Abstract
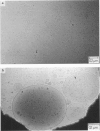
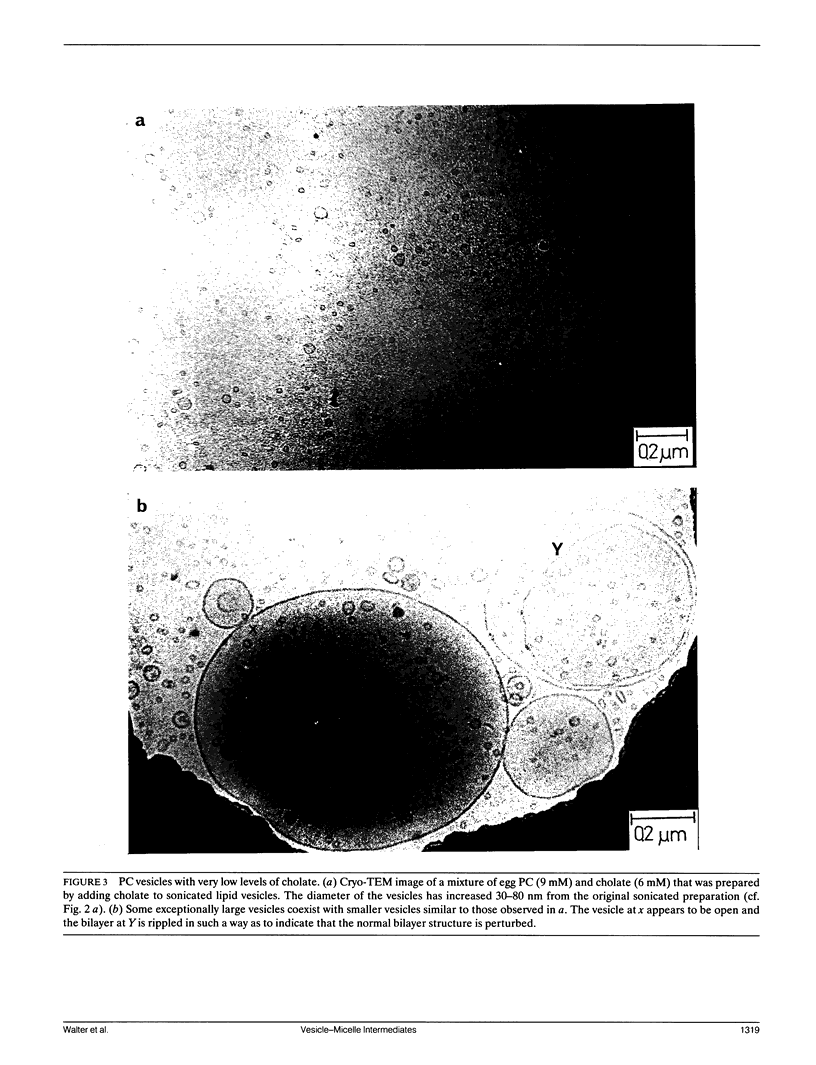
The vesicle-micelle transition of egg phosphatidylcholine (PC) and sodium cholate was described by comparing cryo-transmission electron microscopic (cryo-TEM) images of the structures formed to the associated turbidity changes. These experiments were designed to identify the morphology of the intermediates between vesicles and small spheroidal mixed micelles. With increasing cholate concentration, the vesicular structures changed size and more multilamellar vesicles were seen. Between the apparent upper and lower phase boundaries, three structures were observed: open vesicles, large bilayer sheets (twenty to several hundred nanometers in diameter), and long (150-300 nm) flexible cylindrical micelles. The cylindrical micelles evolved from the edges of the bilayer sheets. At higher relative cholate concentration, the phase boundary was sharply defined by optical clarification of the egg PC-cholate mixtures. Cryo-TEM revealed only small spheroidal mixed micelles at this transition. These results provide the first direct evidence of the structural pathway or of molecular intermediates between a lamellar and a micellar state. Understanding these specific intermediates and the transitions between them is essential to developing reconstitution protocols and properly analyzing either activity or structural data obtained from cholate-dispersed membrane proteins.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson J. J., Shamoo A. E. Anionic detergents as divalent cation ionophores across black lipid membranes. J Membr Biol. 1979 Nov 30;50(3-4):241–255. doi: 10.1007/BF01868891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almog S., Kushnir T., Nir S., Lichtenberg D. Kinetic and structural aspects of reconstitution of phosphatidylcholine vesicles by dilution of phosphatidylcholine-sodium cholate mixed micelles. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2597–2605. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almog S., Litman B. J., Wimley W., Cohen J., Wachtel E. J., Barenholz Y., Ben-Shaul A., Lichtenberg D. States of aggregation and phase transformations in mixtures of phosphatidylcholine and octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1990 May 15;29(19):4582–4592. doi: 10.1021/bi00471a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellare J. R., Davis H. T., Scriven L. E., Talmon Y. Controlled environment vitrification system: an improved sample preparation technique. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1988 Sep;10(1):87–111. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060100111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie J. D., Rakusan T. A., Martinez M. A., Lucia H. L., Rajaraman S., Edwards S. B., Hayden C. K., Jr Hydranencephaly caused by congenital infection with herpes simplex virus. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Jul-Aug;5(4):473–478. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198607000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. L., Schmidt C. F., Lichtenberg D., Litman B. J., Albert A. D. Solubilization of phosphatidylcholine bilayers by octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4576–4582. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg D., Zilberman Y., Greenzaid P., Zamir S. Structural and kinetic studies on the solubilization of lecithin by sodium deoxycholate. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 7;18(16):3517–3525. doi: 10.1021/bi00583a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazer N. A., Benedek G. B., Carey M. C. Quasielastic light-scattering studies of aqueous biliary lipid systems. Mixed micelle formation in bile salt-lecithin solutions. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):601–615. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K. Structural dimorphism of bile salt/lecithin mixed micelles. A possible regulatory mechanism for cholesterol solubility in bile? X-ray structure analysis. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 20;20(2):404–414. doi: 10.1021/bi00505a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. W., Ozarowski J. Sizing of lecithin-bile salt mixed micelles by size-exclusion high-performance liquid chromatography. Biochemistry. 1990 May 15;29(19):4600–4606. doi: 10.1021/bi00471a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ollivon M., Eidelman O., Blumenthal R., Walter A. Micelle-vesicle transition of egg phosphatidylcholine and octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 8;27(5):1695–1703. doi: 10.1021/bi00405a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paternostre M. T., Roux M., Rigaud J. L. Mechanisms of membrane protein insertion into liposomes during reconstitution procedures involving the use of detergents. 1. Solubilization of large unilamellar liposomes (prepared by reverse-phase evaporation) by triton X-100, octyl glucoside, and sodium cholate. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2668–2677. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert R., Beyer K., Wolburg H., Schmidt K. H. Structural changes in membranes of large unilamellar vesicles after binding of sodium cholate. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5263–5269. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Penkett S. A., Chapman D. Studies on simple and mixed bile salt micelles by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;176(1):178–189. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmon Y., Burns J. L., Chestnut M. H., Siegel D. P. Time-resolved cryotransmission electron microscopy. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1990 Jan;14(1):6–12. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060140103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmius J., Lindblom G., Wennerström H., Johansson L. B., Fontell K., Söderman O., Arvidson G. Molecular organization in the liquid--crystalline phases of lecithin--sodium cholate-water systems studied by nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 30;21(7):1553–1560. doi: 10.1021/bi00536a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson P. K., Talmon Y., Walter A. Vesicle-micelle transition of phosphatidylcholine and octyl glucoside elucidated by cryo-transmission electron microscopy. Biophys J. 1989 Oct;56(4):669–681. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82714-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]