Abstract
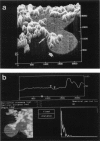
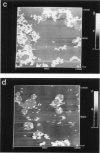
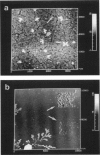
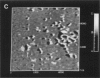
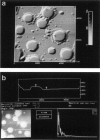
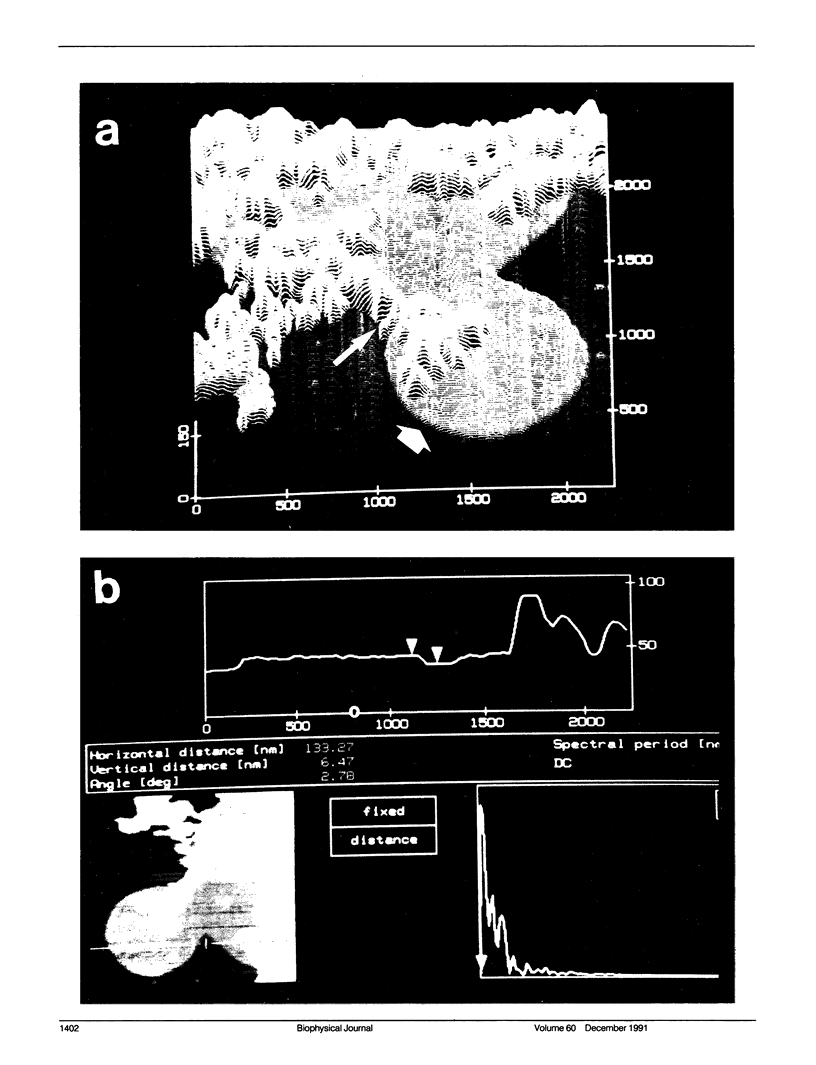
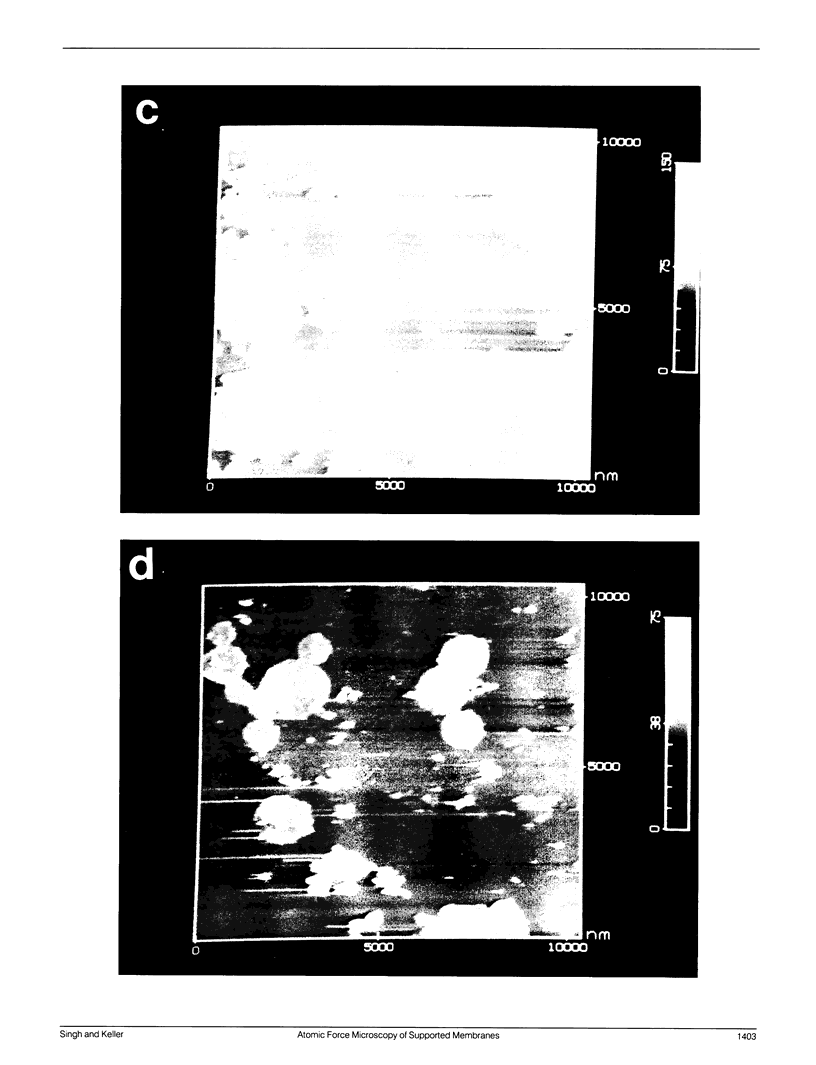
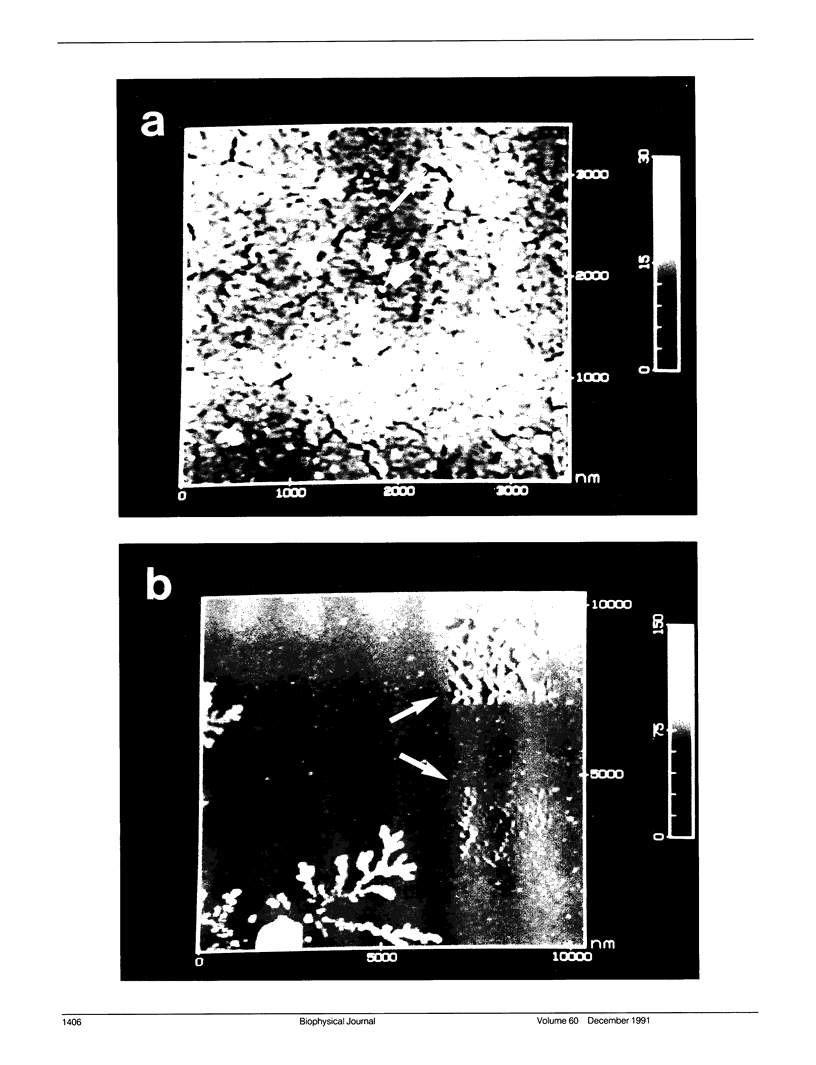
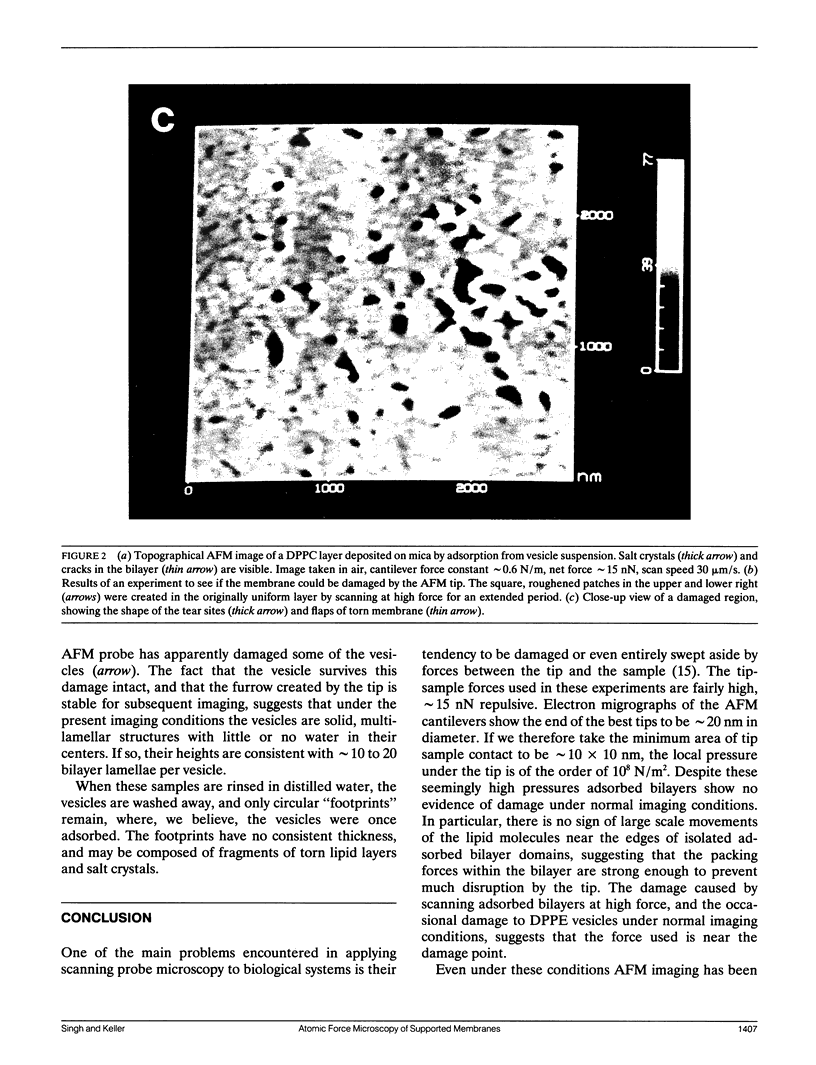
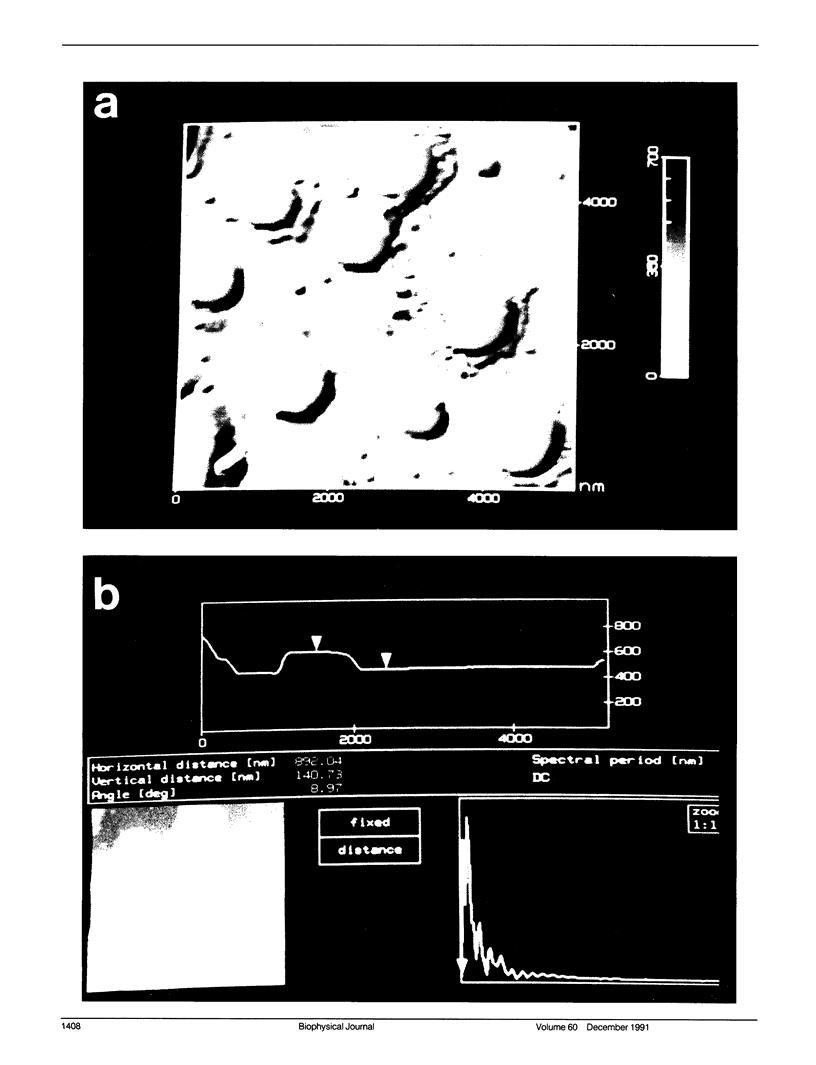
Membrane bilayers of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine (DPPC) and dipalmitoyl phosphatidylethanolamine (DPPE) adsorbed to a freshly cleaved mica substrate have been imaged by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM). The membranes were mounted for imaging by two methods: (a) by dialysis of a detergent solution of the lipid in the presence of the substrate material, and (b) by