Abstract
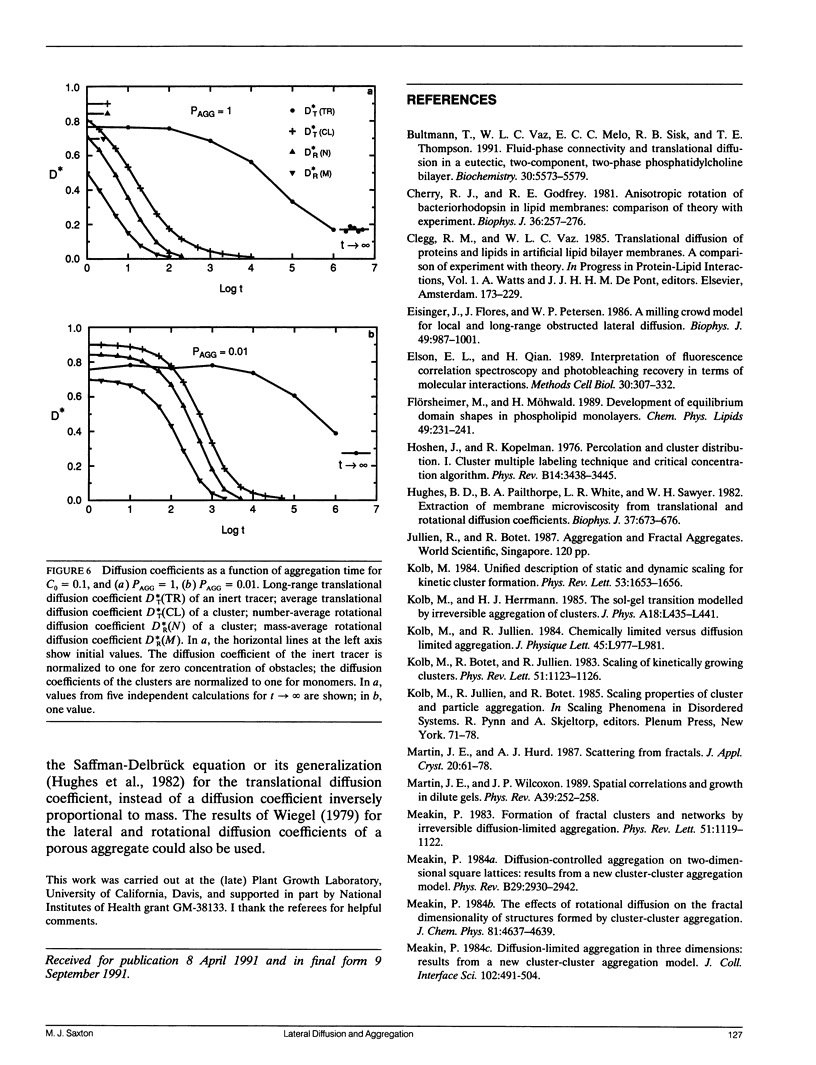
Aggregation in a lipid bilayer is modeled as cluster-cluster aggregation on a square lattice. In the model, clusters carry out a random walk on the lattice, with a diffusion coefficient inversely proportional to mass. On contact, they adhere with a prescribed probability, rigidly and irreversibly. Monte Carlo calculations show that, as expected, rotational diffusion of the aggregating species is highly sensitive to the initial stages of aggregation. Lateral diffusion of an inert tracer obstructed by the aggregate is a sensitive probe of the later stages of aggregation. Cluster-cluster aggregates are much more effective barriers to lateral diffusion of an inert tracer than the same area fraction of random point obstacles is, but random point obstacles are more effective barriers than the same area fraction of compact obstacles. The effectiveness of aggregates as obstacles is discussed in terms of particle-particle correlation functions and fractal dimensions. Results are applicable to aggregation of membrane proteins, and at least qualitatively to aggregation of gel-phase lipid during lateral phase separation.
