Abstract
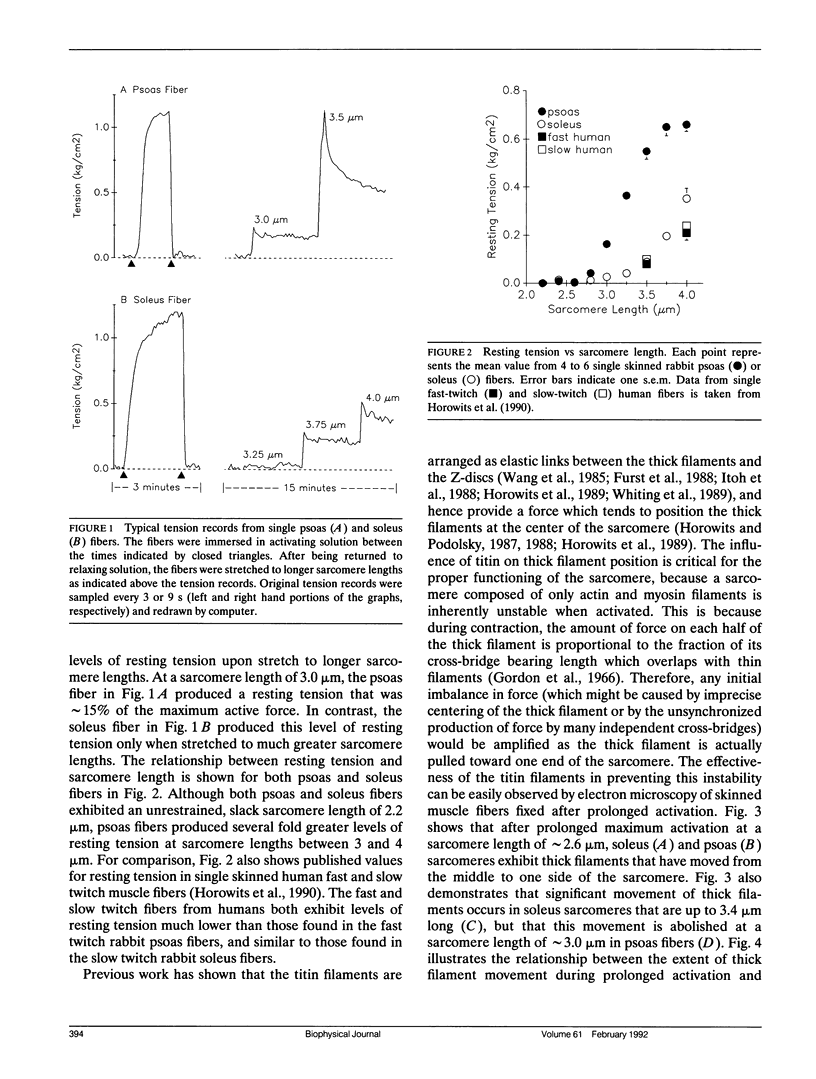
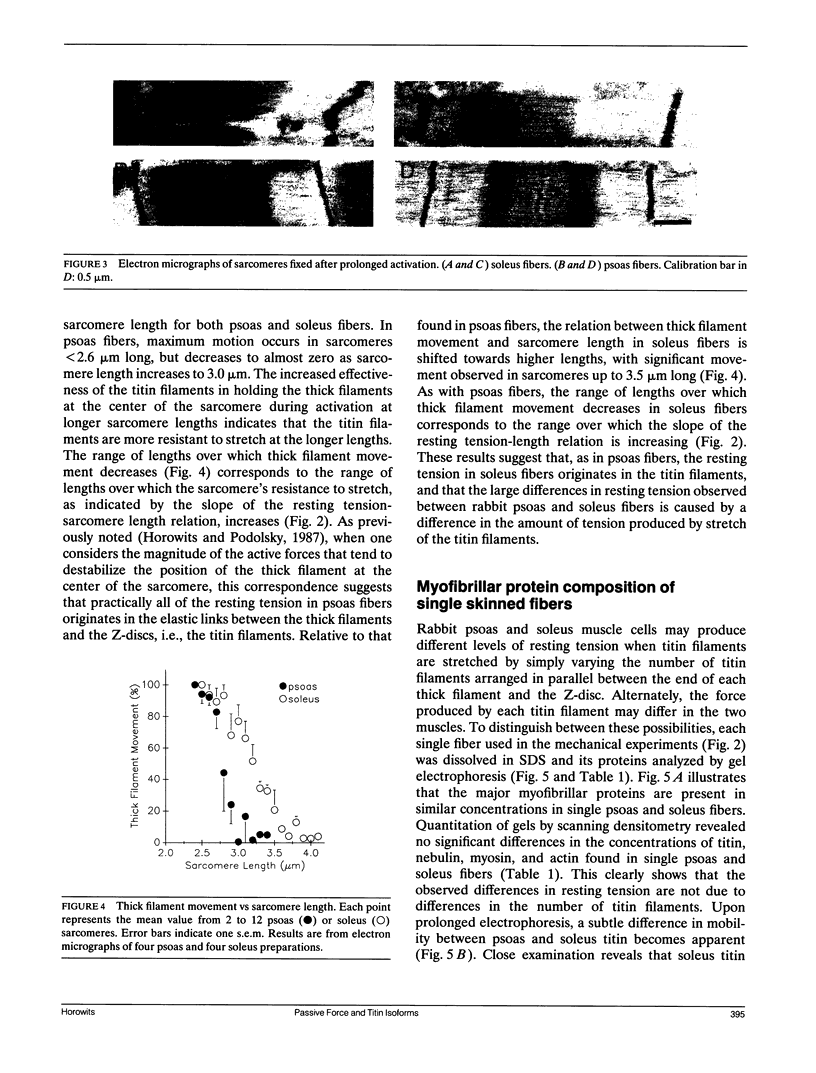
When relaxed striated muscle cells are stretched, a resting tension is produced which is thought to arise from stretching long, elastic filaments composed of titin (also called connectin). Here, I show that single skinned rabbit soleus muscle fibers produce resting tension that is several-fold lower than that found in rabbit psoas fibers. At sarcomere lengths where the slope of the resting tension-sarcomere length relation is low, electron microscopy of skinned fibers indicates that thick filaments move from the center to the side of the sarcomere during prolonged activation. As sarcomeres are stretched and the resting tension sarcomere length relation becomes steeper, this movement is decreased. The sarcomere length range over which thick filament movement decreases is higher in soleus than in psoas fibers, paralleling the different lengths at which the slope of the resting tension-sarcomere length relations increase. These results indicate that the large differences in resting tension between single psoas and soleus fibers are due to different tensions exerted by the elastic elements linking the end of each thick filament to the nearest Z-disc, i.e., the titin filaments. Quantitative gel electrophoresis of proteins from single muscle fibers excludes the possibility that resting tension is less in soleus than in psoas fibers simply because they have fewer titin filaments. A small difference in the electrophoretic mobility of titin between psoas and soleus fibers suggests the alternate possibility that mammalian muscle cells use at least two titin isoforms with differing elastic properties to produce variations in resting tension.
Full text
PDF

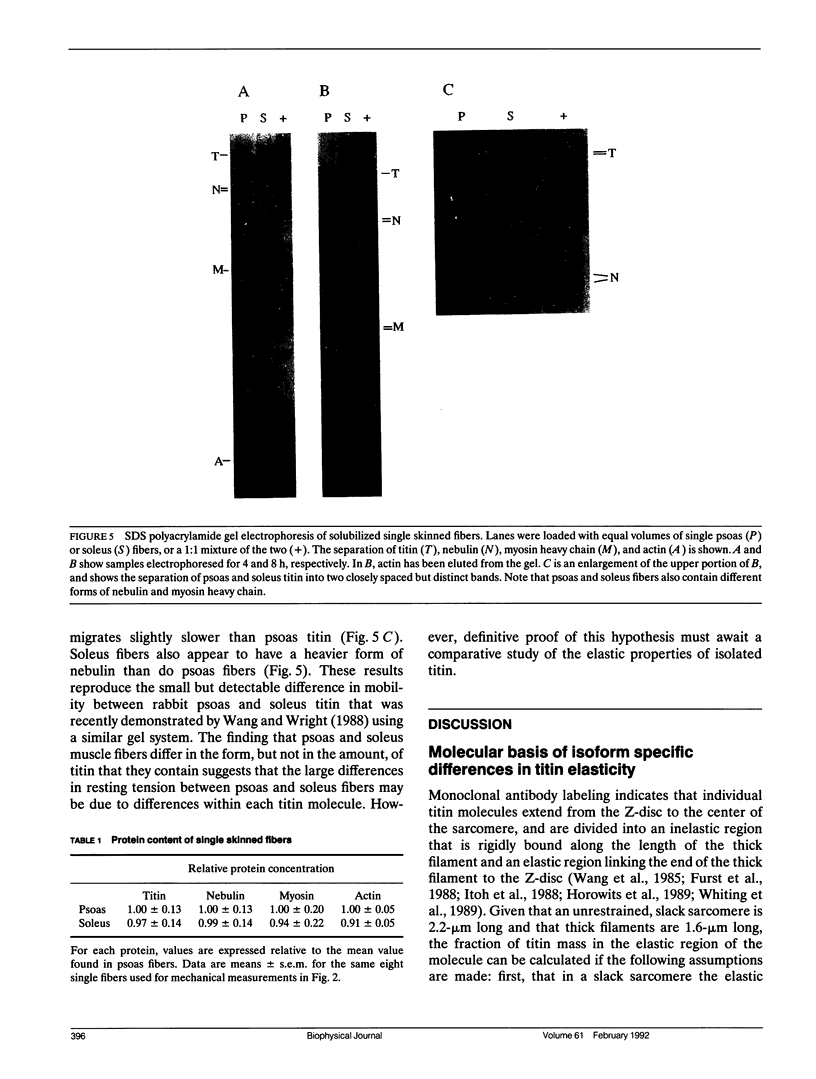


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Freehafer A. A., Peckham P. H., Keith M. W. Determination of muscle-tendon unit properties during tendon transfer. J Hand Surg Am. 1979 Jul;4(4):331–339. doi: 10.1016/s0363-5023(79)80069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu T., Higuchi H., Ishiwata S. Elastic filaments in skeletal muscle revealed by selective removal of thin filaments with plasma gelsolin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):53–62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst D. O., Osborn M., Nave R., Weber K. The organization of titin filaments in the half-sarcomere revealed by monoclonal antibodies in immunoelectron microscopy: a map of ten nonrepetitive epitopes starting at the Z line extends close to the M line. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1563–1572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Simmons R. M. Control of sarcomere length in skinned muscle fibres of Rana temporaria during mechanical transients. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:497–518. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. M., Huxley A. F., Julian F. J. The variation in isometric tension with sarcomere length in vertebrate muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(1):170–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellam D. C., Podolsky R. J. Force measurements in skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(3):807–819. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C., Weber K. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish titins from heart and skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):1099–1108. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowits R., Dalakas M. C., Podolsky R. J. Single skinned muscle fibers in Duchenne muscular dystrophy generate normal force. Ann Neurol. 1990 Jun;27(6):636–641. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowits R., Kempner E. S., Bisher M. E., Podolsky R. J. A physiological role for titin and nebulin in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):160–164. doi: 10.1038/323160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowits R., Maruyama K., Podolsky R. J. Elastic behavior of connectin filaments during thick filament movement in activated skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2169–2176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowits R., Podolsky R. J. The positional stability of thick filaments in activated skeletal muscle depends on sarcomere length: evidence for the role of titin filaments. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2217–2223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowits R., Podolsky R. J. Thick filament movement and isometric tension in activated skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1988 Jul;54(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)82941-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu D. H., Kimura S., Maruyama K. Sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis studies of connectin-like high molecular weight proteins of various types of vertebrate and invertebrate muscles. J Biochem. 1986 May;99(5):1485–1492. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Suzuki T., Kimura S., Ohashi K., Higuchi H., Sawada H., Shimizu T., Shibata M., Maruyama K. Extensible and less-extensible domains of connectin filaments in stretched vertebrate skeletal muscle sarcomeres as detected by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy using monoclonal antibodies. J Biochem. 1988 Oct;104(4):504–508. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J., Moss R. L., Waller G. S. Mechanical properties and myosin light chain composition of skinned muscle fibres from adult and new-born rabbits. J Physiol. 1981 Feb;311:201–218. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzban G. P., Wang K. Giant polypeptides of skeletal muscle titin: sedimentation equilibrium in guanidine hydrochloride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90750-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeit S., Barlow D. P., Gautel M., Gibson T., Holt J., Hsieh C. L., Francke U., Leonard K., Wardale J., Whiting A. A regular pattern of two types of 100-residue motif in the sequence of titin. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):273–276. doi: 10.1038/345273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Kimura S., Yoshidomi H., Sawada H., Kikuchi M. Molecular size and shape of beta-connectin, an elastic protein of striated muscle. J Biochem. 1984 May;95(5):1423–1433. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave R., Fürst D. O., Weber K. Visualization of the polarity of isolated titin molecules: a single globular head on a long thin rod as the M band anchoring domain? J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2177–2187. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen B. L., Brown L. R. The basis for colored silver-protein complex formation in stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1984 Sep;141(2):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAGE S. G., HUXLEY H. E. FILAMENT LENGTHS IN STRIATED MUSCLE. J Cell Biol. 1963 Nov;19:369–390. doi: 10.1083/jcb.19.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville L. L., Wang K. The ultrasensitive silver "protein" stain also detects nanograms of nucleic acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):53–58. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91487-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinick J., Elliott A. Electron microscope studies of thick filaments from vertebrate skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 15;131(1):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., McCarter R., Wright J., Beverly J., Ramirez-Mitchell R. Regulation of skeletal muscle stiffness and elasticity by titin isoforms: a test of the segmental extension model of resting tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7101–7105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Wright J. Architecture of the sarcomere matrix of skeletal muscle: immunoelectron microscopic evidence that suggests a set of parallel inextensible nebulin filaments anchored at the Z line. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2199–2212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting A., Wardale J., Trinick J. Does titin regulate the length of muscle thick filaments? J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90381-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. S., Zollman J., Reuben J. P., Brandt P. W. Human skeletal muscle: properties of the "chemically skinned%" fiber. Science. 1975 Mar 21;187(4181):1075–1076. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4181.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]