Abstract
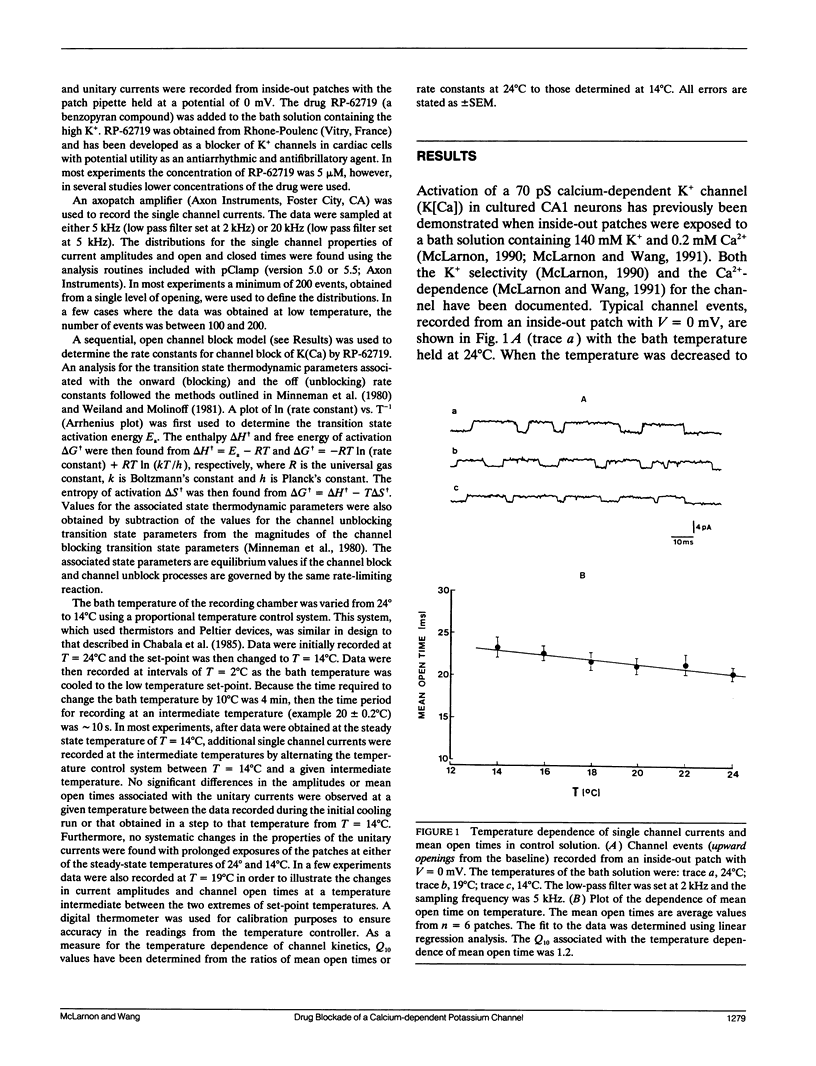
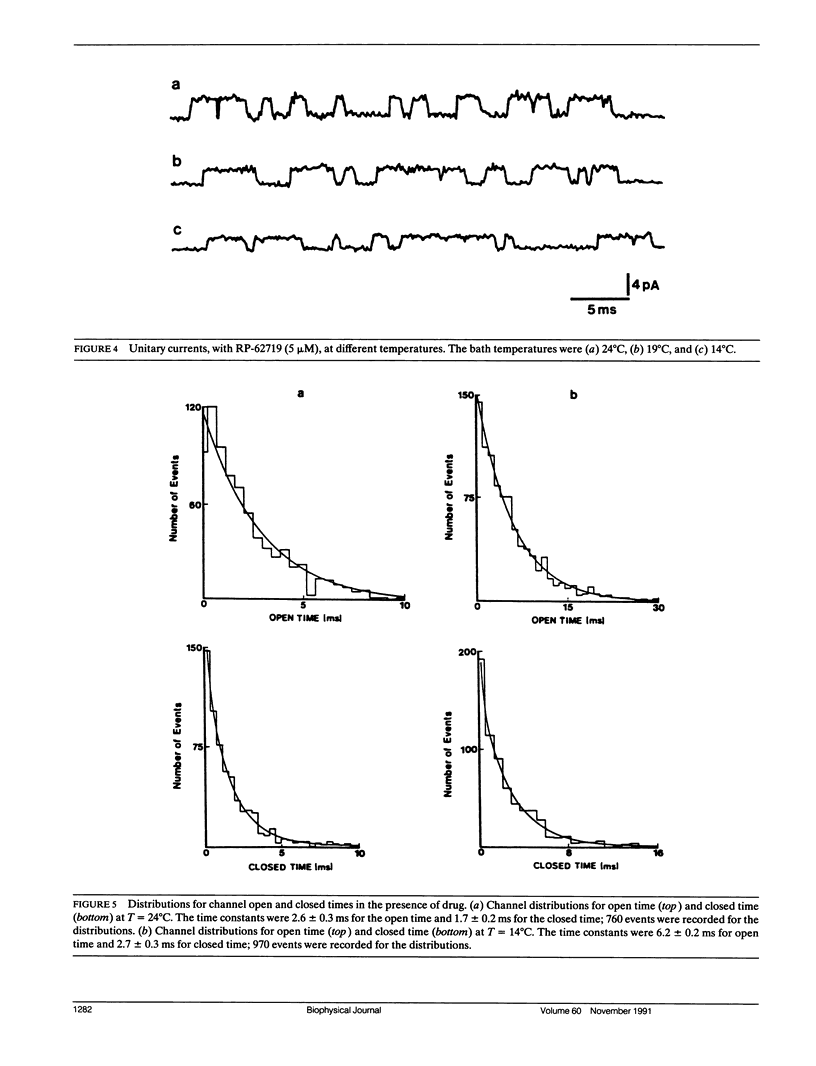
The temperature dependence of drug blockade of a calcium-dependent potassium channel K(Ca) has been studied in cultured CA1 hippocampal neurons. Channel openings from a 70-pS K+ channel were recorded when inside-out patches were exposed to a bath solution containing 140 mM K+ and 0.2 mM Ca2+. The mean open times of channel events were not significantly altered when the bath temperature was lowered from 24 degrees to 14 degrees C (Q10 = 1.2). Introduction of the drug RP-62719 into the bath solution (at 5 microM) resulted in the mean open time of the K(Ca) channel to be diminished by 85% (at 24 degrees C) with no change in the amplitudes of the unitary currents. Over the same temperature range of 24 degrees to 14 degrees C, in the presence of RP-62719, the mean open times were significantly prolonged (Q10 = 2.2). A simple open channel block scheme was used to determine the temperature dependence of the onward- (blocking) and off- (unblocking) rate constants. Thermodynamic analysis, using transition rate theory, showed that the blocking rate constant was associated with a large increase in entropy. The relatively high temperature dependence for channel blockade is not consistent with a rate-limiting process established by simple diffusion of the agent to a channel blocking site. Channel block may involve conformational changes in the channel protein as a consequence of hydrophobic interactions between drug and channel sites.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. Voltage jump analysis of procaine action at frog end-plate. J Physiol. 1977 Jun;268(2):291–318. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Hille B. The inner quaternary ammonium ion receptor in potassium channels of the node of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Apr;59(4):388–400. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.4.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banker G. A., Cowan W. M. Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res. 1977 May 13;126(3):397–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90594-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabala L. D., Sheridan R. E., Hodge D. C., Power J. N., Walsh M. P. A microscope stage temperature controller for the study of whole-cell or single-channel currents. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Aug;404(4):374–377. doi: 10.1007/BF00585351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukes I. D., Cleemann L., Morad M. Tedisamil blocks the transient and delayed rectifier K+ currents in mammalian cardiac and glial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Aug;254(2):560–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French R. J., Shoukimas J. J. Blockage of squid axon potassium conductance by internal tetra-N-alkylammonium ions of various sizes. Biophys J. 1981 May;34(2):271–291. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84849-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Local anesthetics: hydrophilic and hydrophobic pathways for the drug-receptor reaction. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):497–515. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzemann R. Thermodynamic aspects of drug-receptor interactions. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Nov;9(11):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. I. Studies of the unit conductance channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):294–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs E. R., DeCoursey T. E. Mechanisms of potassium channel block in rat alveolar epithelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):459–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUZMANN W. Some factors in the interpretation of protein denaturation. Adv Protein Chem. 1959;14:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60608-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy M. P., Stroud R. M. Changes in conformation upon agonist binding, and nonequivalent labeling, of the membrane-spanning regions of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10911–10916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy M. P., Stroud R. M. Conformational states of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica induced by the binding of agonists, antagonists, and local anesthetics. Equilibrium measurements using tritium-hydrogen exchange. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 10;28(1):40–48. doi: 10.1021/bi00427a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLarnon J. G. Block by a putative antiarrhythmic agent of a calcium-dependent potassium channel in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1990 May 4;112(2-3):210–215. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90205-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLarnon J. G., Quastel D. M. Thermodynamic parameters of end-plate channel blockade. J Neurosci. 1984 Apr;4(4):939–944. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-04-00939.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLarnon J. G., Wang X. P. Actions of cardiac drugs on a calcium-dependent potassium channel in hippocampal neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;39(4):540–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. Diffusion-controlled binding of a peptide neurotoxin to its K+ channel receptor. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 5;29(22):5320–5325. doi: 10.1021/bi00474a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P., Weiland G. A., Molinoff P. B. A comparison of the beta-adrenergic receptor of the turkey erythrocyte with mammalian beta1 and beta2 receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;17(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Steinbach J. H. Local anaesthetics transiently block currents through single acetylcholine-receptor channels. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:153–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. The charge carried by single-channel currents of rat cultured muscle cells in the presence of local anaesthetics. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:663–678. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffa R. B., Porreca F. Thermodynamic analysis of the drug-receptor interaction. Life Sci. 1989;44(4):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starmer C. F., Yeh J. Z., Tanguy J. A quantitative description of QX222 blockade of sodium channels in squid axons. Biophys J. 1986 Apr;49(4):913–920. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83719-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland G. A., Molinoff P. B. Quantitative analysis of drug-receptor interactions: I. Determination of kinetic and equilibrium properties. Life Sci. 1981 Jul 27;29(4):313–330. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