Full text
PDF


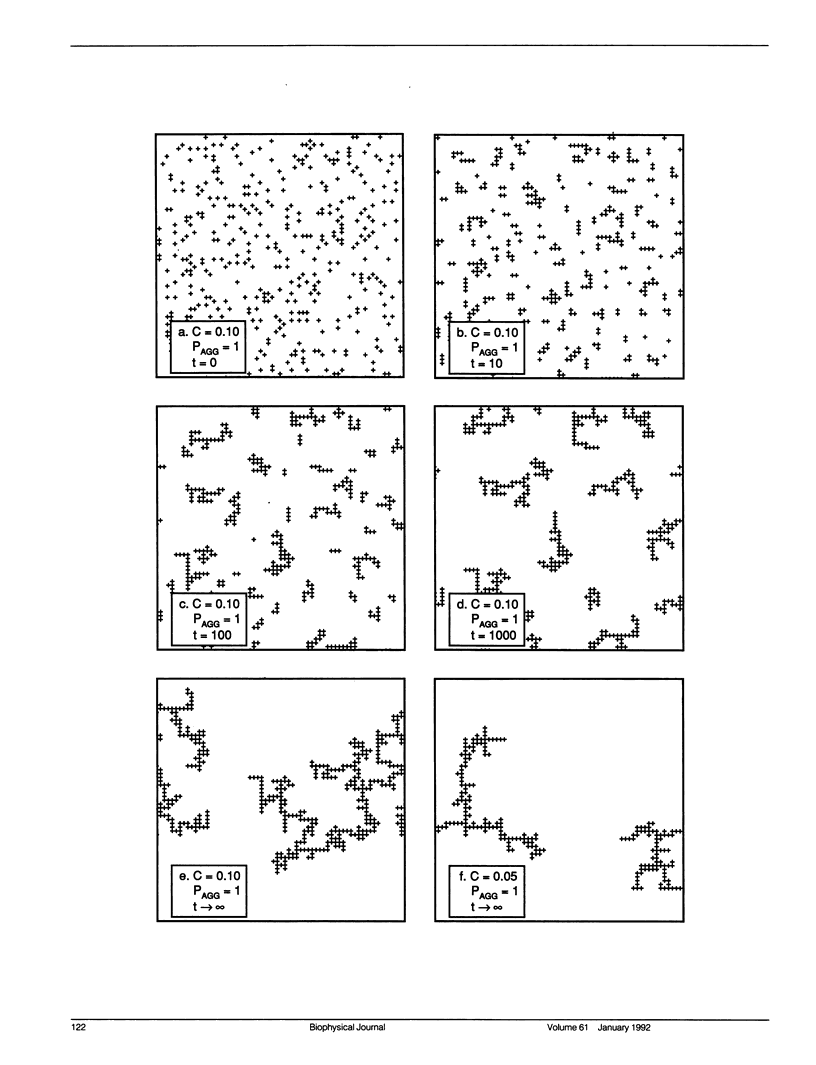
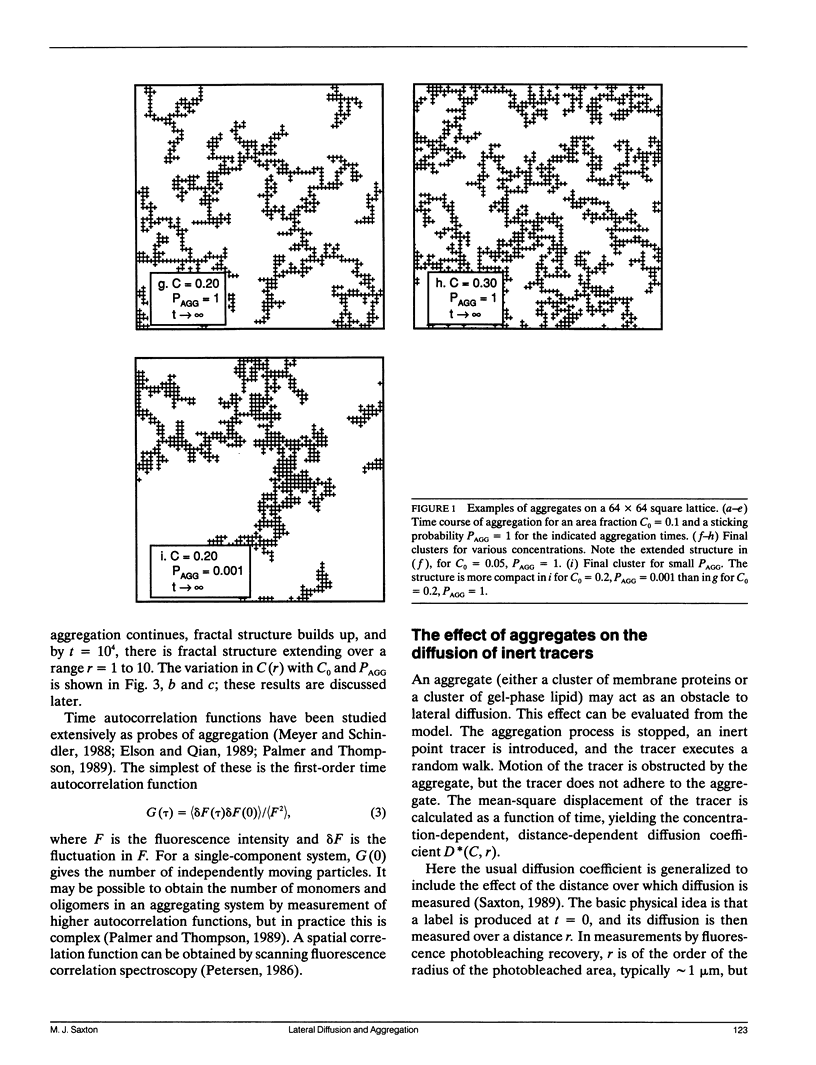
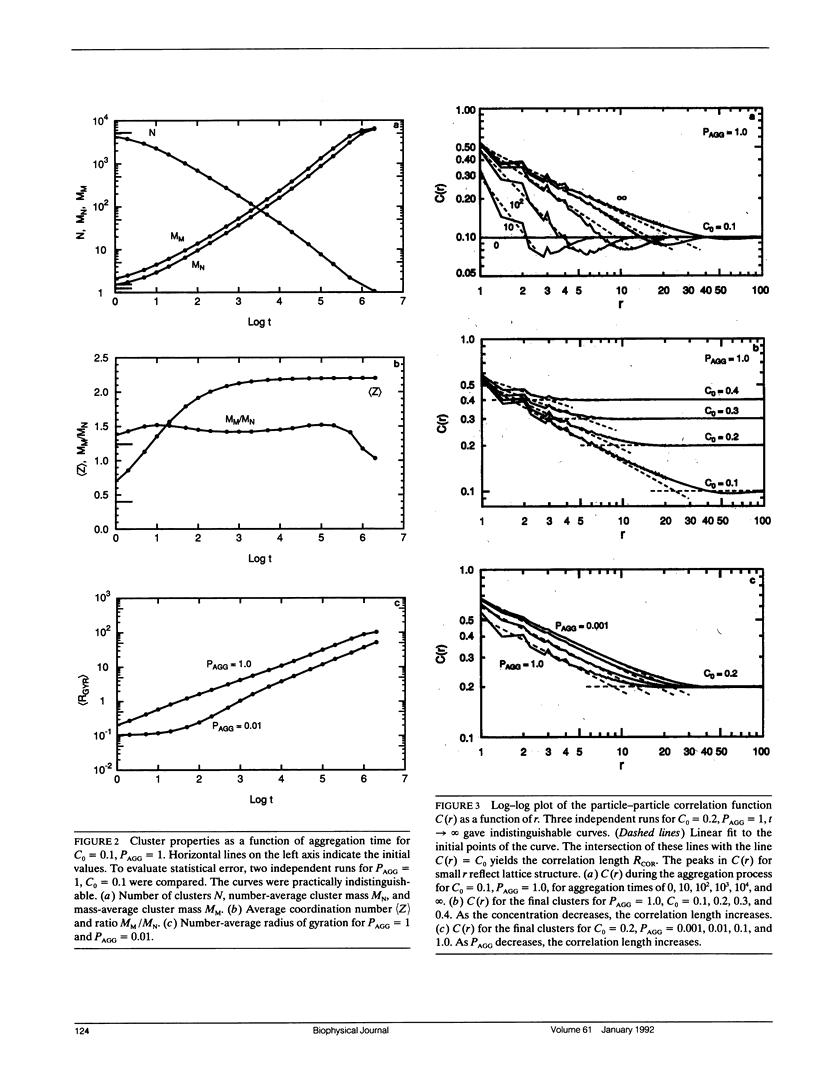
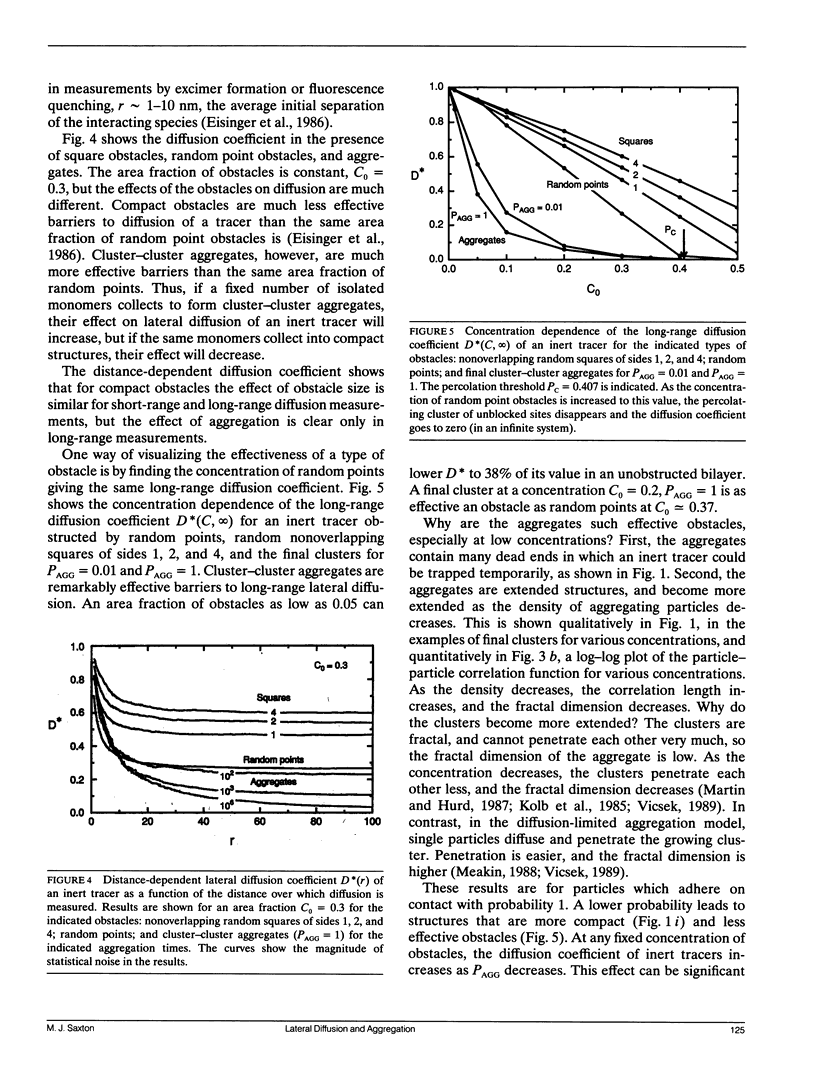


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bultmann T., Vaz W. L., Melo E. C., Sisk R. B., Thompson T. E. Fluid-phase connectivity and translational diffusion in a eutectic, two-component, two-phase phosphatidylcholine bilayer. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 4;30(22):5573–5579. doi: 10.1021/bi00236a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Godfrey R. E. Anisotropic rotation of bacteriorhodopsin in lipid membranes. Comparison of theory with experiment. Biophys J. 1981 Oct;36(1):257–276. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84727-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger J., Flores J., Petersen W. P. A milling crowd model for local and long-range obstructed lateral diffusion. Mobility of excimeric probes in the membrane of intact erythrocytes. Biophys J. 1986 May;49(5):987–1001. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83727-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson E. L., Qian H. Interpretation of fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and photobleaching recovery in terms of molecular interactions. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;30:307–332. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60984-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flörsheimer M., Möhwald H. Development of equilibrium domain shapes in phospholipid monolayers. Chem Phys Lipids. 