adsorption of lipid vesicles onto the substrate surface from a vesicle suspension. The images were taken in air, and show lipid bilayers adhering to the surface either in isolated patches or in continuous sheets, depending on the deposition conditions. Epifluorescence light-microscopy shows that the lipid is distributed on the substrate surfaces as seen in the AFM images. In some instances, when DPPE was used, whole, unfused vesicles, which were bound to the substrate, could be imaged by the AFM. Such membranes should be capable of acting as natural anchors for imaging membrane proteins by AFM.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brian A. A., McConnell H. M. Allogeneic stimulation of cytotoxic T cells by supported planar membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6159–6163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Downing K. H., Hansma P. K. Imaging the membrane protein bacteriorhodopsin with the atomic force microscope. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1473–1480. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82492-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deisenhofer J., Epp O., Miki K., Huber R., Michel H. X-ray structure analysis of a membrane protein complex. Electron density map at 3 A resolution and a model of the chromophores of the photosynthetic reaction center from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake B., Prater C. B., Weisenhorn A. L., Gould S. A., Albrecht T. R., Quate C. F., Cannell D. S., Hansma H. G., Hansma P. K. Imaging crystals, polymers, and processes in water with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1586–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.2928794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller D., Bustamante C., Keller R. W. Imaging of single uncoated DNA molecules by scanning tunneling microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5356–5360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell H. M., Watts T. H., Weis R. M., Brian A. A. Supported planar membranes in studies of cell-cell recognition in the immune system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 12;864(1):95–106. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcester D. L., Miller R. G., Bryant P. J. Atomic force microscopy of purple membranes. J Microsc. 1988 Dec;152(Pt 3):817–821. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1988.tb01454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]