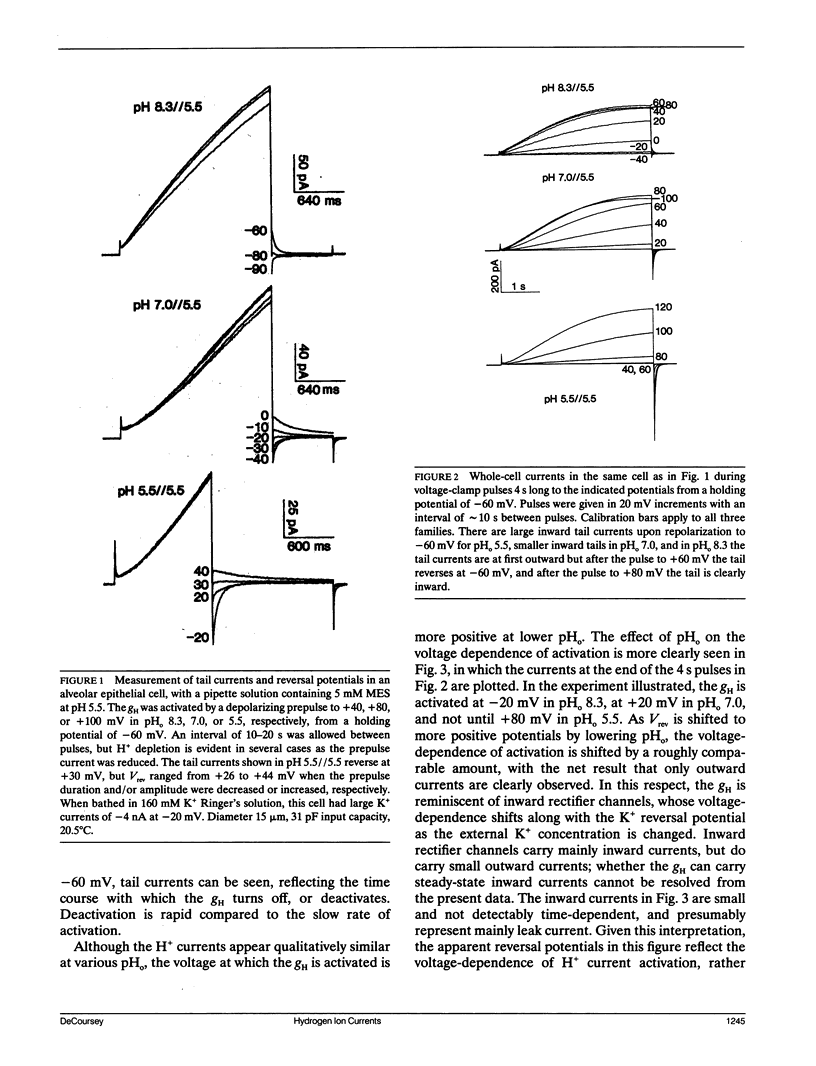
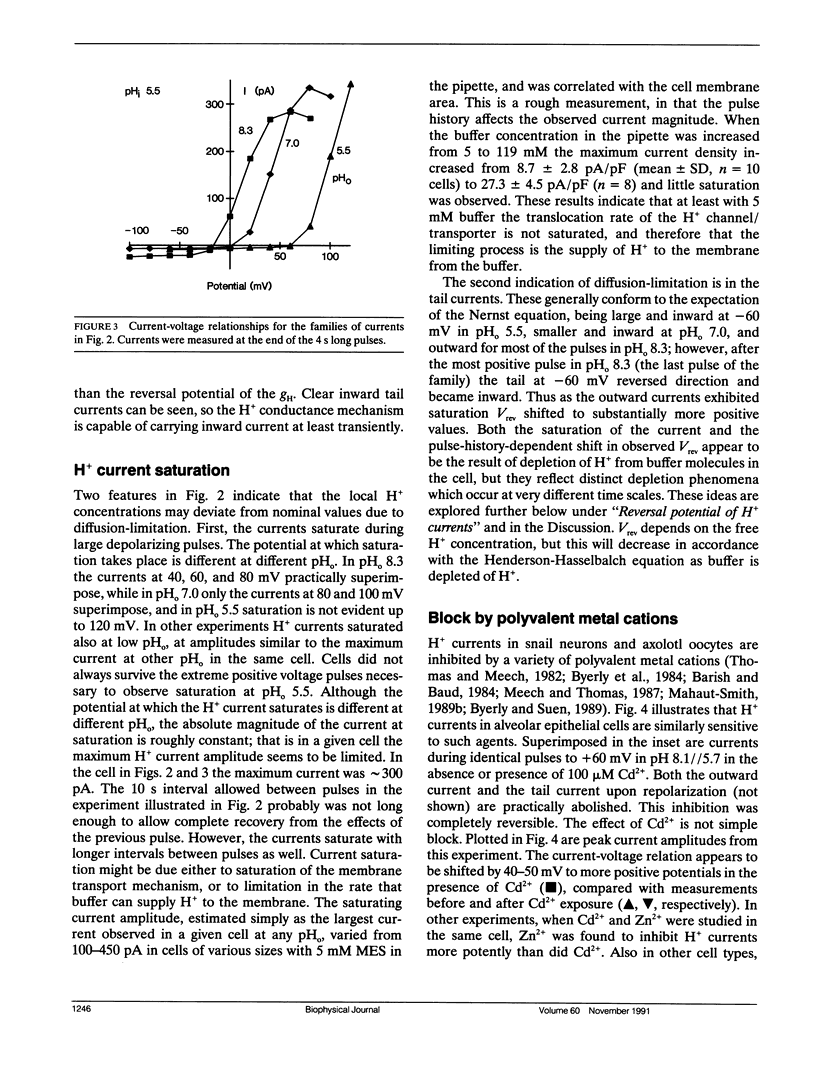
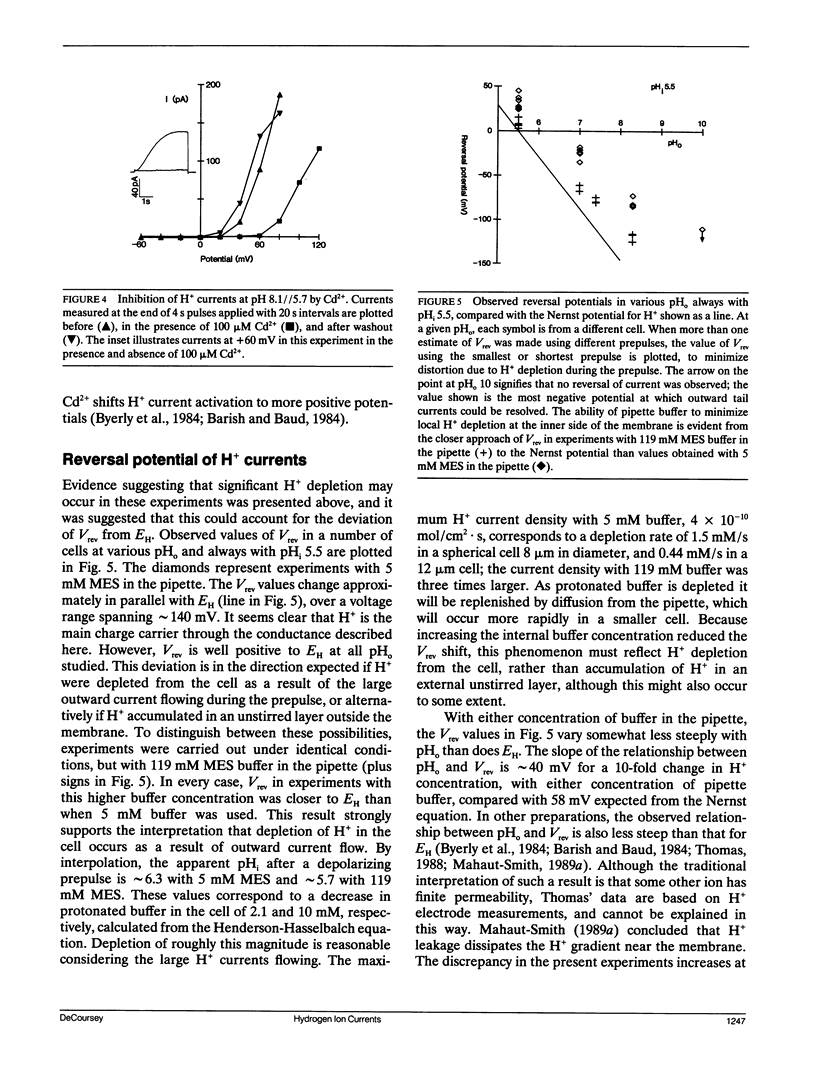
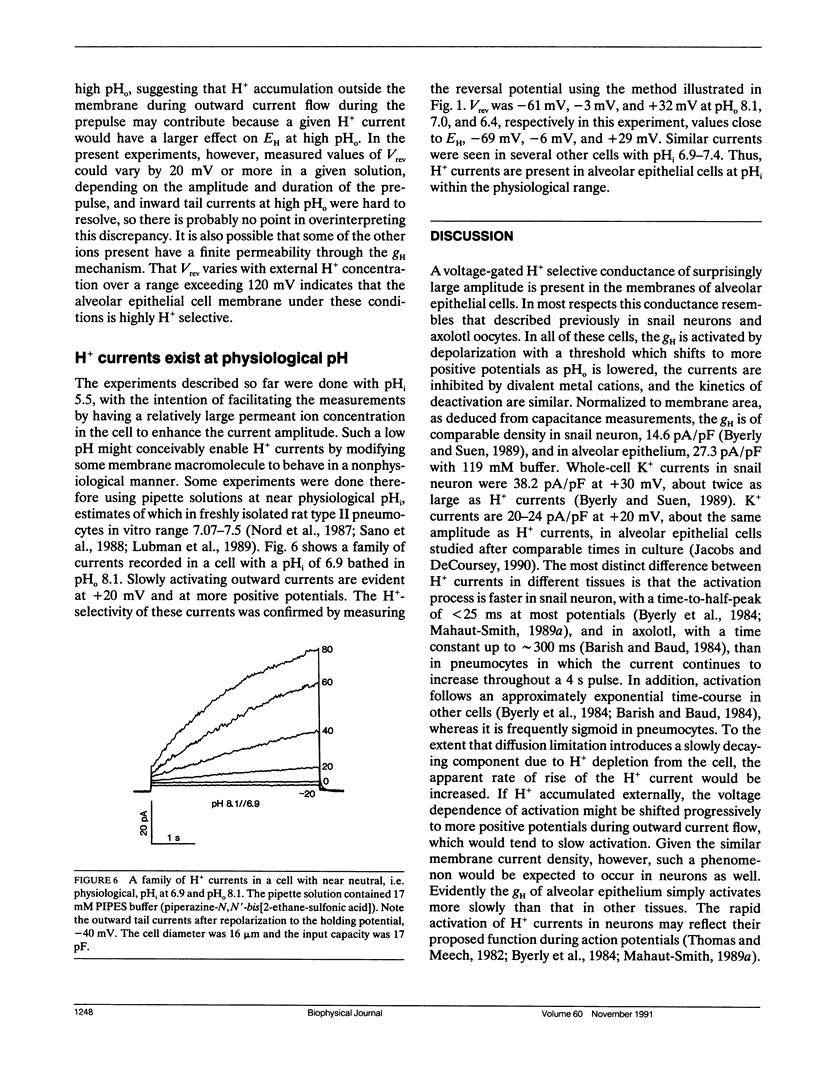
Abstract
Alveolar epithelial cells isolated from rats and maintained in primary culture were studied using the whole-cell configuration of the "patch-clamp" technique. After other ionic conductances were eliminated by replacing permeant ions with N-methyl-D-glucamine methanesulfonate, large voltage-activated hydrogen-selective currents were observed. Like H+ currents in snail neurons and axolotl oocytes, those in alveolar epithelium are activated by depolarization, deactivate upon repolarization, and are inhibited by Cd2+ and Zn2+. Activation of H+ currents is slower in alveolar epithelium than in other tissues, and often has a sigmoid time course. Activation occurs at more positive potentials when external pH is decreased. Saturation of the currents suggests that diffusion limitation may occur; increasing the pipette buffer concentration from 5 to 120 mM at a constant pH of 5.5 increased the maximum current density from 8.7 to 27.3 pA/pF, indicating that the current amplitude can be limited in 5 mM buffer solutions by the rate at which buffer molecules can supply H+ to the membrane. These data indicate that voltage-dependent H+ currents exist in mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. The type 2 cell as progenitor of alveolar epithelial regeneration. A cytodynamic study in mice after exposure to oxygen. Lab Invest. 1974 Jan;30(1):35–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson T. M., Boyd R. D., Platt H. S., Strang L. B. Composition of alveolar liquid in the foetal lamb. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):159–168. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barish M. E., Baud C. A voltage-gated hydrogen ion current in the oocyte membrane of the axolotl, Ambystoma. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:243–263. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr R., Böttger M., Crane F. L., Morré D. J. Electron donation to the plasma membrane redox system of cultured carrot cells stimulates proton release. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 15;1017(1):91–95. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boron W. F. Transport of H+ and of ionic weak acids and bases. J Membr Biol. 1983;72(1-2):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF01870311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Meech R., Moody W., Jr Rapidly activating hydrogen ion currents in perfused neurones of the snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:199–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Suen Y. Characterization of proton currents in neurones of the snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1989 Jun;413:75–89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chander A., Johnson R. G., Reicherter J., Fisher A. B. Lung lamellar bodies maintain an acidic internal pH. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):6126–6131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chander A. Regulation of lung surfactant secretion by intracellular pH. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):L354–L360. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.6.L354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek J. M., Evans M. J., Crandall E. D. Type I cell-like morphology in tight alveolar epithelial monolayers. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Oct;184(2):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90337-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cott G. R., Sugahara K., Mason R. J. Stimulation of net active ion transport across alveolar type II cell monolayers. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 1):C222–C227. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.2.C222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCoursey T. E., Jacobs E. R., Silver M. R. Potassium currents in rat type II alveolar epithelial cells. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:487–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCoursey T. E. State-dependent inactivation of K+ currents in rat type II alveolar epithelial cells. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Apr;95(4):617–646. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.4.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker E. R., Levitt D. G. Use of weak acids to determine the bulk diffusion limitation of H+ ion conductance through the gramicidin channel. Biophys J. 1988 Jan;53(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83062-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G. Isolation and culture of alveolar type II cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 1):L134–L147. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.258.4.L134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Effros R. M., Chinard F. P. The in vivo pH of the extravascular space of the lung. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):1983–1996. doi: 10.1172/JCI106164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrati H., Hawgood S., Williams M. C., Hong K., Benson B. J. Divalent cation and hydrogen ion effects on the structure and surface activity of pulmonary surfactant. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7986–7993. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Cabral L. J., Stephens R. J., Freeman G. Transformation of alveolar type 2 cells to type 1 cells following exposure to NO2. Exp Mol Pathol. 1975 Feb;22(1):142–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(75)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good N. E., Winget G. D., Winter W., Connolly T. N., Izawa S., Singh R. M. Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):467–477. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman B. E., Brown S. E., Crandall E. D. Regulation of transport across pulmonary alveolar epithelial cell monolayers. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Sep;57(3):703–710. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.3.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey B., Lacoste I., Ehrenfeld J. Common channels for water and protons at apical and basolateral cell membranes of frog skin and urinary bladder epithelia. Effects of oxytocin, heavy metals, and inhibitors of H(+)-adenosine triphosphatase. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Apr;97(4):749–776. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrich R., Kurkdjian A., Guern J., Flügge U. I. Comparative studies on the electrical properties of the H+ translocating ATPase and pyrophosphatase of the vacuolar-lysosomal compartment. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2835–2841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. M., Chappell J. B., Jones O. T. Internal pH changes associated with the activity of NADPH oxidase of human neutrophils. Further evidence for the presence of an H+ conducting channel. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 15;251(2):563–567. doi: 10.1042/bj2510563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. M., Chappell J. B., Jones O. T. The superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase of human neutrophils is electrogenic and associated with an H+ channel. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):325–329. doi: 10.1042/bj2460325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs E. R., DeCoursey T. E. Mechanisms of potassium channel block in rat alveolar epithelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):459–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson B. H., Steiner H., Lindskog S. Participation of buffer in the catalytic mechanism of carbonic anhydrase. FEBS Lett. 1976 May 1;64(2):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80317-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasianowicz J., Benz R., McLaughlin S. How do protons cross the membrane-solution interface? Kinetic studies on bilayer membranes exposed to the protonophore S-13 (5-chloro-3-tert-butyl-2'-chloro-4' nitrosalicylanilide). J Membr Biol. 1987;95(1):73–89. doi: 10.1007/BF01869632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg M., Winkler E. The reconstituted isolated uncoupling protein is a membrane potential driven H+ translocator. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3087–3092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04049.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropf D. L., Caldwell J. H., Gow N. A., Harold F. M. Transcellular ion currents in the water mold Achlya. Amino acid proton symport as a mechanism of current entry. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):486–496. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubman R. L., Danto S. I., Crandall E. D. Evidence for active H+ secretion by rat alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):L438–L445. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.6.L438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnerholm G. Pulmonary carbonic anhydrase in the human, monkey, and rat. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Feb;52(2):352–356. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.2.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Williams M. C., Greenleaf R. D., Clements J. A. Isolation and properties of type II alveolar cells from rat lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jun;115(6):1015–1026. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.6.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. J., Williams M. C., Widdicombe J. H., Sanders M. J., Misfeldt D. S., Berry L. C., Jr Transepithelial transport by pulmonary alveolar type II cells in primary culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6033–6037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias R. T., Cohen I. S., Oliva C. Limitations of the whole cell patch clamp technique in the control of intracellular concentrations. Biophys J. 1990 Sep;58(3):759–770. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82418-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Thomas R. C. Voltage-dependent intracellular pH in Helix aspersa neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Sep;390:433–452. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meissner G., Young R. C. Proton permeability of sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6814–6819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody W., Jr Effects of intracellular H+ on the electrical properties of excitable cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1984;7:257–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.07.030184.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G., Locke R. M. Thermogenic mechanisms in brown fat. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jan;64(1):1–64. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielson D. W., Goerke J., Clements J. A. Alveolar subphase pH in the lungs of anesthetized rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nord E. P., Brown S. E., Crandall E. D. Characterization of Na+-H+ antiport in type II alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):C490–C498. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.5.C490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brodovich H., Rafii B., Post M. Bioelectric properties of fetal alveolar epithelial monolayers. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 1):L201–L206. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.258.4.L201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliva C., Cohen I. S., Mathias R. T. Calculation of time constants for intracellular diffusion in whole cell patch clamp configuration. Biophys J. 1988 Nov;54(5):791–799. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83017-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillai R. P., Buescher P. C., Pearse D. B., Sylvester J. T., Eichhorn G. L. 31P NMR spectroscopy of isolated perfused lungs. Magn Reson Med. 1986 Jun;3(3):467–472. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910030313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Neher E. Rates of diffusional exchange between small cells and a measuring patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):204–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00582316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos A., Boron W. F. Intracellular pH. Physiol Rev. 1981 Apr;61(2):296–434. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabolić I., Burckhardt G. Proton pathways in rat renal brush-border and basolateral membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 12;734(2):210–220. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90119-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Cott G. R., Voelker D. R., Mason R. J. The Na+/H+ antiporter in rat alveolar type II cells and its role in stimulated surfactant secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 22;939(3):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. M., Steele L. W., Butcher P. A., Ward M. R., Olver R. E. Sodium-proton exchange across the apical membrane of the alveolar type II cell of the fetal sheep. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 21;1028(1):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90258-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. H., McCoy J. P., Jr, Chu A. E., Dehart P. D., Goldstein I. J. Binding of Griffonia simplicifolia I lectin to rat pulmonary alveolar macrophages and its use in purifying type II alveolar epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 23;885(1):34–42. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayman C. L., Gradmann D. Electrogenic proton transport in the plasma membrane of Neurospora. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):968–971. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85877-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugai N., Ninomiya Y., Oosaki T. Localization of carbonic anhydrase in the rat lung. Histochemistry. 1981;72(3):415–424. doi: 10.1007/BF00501783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Changes in the surface pH of voltage-clamped snail neurones apparently caused by H+ fluxes through a channel. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:313–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C., Meech R. W. Hydrogen ion currents and intracellular pH in depolarized voltage-clamped snail neurones. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):826–828. doi: 10.1038/299826a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Proton channels in snail neurones. Does calcium entry mimic the effects of proton influx? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;574:287–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb25165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R., Apley E. C., Hanke W. Single channel H+ currents through reconstituted chloroplast ATP synthase CF0-CF1. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2827–2834. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