1989 Mar;49(4):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(89)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes B. D., Pailthorpe B. A., White L. R., Sawyer W. H. Extraction of membrane microviscosity from translational and rotational diffusion coefficients. Biophys J. 1982 Mar;37(3):673–676. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin JE, Wilcoxon JP. Spatial correlations and growth in dilute gels. Phys Rev A Gen Phys. 1989 Jan 1;39(1):252–258. doi: 10.1103/physreva.39.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakin P, Vicsek T, Family F. Dynamic cluster-size distribution in cluster-cluster aggregation: Effects of cluster diffusivity. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1985 Jan 1;31(1):564–569. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.31.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Schindler H. Particle counting by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Simultaneous measurement of aggregation and diffusion of molecules in solutions and in membranes. Biophys J. 1988 Dec;54(6):983–993. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83036-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer A. G., 3rd, Thompson N. L. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy for detecting submicroscopic clusters of fluorescent molecules in membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1989 Jun;50(3-4):253–270. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(89)90053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. O., Johnson D. C., Schlesinger M. J. Scanning fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. II. Application to virus glycoprotein aggregation. Biophys J. 1986 Apr;49(4):817–820. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83710-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. O. Scanning fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. I. Theory and simulation of aggregation measurements. Biophys J. 1986 Apr;49(4):809–815. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83709-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffman P. G., Delbrück M. Brownian motion in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3111–3113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton M. J. Lateral diffusion in an archipelago. Distance dependence of the diffusion coefficient. Biophys J. 1989 Sep;56(3):615–622. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82708-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton M. J. Lateral diffusion in an archipelago. The effect of mobile obstacles. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):989–997. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83291-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlüter K., Drenckhahn D. Co-clustering of denatured hemoglobin with band 3: its role in binding of autoantibodies against band 3 to abnormal and aged erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6137–6141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih WY, Aksay IA, Kikuchi R. Reversible-growth model: Cluster-cluster aggregation with finite binding energies. Phys Rev A Gen Phys. 1987 Nov 15;36(10):5015–5019. doi: 10.1103/physreva.36.5015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J., Petersheim M. Lanthanide(III)-phosphatidic acid complexes: binding site heterogeneity and phase separation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 9;1024(1):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90219-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L., Melo E. C., Thompson T. E. Fluid phase connectivity in an isomorphous, two-component, two-phase phosphatidylcholine bilayer. Biophys J. 1990 Jul;58(1):273–275. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82373-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L., Melo E. C., Thompson T. E. Translational diffusion and fluid domain connectivity in a two-component, two-phase phospholipid bilayer. Biophys J. 1989 Nov;56(5):869–876. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82733-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velez M., Barald K. F., Axelrod D. Rotational diffusion of acetylcholine receptors on cultured rat myotubes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2049–2059. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh S. M., Willardson B. M., Kannan R., Labotka R. J., Low P. S. Heinz bodies induce clustering of band 3, glycophorin, and ankyrin in sickle cell erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1155–1160. doi: 10.1172/JCI112696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


